当前位置:网站首页>ACM. Hj48 delete the node with the specified value from the one-way linked list ●●
ACM. Hj48 delete the node with the specified value from the one-way linked list ●●
2022-06-30 07:42:00 【chenyfan_】
HJ48 Deletes the node with the specified value from the one-way linked list ●●
describe
Enter a One way linked list And the value of a node , From the one-way linked list Delete nodes equal to this value , After deletion, if there is no node in the linked list, a null pointer is returned .
Linked list Value cannot be duplicate .
Construction process , For example, enter a row of data as :
6 2 1 2 3 2 5 1 4 5 7 2 2
First parameter 6 Indicates that a total of... Is entered 6 Nodes , The second parameter 2 Indicates that the value of the header node is 2, The rest 2 A group represents the 2 Nodes value Insert page after 1 Node values , Is represented by :
1 2 Expressed as
2->1
The linked list is 2->1
3 2 Expressed as
2->3
The linked list is 2->3->1
5 1 Expressed as
1->5
The linked list is 2->3->1->5
4 5 Expressed as
5->4
The linked list is 2->3->1->5->4
7 2 Expressed as
2->7
The linked list is 2->7->3->1->5->4
The order of the last linked list is 2 7 3 1 5 4
The last parameter is zero 2, Indicates that the node to be deleted is 2 Value
Delete node 2
The result is 7 3 1 5 4
Data range : The length of the linked list meets 1 ≤ n ≤ 1000 1 \le n \le 1000 1≤n≤1000 , The value in the node satisfies 0 ≤ v a l ≤ 10000 0 \le val \le 10000 0≤val≤10000
The test case ensures that the input is legal
Input description :
The input line , There are the following 4 Parts of :
1 Enter the number of linked list nodes
2 Enter the value of the header node
3 Insert each node according to the format
4 Enter the value of the node to be deleted
Output description :
Output one line
Output the sequence after deleting nodes , Add a space after each number
Example
Input :
5 2 3 2 4 3 5 2 1 4 3
Output :
2 5 4 1
explain :
The linked list is 2->5->3->4->1
Delete node 3, Back to you 2->5->4->1
Answer key
1. Linked list Insert Delete
Building linked lists , Then insert the nodes in turn .
When inserting, traverse the linked list to find the pre order node of the inserted node ( Because the elements in the table are different from each other ), Disconnect the pre order node from the post order node , Insert nodes to connect subsequent nodes , Pre order node connection insert node .
The subsequent direct traversal of the linked list output , Do not output the node value to be deleted .
- Time complexity : O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2), Traversal during insertion n−1 Inputs , Each input must traverse the linked list to find the insertion position
- Spatial complexity : O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1), The linked list space belongs to the necessary space , It doesn't belong to extra space

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode{
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int v) : val(v), next(nullptr){
}
ListNode(){
}
};
int cnt = 0;
void insert(ListNode* dummyHead, int val, int pre_v){
ListNode* pre = dummyHead;
ListNode* curr = pre->next; // head
for(int i = 1; i <= cnt; ++i){
if(curr->val == pre_v){
// Find where to insert
pre = curr;
curr = curr->next;
break;
}
curr = curr->next;
}
ListNode* node = new ListNode(val);
pre->next = node;
node->next = curr;
}
int main(){
int n;
int head_val;
while(cin >> n >> head_val){
ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* head = new ListNode(head_val);
dummyHead->next = head;
cnt = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n-1; ++i){
int v, pre_v;
cin >> v >> pre_v;
insert(dummyHead, v, pre_v);
++cnt;
// ListNode* cur = dummyHead->next; // Output list
// for(int j = 0; j <= i+1; ++j){
// cout << cur->val << "->";
// cur = cur->next;
// }
// cout << endl;
}
int del;
cin >> del;
ListNode* pre = dummyHead;
ListNode* curr = dummyHead->next;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(curr->val != del){
cout << curr->val << " ";
}else{
pre->next = curr->next; // Delete the specified node
delete curr;
curr = pre->next;
continue;
}
pre = curr;
curr = curr->next;
}
}
return 0;
}
2. Array simulation
Because the values in the linked list are different from each other , We can use arrays to simulate the addition and deletion of linked lists .
First, add the first element to the array, that is, the header , Then every time we add an element, we use find Function to find which number it is after , That is, find the position where the number in front of it appears , Because the numbers are different from each other, we must find the only one , If it is the last number, add it to the end of the array , If it is in the middle, use insert The function is inserted into the corresponding position .
- Time complexity : O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2), Traversal during insertion n-1 Inputs , Each input call find All functions are O(n), Low deletion and output complexity , Give up
- Spatial complexity : O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1), The array belongs to the necessary space , No extra space
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n, head;
while(cin >> n >> head){
vector<int> array; // Using arrays to simulate linked lists
array.push_back(head);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
int num, pos_num;
cin >> num >> pos_num; // Enter the number to insert and which number to insert after
auto iter = find(array.begin(), array.end(), pos_num); // Find the position to insert behind you
if(iter == array.end()) // ending push_back
array.push_back(num);
else // middle insert
array.insert(iter + 1, num);
}
int remove;
cin >> remove;
array.erase(find(array.begin(), array.end(), remove)); // Find the location of the number you want to remove
for(int i = 0; i < array.size(); i++) // Output
cout << array[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Implementation of binary search in C language
- January 23, 2022 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 6: multiple sequence alignment)
- November 9, 2020 [wgs/gwas] - whole genome analysis (association analysis) process (Part 2)
- NMOS model selection
- 回文子串、回文子序列
- Basic knowledge points
- 2021.11.20 [reading notes] | differential variable splicing events and DTU analysis
- Tue Jun 28 2022 15:30:29 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间) 日期格式化
- STM32 infrared communication 2
- 深度学习——特征点检测和目标检测
猜你喜欢

深度学习——LSTM

Introduction notes to pytorch deep learning (11) neural network pooling layer

Application of stack -- using stack to realize bracket matching (C language implementation)

Analysis of cross clock transmission in tinyriscv
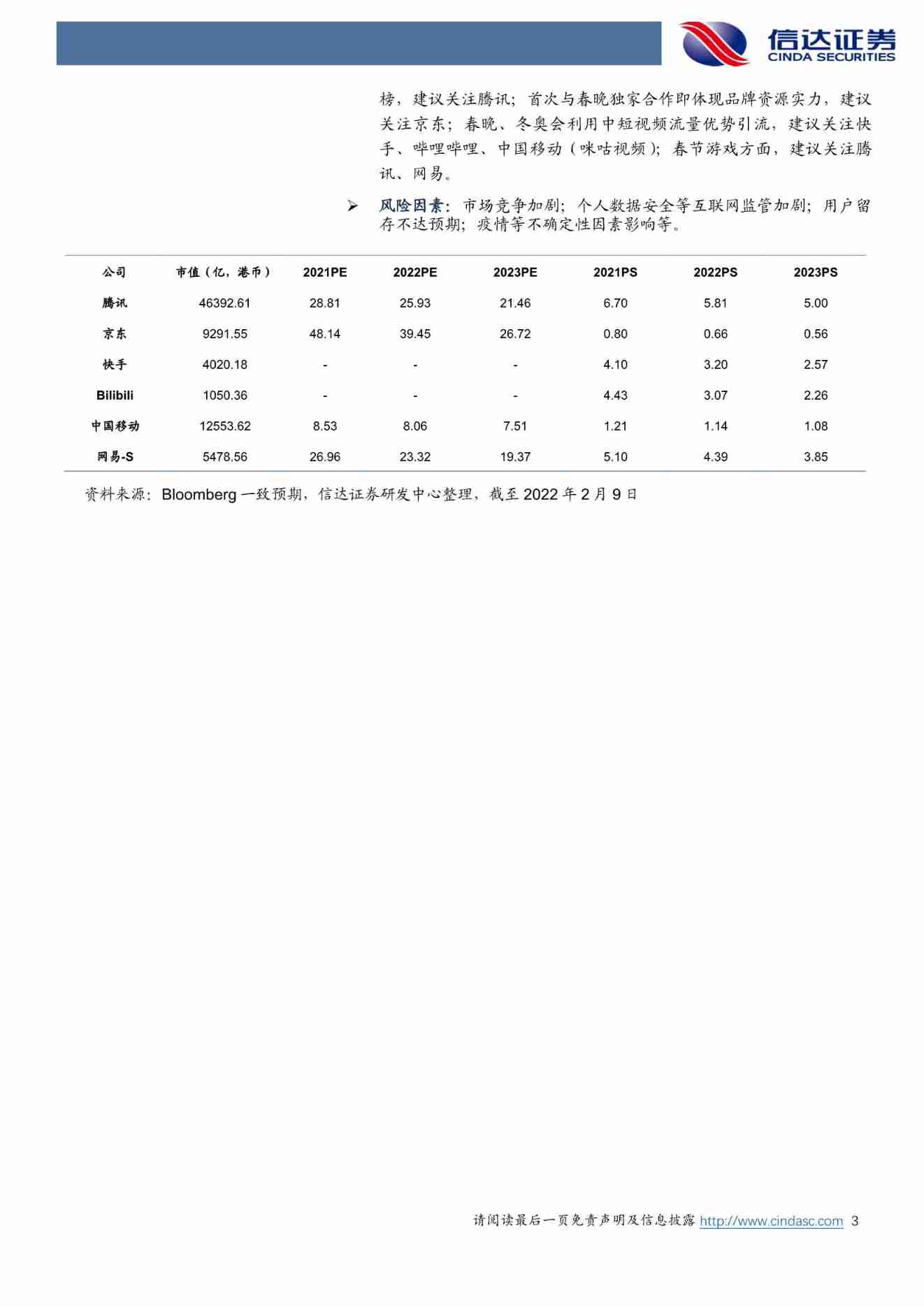
Spring Festival inventory of Internet giants in 2022

深度学习——语言模型和序列生成

期末复习-PHP学习笔记8-mysql数据库
![January 23, 2022 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 6: multiple sequence alignment)](/img/48/cfe6ab95b4d4660e3ac3d84ae5303b.jpg)
January 23, 2022 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 6: multiple sequence alignment)

期末复习-PHP学习笔记9-PHP会话控制

期末复习-PHP学习笔记4-PHP自定义函数
随机推荐
December 19, 2021 [reading notes] - bioinformatics and functional genomics (Chapter 5 advanced database search)
期末复习-PHP学习笔记7-PHP与web页面交互
Combinatorial mathematics Chapter 2 Notes
6月底了,可以开始做准备了,不然这么赚钱的行业就没你的份了
Final review -php learning notes 11-php-pdo database abstraction layer
Desk lamp control panel - brightness adjustment timer
Xiashuo think tank: 42 reports on planet update today (including 23 planning cases)
Xiashuo think tank: 125 planet updates reported today (packed with 101 meta universe collections)
2021-10-29 [microbiology] qiime2 sample pretreatment form automation script
C51 minimum system board infrared remote control LED light on and off
Installation software operation manual (continuous update)
深度学习——循环神经网络
深度学习——使用词嵌入and词嵌入特征
2021 private equity fund market report (62 pages)
C language implements sequential queue, circular queue and chain queue
Final review -php learning notes 5-php array
November 9, 2020 [wgs/gwas] - whole genome analysis (association analysis) process (Part 2)
Personal blog one article multi post tutorial - basic usage of openwriter management tool
期末复习-PHP学习笔记2-PHP语言基础
right four steps of SEIF SLAM