当前位置:网站首页>[CEPH] Introduction to cephfs caps
[CEPH] Introduction to cephfs caps
2022-06-26 15:29:00 【bandaoyu】
Catalog
CAPS Data representation and rules
CAPS Basics
Basic concepts
caps yes mds grant client A license to operate on a file , When one client When you want to make changes to file metadata , Like reading 、 Write 、 Modify permissions and other operations , It must first obtain the corresponding caps These operations can be carried out .
ceph Yes caps The partition granularity of is very fine , And multiple client In the same inode Hold different on caps.
CAPS species
According to the content of metadata ,ceph take caps It is also divided into several categories , Each category is responsible only for certain metadata :
| Category | function |
|---|---|
| PIN | mds Whether or not to inode pin stay cache in |
| AUTH | Authentication related metadata , Mainly owner、group、mode; However, for complete authentication, you need to view ACL Of ,acl The information is kept in xattr in , This requires XATTR dependent cap |
| XATTR | xattr |
| FILE | The most important and complicated one , For file data , And related to file data ize、atime、ctime、mtime etc. |
CAPS PERMISSION species
#define CEPH_CAP_GSHARED 1 /* client can reads (s) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GEXCL 2 /* client can read and update (x) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GCACHE 4 /* (file) client can cache reads (c) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GRD 8 /* (file) client can read (r) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GWR 16 /* (file) client can write (w) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GBUFFER 32 /* (file) client can buffer writes (b) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GWREXTEND 64 /* (file) client can extend EOF (a) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GLAZYIO 128 /* (file) client can perform lazy io (l) */
CAPS COMBINATION
A complete cap adopt 【 Category +permission species 】 form ,client You can apply for multiple categories at the same time caps. however Not every caps You can use each permission, There are some caps Only part of it can be matched permission. of caps Kind and permission Combined use of , There are several rules :
PIN
Binary type , Yes pin On behalf of client Know this inode There is , such mds It must be in its cache Save this inode
AUTH、LINK、XATTR
Only for shared perhaps exclusive
- shared:client The corresponding metadata can be saved locally, cached and used
- exclusive:client Not only can it be used in the local cache , You can also modify
Here are two examples :
- [A]s: some client Yes inode 0x11 Yes As Of cap, At this point, you receive a view 0x11 State system call , that client There is no need to ask mds request , Directly query its own cache and process and reply
- [A]x: some client Yes inode 0x11 Yes Ax Of cap, A modification is received at this time mode System call ,client You can modify it locally and reply , And the modification and change will be notified later mds
FILE
As mentioned earlier ,file Is the most complicated one , Here is File cap Categories of :
| file cap species | client jurisdiction |
|---|---|
| Fs | client Can be mtime and size In the local cache Read and use |
| Fx | client Can be mtime and size In the local cache And modify and read |
| Fr | client Can be synchronized from osd Reading data , But not cache |
| Fc | client File data can be cache In local memory , And directly from cache Chinese Reading |
| Fw | client You can write data synchronously to osd in , But you can't buffer write |
| Fb | client Sure buffer write, First, maintain the written data in your own memory , Reunite flush To the rear end |
CAPS management
LOCK
caps from mds Conduct management , It divides metadata into parts , Each part has a special lock (SimpleLock、ScatterLock、FileLock) To protect the ,mds Determined by the status of these locks caps How can I allocate .
mds The state machine of each lock is maintained internally , Its content is very complicated , It's also mds Guarantee caps The key to distribution accuracy and data consistency .
CAPS How to change
- mds For each client Grant and remove caps, Usually by others client Your behavior triggers
- example : such as client1 Already have inode 0x111 Of cache read Of cap, here client2 To write to this file , That's obviously except for granting client2 Write response caps At the same time , And deprive client1 Of cache read Of cap
- When client Removed caps when , It must stop using the cap, And give mds Respond to the confirmation message .mds Need to wait to receive client Only after the confirmation message of revoke.( If client Hang up or don't reply for some reason ack What do I do ?)
- client It is not easy to stop using , Different scenarios require completely different processing :
- example 1:client Removed cache read cap, Put it directly file Of cache Delete , And change the status , So next time read When the request comes in , Or to osd To read
- example 2:client Removed buffer write cap, A large amount of data has been cached, but not yet flush, Then you need to flush To osd, Change the status and confirm , This may take a long time
Let's take a look at an example of modifying permissions to actually feel :
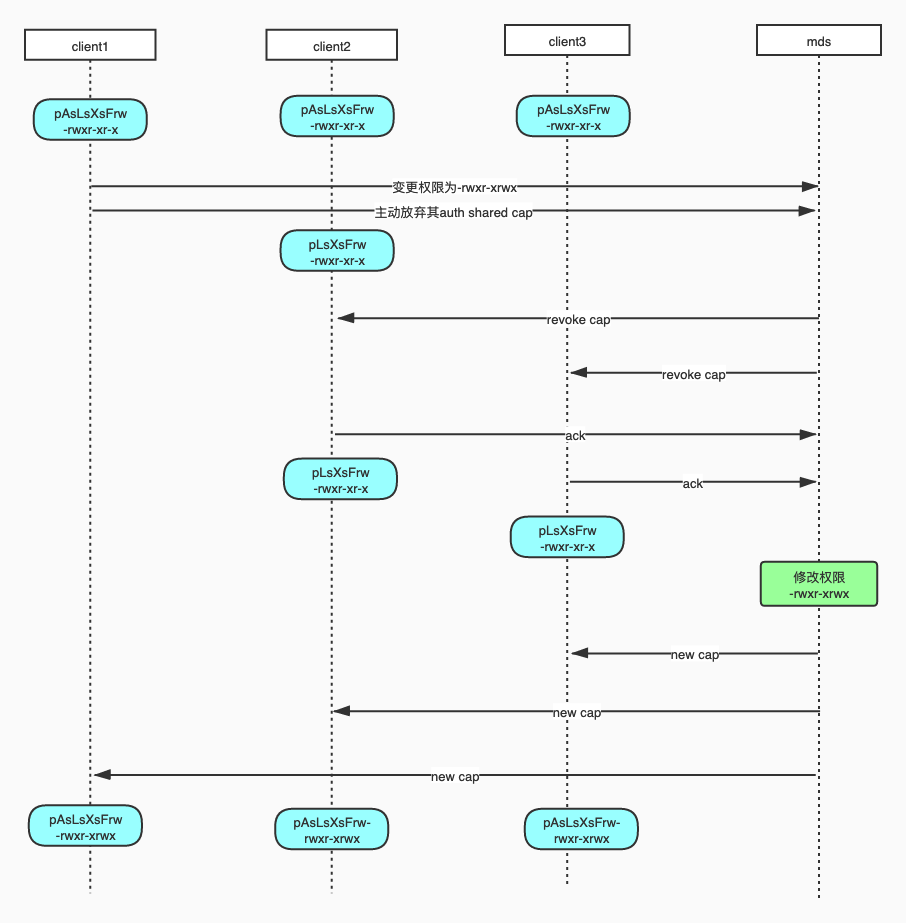
CAPS Related alarms
Here are some caps Relevant main alarm information , For reference, check the problems :
| The alarm information | problem |
|---|---|
| Client failing to respond to capability release | mds Issued revoke cap Message but client No reply |
| Client failing to cache pressure | mds Send message request client Remove some pinned inode To reduce memory usage , but client No, drop Enough or no reply fast enough |
summary
- mds Need to remember all client pin Of inode,
- mds Of cache Need to be compared with client Of cache more
- caps By mds and client The end cooperates to maintain , therefore client Normal operation is required , Otherwise, it may block other client( That is to say, the question raised above , Will be block?)
CAPS Code related
CAPS Data representation and rules
One client Can have many types (A,L,X,F) Of caps, Every type of caps There are also many kinds. permission type (s,x,c,r,w,b,a,l). So how to express so many types of caps Well ?
- ceph First, each type is specified cap Of bit Range , Guarantee different types of cap Of bit The scope does not overlap .
/* generic cap bits */
#define CEPH_CAP_GSHARED 1 /* client can reads(s) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GEXCL 2 /* client can read and update(x) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GCACHE 4 /* (file) client can cache reads(c) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GRD 8 /* (file) client can read(r) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GWR 16 /* (file) client can write(w) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GBUFFER 32 /* (file) client can buffer writes(b) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GWREXTEND 64 /* (file) client can extend EOF(a) */
#define CEPH_CAP_GLAZYIO 128 /* (file) client can perform lazy io(l) */
/* per-lock shift */
#define CEPH_CAP_SAUTH 2 // A
#define CEPH_CAP_SLINK 4 // L
#define CEPH_CAP_SXATTR 6 // X
#define CEPH_CAP_SFILE 8 // F
- By defining each type permission Type of bit Bits and each cap Offset of type , Combine the two by shifting to form a single cap.
#define CEPH_CAP_AUTH_SHARED (CEPH_CAP_GSHARED << CEPH_CAP_SAUTH) // As
#define CEPH_CAP_AUTH_EXCL (CEPH_CAP_GEXCL << CEPH_CAP_SAUTH) // Ax
#define CEPH_CAP_LINK_SHARED (CEPH_CAP_GSHARED << CEPH_CAP_SLINK) // Ls
#define CEPH_CAP_LINK_EXCL (CEPH_CAP_GEXCL << CEPH_CAP_SLINK) // Lx
#define CEPH_CAP_XATTR_SHARED (CEPH_CAP_GSHARED << CEPH_CAP_SXATTR) // Xs
#define CEPH_CAP_XATTR_EXCL (CEPH_CAP_GEXCL << CEPH_CAP_SXATTR) // Xx
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE(x) (x << CEPH_CAP_SFILE)
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_SHARED (CEPH_CAP_GSHARED << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fs
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_EXCL (CEPH_CAP_GEXCL << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fx
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_CACHE (CEPH_CAP_GCACHE << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fc
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_RD (CEPH_CAP_GRD << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fr
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_WR (CEPH_CAP_GWR << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fw
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER (CEPH_CAP_GBUFFER << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fb
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_WREXTEND (CEPH_CAP_GWREXTEND << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fa
#define CEPH_CAP_FILE_LAZYIO (CEPH_CAP_GLAZYIO << CEPH_CAP_SFILE) // Fl
- Then use the or operator to change the cap Combine to form multiple caps
More vivid use of graphics to express :
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
| p | _ |As x |Ls x |Xs x |Fs x c r w b a l |
+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+---+
| PIN | AUTH | LINK | XATTR | FILE
0 2 4 6 8
There are two more points to note here :
- pin cap It only needs bit position 0, therefore bit position 1 It is useless to be idle
- except file cap, None of the other types will occupy 2bit above , So the file cap Put it high
FUSE WRITE example
An instance
Let's say fuse client write For example , Briefly analyze fuse write when caps Code logic :
notes : Only and are intercepted caps Relevant part of the code
int64_t Client::_write(Fh *f, int64_t offset, uint64_t size, const char *buf,
const struct iovec *iov, int iovcnt)
{
want = CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER;
// Need to own file write(CEPH_CAP_FILE_WR) and auth shared(CEPH_CAP_AUTH_SHARED) caps only ( namely FwAs) Be able to write ,get_caps If there is no caps will
// Whereabouts mds Apply and wait for return
int r = get_caps(in, CEPH_CAP_FILE_WR|CEPH_CAP_AUTH_SHARED, want, &have, endoff);
if (r < 0)
return r;
/* clear the setuid/setgid bits, if any */
if (unlikely(in->mode & (S_ISUID|S_ISGID)) && size > 0) {
struct ceph_statx stx = { 0 };
// Add this inode For the caps Reference count of and check the caps Whether it is in use
put_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_AUTH_SHARED);
r = __setattrx(in, &stx, CEPH_SETATTR_KILL_SGUID, f->actor_perms);
if (r < 0)
return r;
} else {
put_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_AUTH_SHARED);
}
// If there is buffer perhaps lazy io cap Directly in objectcacher cache Write in
if (cct->_conf->client_oc &&
(have & (CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER | CEPH_CAP_FILE_LAZYIO))) {
// do buffered write
if (!in->oset.dirty_or_tx)
get_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_FILE_CACHE | CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER);
get_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER);
// async, caching, non-blocking.
// Cache write calls , asynchronous 、cache、 Non blocking
r = objectcacher->file_write(&in->oset, &in->layout,
in->snaprealm->get_snap_context(),
offset, size, bl, ceph::real_clock::now(),
0);
put_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER);
if (r < 0)
goto done;
// flush cached write if O_SYNC is set on file fh
// O_DSYNC == O_SYNC on linux < 2.6.33
// O_SYNC = __O_SYNC | O_DSYNC on linux >= 2.6.33
if ((f->flags & O_SYNC) || (f->flags & O_DSYNC)) {
_flush_range(in, offset, size);
}
} else {// without buffer cap, Directly through osd Write
if (f->flags & O_DIRECT)
_flush_range(in, offset, size);
// simple, non-atomic sync write
C_SaferCond onfinish("Client::_write flock");
unsafe_sync_write++;
get_cap_ref(in, CEPH_CAP_FILE_BUFFER); // released by onsafe callback
// Synchronous write calls
filer->write_trunc(in->ino, &in->layout, in->snaprealm->get_snap_context(),
offset, size, bl, ceph::real_clock::now(), 0,
in->truncate_size, in->truncate_seq,
&onfinish);
client_lock.Unlock();
// After writing, wait here through the condition variable , Wake up when the writing is finished , Perform some cleanup and return to
onfinish.wait();
client_lock.Lock();
_sync_write_commit(in);
}
}
Reference link
[1] What are “caps”? (And Why Won’t my Client Drop Them?)
[2] cephfs capabilities
from :cephfs caps brief introduction _https://blog.csdn.net/jiang4357291/article/details/103738524
cephfs caps brief introduction - https://www.freesion.com/article/3041236135/
边栏推荐
- MySQL数据库基本SQL语句教程之高级操作
- 一键分析硬件/IO/全国网络性能脚本(强推)
- 【文件】VFS四大struct:file、dentry、inode、super_block 是什么?区别?关系?--编辑中
- PHP file upload 00 truncation
- How to load the contour CAD drawing of the engineering coordinate system obtained by the designer into the new earth
- Database - sequence
- 【SNMP】snmp trap 介绍、安装、命令|Trap的发送与接收代码实现
- 在校生学习生涯总结(2022)
- Unity C# 网络学习(十)——UnityWebRequest(一)
- 【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB单据受理-事务执行介绍
猜你喜欢

Halcon C # sets the form font and adaptively displays pictures
![[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb system user group introduction](/img/7b/8c4f1549054ee8c0184495d9e8e378.png)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb system user group introduction
![[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb doc acceptance - create business introduction](/img/05/8ec56393cac534cb5a00c10a1a9f32.png)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] tcapulusdb doc acceptance - create business introduction
Evaluate:huggingface评价指标模块入门详细介绍
Mr. Du said that the website was updated with illustrations

RestCloud ETL解决shell脚本参数化

Utilisation d'abortcontroller

Vsomeip3 dual computer communication file configuration

刷题笔记(十九)--二叉树:二叉搜索树的修改与构造

How to load the contour CAD drawing of the engineering coordinate system obtained by the designer into the new earth
随机推荐
[CEPH] cephfs internal implementation (I): Concept -- undigested
数据库-视图
Evaluate:huggingface detailed introduction to the evaluation index module
Restcloud ETL extracting dynamic library table data
RestCloud ETL与Kettle对比分析
SAP sales data actual shipment data export sales
High frequency interview 𞓜 Flink Shuangliu join
Seurat to h5ad summary
1. accounting basis -- several major elements of accounting (general accounting theory, accounting subjects and accounts)
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb general documents
Lexin AWS IOT expresslink module achieves universal availability
vsomeip3 双机通信文件配置
Learning memory barrier
买股票通过券商经理的开户二维码开户资金是否安全?想开户炒股
Particle filter PF -- Application in maneuvering target tracking (particle filter vs extended Kalman filter)
[CEPH] cephfs internal implementation (IV): how is MDS started-- Undigested
【TcaplusDB知识库】TcaplusDB常规单据介绍
[tcapulusdb knowledge base] Introduction to tcapulusdb data structure
音视频学习(三)——sip协议
乐鑫 AWS IoT ExpressLink 模组达到通用可用性
