当前位置:网站首页>Golang分布式应用之定时任务
Golang分布式应用之定时任务
2022-08-02 01:52:00 【qingwave】
在系统开发中,有一类任务不是立即执行,而是在未来某个时间点或者按照一定间隔去执行,比如日志定期压缩、报表制作、过期数据清理等,这就是定时任务。
在单机中,定时任务通常需要实现一个类似crontab的系统,一般有两种方式:
- 最小堆,按照任务执行时间建堆,每次取最近的任务执行
- 时间轮,将任务放到时间轮列表中,每次转动取对应的任务列表执行
最小堆
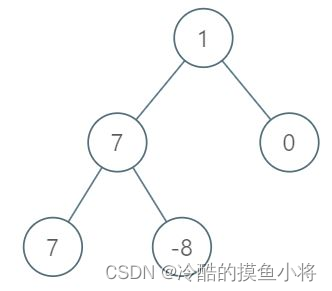
最小堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树,任意非叶子节点的值不大于其子节点,如图

通过最小堆,根据任务最近执行时间键堆,每次取堆顶元素即最近需要执行的任务,设置timer定时器,到期后触发任务执行。由于堆的特性每次调整的时间复杂度为O(lgN),相较于普通队列性能更快。
在container/heap中已经实现操作堆的相关函数,我们只需要实现定期任务核心逻辑即可。
// 运行
func (c *Cron) Run() error {
// 设置cron已启动,atomic.Bool来保证并发安全
c.started.Store(true)
// 主循环
for {
// 如果停止则退出
if !c.started.Load() {
break
}
c.runTask()
}
return nil
}
// 核心逻辑
func (c *Cron) runTask() {
now := time.Now()
duration := infTime
// 获取堆顶元素
task, ok := c.tasks.Peek()
if ok {
// 如果已删除则弹出
if !c.set.Has(task.Name()) {
c.tasks.Pop()
return
}
// 计算于当前时间查找,设置定时器
if task.next.After(now) {
duration = task.next.Sub(now)
} else {
duration = 0
}
}
timer := time.NewTimer(duration)
defer timer.Stop()
// 当有新元素插入直接返回,防止新元素执行时间小于当前堆顶元素
select {
case <-c.new:
return
case <-timer.C:
}
// 弹出任务,执行
go task.Exec()
// 计算下次执行时间,如果为0说明任务已结束,否则重新入堆
task.next = task.Next(time.Now())
if task.next.IsZero() {
c.set.Delete(task.Name())
} else {
c.tasks.Push(task)
}
}
主要逻辑可总结为:
- 将任务按照下次执行时间建最小堆
- 每次取堆顶任务,设置定时器
- 如果中间有新加入任务,转入步骤2
- 定时器到期后执行任务
- 再次取下个任务,转入步骤2,依次执行
时间轮
另一种实现Cron的方式是时间轮,时间轮通过一个环形队列,每个插槽放入需要到期执行的任务,按照固定间隔转动时间轮,取插槽中任务列表执行,如图所示:

时间轮可看作一个表盘,如图中时间间隔为1秒,总共60个格子,如果任务在3秒后执行则放为插槽3,每秒转动次取插槽上所有任务执行。
如果执行时间超过最大插槽,比如有个任务需要63秒后执行(超过了最大格子刻度),一般可以通过多层时间轮,或者设置一个额外变量圈数,只执行圈数为0的任务。
时间轮插入的时间复杂度为O(1),获取任务列表复杂度为O(1),执行列表最差为O(n)。对比最小堆,时间轮插入删除元素更快。
核心代码如下:
// 定义
type TimeWheel struct {
interval time.Duration // 触发间隔
slots int // 总插槽数
currentSlot int // 当前插槽数
tasks []*list.List // 环形列表,每个元素为对应插槽的任务列表
set containerx.Set[string] // 记录所有任务key值,用来检查任务是否被删除
tricker *time.Ticker // 定时触发器
logger logr.Logger
}
func (tw *TimeWheel) Run() error {
tw.tricker = time.NewTicker(tw.interval)
for {
// 通过定时器模拟时间轮转动
now, ok := <-tw.tricker.C
if !ok {
break
}
// 转动一次,执行任务列表
tw.RunTask(now, tw.currentSlot)
tw.currentSlot = (tw.currentSlot + 1) % tw.slots
}
return nil
}
func (tw *TimeWheel) RunTask(now time.Time, slot int) {
// 一次执行任务列表
for item := taskList.Front(); item != nil; {
task, ok := item.Value.(*TimeWheelTask)
// 任务圈数大于0,不需要执行,将圈数减一
if task.circle > 0 {
task.circle--
item = item.Next()
continue
}
// 运行任务
go task.Exec()
// 计算任务下次运行时间
next := item.Next()
taskList.Remove(item)
item = next
task.next = task.Next(now)
if !task.next.IsZero() {
tw.add(now, task)
} else {
tw.Remove(task.Name())
}
}
}
// 添加任务,计算下一次任务执行的插槽与圈数
func (tw *TimeWheel) add(now time.Time, task *TimeWheelTask) {
if !task.initialized {
task.next = task.Next(now)
task.initialized = true
}
duration := task.next.Sub(now)
if duration <= 0 {
task.slot = tw.currentSlot + 1
task.circle = 0
} else {
mult := int(duration / tw.interval)
task.slot = (tw.currentSlot + mult) % tw.slots
task.circle = mult / tw.slots
}
tw.tasks[task.slot].PushBack(task)
tw.set.Insert(task.Name())
}
时间轮的主要逻辑如下:
- 将任务存在对应插槽的时间
- 通过定时间模拟时间轮转动
- 每次到期后遍历当前插槽的任务列表,若任务圈数为0则执行
- 如果任务未结束,计算下次执行的插槽与圈数
- 转入步骤2,依次执行
总结
本文主要总结了定时任务的两种实现方式,最小堆与时间轮,并分析其核心实现逻辑。
对于执行分布式定时任务,可以借助延时消息队列或者直接使用Kubernetes的CronJob。
自己开发的话可以借助Etcd:
- 中心节点Coordinator将任务按照一定算法(Hash、轮询、或者更复杂的分配算法)将任务与工作节点Worker绑定
- 每个Worker添加到有绑定到自己的任务则取出放到本地的Cron中
- 如果Worker挂掉,执行将其上任务重新绑定即可
本文所有代码见https://github.com/qingwave/gocorex/tree/main/x/cron
Explore more in https://qingwave.github.io
边栏推荐
- Navicat数据显示不完全的解决方法
- 60种特征工程操作:使用自定义聚合函数【收藏】
- Fly propeller power space future PIE - Engine Engine build earth science
- typescript29-枚举类型的特点和原理
- JDBC PreparedStatement 的命名参数实现
- 华为5年女测试工程师离职:多么痛的领悟...
- 大话西游无法登陆解决
- Record the pits where an error occurs when an array is converted to a collection, and try to use an array of packaging types for conversion
- 第一次写对牛客的编程面试题:输入一个字符串,返回该字符串出现最多的字母
- Fundamentals of Cryptography: X.690 and Corresponding BER CER DER Encodings
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
"Introduction to Natural Language Processing Practice" Question Answering Robot Based on Knowledge Graph
Hiring a WordPress Developer: 4 Practical Ways
使用百度EasyDL实现厂区工人抽烟行为识别
C语言之插入字符简单练习
ofstream,ifstream,fstream读写文件
【ORB_SLAM2】SetPose、UpdatePoseMatrices
Win Go开发包安装配置、GoLand配置
libcurl访问url保存为文件的简单示例
Force buckle, 752-open turntable lock
【服务器数据恢复】服务器Raid5阵列mdisk磁盘离线的数据恢复案例
软件测试 接口自动化测试 pytest框架封装 requests库 封装统一请求和多个基础路径处理 接口关联封装 测试用例写在yaml文件中 数据热加载(动态参数) 断言
Data transfer at the data link layer
Entry name ‘org/apache/commons/codec/language/bm/gen_approx_greeklatin.txt’ collided
电子制造仓储条码管理系统解决方案
雇用WordPress开发人员:4个实用的方法
6-25漏洞利用-irc后门利用
Basic use of typescript34-class
喜报 | AR 开启纺织产业新模式,ALVA Systems 再获殊荣!
记录一次数组转集合出现错误的坑点,尽量使用包装类型数组进行转换
传统企业数字化转型需要经过几个阶段?