当前位置:网站首页>C++ exception implementation mechanism
C++ exception implementation mechanism
2020-11-09 23:48:00 【shzwork】
、C Function calls and returns
To understand C++ Before the exception mechanism is implemented , First of all, we should understand the call and return mechanism of a function , This involves ESP and EBP register . Let's take a look at the flow of function calls and returns .
The following is the call Convention __stdcall Call function test(int p1,int p2) Assembly code for
Suppose the stack pointer before the function is executed ESP by NN
push p2 ; Parameters 2 Push , ESP -= 4h , ESP = NN - 4h
push p1 ; Parameters 1 Push , ESP -= 4h , ESP = NN - 8h
call test ; Press in return address ESP -= 4h, ESP = NN - 0Ch
{
push ebp ; Protect the previous EBP The pointer , EBP Push , ESP-=4h, ESP = NN - 10h
mov ebp, esp ; Set up EBP The pointer points to the top of the stack NN-10h
mov eax, dword ptr [ebp+0ch] ;ebp+0ch by NN-4h, The parameter 2 The location of
mov ebx, dword ptr [ebp+08h] ;ebp+08h by NN-8h, The parameter 1 The location of
sub esp, 8 ; Space occupied by local variables ESP-=8, ESP = NN-18h
...
add esp, 8 ; Release local variables , ESP+=8, ESP = NN-10h
pop ebp ; Out of the stack , recovery EBP, ESP+=4, ESP = NN-0Ch
ret 8 ;ret return , Pop up return address ,ESP+=4, ESP=NN-08h, Add the operands after 8 To balance the stack ,ESP+=8,ESP=NN, Restore the stack before entering the function .
}
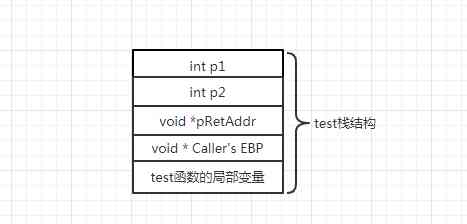
The function stack architecture mainly carries the following parts :
1、 Pass parameters : Usually , Function call parameters are always at the top of the function stack framework .
2、 Pass the return address : Tell the callee return The sentence should be return Where to go? , Usually points to the next statement of the function call ( Offset in code snippet ).
3、 Holds the current stack pointer of the caller : Easy to clean up all local variables of the callee 、 And restore the caller's scene .
4、 Store all local variables in the current function : Do you remember ? As mentioned earlier, all local and temporary variables are stored on the stack .
2、C++ Function call
First of all, make it clear , here “C++ function ” Refer to :
1、 This function may throw an exception directly or indirectly : That is, the definition of the function is stored in a C++ compile ( Not tradition C) In the unit , And this function doesn't use “throw()” Anomaly filter
2、 The definition of this function uses try block .
One of the above two can be satisfied . In order to be able to successfully catch exceptions and complete stack fallback correctly (stack unwind), The compiler must introduce some additional data structures and corresponding processing mechanisms . Let's first take a look at the stack framework with exception handling mechanism :

From the figure 2 so , At every C++ There are some more things in the stack framework of the function . Observe carefully , You'll find that , The extra thing is just one EXP Type of structure . Further analysis will reveal that , This is a typical one-way linked list structure :
piPrev The member points to the previous node in the linked list , It is mainly used to search for matching catch block , And complete the stack fallback .
piHandler Members point to the data structures necessary for exception capture and stack fallback ( It's mainly two tables with key data :“try” Block table :tblTryBlocks And “ Stack fallback table ”:tblUnwind).
nStep Members are used to locate try block , And find the right entry in the stack fallback table .
It should be noted that : The compiler will do it for every “C++ function ” Define a EHDL structure , But only for the inclusion of “try” Function definition of block tblTryBlocks member . Besides , The exception handler also maintains a pointer to the current exception handling framework for each thread . This pointer points to the end of the exception handler list , Usually stored in some place TLS A trough or place where a similar effect can be achieved .
3、 Stack back (stack unwind)
“ Stack back ” Is accompanied by the introduction of exception handling mechanism C++ A new concept in , It is mainly used to ensure that the exception is thrown 、 After capturing and processing , All objects whose lifetime has ended will be destructed correctly , The space they occupy will be recycled correctly . Let's take a look at how the compiler implements the stack fallback mechanism :

In the picture “FuncUnWind” Within the function , All real codes are shown in black and blue font , The code generated by the compiler is indicated in gray and orange fonts . here , The picture shows nStep Variables and tblUnwind The role of members is very obvious .
nStep Variables are used to track the construction of local objects within a function 、 In the stage of deconstruction . And then with the compiler generated for each function tblUnwind surface , Then we can complete the unwinding mechanism . In the table pfnDestroyer Field records the destruct operations that should be performed in the corresponding phase ( Destructor pointer );pObj Field records the corresponding object this Pointer offset . take pObj The offset value of the reference plus the current stack frame base address (EBP), That is to put in pfnDestroyer Of a destructor this The pointer , In this way, the destruct of the object is completed . and nNextIdx The field points to the row of the next object to be destructed ( Subscript ).
When an exception occurs , The exception handler first checks for... In the current function stack framework nStep value , And pass piHandler obtain tblUnwind[] surface . And then nStep Bring it into the table as a subscript , Perform the destruct operation defined by this line , And then turn from nNextIdx The next line to point to , until nNextIdx by -1 until . After the stack fallback of the current function is finished , The exception handler can follow the current function stack frame piPrev The value of is traced back to the previous node in the exception handling chain , Until all the fallback work is done .
It is worth mentioning that ,nStep The value of is completely determined at compile time , The runtime only needs to perform a few simple integer immediate assignments ( It is usually assigned directly to CPU One of the registers in ). Besides , For all internal types and using the default construct 、 destructor ( And all its members and base classes also use the default method ) The type of , Its creation and destruction do not affect nStep Value .
Be careful : If in the stack fallback process , An exception was thrown again due to a call to a destructor ( The exception in the exception ), Is considered a serious failure of the exception handling mechanism . At this point, the process will be forcibly prohibited . To prevent this , Should be used in all destructors that may throw exceptions “std::uncaught_exception()” Method to determine whether stack rollback is currently in progress ( namely : There is an exception that has not been caught or has not been fully processed ). " , You should prevent the exception from being thrown again .
4、 Exception trapping
When an exception is thrown , It will immediately trigger C++ Exception capture mechanism of :
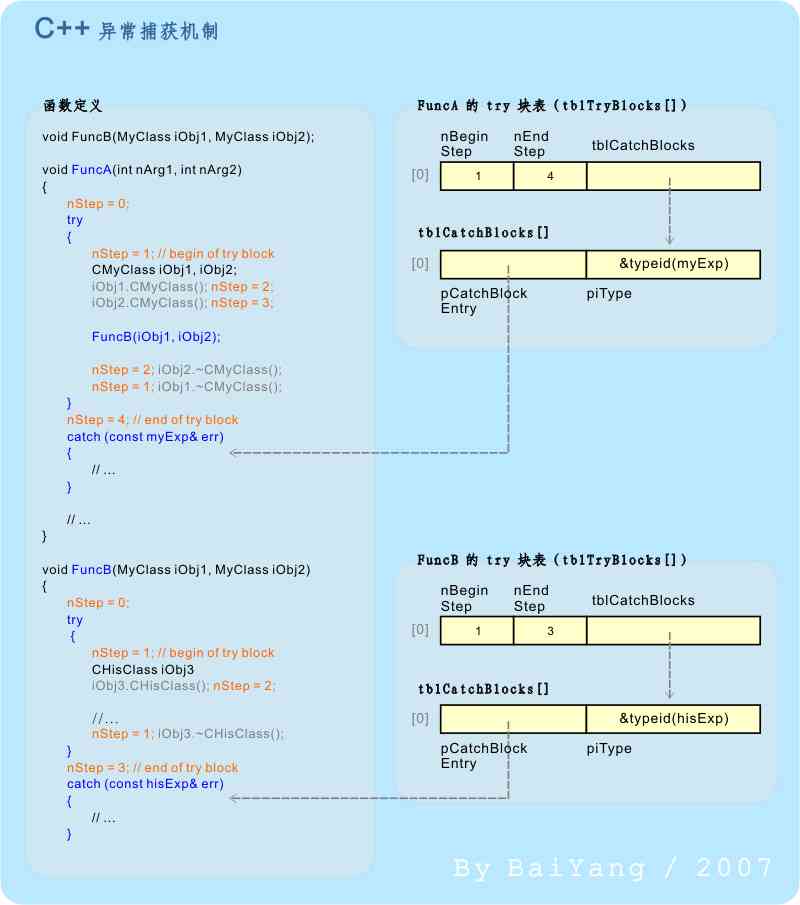
In the last section , We have seen nStep Variable in tracking object construction 、 The role of the structure . actually nStep Besides being able to track object creation 、 Beyond the destruction stage , It can also identify whether the current execution point is in try In block , as well as ( If the current function has more than one try Block words ) Where on earth try In block . It's through every try The entrance and exit of the block are respectively nStep Give a unique ID value , And ensure nStep In the corresponding try Changes within a block are implemented within this range .
In the specific implementation of exception capture , First ,C++ The exception handler checks whether the location of the exception is in one of the current functions try Within the block . This can be done by changing the current function's nStep The values are in the order of piHandler Point to tblTryBlocks[] The range of items in the table is [nBeginStep, nEndStep) To complete .
for example : If the figure 4 Medium FuncB stay nStep == 2 There was an exception when , By comparing FuncB Of tblTryBlocks[] Table discovery 2∈[1, 3), So the anomaly occurs in FuncB The first one in try In block .
secondly , If the exception occurs at a location in the current function try block , Then try to match the tblTryBlocks[] In the corresponding entry tblCatchBlocks[] surface .tblCatchBlocks[] The table records and specifies try Block matching appears all of catch Block related information , Including this catch The type of exception and its starting address that can be captured by a block .
If you find a match catch block , Copy the current exception object here catch block , Then jump to its entry address and execute the code in the block .
otherwise , It indicates that the location of the exception is not in the current function try block , Or this try There is no... In the block that matches the current exception catch block , At this point, it goes along the function stack frame piPrev The address referred to ( namely : The last node in the exception handling chain ) Repeat the process step by step , Until we find a match catch Block or arrive at the first node of the exception handling chain . For the latter , We call an uncapped exception occurred , about C++ For exception processors , An uncapped exception is a serious error , Will cause the current process to be forced to end .
5、 Throw an exception
Let's talk about the whole thing C++ The last link in the exception handling mechanism , Throw exception :

In compiling a paragraph C++ Code , The compiler will take all throw The statement is replaced by its C++ A specified function in the runtime library , Here we call it __CxxRTThrowExp( Like all other data structures and property names mentioned in this article , In practice, it can be any name ). This function receives a compiler approved internal structure ( We call it the EXCEPTION structure ). This structure contains the starting address of the object to be thrown 、 The destructor used to destroy it , As well as its type_info Information . For not enabled RTTI Mechanism ( The compiler has disabled RTTI Mechanism or no virtual table is used in the class hierarchy ) Exception class hierarchy of , It may also contain all of its base classes type_info Information , In order to correspond with catch Block to match .
In the dark gray box in the picture , We use C++ Pseudo code shows the function FuncA Medium “throw myExp(1);” The way statements will eventually be translated by the compiler . In fact, in most cases ,__CxxRTThrowExp Function is what we mentioned many times before “ Exception handler ”, Exception capture and stack fallback and other important work is done by it .
__CxxRTThrowExp First receive ( And save )EXCEPTION object ; And then from TLS:Current ExpHdl Corresponding to the current function piHandler、nStep And other exception processing related data ; And according to the mechanism mentioned above, exception capture and stack rollback are completed . So it's done, including “ Throw out ”->“ Capture ”->“ Back off ” And so on .
6、 summary
That's all C++ The implementation principle of exception , Of course, other language exception capture mechanism is the same idea to achieve exception handling .
版权声明
本文为[shzwork]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- asp.net core中使用Serilog以及自定义Enricher
- Apache Hadoop的重要组成
- js label语法跳出多重循环
- Top 5 Chinese cloud manufacturers in 2018: Alibaba cloud, Tencent cloud, AWS, telecom, Unicom
- CUDA_ constant memory
- 日常页码样式问题
- LeetCode-378. 有序矩阵中第K小的元素
- asp.net Using serilog in core and customizing enrich
- 没有磁盘空间 No space left on device
- 京淘项目day10
猜你喜欢

白山云科技入选2020中国互联网企业百强

【LeetCode】 92 整数反转
必看!RDS 数据库入门一本通(附网盘链接)

公网IP地址和SSL证书可以提升SEO吗?
How to make a set of K reverse linked lists

Day84: Luffy: preferential activity strategy & User Authentication & checking / settlement of shopping cart goods

C + + game development

Top 5 Chinese cloud manufacturers in 2018: Alibaba cloud, Tencent cloud, AWS, telecom, Unicom

Function calculation advanced IP query tool development
Brief analysis of LinkedList source code
随机推荐
CUDA_存储器模型
快来学习!个性化推荐系统开发指南(附网盘链接)
Leetcode 49 letter heterotopic word grouping
CUDA_全局内存及访问优化
LeetCode 50 Pow(x,n)
Can't find other people's problem to solve
Baishan cloud technology is selected as the top 100 Internet enterprises in China in 2020
2020-11-09:谈谈布隆过滤器和布谷鸟过滤器的相同点和不同点?
Visit 2020 PG Technology Conference
【CentOS7操作系统安全加固系列】第(2)篇
Day84: Luffy: preferential activity strategy & User Authentication & checking / settlement of shopping cart goods
商品后台系统优化
asp.net core中使用Serilog以及自定义Enricher
11.9
C / C + + Programming Notes: C language development tank war! In memory of our lost little overlord game
What is the SRM system? SRM supplier management system functions
Error running app: default activity not found solution
How much is the cost of CRM system?
CUDA_共享内存、访存机制、访问优化
Dongge ate grapes when he ate an algorithm problem!
