当前位置:网站首页>JUC(三):锁核心类AQS ing
JUC(三):锁核心类AQS ing
2022-08-03 11:36:00 【学到的心态】
一. AbstractQueuedSynchronizer简介
用来构建锁和同步器的框架,使用AQS能简单且高效的构造出大量的构造器,比如ReentrantLock,Semaphore。当然我们也可以利用AQS轻松构建出符合自己需求的同步器。
1. AQS 核心思想
核心思想是,如果被请求的共享资源空闲,则将当前请求的线程设置为有效的工作线程,并锁定资源。如果资源被占用,那就需要一套线程堵塞以及被唤醒时锁分配的机制(CLH),即将线程加入到队列中。
AQS是将线程封装成CLH锁队列的一个节点(Node)来实现锁的分配。
AQS使用一个int成员变量表示同步状态,通过FIFO队列来完成排队,AQS通过CAS完成对状态的修改。
private volatile int state;//共享变量,使用volatile修饰保证线程可见性
//返回同步状态的当前值
protected final int getState() {
return state;
}
// 设置同步状态的值
protected final void setState(int newState) {
state = newState;
}
//原子地(CAS操作)将同步状态值设置为给定值update如果当前同步状态的值等于expect(期望值)
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
2. AQS 对资源的共享方式
AQS定义两种资源共享方式
- Exclusive(独占):只有一个线程能执行,如ReentrantLock。又分为公平锁和非公平锁:
- 公平锁:按照队列中的排队顺序去获取锁
- 非公平锁:无视队列顺序,谁抢到就是谁的
- share(共享):多个线程可同时执行,如Semaphore/CountDownLatch。
不同的自定义同步器争用共享资源的方式也不同。自定义同步器在实现时只需要实现共享资源 state 的获取与释放方式即可,至于具体线程等待队列的维护(如获取资源失败入队/唤醒出队等),AQS已经在上层已经帮我们实现好了。
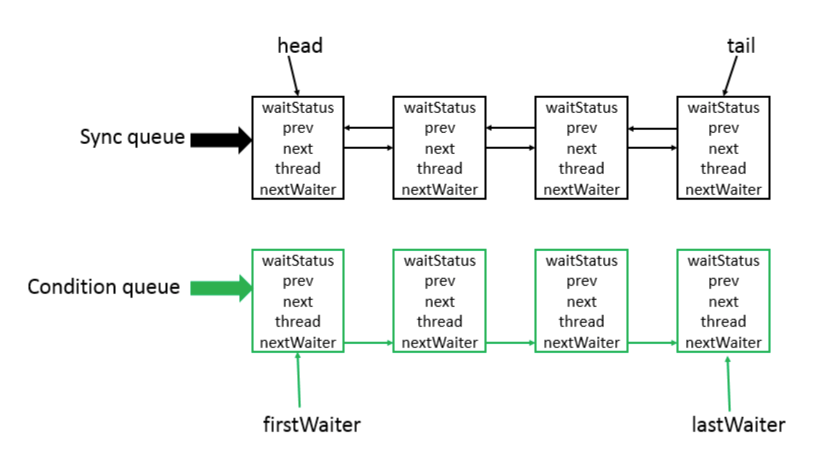
二. AbstractQueuedSynchronizer数据结构
底层数据结构使用CLH队列(一个虚拟的双向队列:虚拟:即不存在队列实例,仅存在节点之间的关联关系)。
AQS是将(请求资源的)线程封装成CLH锁队列的一个节点来实现锁的分配。
- sync queue 同步队列,使用的是双向链表,其中head节点主要用作后续的调度
- condition queue 不是必须的,是一个单向链表,只有使用condition时才会使用此单向链表。
三. AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
内部类 - Node类
static final class Node {
// 模式,分为共享与独占
// 共享模式
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
// 独占模式
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 结点状态
// CANCELLED,值为1,表示当前的线程被取消
// SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前节点的后继节点包含的线程需要运行,也就是unpark
// CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中
// PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行
// 值为0,表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 结点状态
volatile int waitStatus;
// 前驱和后继
volatile Node prev;
volatile Node next;
// 结点所对应的线程
volatile Thread thread;
// 下一个等待者
Node nextWaiter;
// 结点是否在共享模式下等待
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
// 获取前驱结点,若前驱结点为空,抛出异常
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
// 保存前驱结点
Node p = prev;
if (p == null) // 前驱结点为空,抛出异常
throw new NullPointerException();
else // 前驱结点不为空,返回
return p;
}
// 无参构造方法
Node() {
// Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
// 构造方法
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) {
// Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
// 构造方法
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) {
// Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
内部类 - conditionObject类
此类实现了Condition接口,Condition接口定义了条件操作规范,具体如下
public interface Condition {
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号或被中断之前一直处于等待状态
void await() throws InterruptedException;
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号之前一直处于等待状态,不响应中断
void awaitUninterruptibly();
//等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态
long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException;
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定等待时间之前一直处于等待状态。此方法在行为上等效于: awaitNanos(unit.toNanos(time)) > 0
boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
// 等待,当前线程在接到信号、被中断或到达指定最后期限之前一直处于等待状态
boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException;
// 唤醒一个等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则选择其中的一个唤醒。在从 await 返回之前,该线程必须重新获取锁。
void signal();
// 唤醒所有等待线程。如果所有的线程都在等待此条件,则唤醒所有线程。在从 await 返回之前,每个线程都必须重新获取锁。
void signalAll();
}
类的属性
属性中包含了头节点head,尾结点tail,状态state、自旋时间spinForTimeoutThreshold,还有AbstractQueuedSynchronizer抽象的属性在内存中的偏移地址,通过该偏移地址,可以获取和设置该属性的值,同时还包括一个静态初始化块,用于加载内存偏移地址。
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984972572414691L;
// 头/尾 节点
private transient volatile Node head;
private transient volatile Node tail;
// 状态
private volatile int state;
// 自旋时间
static final long spinForTimeoutThreshold = 1000L;
// Unsafe类实例
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
/** * 内存地址 */
// state内存偏移地址
private static final long stateOffset;
// head内存偏移地址
private static final long headOffset;
// state内存偏移地址
private static final long tailOffset;
// tail内存偏移地址
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
// next内存偏移地址
private static final long nextOffset;
}
类的核心方法 - acquire方法
该方法以独占模式获取(资源),忽略中断,即线程在aquire过程中,中断此线程是无效的。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
首先调用tryAcquire方法,调用此方法的线程会试图在独占模式下获取对象状态。此方法应该查询是否允许它在独占模式下获取对象状态,如果允许,则获取它。
若tryAcquire失败,则调用addWaiter方法,将调用此方法的线程封装成为一个结点并放入Sync queue。
调用acquireQueued方法,此方法完成的功能是Sync queue中的结点不断尝试获取资源,若成功,则返回true,否则,返回false。
首先分析addWaiter方法
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 新生成一个结点,默认为独占模式
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
// 保存尾结点
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
// 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
// 比较pred是否为尾结点,是则将尾结点设置为node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
pred.next = node;
return node; // 返回新生成的结点
}
}
enq(node); // 尾结点为空(即还没有被初始化过),或者是compareAndSetTail操作失败,则入队列
return node;
}
//enq方法会使用无限循环来确保节点的成功插入。
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
// 无限循环,确保结点能够成功入队列
// 保存尾结点
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// 尾结点为空,即还没被初始化
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) // 头节点为空,并设置头节点为新生成的结点
tail = head; // 头节点与尾结点都指向同一个新生结点
} else {
// 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化过
// 将node结点的prev域连接到尾结点
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
// 比较结点t是否为尾结点,若是则将尾结点设置为node
// 设置尾结点的next域为node
t.next = node;
return t; // 返回尾结点
}
}
}
}
现在,分析acquireQueue方法。其源码如下
// sync队列中的结点在独占且忽略中断的模式下获取(资源)
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
// 标志
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 中断标志
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 无限循环
// 获取node节点的前驱结点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 前驱为头节点并且成功获得锁
setHead(node); // 设置头节点
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false; // 设置标志
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
首先获取当前节点的前驱节点,如果前驱节点是头节点并且能够获取(资源),代表该当前节点能够占有锁,设置头节点为当前节点,返回。否则,调用shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire和parkAndCheckInterrupt方法,首先,我们看shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法,代码如下
// 当获取(资源)失败后,检查并且更新结点状态
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取前驱结点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) // 状态为SIGNAL,为-1
/* * This node has already set status asking a release * to signal it, so it can safely park. */
// 可以进行park操作
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
// 表示状态为CANCELLED,为1
/* * Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and * indicate retry. */
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0); // 找到pred结点前面最近的一个状态不为CANCELLED的结点
// 赋值pred结点的next域
pred.next = node;
} else {
// 为PROPAGATE -3 或者是0 表示无状态,(为CONDITION -2时,表示此节点在condition queue中)
/* * waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we * need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to * retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking. */
// 比较并设置前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
// 不能进行park操作
return false;
}
只有当该节点的前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL时,才可以对该结点所封装的线程进行park操作。否则,将不能进行park操作。再看parkAndCheckInterrupt方法,源码如下
// 进行park操作并且返回该线程是否被中断
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 在许可可用之前禁用当前线程,并且设置了blocker
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted(); // 当前线程是否已被中断,并清除中断标记位
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt方法里的逻辑是首先执行park操作,即禁用当前线程,然后返回该线程是否已经被中断。再看final块中的cancelAcquire方法,其源码如下:
// 取消继续获取(资源)
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// Ignore if node doesn't exist
// node为空,返回
if (node == null)
return;
// 设置node结点的thread为空
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
// 保存node的前驱结点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0) // 找到node前驱结点中第一个状态小于0的结点,即不为CANCELLED状态的结点
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
// 获取pred结点的下一个结点
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
// 设置node结点的状态为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
// node结点为尾结点,则设置尾结点为pred结点
// 比较并设置pred结点的next节点为null
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// node结点不为尾结点,或者比较设置不成功
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
int ws;
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
// (pred结点不为头节点,并且pred结点的状态为SIGNAL)或者
// pred结点状态小于等于0,并且比较并设置等待状态为SIGNAL成功,并且pred结点所封装的线程不为空
// 保存结点的后继
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0) // 后继不为空并且后继的状态小于等于0
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next); // 比较并设置pred.next = next;
} else {
unparkSuccessor(node); // 释放node的前一个结点
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
该方法完成的功能就是取消当前线程对资源的获取,即设置该结点的状态为CANCELLED,接着我们再看unparkSuccessor方法,源码如下
// 释放后继结点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/* * If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try * to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this * fails or if status is changed by waiting thread. */
// 获取node结点的等待状态
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) // 状态值小于0,为SIGNAL -1 或 CONDITION -2 或 PROPAGATE -3
// 比较并且设置结点等待状态,设置为0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/* * Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally * just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null, * traverse backwards from tail to find the actual * non-cancelled successor. */
// 获取node节点的下一个结点
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
// 下一个结点为空或者下一个节点的等待状态大于0,即为CANCELLED
// s赋值为空
s = null;
// 从尾结点开始从后往前开始遍历
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0) // 找到等待状态小于等于0的结点,找到最前的状态小于等于0的结点
// 保存结点
s = t;
}
if (s != null) // 该结点不为为空,释放许可
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
该方法的作用就是为了释放node节点的后继结点。
对于cancelAcquire与unparkSuccessor方法,如下示意图可以清晰的表示
类的核心方法 - release方法
以独占模式释放对象,其源码如下:
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 释放成功
// 保存头节点
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) // 头节点不为空并且头节点状态不为0
unparkSuccessor(h); //释放头节点的后继结点
return true;
}
return false;
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer总结
对于AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的分析,最核心的就是sync queue的分析。
- 每一个结点都是由前一个结点唤醒
- 当结点发现前驱结点是head并且尝试获取成功,则会轮到该线程运行。
- condition queue中的结点向sync queue中转移是通过signal操作完成的。
- 当结点的状态为SIGNAL时,表示后面的结点需要运行
参考:https://pdai.tech/md/java/thread/java-thread-x-lock-AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.html
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

FR9811S6 SOT-23-6 23V, 2A Synchronous Step-Down DC/DC Converter
在线生成接口文档

Babbitt | Metaverse daily must-read: Players leave, platforms are shut down, and the digital collection market is gradually cooling down. Where is the future of the industry?...
Polymorphism in detail (simple implementation to buy tickets system simulation, covering/weight definition, principle of polymorphism, virtual table)

面试突击71:GET 和 POST 有什么区别?
机器学习(第一章)—— 特征工程

html网页如何获取后台数据库的数据(html + ajax + php + mysql)
【一起学Rust 基础篇】Rust基础——变量和数据类型
RICON:NER SOTA 又来!
MySQL之json数据操作
随机推荐
通过组策略安装软件和删除用户配置文件
Fastjson反序列化
Skills required to be a good architect: How to draw a system architecture that everyone will love?What's the secret?Come and open this article to see it!...
ThreadLocal源码解析及使用场景
Machines need tokens more than people
距LiveVideoStackCon 2022 上海站开幕还有3天!
使用.NET简单实现一个Redis的高性能克隆版(一)
字符串本地化和消息字典(二)
永寿 永寿农特产品-苹果
赛灵思MPSOC裸机下的 USB调试实验
[错题]电路维修
字节最爱问的智力题,你会几道?
JS快速高效开发技巧指南(持续更新)
零拷贝、MMAP、堆外内存,傻傻搞不明白...
增加WebView对localStorage的支持
基于Sikuli GUI图像识别框架的PC客户端自动化测试实践
bash case用法
深度学习跟踪DLT (deep learning tracker)
在线生成接口文档
GET 和 POST 有什么区别?
