当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree (construction)
Binary tree (construction)
2022-06-12 12:39:00 【Joey Liao】
Binary tree ( Programme ), First, I will repeat the general outline of binary tree problem solving summarized in the previous article :
- Whether you can get the answer by traversing the binary tree ? If possible , Use one
traverseWith external variables , This is called 「 Traverse 」 The mode of thinking .- Whether a recursive function can be defined , Pass the subproblem ( subtree ) The answer to the original question ? If possible , Write the definition of this recursive function , And make full use of the return value of this function , This is called 「
Break down the problem」 The mode of thinking .No matter which mode of thinking you use , You need to think :
If you extract a binary tree node separately , What does it need to do ? When do I need to ( front / in / Post sequence position ) do ? You don't have to worry about other nodes , Recursive functions will help you perform the same operation on all nodes .
The construction problem of binary tree is generally using 「 Break down the problem 」 The idea of : Build a whole tree = The root node + Construct the left subtree + Construct the right subtree .
List of articles
Construct the largest binary tree
Force to buckle 654 topic 「 The largest binary tree 」
Each binary tree node can be considered as the root node of a subtree , For the root node , The first thing to do, of course, is to find a way to construct yourself first , Then try to construct your own left and right subtrees .
therefore , We need to traverse the array to find the maximum value maxVal, So that the root node root Make it out , Then on maxVal The array on the left and the array on the right are constructed recursively , As root Right and left subtrees .
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
return build(nums,0,nums.length);
}
// Definition : take nums[lo..hi] Construct a tree that meets the conditions , Return root node
public TreeNode build(int[] nums,int left,int right){
// base case
if(left>=right) return null;
int maxPo=-1;
int max=-1;
// Find the maximum value in the array and the corresponding index
for(int i=left;i<right;i++){
if(nums[i]>max){
max=nums[i];
maxPo=i;
}
}
// First construct the root node
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(max);
// Recursive call to construct the left and right subtrees
root.left=build(nums,left,maxPo);
root.right=build(nums,maxPo+1,right);
return root;
}
}
Through the results of preorder and inorder traversal, a binary tree is constructed
Force to buckle 105 topic 「 Construct a binary tree from preorder and mediocre traversal sequences 」
class Solution {
Map<Integer,Integer> inMap=new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int n=preorder.length;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
inMap.put(inorder[i],i);
}
return build(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
public TreeNode build(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr){
// Out-of-service = Symbol , because prel and prer I haven't used it yet
if(prel>prer) return null;
// Build the root node
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[prel]);
// Find the location of the root node in the middle order traversal
int po=inMap.get(preorder[prel]);
// Find preorder traversal root How many left nodes are there
int leftNum=po-inl;
root.left=build(preorder,inorder,prel+1,prel+leftNum,inl,po-1);
root.right=build(preorder,inorder,prel+leftNum+1,prer,po+1,inr);
return root;
}
}
Through the results of post order and middle order traversal, a binary tree is constructed
Force to buckle 106 topic 「 Construct binary tree from post order and middle order traversal sequence 」:
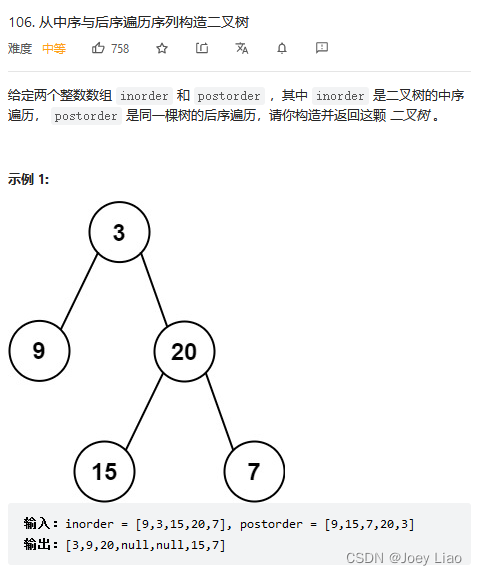
The key difference between this question and the previous one is , Postorder traversal is the opposite of preorder traversal , The corresponding value of the root node is postorder Last element of .
The overall algorithm framework is very similar to the previous question , We still write an auxiliary function build:
// Storage inorder Median to index mapping
HashMap<Integer, Integer> valToIndex = new HashMap<>();
TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
valToIndex.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1,
postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
/* build Definition of function : The post order traversal array is postorder[postStart..postEnd], The middle order traversal array is inorder[inStart..inEnd], Construct a binary tree , Returns the root node of the binary tree */
TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd,
int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (inStart > inEnd) {
return null;
}
// root The value corresponding to the node is the last element of the array after traversal
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];
// rootVal Traverses the index in the array in the middle order
int index = valToIndex.get(rootVal);
// The number of nodes in the left subtree
int leftSize = index - inStart;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// Recursively construct left and right subtrees
root.left = build(inorder, inStart, index - 1,
postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1);
root.right = build(inorder, index + 1, inEnd,
postorder, postStart + leftSize, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
Construct a binary tree by traversing the results of post order and pre order
Force to buckle 889 topic 「 Construct binary tree according to preorder and postorder traversal 」

Through the preface and the middle order , Or the only original binary tree can be determined by the traversal result in the post order , However, the unique original binary tree cannot be determined through the pre - and post - order traversal results .
But then again , Restore the binary tree with the results of post order traversal and pre order traversal , The solution logic is not different from the first two questions , It is also built by controlling the indexes of the left and right subtrees :
First, the first element of the pre order traversal result or the last element of the post order traversal result is determined as the value of the root node .
Then take the second element of the preorder traversal result as the value of the root node of the left subtree .
Find the value of the root node of the left subtree in the post order traversal result , Thus, the index boundary of the left subtree is determined , Then determine the index boundary of the right subtree , Recursively construct left and right subtrees .
class Solution {
// Storage postorder Median to index mapping
HashMap<Integer, Integer> valToIndex = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode constructFromPrePost(int[] preorder, int[] postorder) {
for (int i = 0; i < postorder.length; i++) {
valToIndex.put(postorder[i], i);
}
return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1,
postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
// Definition : according to preorder[preStart..preEnd] and postorder[postStart..postEnd]
// Building a binary tree , And return the root node .
TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd,
int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
if (preStart > preEnd) {
return null;
}
if (preStart == preEnd) {
return new TreeNode(preorder[preStart]);
}
// root The value corresponding to the node is the first element of the array in the preorder traversal
int rootVal = preorder[preStart];
// root.left The value of is the second element of the preorder traversal
// The key to construct a binary tree through preorder and postorder traversal is to pass through the root node of the left subtree
// determine preorder and postorder The element interval of the left and right subtrees in
int leftRootVal = preorder[preStart + 1];
// leftRootVal Traverse the index in the array in the following order
int index = valToIndex.get(leftRootVal);
// Number of elements in the left subtree
int leftSize = index - postStart + 1;
// First construct the current root node
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// Recursively construct left and right subtrees
// The index boundary of the left and right subtrees is deduced according to the root node index and the number of elements of the left subtree
root.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + leftSize,
postorder, postStart, index);
root.right = build(preorder, preStart + leftSize + 1, preEnd,
postorder, index + 1, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}
The code is very similar to the first two questions , We can look at the code and think , Why the binary tree restored by preorder traversal and postorder traversal results may not be unique ?
The key lies in this sentence :
int leftRootVal = preorder[preStart + 1];
We assume that the second element of the preorder traversal is the root node of the left subtree , But in fact, the left subtree may be a null pointer , Then this element should be the root node of the right subtree . Since it is impossible to judge with certainty , Therefore, the final answer is not unique .
thus , The problem of restoring a binary tree by traversing the results of preorder and postorder is also solved .
Finally, echo the previous article , The construction problem of binary tree is generally using 「 Break down the problem 」 The idea of : Build a whole tree = The root node + Construct the left subtree + Construct the right subtree . First find the root node , Then find the elements of the left and right subtrees according to the value of the root node , Then recursively construct the left and right subtrees .
边栏推荐
- [HXBCTF 2021]easywill
- Object value taking method in JS And []
- Geek challenge 2021 Web
- 数组——双指针技巧秒杀七道数组题目
- VNCTF2022 [WEB]
- itk neighbhood
- imx6-uboot添加lvds1显示
- TRON-api-波场转账查询接口-PHP版本-基于ThinkPHP5封装-附带接口文档-20220602版本-接口部署好适用于任何开发语言
- Point cloud registration -- GICP principle and its application in PCL
- Ace configures IPv6, vs statically compiles ace Library
猜你喜欢

【您编码,我修复】WhiteSource正式更名为Mend

二叉树(思路篇)
Time series database - incluxdb2 docker installation
![[HXBCTF 2021]easywill](/img/a2/8bf7d78fccf0d365490a84a8a9883d.jpg)
[HXBCTF 2021]easywill

Advanced C language -- storage of deep anatomical data in memory (with exercise)

MySQL 分区表介绍与测试

你不会只会用console.log()吧?

Numpy numerical calculation basis

Deep analysis of advanced pointer -- advanced chapter of C language

C语言进阶篇——万字详解指针和qsort函数
随机推荐
Buu question brushing record - 5
sublime_text使用
[HXBCTF 2021]easywill
What can LDAP and SSO integration achieve?
From simple to deep - websocket
NDT registration principle
常数时间删除/查找数组中的任意元素
In depth anatomy of C language - key words & supplementary contents
八大误区,逐个击破(2):性能差?应用程序少?你对云的这些担心很多余!
vtk 三视图
LDAP和SSO集成能实现什么效果?
AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.12)
二叉树(思路篇)
VGg small convolution instead of large convolution vs deep separable convolution
NewOJ Week 10题解
Reasons for college students' leave
什么时候运用二分搜索
Ace configures IPv6, vs statically compiles ace Library
vtk 图像序列鼠标交互翻页
Cocktail sort