当前位置:网站首页>再回顾集合容器
再回顾集合容器
2022-07-01 18:46:00 【小山学Java】
数据结构和算法
算法:
- 解决问题的方法
- 解决问题的具体流程
- 评价这个算法的具体指标
- 时间复杂度
- 空间复杂度
数据结构:
就是在计算机缓存,内存,硬盘,如何组织管理数据的。重点在结构上,是按照什么结构来组织管理我们的数据。
- 逻辑结构:思想上的结构 —》卧室、客厅、厨房 —》线性表(数据,链表),图、树、栈、队列
- 物理结果:真实结构 —》钢筋混凝土 ——》紧密结构(顺序结构),跳转结构(链式结构)
紧密结构、跳转结构
紧密结构:数组
优点:寻址快–》查找元素快
缺点:删除和增加元素效率低
跳转结构:链表
- 单项链表
- 双向链表
- 循环链表
优点:删除元素,和插入元素效率高
缺点:查询元素效率低
集合和数组的区别
数组和集合都是对多个数据进行存储的操作,简称容器。
集合:
- 集合可以存放不同类型的数据
- 集合的长度是可变的
数组:
- 数组一旦指定了长度,就不可以被更改了
- 数组只能存放同一种类型的数据
集合的应用场景

Collection
Collection接口中的常用方法:
增加:add(E e) addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 删除:clear() removeAll(Collection<?> c)
修改:
查看:iterator() size()
判断:contains(Object o) equals(Object o)
package com.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
public class Collection_void {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Collection接口中的方法 增加:add(E e) addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 删除:clear() removeAll(Collection<?> c) 修改: 查看:iterator() size() 判断:contains(Object o) equals(Object o) */
//接口不能创建对象,利用实现类创建对象 (多态性的表现)
Collection col = new ArrayList();
//调用方法
//集合的特点:只能存储引用数据类型的数据,不能存储基本数据类型的数据
//基本数据类型自动装箱,对应的包装类 int---》Integer
col.add(18);
col.add(20);
col.add(22);
System.out.println(col/* .toString() */);
//数组转集合
List list = Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{
12, 23, 43, 15, 31, 33});
col.addAll(list);
System.out.println(col);
//clear() 清空集合元素
col.clear();
System.out.println("集合数组中的元素:"+col.size());
System.out.println("集合是否为空:"+col.isEmpty());
// remove()删除集合中指定位置的元素
List col2 = new ArrayList<>();
col2.add(18);
col2.add(20);
col2.add(22);
List col3 = new ArrayList<>();
col3.add(18);
col3.add(20);
col3.add(22);
System.out.println("equals相比:"+col2.equals(col3)); //equals比较的是对象都引用
System.out.println("== 相比:"+(col2 == col3)); //==比较的是内存地址
}
}
集合的遍历方式:
public class Collection_Iterator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(12);
list.add(32);
list.add(33);
//方式一:for循环遍历
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("for循环方式遍历:"+list.get(i));
}
//方式二:增强for循环遍历
for(Object o :list){
System.out.println("增强for循环方式遍历:"+o);
}
//方式三:iterator遍历
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println("iterator方式遍历:"+it.next());
}
}
}
List接口
List接口中的常用方法:
扩展的方法都和索引有关
增加:add(int index, E element)
修改: set(int index, E element)
删除:remove(int index) remove(Object o)
查询:get(int index)
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* list接口的常用方法: 增加:add(int index, E element) 修改: set(int index, E element) 删除:remove(int index) remove(Object o) 查询:get(int index) */
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(12);
list.add(43);
list.add(34);
list.add(32);
list.add(2);
System.out.println(list);
list.add(3,66);
System.out.println(list);
list.set(3,77);
System.out.println(list);
//在集合存入是Integer类型的数据时,调用remove方法执行的是 remove(int index)
list.remove(2);
System.out.println(list);
Object o = list.get(0);
//List 集合遍历
//方式一:普通for循环
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
ArrayList实现类
JKD1.7中的源码:
问题:冗余操作
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E>
可以发现 ArrayList实现了List接口,ArrayList的父类AbstractList也实现了List接口,冗余操作。
ArrayList底层重要属性:
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */
private int size;
底层数组: elementData
初始化长度:10
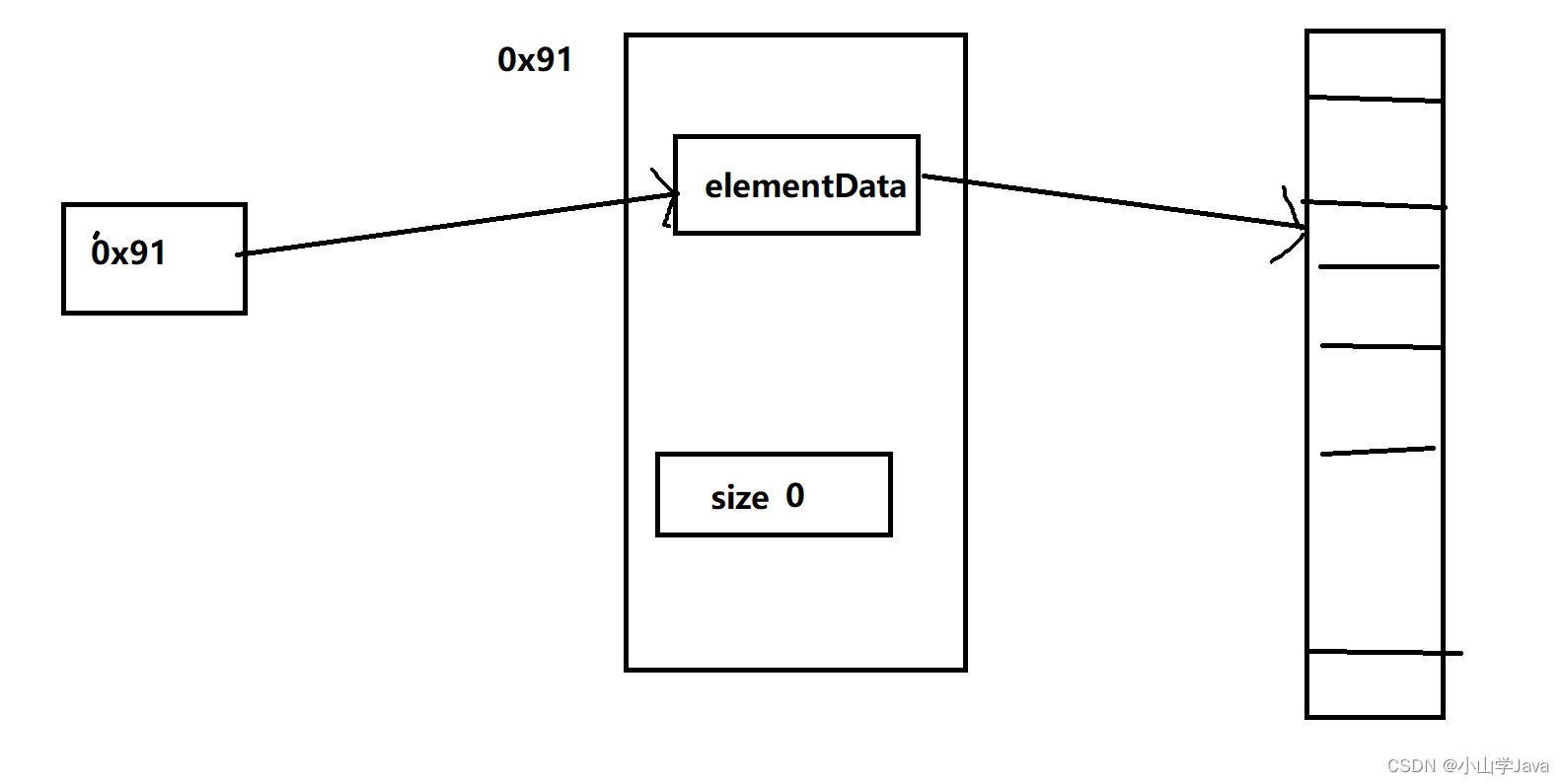
调用add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
//调用add方法下个底层数组中添加元素
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!! //扩容时的方法
elementData[size++] = e; //最开始size为0,添加元素以后size+1操作
return true; //添加成功返回 true
}
ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity)
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity)
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity); //扩容
}
grow(int minCapacity)
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //扩容1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//将老数组的内容复制到新数组中,返回新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
当数组的长度初始化为10,在底层用调用grow()方法进行数组的扩容,扩容为原数组的1.5倍
JDK1.8中的源码:
JKD1.8底层的重要属性
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/** * The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains). * * @serial */
private int size;
调用空构造器
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
// 在JDK1.8中调用空构造器的时候,底层elementData的初始化为空的数组
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {
};
调用add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity)
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity)
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
return minCapacity;
}
DEFAULT_CAPACITY
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity)
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
grow(int minCapacity) 扩容
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
底层数组,在调用构造器的时候为空,在调用add方法之后,数组初始值为10
Vector实现类
底层的属性
protected Object[] elementData; //elementData数组
/** * The number of valid components in this {@code Vector} object. * Components {@code elementData[0]} through * {@code elementData[elementCount-1]} are the actual items. * * @serial */
protected int elementCount; //elementCount 表示数组中的有效长度
调用构造器
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0);
}
public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {
super();
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;
}
底层的数组长度还是10
查看add方法
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = e;
return true;
}
ensureCapacityHelper
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
grow(int minCapacity)
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); //底层扩容的长度为2倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
ArrayList 和Vector 的区别
ArrayList 底层扩容长度为原数组长度的1.5倍,Vector底层扩容为原数组长度的2倍
ArrayLIst是线程不安全的(效率高),Vector是线程安全的(效率低)
泛型
总结:
JDK1.5之后使用泛型
在编译时期就会对其类型进行检查,不是泛型对应的类型就不可以添加到这个集合。
泛型实际就是 < >引起来的参数类型,这个参数类型,具体在使用的时候才会确定具体的类型。
泛型的类型:都是引用数据类型,不能是基本数据类型
细节:
【1】泛型类可以定义多个参数类型
public class Generics_Test02<A,B,C> {
public Generics_Test02(A a,B b,C c) {
}
}
【2】泛型类的构造器方法上不能添加泛型
public Generics_Test02()/*<A,B,C>*/ {
}
【3】不同泛型的引用类型不可以相互赋值
【4】泛型如果不指定,那就会被擦除,泛型对象的类型默认是Object类型
【5】泛型类中的静态方法不能使用类的泛型,因为static优先于对象存在
public class Generics_Test02<A,B,C> {
public /*static*/ void aVoid(A a){
}
}
【6】创建数组时,不能使用泛型的名称为数组的名称
public /*static*/ void aVoid(A a){
A[] a = new A[10];
}
泛型方法
【1】泛型方法要求:这个泛型方法对应的泛型参数,和当前的这个类无关
public class Generics_Test02<A> {
//不是泛型方法
public void a(A a){
}
//是泛型方法
public <T> void b(T t){
}
}
【2】泛型方法的类型是在调用该方法的是确定
【3】泛型方法可以是静态方法
泛型参数存在的继承情况
A和B是子类父类的关系,但是G (A) 和 G(B) 不存在继承关系,是并列关系
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object obj = new Object();
String str = new String();
obj = str; //多态的一种形式,父类引用指向子类对象
Object[] objArr = new Object[10];
String[] strArr = new String[10];
objArr = strArr;//多态的一种形式,父类引用指向子类对象
List<Object> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
//list1 = list2 报错
}
通配符
【1】在没用通配符的时候,下面的a方法相当于方法的重复定义 报错
public class Demo02 {
public void a(List<Object> list){
}
public void a(List<String> list){
}
public void a(List<Integer> list){
}
}
【2】引入通配符
A和B是子类父类的关系,但是G (A) 和 G(B) 不存在继承关系,是并列关系,引入通配符之后G<?> 则是G (A) 和 G(B) 的父类
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Object> list3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<?> list = null;
list = list1;
list = list2;
list = list3;
}
【3】通配符的使用
public void a(List<?> list){
//内部遍历的时候使用Object即可,不用?接收
for(Object o : list){
System.out.println(o);
}
//2、数据的写入操作
// list.add("abc"); 使用通配符,不能随意的写入操作
//3.数据的读取
Object o = list.get(0); //数据读取的时候,必须使用Object类型接收
}
泛型受限
<? extends T> 泛型的上限 T
<? super T> 泛型的下限 T
public static void main(String[] args) {
//a b c 三个集合是并列的关系
List<Object> a = new ArrayList<>();
List<Person> b = new ArrayList<>();
List<Student> c = new ArrayList<>();
//开始使用泛型受限
//泛型的上限是 Person
List<? extends Person> list = null;
list = a; //报错
list = b;
list = c;
//泛型的下限是 Person
List<? super Person> list1 = null;
list1 = a;
list1 = b;
list1 = c; //报错
}
LinkedList实现类
LinkedList 可以添加重复元素
LinkedList常用方法:
增加: addFirst(E e) addLast(E e)
offer(E e) offerFirst(E e) offerLast(E e)
修改:
删除:poll() pollFirst() pollLast() --》 jdk1.6以后对removeListFirst()的优化,增加了程序的健壮性
removeFirst() removeLast()
判断:
查看:element()
getFirst() getLast()
indexOf(Object o) lastIndexOf(Object o)
peek() peekFirst() peekLast()
LinkedList底层原理
物理结构:跳转结构
逻辑结构:线性表(链表)
LinkedList是一个双向链表

模拟LinkedList源码
Node节点类
public class Node {
//上一个元素地址
private Node pre;
//当前存入的元素
private Object obj;
//下一个元素地址
private Node next;
}
MyLinkedList
public class MyLinkedList {
//链中一定有一个首节点
Node first;
//链中一定有一个尾结点
Node last;
//计数器
int count = 0;
public MyLinkedList(){
}
//添加元素
public void add(Object obj){
if (first == null){
//证明你添加的元素是第一个元素
//将添加的元素封装成一个对象
Node n = new Node();
n.setPre(null);
n.setObj(obj);
n.setNext(n);
first = n; //当前链中第一个节点变为n
last = n; //当前链中最后一个节点变为n
}else {
//证明已经不是链中第一个节点了
//将添加的元素封装成一个对象
Node n = new Node();
n.setPre(last); //n的上一个节点一定是当前链中最后一个节点
n.setObj(obj);
n.setNext(null);
//当前链中最后一个节点的下一个元素
last.setNext(n);
//将最后一个节点变为n
last = n;
}
//链中元素+1
count++;
}
//得到集合中元素的数量
public int getSize(){
return count;
}
//通过下标得到元素
public Object get(int index){
//获取链表的头元素
Node n = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
n = n.getNext();
}
return n.getObj();
}
}
输出:
class TestDe{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个MyLinkedList集合对象
MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();
myLinkedList.add("aa");
myLinkedList.add("bb");
myLinkedList.add("cc");
for (int i = 0; i < myLinkedList.getSize(); i++) {
System.out.println(myLinkedList.get(i));
}
}
}
LinkedList源码
public class LinkedList<E> //泛型类,泛型对象在实例化的时候指定
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
transient int size = 0; //集合中元素的数量
transient Node<E> first;//链表的首节点
transient Node<E> last; //链表的尾结点
}
//静态内部类
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //当前元素
Node<E> next; //下一个元素地址
Node<E> prev; //上一个元素地址
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
//添加元素操作
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
//添加的元素e
final Node<E> l = last; //将当前链表的last元素节点给l,如果是第一个元素的话 l 为null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null) //如果添加的是第一个节点,将链表的first指向为新节点
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
//获取集合中的元素数量
public int size() {
return size;
}
//通过索引得到元素
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
//若果你传入的index下标,在链表的前半段,那么从前往后找,如果在后半段,从后往前找
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
LinkedList:底层是一个双向链表
面试题iterator 、Iterator、Iterable
【1】iterator 、Iterator、Iterable对应关系

ListIterator
【1】在使用iteartor 方法遍历集合的时候,如果想增加或元素的时候,会抛出一个并发修改异常
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("abc");
arrayList.add("cde");
arrayList.add("eee");
Iterator<String> it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
if (it.next().equals("cde")){
arrayList.add("ccceee");
}
}
}
Exception in thread "main" java.util.ConcurrentModificationException
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.checkForComodification(ArrayList.java:907)
at java.util.ArrayList$Itr.next(ArrayList.java:857)
出错原因
Iterator 和 arrayList 同时在对集合进行操作
【2】ListIterator 解决
因为listIterator 继承了Iterator接口,并在此基础上,增加了一些,添加和删除的方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("abc");
arrayList.add("cde");
arrayList.add("eee");
ListIterator<String> it = arrayList.listIterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
if ("cde".equals(it.next())){
it.add("ccceee");
}
}
System.out.println(it.toString());
}
Set接口
特点是,元素的值唯一,无序
HashSet 简要原理图
底层结构:数组+链表=哈希表
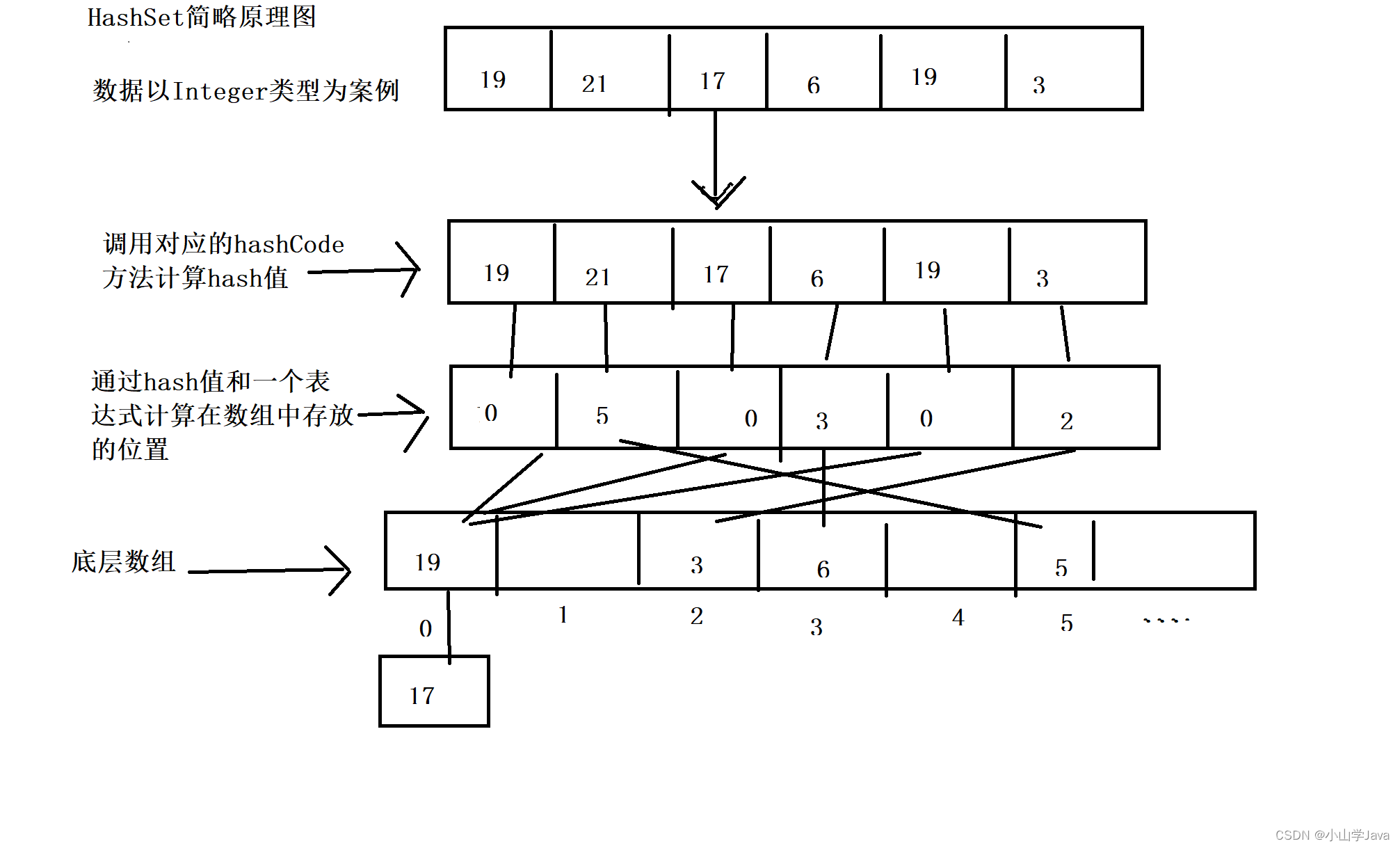
LinkedHashSet实现类
特点:有序,唯一,输入和输出的顺序一致。
底层原理就是在HashSet的基础上多了一个总的链表,这个总链表将存入的元素放在一起,方便遍历。
比较器compareTo的使用
引用数据类型或者自定义数据类型,implements Comparable 重写 compareTo方法,完成比较器。
内部比较器
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private Integer age;
private Integer height;
private String name;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(Integer height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer age, Integer height, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//按照年龄进行比较
// return (this.age - o.getAge());
//按照身高进行比较
// return (this.height - o.getHeight());
//按照姓名进行比较
return this.name.compareTo(o.getName());
}
}
外部比较器
外部比较器 implements Comparator重写 compare 方法
public class Student {
private Integer age;
private Integer height;
private String name;
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(Integer height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Student() {
}
public Student(Integer age, Integer height, String name) {
this.age = age;
this.height = height;
this.name = name;
}
}
class MyComparable implements Comparator<Student> {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//若果年龄相同则比较姓名
if (o1.getAge() == o2.getAge()){
return o1.getName().compareTo(o1.getName());
}
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student(10,170,"lisi");
Student s2 = new Student(10,180,"lisi");
//实例化外部比较器
MyComparable myComparable = new MyComparable();
System.out.println(myComparable.compare(s1, s2));
}
TreeSet实现类
【1】特点:存入Integer数据类型数据,唯一,按照升序进行排了遍历。
【2】原理:底层是一个二叉树 (逻辑结构)
底层原理是使用比较器的方式进行存入是比较,若果是自定义对象,必须实现内部比较器,或者外部比较器。
二叉树的遍历方式:
中(根)序遍历:左 根 右 ===》 TreeSet 使用的是中序遍历
先(根)序遍历:根 左 右
后(根)序遍历:左 右 根
Map
HashMap实现类
线程不安全的,效率高!
特点:无序,唯一的key,按照key的长度进行总结的,因为底层key遵照哈希表的结构(数组+链表)
哈希表的原理:比如放入这个集合的数据对应的那个类,必须重写hashCode和equals方法
LinkedHashMap实现类
哈希表+链表,唯一,有序(按照输入的顺序输出)
HashTable实现类
线程安全的,效率低! key不可以存储null值
JDK1.7 HashMap的简单原理
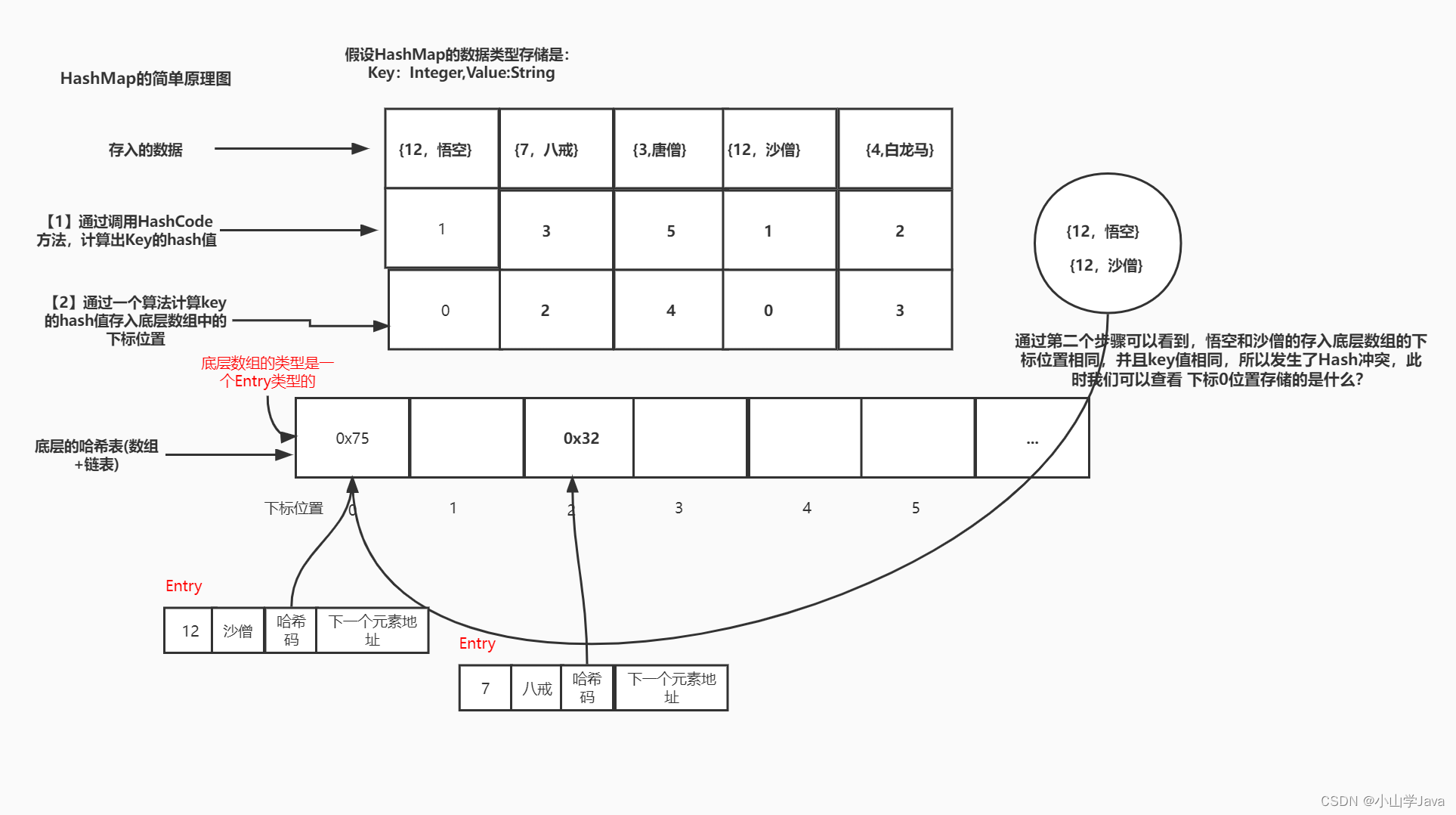
JDK1.7 HashMap源码分析
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
{
//定义了初始化长度
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //负载因子
static final Entry<?,?>[] EMPTY_TABLE = {
}; //底层的主数组
transient int size; //集合中添加的元素的数量
int threshold; //这个变量是数组扩容的边界值
final float loadFactor; //接收负载因子
//空构造器把 16 和 0.75f 传进去了
public HashMap() {
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
//带参数的构造器
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
int capacity = 1;
while(capacity < initaliCapacity){
capacity << 1;
}
//负载因子为 0.75
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// threshold = 16* 0.75 = 12
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
//创建主数组,主数组的长度为16
table = new Entry[capacity] ;
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}
//存储数据的方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
//对于null值做了一个判断,允许null值
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//获取hash值
int hash = hash(key);
//通过hash值,得到在底层的位置
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//如果放入的数组的位置上没有元素的话,直接添加元素,不用走for循环
for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
//发生hash碰撞的时候,先比较hash值
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
//hash 方法计算hash值
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = hashSeed;
if (0 != h && k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
//二次散列,没有直接用hashCode,解决hash冲突
h ^= k.hashCode();
// This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by
// constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded
// number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor).
// 扰动函数
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
//通过hash值计算出位置
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
// assert Integer.bitCount(length) == 1 : "length must be a non-zero power of 2";
return h & (length-1);
}
//添加元素方法
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//创建一个entry的对象
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
//创建entry方法
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; //jdk1.7 链表的头插入法
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
}
经典面试题
【1】为什么负载因子是0.75
如果装填因子为1 的话,空间利用率得到了满足,很容易发生碰撞,产生列表—》查询效率低
如果装填因子为0.5的话,碰撞概率低,扩容概率高,产生链表的概率低,查询效率高,空间利用率低。
【2】主数组的长度,为什么必须为2^n
1、 h&(length - 1) 等效 h% length
2、防止hash冲突
HashSet底层源码
HashSet底层就是一个HashMap
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
//构造器
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
//add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
}
TreeMap底层源码
【1】简单原理的大致介绍

【2、源码分析】
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements NavigableMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
//外部比较器
private final Comparator<? super K> comparator;
//树的根节点
private transient Entry<K,V> root = null;
//集合中元素的数量
private transient int size = 0;
//空构造器,
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null; //如果使用空构造器,那么就使用内部比较器
}
//如果使用有参构造器,那么相当于指定了外部比较器
public TreeMap(Comparator<? super K> comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
//静态内部类entry类
static final class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
K key;
V value;
Entry<K,V> left = null;
Entry<K,V> right = null;
Entry<K,V> parent;
boolean color = BLACK;
/** * Make a new cell with given key, value, and parent, and with * {@code null} child links, and BLACK color. */
Entry(K key, V value, Entry<K,V> parent) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.parent = parent;
}
//put 方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
//如果放入的是第一对元素,那么t的值为null
Entry<K,V> t = root;
if (t == null) {
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//根节点确定
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
int cmp;
Entry<K,V> parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
//将外部比较器赋值给 cpr
Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator;
//cpr 不等于空,意味着调用了有参构造器,指定了外部比较器
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//cpr 等于空,意味着调用的空构造器,使用的是内部比较器
else {
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
else
parent.right = e;
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
}
TreeSet底层源码
唯一有序,二叉树
public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;
//构造器
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());
}
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
}
数据结构 - 栈
特点:先进后出
Stack
Stack类的底层继承了Vector,实际存储的也是一个线程安全的对象数组,在Vector的基础上,添加了一些额外的功能,Stack遵循先进后出的原则。
源码分析:
public
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/** * Creates an empty Stack. */
public Stack() {
}
//push添加元素,并反回添加的元素
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
// pop查看栈顶的元素,并移除
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
//移除操作
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
//peek 也是查看栈顶的元素,但是不移除
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
//空值判断
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
}
同步容器(Synchronized)
将线程不安全的结合:ArrayList,HashMap 转换成线程安全的。
【1】使用Collections.synchronized**方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = Collections.singletonList(new ArrayList<>());
HashMap map = (HashMap) Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>());
}
线程不安全测试:
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//通过同步类容器解决线程安全问题
final List<Object> oldlsit = Collections.synchronizedList(arrayList);
//创建一个线程池
ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
es.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
arrayList.add("aa");
}
});
}
//关闭线程池资源
es.shutdown();
//监控线程是否执行完毕
while (true){
//线程池里的线程都执行完毕后,返回true
if (es.isTerminated()){
System.out.println("所有的子线程都执行完毕");
System.out.println(arrayList.size());
break;
}
}
}
同步容器 源码分析
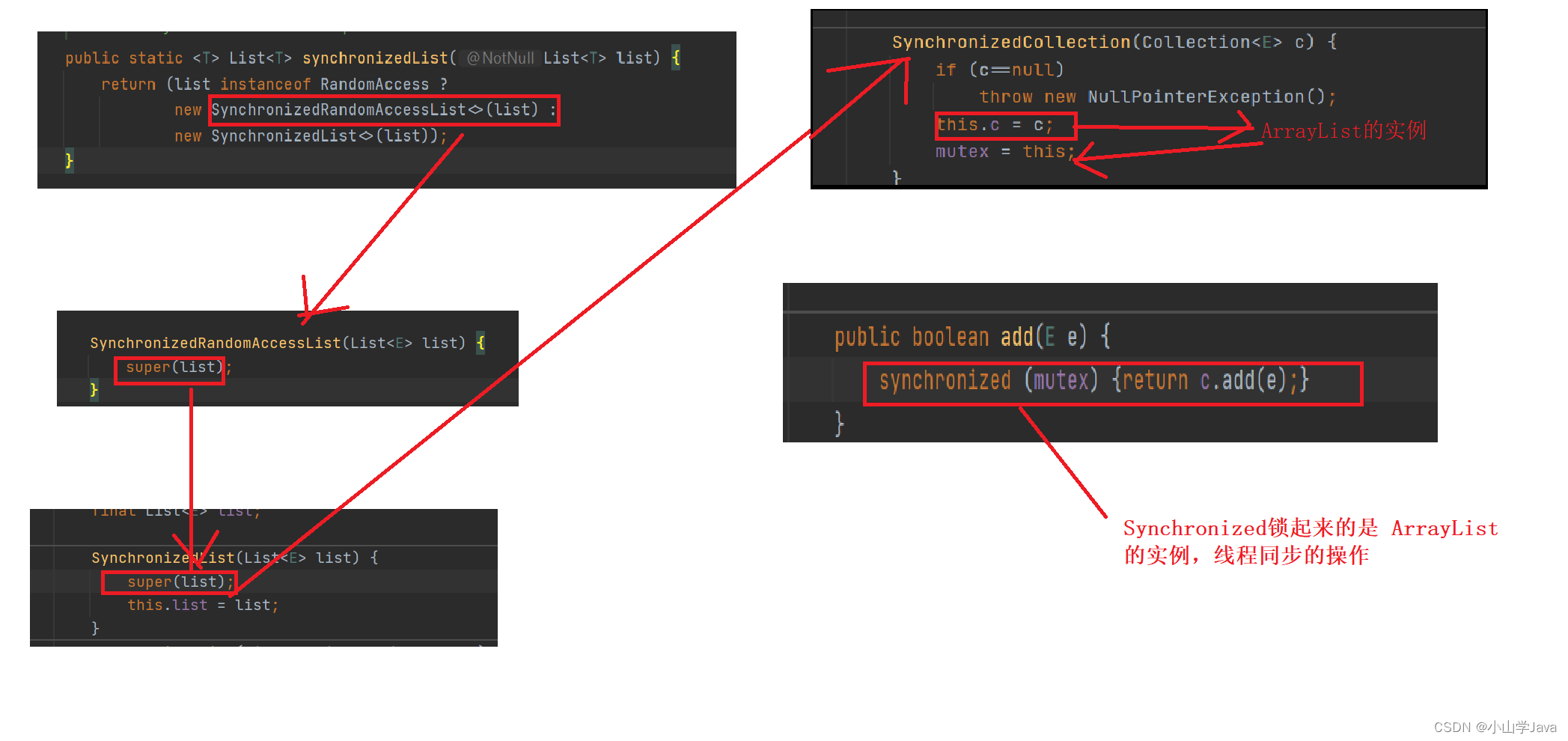
ConcurrentMap并发容器
JKD1.5之后使用ConcurrentHashMap 替代了HashMap,HashTable,提升了程序的性能,解决了并发问题。
HashMap:效率高、线程不安全
HashTable:效率低,线程安全
ConcurrentHashMap:效率比 HashTable高,线程安全
ConcurrentHashMap和 HashTable效率测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
final ConcurrentMap<String,Integer> map = new ConcurrentHashMap()
final Hashtable<String,Integer> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int j = 0; j < 1000000; j++) {
map.put("test"+j,j);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("所需要的时间为:"+(endTime - startTime));
}
}).start();
}
}
CopyOnWriteArrayList源码
public class CopyOnWriteArrayList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable {
private volatile transient Object[] array;
public CopyOnWriteArrayList() {
setArray(new Object[0]);
}
final void setArray(Object[] a) {
array = a;
}
//add方法
public boolean add(E e) {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
//获取到array数组赋值给elements
Object[] elements = getArray();
//arrays数组的长度
int len = elements.length;
//复制操作
Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);
newElements[len] = e;
//array数组的指向改变
setArray(newElements);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
CopyOnWriteArraySet
CopyOnWriteArraySet 的底层实际上就是 CopyOnWriteArrayList。
public class CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>
implements java.io.Serializable {
//顶层是 CopyOnArrayList
private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<E> al;
}
边栏推荐
- DTD modeling
- Cookie和Session的相关概念
- [SQL optimization] the difference between with as and temporary tables
- [go ~ 0 to 1] day 5 July 1 type alias, custom type, interface, package and initialization function
- 任务:拒绝服务DoS
- How to correctly use vertx to operate redis (3.9.4 with source code analysis)
- Opencv video quality diagnosis - VIDEO occlusion diagnosis
- 一文读懂C语言中的结构体
- Learning records of building thingsboard, an Internet of things platform
- Solution and summary of Nacos startup failure
猜你喜欢

Native JS creates a calendar - supports mouse wheel scrolling to select months - and can be ported to any framework

求各种极限的方法

Cookie和Session的相关概念
Task: denial of service DOS

Regular expression =regex=regular expression
EasyGBS网络不稳定情况下重复请求视频拉流问题的优化

Axure does not display catalogs
JS的Proxy
![Thesis reading [distinctive late semantic graph for video capturing]](/img/d4/4f84a73a9127fa87bb0a74c4655d15.png)
Thesis reading [distinctive late semantic graph for video capturing]
![[go ~ 0 to 1] day 5 July 1 type alias, custom type, interface, package and initialization function](/img/1e/bed6a761f07c052e43b1e3b1701760.png)
[go ~ 0 to 1] day 5 July 1 type alias, custom type, interface, package and initialization function
随机推荐
MySQL signale une erreur can 't create table' demo01. TB Étudiant '(errno: 150)
Collect Tiktok video
【无标题】
类加载机制
Why must we move from Devops to bizdevops?
uni-app商品分类
Basic knowledge of audio coding and decoding
精耕渠道共谋发展 福昕携手伟仕佳杰开展新产品培训大会
Botu V16 obtains the system time and converts it into a string
Thesis reading [distinctive late semantic graph for video capturing]
面试题 16.16. 部分排序-双指针法
自定义插入页面标签以及实现类似通讯录的首字母搜索
mysql 報錯 Can‘t create table ‘demo01.tb_Student‘ (errno: 150)*
torch.nn.functional.interpolate函数
JS ternary expression complex condition judgment
直播HLS协议
研究了11种实时聊天软件,我发现都具备这些功能…
Simplified pinduoduo product data
What is the essential difference between Bi development and report development?
Ffmpeg common commands (2)