当前位置:网站首页>Tensorflow realizes verification code recognition (III)
Tensorflow realizes verification code recognition (III)
2022-07-03 15:20:00 【alw_ one hundred and twenty-three】
Building blocks
When the data is ready , It's all about defining the network structure , Defining the network structure means building blocks . The building blocks on my side are dark purple :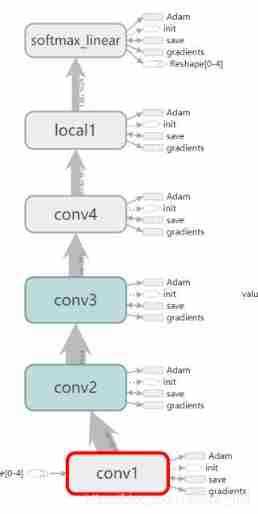
It can be seen that I built 4 Layer convolution +1 layer FC+1 layer softmax Spicy chicken blocks , The code for building blocks is maozi :
# Reasoning
def __inference(self, images, keep_prob):
images = tf.reshape(images, (-1, utility.IMG_HEIGHT, utility.IMG_WIDTH, 1))
# be used for tensorboard Visualize the original image in
tf.summary.image('src_img', images, 5)
with tf.variable_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel = self.__weight_variable('weights_1', shape=[5, 5, 1, 64])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases_1', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(images, kernel), biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv1/weights_1', kernel)
tf.summary.histogram('conv1/biases_1', biases)
kernel_2 = self.__weight_variable('weights_2', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64])
biases_2 = self.__bias_variable('biases_2', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(conv1, kernel_2), biases_2)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv1/weights_2', kernel_2)
tf.summary.histogram('conv1/biases_2', biases_2)
# Used to visualize the image after convolution of the first layer
conv1_for_show1 = tf.reshape(conv1[:, :, :, 1], (-1, 60, 160, 1))
conv1_for_show2 = tf.reshape(conv1[:, :, :, 2], (-1, 60, 160, 1))
conv1_for_show3 = tf.reshape(conv1[:, :, :, 3], (-1, 60, 160, 1))
tf.summary.image('conv1_for_show1', conv1_for_show1, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv1_for_show2', conv1_for_show2, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv1_for_show3', conv1_for_show3, 5)
# max pooling
pool1 = self.__max_pool_2x2(conv1, name='pool1')
with tf.variable_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = self.__weight_variable('weights_1', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases_1', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(pool1, kernel), biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv2/weights_1', kernel)
tf.summary.histogram('conv2/biases_1', biases)
kernel_2 = self.__weight_variable('weights_2', shape=[5, 5, 64, 64])
biases_2 = self.__bias_variable('biases_2', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(conv2, kernel_2), biases_2)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv2/weights_2', kernel_2)
tf.summary.histogram('conv2/biases_2', biases_2)
# Used to visualize the image after convolution of the second layer
conv2_for_show1 = tf.reshape(conv2[:, :, :, 1], (-1, 30, 80, 1))
conv2_for_show2 = tf.reshape(conv2[:, :, :, 2], (-1, 30, 80, 1))
conv2_for_show3 = tf.reshape(conv2[:, :, :, 3], (-1, 30, 80, 1))
tf.summary.image('conv2_for_show1', conv2_for_show1, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv2_for_show2', conv2_for_show2, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv2_for_show3', conv2_for_show3, 5)
# max pooling
pool2 = self.__max_pool_2x2(conv2, name='pool2')
with tf.variable_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel = self.__weight_variable('weights', shape=[3, 3, 64, 64])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(pool2, kernel), biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv3/weights', kernel)
tf.summary.histogram('conv3/biases', biases)
kernel_2 = self.__weight_variable('weights_2', shape=[3, 3, 64, 64])
biases_2 = self.__bias_variable('biases_2', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(conv3, kernel_2), biases_2)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv3/weights_2', kernel_2)
tf.summary.histogram('conv3/biases_2', biases_2)
conv3_for_show1 = tf.reshape(conv3[:, :, :, 1], (-1, 15, 40, 1))
conv3_for_show2 = tf.reshape(conv3[:, :, :, 2], (-1, 15, 40, 1))
conv3_for_show3 = tf.reshape(conv3[:, :, :, 3], (-1, 15, 40, 1))
tf.summary.image('conv3_for_show1', conv3_for_show1, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv3_for_show2', conv3_for_show2, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv3_for_show3', conv3_for_show3, 5)
pool3 = self.__max_pool_2x2(conv3, name='pool3')
with tf.variable_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel = self.__weight_variable('weights', shape=[3, 3, 64, 64])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases', [64])
pre_activation = tf.nn.bias_add(self.__conv2d(pool3, kernel), biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(pre_activation, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('conv4/weights', kernel)
tf.summary.histogram('conv4/biases', biases)
conv4_for_show1 = tf.reshape(conv4[:, :, :, 1], (-1, 8, 20, 1))
conv4_for_show2 = tf.reshape(conv4[:, :, :, 2], (-1, 8, 20, 1))
conv4_for_show3 = tf.reshape(conv4[:, :, :, 3], (-1, 8, 20, 1))
tf.summary.image('conv4_for_show1', conv4_for_show1, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv4_for_show2', conv4_for_show2, 5)
tf.summary.image('conv4_for_show3', conv4_for_show3, 5)
pool4 = self.__max_pool_2x2(conv4, name='pool4')
# Fully connected layer
with tf.variable_scope('local1') as scope:
reshape = tf.reshape(pool4, [images.get_shape()[0].value, -1])
weights = self.__weight_variable('weights', shape=[4*10*64, 1024])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases', [1024])
local1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(reshape, weights) + biases, name=scope.name)
tf.summary.histogram('local1/weights', kernel)
tf.summary.histogram('local1/biases', biases)
local1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(local1, keep_prob)
tf.summary.tensor_summary('local1/dropout', local1_drop)
# Output layer
with tf.variable_scope('softmax_linear') as scope:
weights = self.__weight_variable('weights', shape=[1024, self.__CHARS_NUM * self.__CLASSES_NUM])
biases = self.__bias_variable('biases', [self.__CHARS_NUM * self.__CLASSES_NUM])
result = tf.add(tf.matmul(local1_drop, weights), biases, name=scope.name)
reshaped_result = tf.reshape(result, [-1, self.__CHARS_NUM, self.__CLASSES_NUM])
return reshaped_result
Training
The second article has said that the data is dump become tfrecords, Then use the queue to read tfrecords, So when training, you must run the queue , Let the queue go from tfrecords Keep getting data in . But it's definitely not a good idea to use a single thread to get data , Therefore, it should be the main thread that creates a sub thread dedicated to inserting data into the queue . The main thread only needs to get data from the queue for training when necessary . The operation of synchronization between these threads tf It's sealed ,tf.train.Coordinator() Can instantiate a thread coordinator ,tf.train.start_queue_runners() Will be able to graph All queues in run get up , And return the corresponding sub thread of the management queue . So the code is purple :
with tf.Session() as sess:
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
tf.local_variables_initializer().run()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(utility.LOG_DIR, sess.graph)
coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
try:
step = 0
while not coord.should_stop():
start_time = time.time()
_, loss_value, performance, summaries = sess.run([train_op, loss, accuracy, summary_op])
duration = time.time() - start_time
if step % 10 == 0:
print('>> Trained %d Lots : loss = %.2f (%.3f sec), The correct quantity of this batch = %d' % (step, loss_value, duration, performance))
if step % 100 == 0:
writer.add_summary(summaries, step)
saver.save(sess, utility.MODEL_DIR, global_step=step)
step += 1
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
print(' End of training ')
saver.save(sess, utility.MODEL_DIR, global_step=step)
coord.request_stop()
finally:
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
demo The complete code of is in :https://github.com/aolingwen/fuck_verifycode
The code is written in a rough way , Welcome to correct . If it helps you , Still hope fork or star One , thank you !
边栏推荐
- Dataframe returns the whole row according to the value
- 【Transformer】入门篇-哈佛Harvard NLP的原作者在2018年初以逐行实现的形式呈现了论文The Annotated Transformer
- Global and Chinese markets of AC electromechanical relays 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Search in the two-dimensional array of leetcode sword offer (10)
- Global and Chinese market of air cargo logistics 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- Using notepad++ to build an arbitrary language development environment
- Baidu AI Cloud helps Shizuishan upgrade the smart health care model of "Internet + elderly care services"
- socket.io搭建分布式Web推送服务器
- Halcon and WinForm study section 1
- [transformer] Introduction - the original author of Harvard NLP presented the annotated transformer in the form of line by line implementation in early 2018
猜你喜欢

Kubernetes 进阶训练营 Pod基础
![[Yu Yue education] scientific computing and MATLAB language reference materials of Central South University](/img/83/922efb4f88843f1b7feaccf2b515b9.jpg)
[Yu Yue education] scientific computing and MATLAB language reference materials of Central South University

Jvm-02-class loading subsystem
![[transformer] Introduction - the original author of Harvard NLP presented the annotated transformer in the form of line by line implementation in early 2018](/img/2b/b23aeab584f89be6678c0fe059d4b6.png)
[transformer] Introduction - the original author of Harvard NLP presented the annotated transformer in the form of line by line implementation in early 2018
视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)-4.通信管理

Chapter 04_ Logical architecture
Visual upper system design and development (Halcon WinForm) -5 camera

需要知道的字符串函数

Jvm-09 byte code introduction

Jvm-03-runtime data area PC, stack, local method stack
随机推荐
Kubernetes - yaml file interpretation
MySQL reports an error: [error] mysqld: file '/ mysql-bin. 010228‘ not found (Errcode: 2 “No such file or directory“)
使用Tengine解决负载均衡的Session问题
The method of parameter estimation of user-defined function in MATLAB
The state does not change after the assignment of El switch
Halcon与Winform学习第一节
[Yu Yue education] scientific computing and MATLAB language reference materials of Central South University
PyTorch crop images differentiablly
Atlas atlas torque gun USB communication tutorial based on mtcom
【Transform】【NLP】首次提出Transformer,Google Brain团队2017年论文《Attention is all you need》
Idea does not specify an output path for the module
Using TCL (tool command language) to manage Tornado (for VxWorks) can start the project
视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)
视觉上位系统设计开发(halcon-winform)-6.节点与宫格
基础SQL教程
Characteristics of MySQL InnoDB storage engine -- Analysis of row lock
Introduction to redis master-slave, sentinel and cluster mode
Use of Tex editor
详解指针进阶1
GCC cannot find the library file after specifying the link library path