当前位置:网站首页>[@property enhancement in Objective-C language]
[@property enhancement in Objective-C language]
2022-08-03 03:02:00 【morning breeze】
Foreword
What are @property enhancements?
Writing before Xcode 4.4:
1) @property only generates the declaration of getter and setter;
@synthesize only generates the implementation of getter and setter;
properties have to be written by themselves;
This way of writing is before Xcode4.4. After Xcode4.4, Xcode made an enhancement to @property
1. What does @property enhance?
After Xcode4.4, you only need to write a @property, it will:
1) automatically generate private properties for you,
2) help you generate getter and setter declarations,
3)Helps you generate getter and setter implementations.
Second, use steps
1. For example, there is such a class:
@interface Student : NSObject
@end
@implementation Student
@end
1) I don't do anything, I just write a statement like this:
@interface Student : NSObject
@property NSString *name;
@end
2) It already does it for youThere are many things:
a) Automatically generate a private property for you: the type of the property is the same as the type of @property, the name of the property is the same as the name of @property, and an underscore is automatically added in front;
b) AutomaticallyHelp you to generate the declaration of the getter and setter method of this property;
c) Automatically help you generate the implementation of the getter and setter method of this property:
Implementation of the setter: directly assign the value of the parameter to the automatically generated privateProperty;
The implementation of getter: directly return the value of the generated private property;
2. Use Note:
1) The type of @property must be the same as the type of the property to be generated;
2) The name of @property must be the same as the name of the property, just remove the underscore;
For example: @property intage;
3) @property can also be declared in batches; the types must be the same;
For example: @property float height, weight;
4) @property automatically generates method implementation without any logic verification;
setter: direct assignment;
getter: direct return;
5) If you want to do logic verification, just rewrite the setter method, for example:
(void)setAge:(int)
{
if(age >= 0 && age <= 120)
{
_age = age;
}
}
After you override the setter method, will the getter method be automatically generated?The answer is: yes!
If you rewrite the getter, the setter will be automatically generated;
If you rewrite the getter and the setter at the same time, @property will not automatically generate the private property.then what should we do?Declare private properties in @implementation yourself!
6) From today, if you want to write 1 property for the class, and encapsulate the setter and getter for this property, 1 @property will do it.
7) Can this @property be inherited?
The answer is: it can be inherited by subclasses, but since the properties generated by @property are private properties, they cannot be directly accessed by subclasses. If you must access them, they can only be accessed through setter and getter methods.
For example, there is an Animal class:
@interface Animal : NSObject
@property NSString *name;
@end
At this time, an underlined name of type NSString * is automatically generatedPrivate properties, and getter and setter methods are automatically generated.
At this time, there is a Pig class that inherits from the Animal class:
@interface Pig : Animal@end
At this time, does the Pig class inherit from the Animal class?Can it inherit the _name of type Animal's private property NSString *?The answer is: yes.Can getter and setter methods be inherited?The answer is: yes.
However, in the method implementation of the Pig class, can it access the _name attribute through self->_name?The answer is: no.
@implementation Pig- (void)test
{
self->
}
@end
This is not prompted and cannot be accessed.Can't access, why?Private, invisible.
But how can you access it, by calling the setter method and getter method through the super keyword, for example:
@implementation Pig - (void)test
{
[super setName:@“jack”];
}
@end
You can also access the setter and getter methods through the self keyword, for example:
@implementation Pig - (void)test
{
[self setName:@“jack”];
}
@end
Of course, you can also access setter and getter methods by calling the self keyword and dot syntax, for example:
@implementation Pig - (void)test
{
self.name = @"jack";
}
@end
- (void)test
Summary
At this point, @property is officially over, 3 articles have been written, and this @property has nothing else.
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

优秀的 Verilog/FPGA开源项目总结及交流群

v-if条件判断及v-show
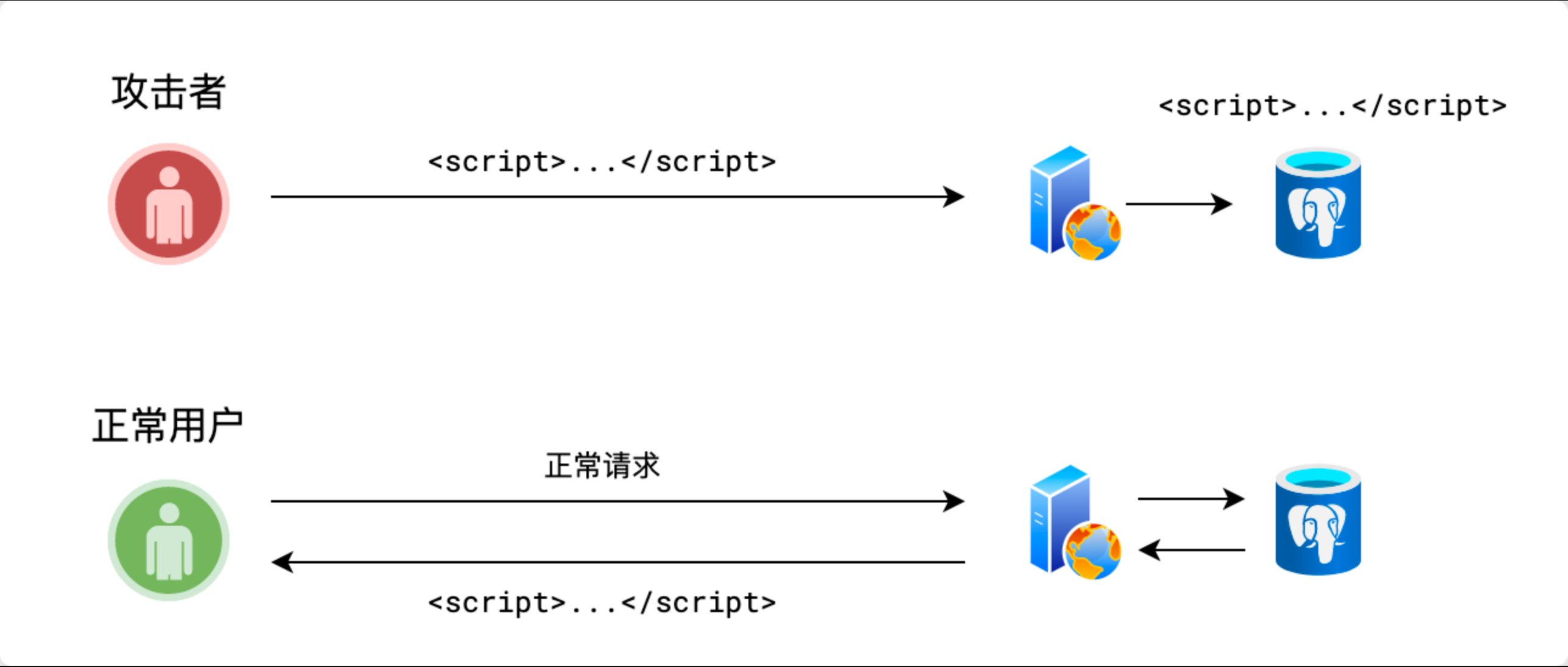
XSS攻击
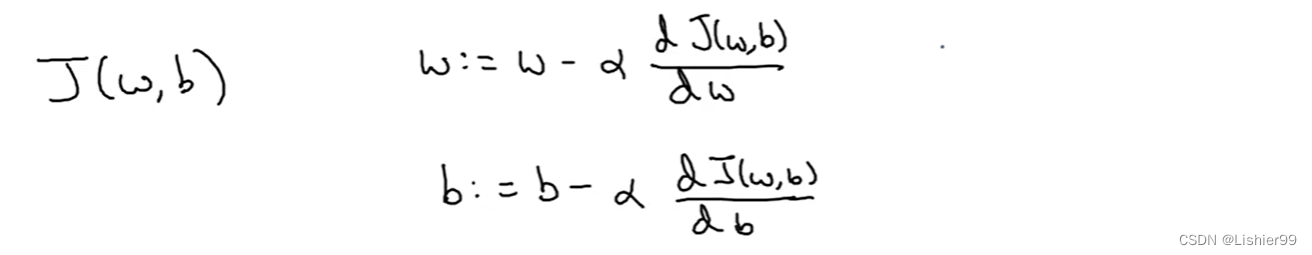
吴恩达深度学习deeplearning.ai——第一门课:神经网络与深度学习——第二节:神经网络基础(上)
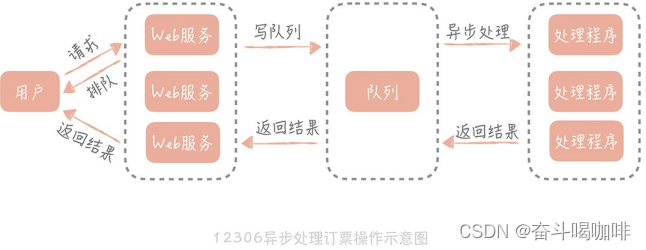
大厂标配 | 百亿级并发系统设计 | 学完薪资框框涨

爆款视频怎么做?这里或许有答案
Brute force recursion to dynamic programming 07 (516. Longest palindrome subsequence)
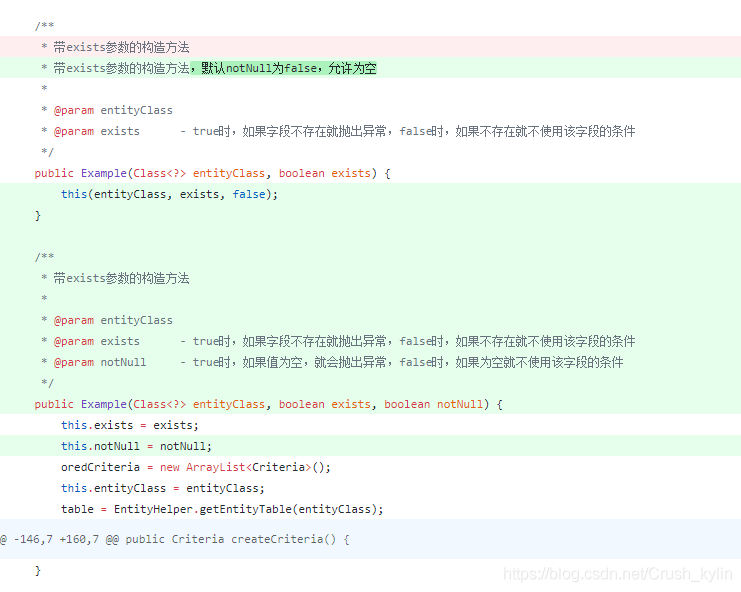
[Example构造方法增加notNull参数,默认false,允许值为null,值为null的时候不加入到条件中
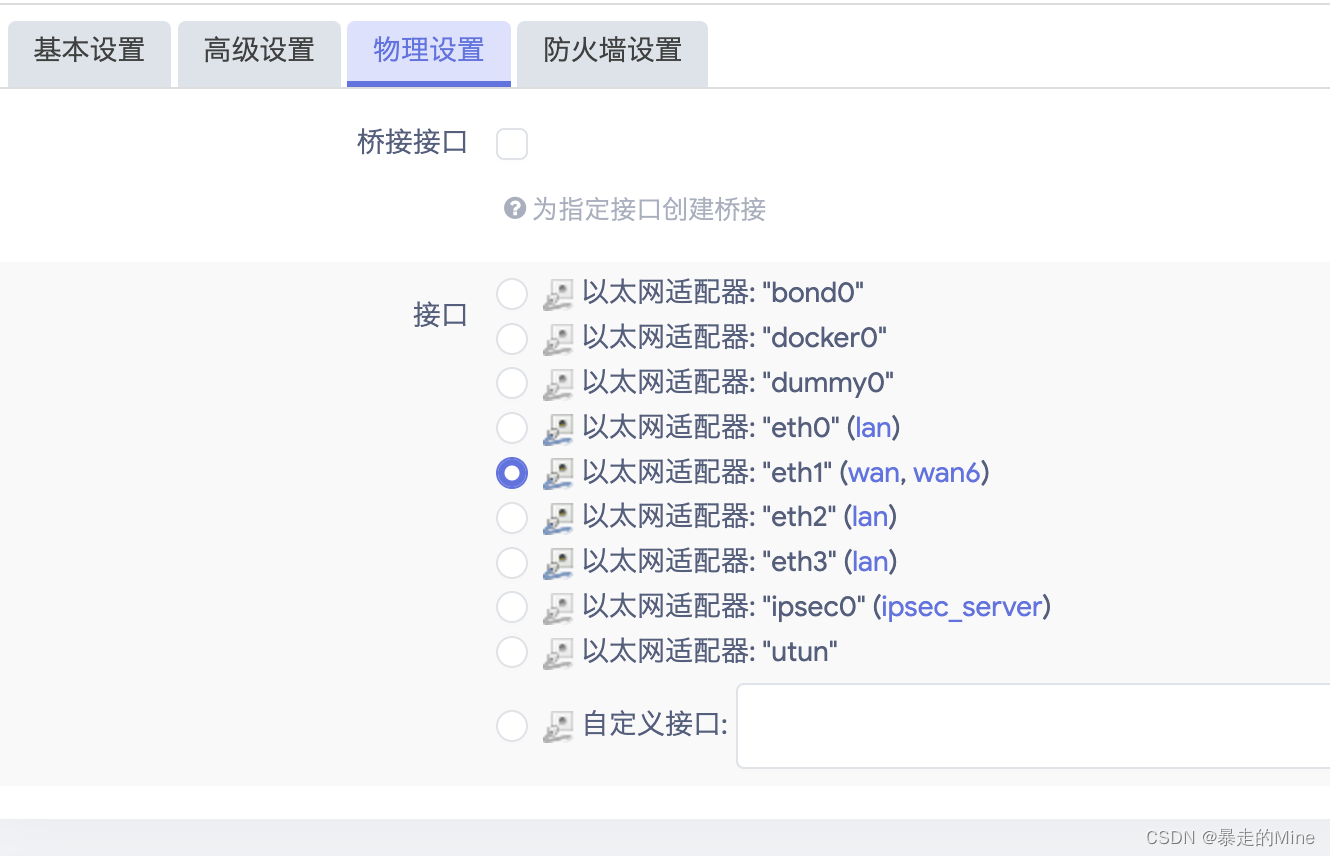
OpenWRT设置ipv6网络
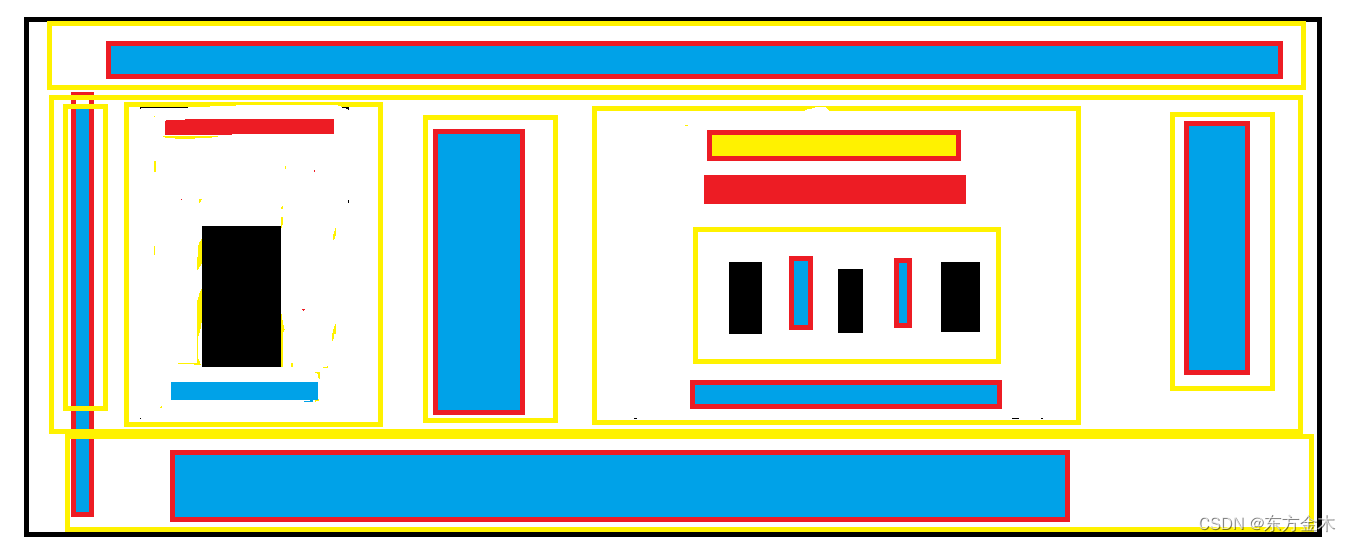
超级复杂可贴图布局的初级智能文本提示器
随机推荐
JVM内部结构图及各模块运行机制总结
面试题整理1
v-if条件判断及v-show
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
【面经】被虐了之后,我翻烂了equals源码,总结如下
浅谈敏捷开发
担心的事情
Go高性能之方法接收器 - 指针vs值
怎么从零编写一个 v3 版本的 chrome 浏览器插件实现 CSDN 博客网站的暗黑和明亮主题切换?
8-jwt工具类
做快乐的事情
暴力递归到动态规划 08(小马走象棋)
pytorch 中 permute()函数的用法
numpy PIL tensor之间的相互转换
mysql binlog日期解析成yyyy-MM-dd
Incorrect datetime value: ‘2022-01-01‘ for function str_to_date
openCV第一篇
7-Redis工具类
20、商品微服务-web层实现
SAP ABAP Gateway Client 里 OData 测试的 PUT, PATCH, MERGE 请求有什么区别