当前位置:网站首页>Using matlab to solve the linear optimization problem based on matlab dynamic model of learning notes _11 】 【
Using matlab to solve the linear optimization problem based on matlab dynamic model of learning notes _11 】 【
2022-08-03 23:52:00 【crooked babi】
题目:

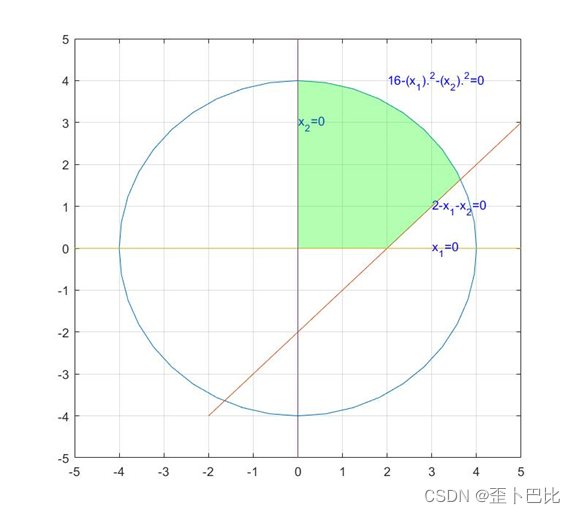
(1)Draw the feasible domain range
question1.m
%% Mark the function
r=4;
a1=0;
a2=0;
theta=0:pi/20:2*pi;
x_1=a1+r*cos(theta);
x_2=a2+r*sin(theta);
plot(x_1,x_2);
hold on
text(2,4,'16-(x_1)^2-(x_2)^2=0','color','b'); %在坐标点(6.8,4)显示x1=7this function line
L2=[-2,-4;5,3];
plot(L2(:,1),L2(:,2));hold on %x2最大值为3
text(3,1,'2-x_1-x_2=0','color','b'); %从点L2(:,1)到点L2(:,2)
L3=[-5,0;5 0];
plot(L3(:,1),L3(:,2));hold on
text(3,0,'x_1=0','color','b')
L4=[0,-5;0,5];
plot(L4(:,1),L4(:,2));
text(0,3,'x_2=0','color','b')
grid on
%% 填充
[X1,X2]=meshgrid(0:0.01:5,0:0.01:5);%draw area
idX1=(X1.*X1+X2.*X2<=16)&(-X2+X1<=2)&(X1>=0)&(X2>=0);
X1=X1(idX1);
X2=X2(idX1);
k=convhull(X1,X2); %计算面积
h=fill(X1(k),X2(k),'g'); %绿色填充
set(h,'edgealpha',0,'facealpha',0.3) %边界,透明度
(2)利用fminconSolve separately without constraints、Constrain the optimal solution
Matlab中的fminconThe function can be used to find the minimum of a constrained nonlinear multivariate function,This is used to find the optimal solution here.
fmincon函数参考:
MatlabSolve nonlinear programs,fmincon函数的用法总结_Xiao Zhu~的博客-CSDN博客_fmincon函数用法
官方帮助文档:https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/optim/ug/fmincon.html? searchHighlight=fmincon&s_tid=srchtitle_fmincon_1
(2.1)Unconstrained optimal solution
目标函数fun1.m:
%目标函数
function f=fun1(x)
f=(x(1)-2).^2+(x(2)-5).^2
end
Unconstrained optimal solutionquestion2_1.m:
%% Mark the function
r=4;
a1=0;
a2=0;
theta=0:pi/20:2*pi;
x_1=a1+r*cos(theta);
x_2=a2+r*sin(theta);
plot(x_1,x_2);
hold on
text(2,4,'16-(x_1)^2-(x_2)^2=0','color','b'); %在坐标点(6.8,4)显示x1=7this function line
L2=[-2,-4;5,3];
plot(L2(:,1),L2(:,2));hold on %x2最大值为3
text(3,1,'2-x_1-x_2=0','color','b'); %从点L2(:,1)到点L2(:,2)
L3=[-5,0;5 0];
plot(L3(:,1),L3(:,2));hold on
text(3,0,'x_1=0','color','b')
L4=[0,-5;0,5];
plot(L4(:,1),L4(:,2));
text(0,3,'x_2=0','color','b')
grid on
%% 填充
[X1,X2]=meshgrid(0:0.01:5,0:0.01:5);%draw area
idX1=(X1.*X1+X2.*X2<=16)&(-X2+X1<=2)&(X1>=0)&(X2>=0);
X1=X1(idX1);
X2=X2(idX1);
k=convhull(X1,X2); %计算面积
h=fill(X1(k),X2(k),'g'); %绿色填充
set(h,'edgealpha',0,'facealpha',0.3) %边界,透明度
%问题2.1主函数
options=optimset;
x0=[0;0];%给定初值
lb=[0;0];%Function lower bound
ub=[5;5];%upper limit of the function
[x,y]=fmincon('fun1',x0,[],[],[],[],lb,ub)
%加标注
text(-3,2,'X*(1)=2.0000')
text(-2.1,1.6,'4.9994')
text(-3,1.2,'f(X*(1))=4.1847e-07')
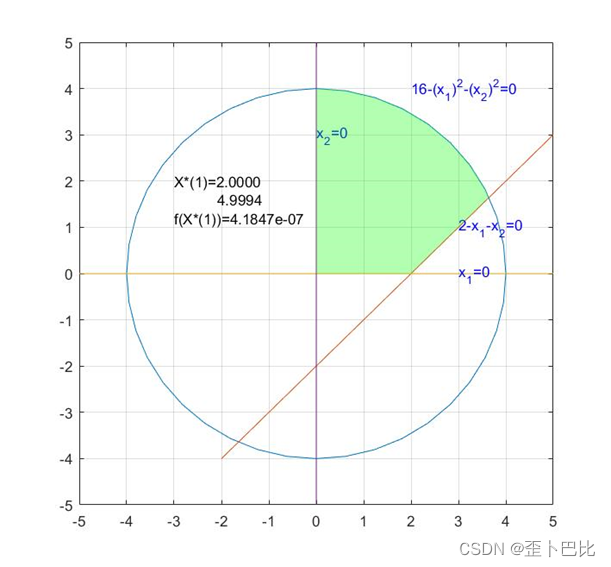
(2.2)Constrain the optimal solution
目标函数fun1.m:
%目标函数
function f=fun1(x)
f=(x(1)-2).^2+(x(2)-5).^2
end
Nonlinear constraint functionfun2.m:
%Nonlinear constraint function
function[g,h]=fun2(x)
%matlab中默认g<=0,If it does not correspond, it needs to be reversed
g(1)=-16+x(2).^2+x(1).^2;
g(2)=-2+x(1)+x(2);
h=[];%Use null instead when there is no equality constraint
end
Unconstrained optimal solutionquestion2_2.m:
%% Mark the function
r=4;
a1=0;
a2=0;
theta=0:pi/20:2*pi;
x_1=a1+r*cos(theta);
x_2=a2+r*sin(theta);
plot(x_1,x_2);
hold on
text(2,4,'16-(x_1)^2-(x_2)^2=0','color','b'); %在坐标点(6.8,4)显示x1=7this function line
L2=[-2,-4;5,3];
plot(L2(:,1),L2(:,2));hold on %x2最大值为3
text(3,1,'2-x_1-x_2=0','color','b'); %从点L2(:,1)到点L2(:,2)
L3=[-5,0;5 0];
plot(L3(:,1),L3(:,2));hold on
text(3,0,'x_1=0','color','b')
L4=[0,-5;0,5];
plot(L4(:,1),L4(:,2));
text(0,3,'x_2=0','color','b')
grid on
%% 填充
[X1,X2]=meshgrid(0:0.01:5,0:0.01:5);%draw area
idX1=(X1.*X1+X2.*X2<=16)&(-X2+X1<=2)&(X1>=0)&(X2>=0);
X1=X1(idX1);
X2=X2(idX1);
k=convhull(X1,X2); %计算面积
h=fill(X1(k),X2(k),'g'); %绿色填充
set(h,'edgealpha',0,'facealpha',0.3) %边界,透明度
%问题2.2主函数
options=optimset;
x0=[0;0];%给定初值
lb=[0;0];%Function lower bound
ub=[5;5];%upper limit of the function
[x,y]=fmincon('fun1',x0,[],[],[],[],lb,ub,'fun2')
%加标注
text(-3,2,'X*(2)=0.0000')
text(-2.1,1.6,'2.0000')
text(-3,1.2,'f(X*(2))=13') 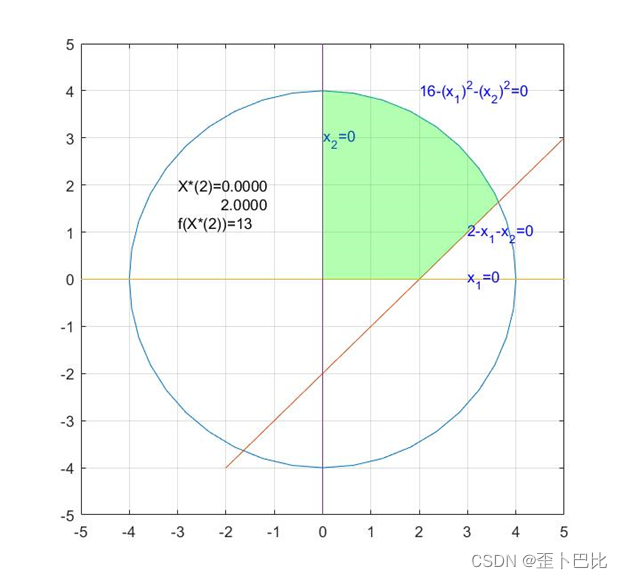
(3)Linearly constrained optimal solution
目标函数fun1.m:
%目标函数
function f=fun1(x)
f=(x(1)-2).^2+(x(2)-5).^2
end
Linear constraint functionfun3.m:
%Linear constraint function
function[g,h]=fun3(x)
%matlab中默认g<=0,If it does not correspond, it needs to be reversed
g(1)=-16+x(2).^2+x(1).^2;
g(2)=-2+x(1)+x(2);
%线性约束条件
h=x(1)-x(2);
end
Linearly constrained optimal solutionquestion3.m:
%% Mark the function
r=4;
a1=0;
a2=0;
theta=0:pi/20:2*pi;
x_1=a1+r*cos(theta);
x_2=a2+r*sin(theta);
plot(x_1,x_2);
hold on
text(2,4,'16-(x_1)^2-(x_2)^2=0','color','b'); %在坐标点(6.8,4)显示x1=7this function line
L2=[-2,-4;5,3];
plot(L2(:,1),L2(:,2));hold on %x2最大值为3
text(3,1,'2-x_1-x_2=0','color','b'); %从点L2(:,1)到点L2(:,2)
L3=[-5,0;5 0];
plot(L3(:,1),L3(:,2));hold on
text(3,0,'x_1=0','color','b')
L4=[0,-5;0,5];
plot(L4(:,1),L4(:,2));
text(0,3,'x_2=0','color','b')
grid on
%% 填充
[X1,X2]=meshgrid(0:0.01:5,0:0.01:5);%draw area
idX1=(X1.*X1+X2.*X2<=16)&(-X2+X1<=2)&(X1>=0)&(X2>=0);
X1=X1(idX1);
X2=X2(idX1);
k=convhull(X1,X2); %计算面积
h=fill(X1(k),X2(k),'g'); %绿色填充
set(h,'edgealpha',0,'facealpha',0.3) %边界,透明度
%问题3主函数
options=optimset;
x0=[0;0];%给定初值
lb=[0;0];%Function lower bound
ub=[5;5];%upper limit of the function
[x,y]=fmincon('fun1',x0,[],[],[],[],lb,ub,'fun3')
%加标注
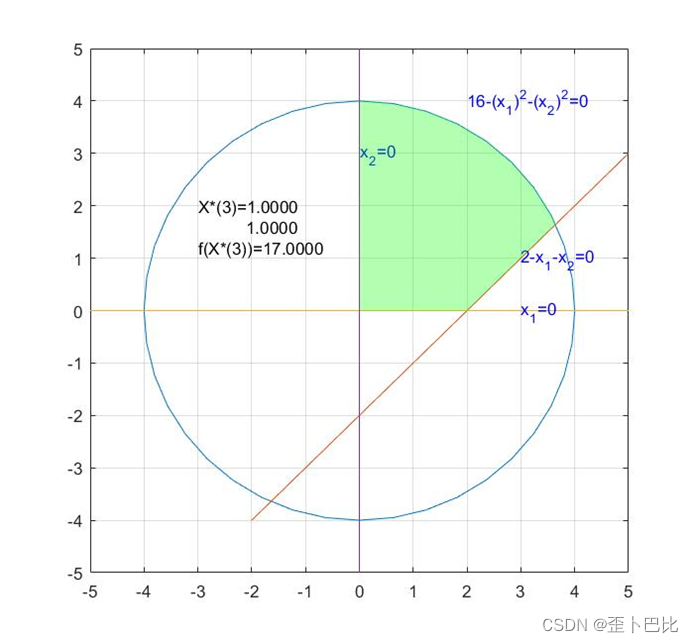
text(-3,2,'X*(3)=1.0000')
text(-2.1,1.6,'1.0000')
text(-3,1.2,'f(X*(3))=17.0000')
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Justin Sun was invited to attend the 36氪 Yuan Universe Summit and delivered a keynote speech
689. 三个无重叠子数组的最大和
Creo9.0 绘制中心线
CAS: 178744-28-0, mPEG-DSPE, DSPE-mPEG, methoxy-polyethylene glycol-phosphatidylethanolamine supply
Flutter教程之为什么 Flutter 是创业的最佳选择?
小身材有大作用——光模块寿命分析(二)
Walk the Maze BFS
MCS-51单片机,定时1分钟,汇编程序
FinClip, help smart TV more imagination
重新认识浏览器的渲染过程
Fluorescein-PEG-CLS, cholesterol-polyethylene glycol-fluorescein scientific research reagent
【MySQL —— 索引】
Why Flutter Flutter of tutorials is the best choice for business?
并查集详解
The Chinese Valentine's Day event is romantically launched, don't let the Internet slow down and miss the dark time
[2022强网杯] polydiv和gamemaster
Pytest学习-skip/skipif
HNUCM 您好中国
End-to-End Lane Marker Detection via Row-wise Classification
【LeetCode】最长公共子序列(动态规划)