当前位置:网站首页>Scala basics [HelloWorld code parsing, variables and identifiers]
Scala basics [HelloWorld code parsing, variables and identifiers]
2022-07-05 20:10:00 【hike76】
List of articles
One introduction
1 hello scala world Code parsing
package com.hike.bigdata.scala.chapter01
/** * scala Language is based on java Developed * * package:java In the package * * object: Declare an object , At compile time , It will be compiled into two class files * The declared object is of type : The current object +$ * java: * User user = new User(); * user.setName(); * scala: * Scala01_HelloWorld = new Scala01_HelloWorld$(); * * Scala01_HelloWorld: Object name * * def: Declare the keyword of the method * * main:scala The entry method name of the program , No, main, The program cannot be executed * * (): Method * * args: Array[String]: Parameters * java: * String[] args, Strong type language , Determine the type of variable before running * In the process of development , Variable name is more important than variable type * therefore scala Write the name first , Add a colon between the name and type as a separator * scala: * args:Array[String] * args: Parameter name * Array[String]: Parameter type * : Separator * * Array[String]:Array It's an array type * scala Language is a completely object-oriented language , So all things are objects * Arrays are also objects , There are also their own types , The type is :Array, there [] For generics * * java In the array : * String[]:String Represents the type of elements in an array ,[] Represents an array , * Array in java There is no type in * : Unit => stay scala in : * name : type * Parameter name : Parameter type * Variable name : Variable type * Method name : Method 's return value type * * Unit Represents the return value type ,Unit yes scala New types in , To replace void keyword , Indicates that there is no return value * void Keyword problem : Return value , Add the type of variable , Such as int String * Return no value , Add keywords , Not unified * Equals to equating keywords with types , Unreasonable , So there is Unit type * =: assignment * * {}: Method body * * System.out.println("Hello Scala World"):java Code * scala Language based java Language development , So most of the java The code can be directly in scala Use in * * The code may not need to end with a semicolon ,scala It is recommended that there is only one logic in a line of code , Then the semicolon can be omitted * If there is more than one logic in a line, you need to add a semicolon */
object Scala01_HelloWorld {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
System.out.println("Hello Scala World")
}
}
2 Decompile
If you only parse the syntax through code , Can't understand its real implementation principle .scala Language is based on Java Language development , So it will also be compiled as class file , Then we can decompile instructions javap -v Class name or decompiler jd-gui.exe see scala Compiled code , Through comparison and java The relationship between languages , To master the implementation principle of specific code .
3 Associated source code
In the use of Scala In the process , To find out Scala The underlying mechanism , Need to check the source code , Then you need to associate and view Scala The source package .
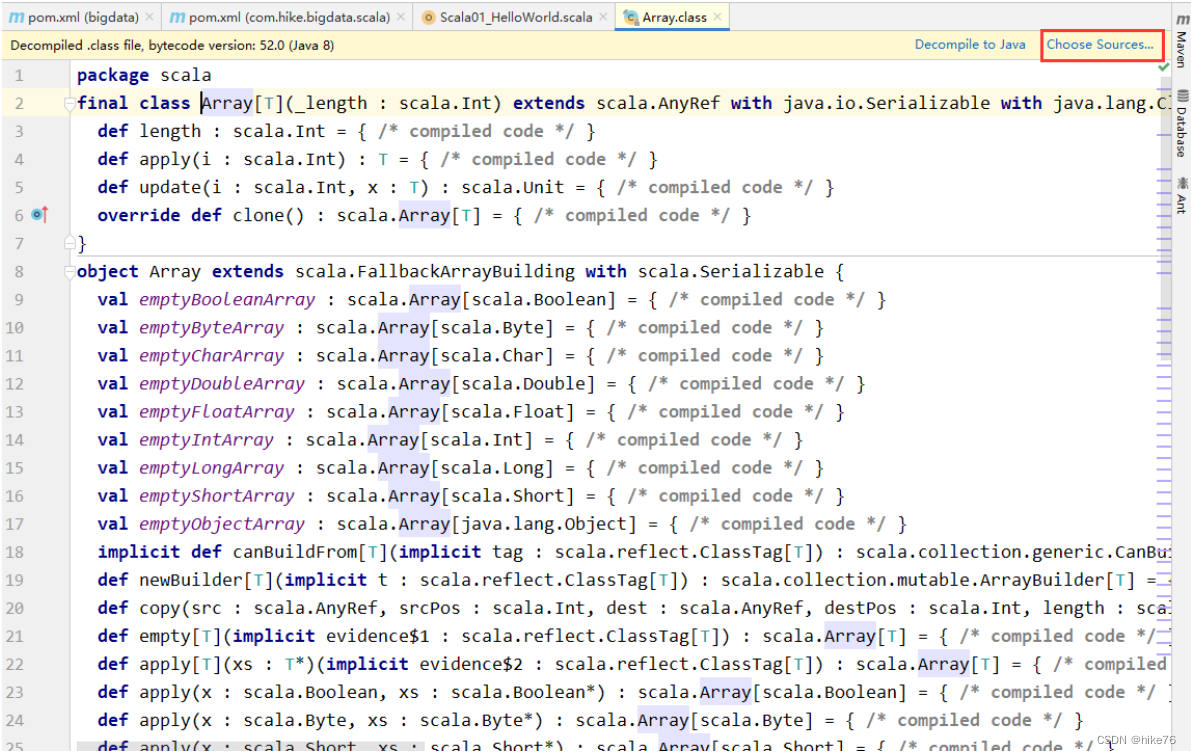
Download the source code , Choose the path .
Two Variables and data types
1 Variable
Variable is a convenient placeholder , Used to refer to the memory address of the computer , Variables take up a certain amount of memory space after they are created . Data types based on variables , The operating system allocates memory and decides what will be stored in reserved memory . therefore , By assigning different data types to variables , You can store integers in these variables , Decimals or letters .
(1) Variable declarations
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// TODO Variable
// Java Variable declaration in : String name = "zhangsan";
// scala Variable declaration in (1):var Variable name : Variable type = A variable's value
var name_var : String = "zhangsan"
// Some variables in some scenarios , Cannot reassign after initialization
// scala Variable declaration in (2):val Variable name : Variable type = A variable's value
val name_fin : String = "lisi"
}
If the type of variable can be inferred from the value of the variable , Then you can omit the type declaration , Omission here , It's not that you don't declare , But by the Scala The compiler automatically declares the compiled at compile time .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// TODO Variable
// In strongly typed languages , The declaration of types should be consistent
// If you know clearly what type of variable value is , Then the type of variable can be omitted without writing
// If polymorphism is used , Type cannot be omitted
var name = "zhangsan"
println(name)
}
(2) Variable initialization
Java Variables in syntax can be initialized before use , however Scala It is not allowed in grammar , Must be displayed for initialization .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
var username // Error
val username = "zhangsan" // OK
}
(3) Volatile variables
Variable whose value can be changed , It is called a variable variable , But the variable type cannot be changed , Scala Use the keyword... For variable variables in var Make a statement .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// User name
var username : String = "zhangsan"
username = "lisi" // OK
username = true // Error
}
(4) Immutable variable
A variable whose value cannot be changed once initialized , Call it an immutable variable .Scala Use keywords in immutable variables val Make a statement , Be similar to Java In language final keyword .
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// User name
val username : String = "zhangsan"
username = "lisi" // Error
username = true // Error
}
val and var Two modifiers , Recommended val
Java Why is the string in called immutable string : Because in java The definition of string in is private final char[] value;, also String Class does not provide any method to change the content . All methods that operate on strings will produce new strings .
trim Method is used to remove half width spaces at the beginning and end of a string .( Europe and America are half width , Asia and Europe are all corners )
2 identifier
(1) Identifier definition rules
Scala Identifier and java The identifiers of are basically the same , Two forms of flags can be used , Characters, numbers and symbols .
- Characters begin with letters or underscores , It can be followed by letters or numbers , stay Scala in [ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly also see do by word mother . however and With open head Of mark knowledge operator by Protect leave Of S c a l a Ed translate device production raw Of mark Records operator send use , Should be use cheng order Should be The avoid Exemption send use Also seen as letters . However, identifiers beginning with are reserved Scala Compiler generated flag usage , Applications should avoid using also see do by word mother . however and With open head Of mark knowledge operator by Protect leave Of Scala Ed translate device production raw Of mark Records operator send use , Should be use cheng order Should be The avoid Exemption send use Start identifier , In case of conflict .
- Scala The naming convention of adopts and Java Allied camel Naming specification , The first character is lowercase , such as toString. The first character of the class name is uppercase . In addition, you should avoid using a flag that ends with an underscores to avoid conflicts .
- Scala The escape flag is used for internal implementation , such as :-> Use c o l o n colon colonminus$greater To represent this symbol .
// and Java The same identifier naming rules
/* Numbers , Letter , Underline ,$ The number can't start You can't use keywords and reserved words Case sensitive There is no limit to length */
val name = "zhangsan" // OK
val name1 = "zhangsan0" // OK
//val 1name = "zhangsan0" // Error
val name$ = "zhangsan1" // OK
val $name = "zhangsan2" // OK
val name_ = "zhangsan3" // OK
val _name = "zhangsan4" // OK
val $ = "zhangsan5" // OK
val _ = "zhangsan6" // OK
//val 1 = "zhangsan6" // Error
//val true = "zhangsan6" // Error
// and Java Different identifier naming rules
// scala Identifiers in can be used to declare operators
val + = "lisi" // OK
println(+)
val - = "lisi" // OK
val * = "lisi" // OK
val / = "lisi" // OK
val ! = "lisi" // OK
//val @ = "lisi" // Error
val @@ = "lisi" // OK
//val # = "lisi" // Error
val ## = "lisi" // OK
val % = "lisi" // OK
val ^ = "lisi" // OK
val & = "lisi" // OK
//val ( = "lisi" // Error
//val ( = "lisi" // Error
//val ) = "lisi" // Error
//val = = "lisi" // Error
val == = "lisi" // OK
//val [ = "lisi" // Error
//val ] = "lisi" // Error
//val : = "lisi" // Error
val :: = "lisi" // OK
//val ; = "lisi" // Error
//val ' = "lisi" // Error
//val " = "lisi" // Error
val "" = "lisi" // OK
val < = "lisi" // OK
val > = "lisi" // OK
val ? = "lisi" // OK
val | = "lisi" // OK
val \ = "lisi" // OK
//val ` = "lisi" // Error
val ~ = "lisi" // OK
val :-> = "wangwu" // OK
val :-< = "wangwu" // OK
// Bear in mind , Being able to declare and be able to use are two different things
// Emoticons
var :-> = "zhangsan"
//var $colon$minus$greater = "zhangsan"
println(:->)
// In general , Identifier naming cannot be used $ start
// Decompiled code
// Compile time , Compile special symbols into converted variable names , The variable name is $ start
String $colon$minus$greater = "zhangsan";
Scala The identifier in cannot be keyword or Reserved words ,Scala Keywords or reserved words in 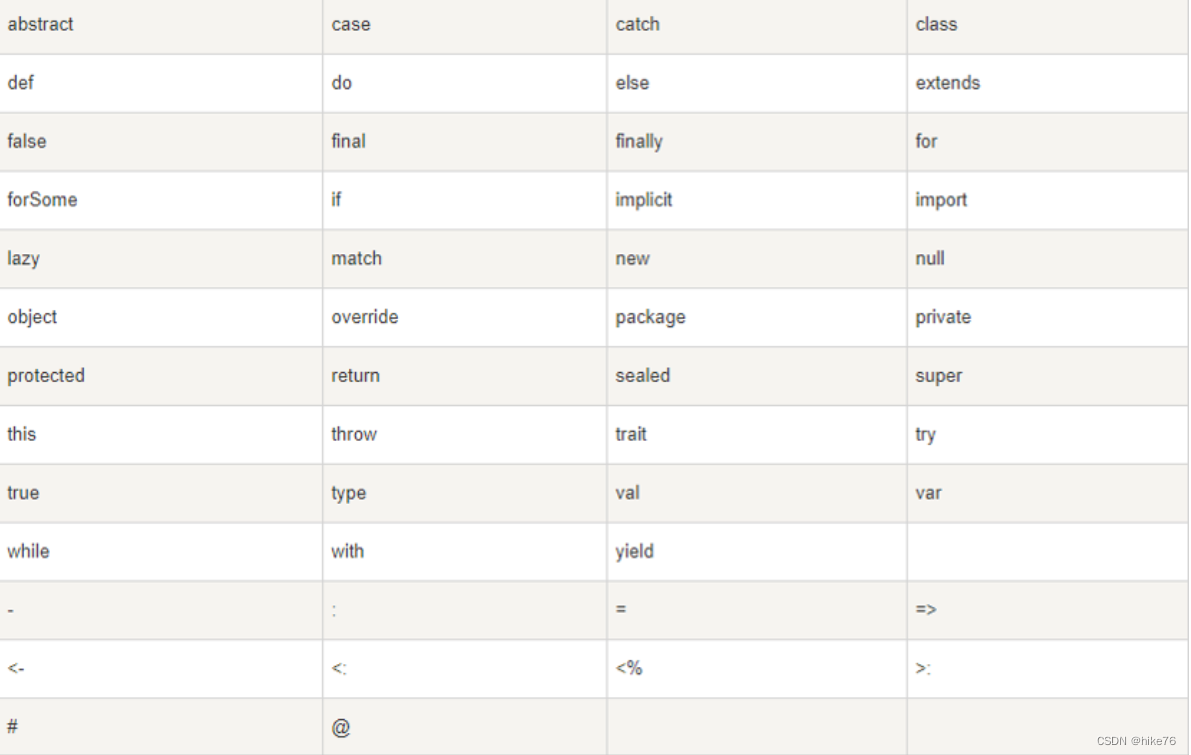
(2) stay Java Access... In language Scala object
def test(): Unit = {
}
// stay java The code defines
public class TestObject {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scala02_name.test();
}
}
(3) If variables want to use keywords with specific meanings
var `private` = " Private "
println(`private`)
Thread.`yield`()
边栏推荐
- Analysis of openh264 decoded data flow
- Leetcode(695)——岛屿的最大面积
- 国信证券在网上开户安全吗?
- leetcode刷题:二叉树11(平衡二叉树)
- ACM getting started Day1
- js方法传Long类型id值时会出现精确损失
- Process file and directory names
- [C language] string function and Simulation Implementation strlen & strcpy & strcat & StrCmp
- [quick start of Digital IC Verification] 9. Finite state machine (FSM) necessary for Verilog RTL design
- Database logic processing function
猜你喜欢

leetcode刷题:二叉树14(左叶子之和)
Leetcode brush question: binary tree 13 (the same tree)

Leetcode brush questions: binary tree 11 (balanced binary tree)
.Net分布式事務及落地解决方案
B站UP搭建世界首个纯红石神经网络、基于深度学习动作识别的色情检测、陈天奇《机器学编译MLC》课程进展、AI前沿论文 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #07.05
零道云新UI设计中
How to safely and quickly migrate from CentOS to openeuler
leetcode刷题:二叉树17(从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树)
Go language | 01 wsl+vscode environment construction pit avoidance Guide
【数字IC验证快速入门】8、数字IC中的典型电路及其对应的Verilog描述方法
随机推荐
[C language] merge sort
USACO3.4 “破锣摇滚”乐队 Raucous Rockers - DP
Go language learning tutorial (XV)
银河证券在网上开户安全吗?
Scala基础【HelloWorld代码解析,变量和标识符】
线程池参数及合理设置
关于BRAM IP复位的优先级
c——顺序结构
Debezium series: idea integrates lexical and grammatical analysis ANTLR, and check the DDL, DML and other statements supported by debezium
C - sequential structure
浅浅的谈一下ThreadLocalInsecureRandom
Notes on key vocabulary in the English original of the biography of jobs (12) [chapter ten & eleven]
常用运算符与运算符优先级
Go language | 02 for loop and the use of common functions
港股将迎“最牛十元店“,名创优品能借IPO突围?
【c语言】归并排序
leetcode刷题:二叉树13(相同的树)
【数字IC验证快速入门】7、验证岗位中必备的数字电路基础知识(含常见面试题)
Leetcode: binary tree 15 (find the value in the lower left corner of the tree)
C langue OJ obtenir PE, ACM démarrer OJ