当前位置:网站首页>Summary of common loss functions in pytorch
Summary of common loss functions in pytorch
2022-06-30 05:13:00 【Wu lele~】
List of articles
Preface
This paper mainly introduces pytorch The loss function commonly used in API Use .
1. Classified loss
1.1. nn.BCELoss()
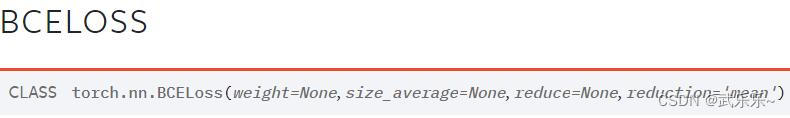
nn.BCELoss() Used to calculate binary classification problems , Use default initialization , namely reduction='mean’ Is to return loss Mean across all samples . stay forward In the method , Accepted input and target Must be the same shape, And target yes one-hot code , and input Need to pass in advance sigmoid Handle .
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Binary cross entropy loss function , You can only deal with dichotomies
# Hypothetical processing Dichotomous problem , And batch =2
input = torch.Tensor([[-1,1],[1,2]]) # input: [2,2]
input = input.sigmoid()
# Turn into one-hot
target = torch.Tensor([0,1]) # shape:[2]
onehot_target = torch.eye(2)[target.long(), :]
Loss = nn.BCELoss() # Use default initialization
loss1 = Loss(input, onehot_target)
loss2 = F.binary_cross_entropy(input, onehot_target) # 1.0167
1.2. nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
The loss function is the integration of sigmoid To deal with , Is this time input Is the direct network output , There is no need to add sigmoid Handle .
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
# Binary cross entropy loss function , You can only deal with dichotomies
# Hypothetical processing Dichotomous problem , And batch =2
input = torch.Tensor([[-1,1],[1,2]]) # input: [2,2]
# Turn into one-hot
target = torch.Tensor([0,1]) # shape:[2]
onehot_target = torch.eye(2)[target.long(), :]
Loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() # Use default initialization
loss1 = Loss(input, onehot_target)
loss2 = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(input, onehot_target)
print(loss1, loss2) # [1.0167]
1.3. Multi class cross entropy loss function
1) When solving multi classification problems , The formula is as follows :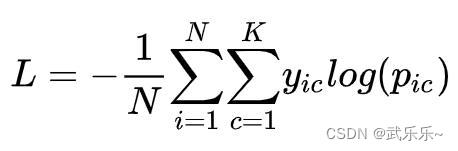
among N Is the total number of samples ,K It's a category ,pic It means the first one i Samples belong to c Categories . It's more abstract , Suppose you now need to manually implement the code for the above formula : Suppose there is 3 Samples (N=3), Each of them p Assume that after softmax Handle , The sum of probabilities is 1, And will label Turn into one-hot code .
First, do not consider the outermost summation symbol , First calculate the sum of the inner layers :L1,L2,L3, The summation symbol in the outer layer of the calculation can .
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
p = torch.Tensor([[0.2,0.3,0.5],[0.1,0.7,0.2],[0.4,0.5,0.1]])
label = torch.Tensor([0,1,2])
onehot = torch.eye(3)[label.long(), :]
# Calculate the cross entropy of each sample separately
p = torch.log(p) # Take the logarithm
loss = torch.sum(onehot * p)# Multiply and sum the corresponding elements
# In computing the outer summation symbol
loss = -loss / p.shape[0]
print(loss) # 1.4429
2) To simplify the above process (label Need to be one-hot=),torch use ==nn.NLLLoss()== It is encapsulated , Simplify the above code :
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
Loss = nn.NLLLoss()
p = torch.Tensor([[0.2,0.3,0.5],[0.1,0.7,0.2],[0.4,0.5,0.1]])
label = torch.Tensor([0,1,2]).long()
#onehot = torch.eye(3)[label.long(), :]
# Calculate the cross entropy of each sample separately
p = torch.log(p) # Take the logarithm
loss = Loss(p, label)
#loss = torch.sum(onehot * p)# Multiply and sum the corresponding elements
# In computing the outer summation symbol
#loss = -loss / p.shape[0]
print(loss) # 1.4429
3) The above process is not simple enough , because p need softmax+log operation , therefore ,torch Further encapsulation , Namely :
Don't worry about parameters , Use it directly :
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
p = torch.randn(4,3) # Network direct output , Not through Softmax
label = torch.Tensor([0,1,2,0]).long() #
# First, use the common method to calculate
log_p = F.log_softmax(p)
Loss = nn.NLLLoss()
loss1 = Loss(log_p, label)
# use CrossEP Under calculation
Loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss2 = Loss(p, label)
print(loss1, loss2) # The two results are consistent
Make a brief summary : Cross entropy loss function :log + softmax + one-hot The integrators of , here pred Just be [N,C] without Softmax To deal with the ,label Just be [N] The element inside is the normal category label . Then incoming API We can get the cross entropy loss .
4) Of course , Here is an additional parameter to note :ignore_index, The function is to ignore the loss of a certain category . For example, set to 0, Just get rid of 0 The loss value of this part , And in Not 0 The average loss on the element .
from math import log
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
p = torch.Tensor([[0.1, 0.2, 0.3],[0.4, 0.5, 0.6],[0.1,0.2,0.3]]) #[2,3]
label = torch.Tensor([0, 1, 1]).long() # [2]
# Now suppose you remove the tag as 0 The loss of
Loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss(ignore_index=0)
loss3 = Loss(p, label)
print(loss3) # 1.1019
print(' verification ignore_index')
p = F.softmax(p) # Yes p Conduct softmax
onehot = torch.eye(3)[label.long(), :]
# Calculate the cross entropy of each sample separately
p = torch.log(p)
v = (onehot * p)
loss = torch.sum(v[1:]) # Remove the label as 0 The loss of
# In computing the outer summation symbol
loss = -loss / 2 # 2 A non 0, so /2
print(loss) #
1.4.Focal_loss
After introducing the cross entropy loss , I have to introduce some common Focal loss. Take a look first focal loss Formula :

It can be seen from the formula that , Realization focal loss First realize CE(pt), Two dimensional cross entropy loss function , It can be used directly sigmoid Operation of the nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(), And target need one-hot code .
In the presence of CE after , It needs to be solved separately pt that will do , Note that you need to add sigmoid! in addition , In the paper alpha_t Solution and pt equally :
Post here focal loss Classic implementation :
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class FocalLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,alpha=0.25,gamma=2.0,reduce='sum'):
super(FocalLoss,self).__init__()
self.alpha = alpha
self.gamma = gamma
self.reduce = reduce
def forward(self,classifications,targets):
# classifcation:[N,K]
# targets: [N,K] Of one-hot code
alpha = self.alpha
gamma = self.gamma
classifications = classifications.view(-1) # Not pass sigmoid Of classification;
targets = targets.view(-1) # Should be one-hot
# ce_loss: In the corresponding formula -log(pt), That is, ordinary Cross entropy loss ;--> This function receives messages that have not been sigmoid Function of ;
ce_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(classifications, targets.float(), reduction="none")
#focal loss
p = torch.sigmoid(classifications) # after sigmoid
p_t = p * targets + (1 - p) * (1 - targets) # Calculation pt
loss = ce_loss * ((1 - p_t) ** gamma) # -log(pt) * (1-pt) ** ganmma
if alpha >= 0:
# In the corresponding formula alpha_t Control the weight of the loss
alpha_t = alpha * targets + (1 - alpha) * (1 - targets) # and pt The solution process is the same
loss = alpha_t * loss # Final focal loss
if self.reduce=='sum':
loss = loss.sum()
elif self.reduce=='mean':
loss = loss.mean()
else:
raise ValueError('reduce type is wrong!')
return loss
2. Return to loss
边栏推荐
- Untiy3d controls scene screenshots through external JSON files
- Unity scroll view element drag and drop to automatically adsorb centering and card effect
- pycharm 数据库工具
- 003-JS-DOM-Attr-innerText
- [note] usage model tree of the unity resource tree structure virtualizingtreeview
- Four methods of unity ugui button binding events
- Unity script life cycle and execution sequence
- Configuration and use of controllers and routes in nestjs
- Unity3d learning notes-1 (C # learning)
- Revit二次开发---未打开项目使用面板功能
猜你喜欢

Unity/ue reads OPC UA and OPC Da data (UE4)

Oracle-数据的基本操作
MinGW-w64下载文件失败the file has been downloaded incorrectly!

pytorch中常用损失函数总结

Force buckle 349 Intersection of two arrays

【VCS+Verdi联合仿真】~ 以计数器为例

How does unity use mapbox to implement real maps in games?

Unity packaging and publishing webgl error reason exception: failed building webgl player

Pycharm database tool

Unity + hololens publishing settings
随机推荐
[note] usage model tree of the unity resource tree structure virtualizingtreeview
Unity ugui text value suspended enlarged display add text background
Four methods of unity ugui button binding events
力扣704. 二分查找
Solution to Autowired annotation warning
Another download address for typro
Unity- the camera follows the player
力扣209. 长度最小的子数组
Display steerable 3D model in front of unity UI
Unity multiple UI page turning left and right
The difference between SVG and canvas
Unity publishing /build settings
Some problems encountered in unity steamvr
C # three ways to obtain web page content
Pytorch的安装以及入门使用
Unity download and installation website
Go Land no tests were Run: FMT cannot be used. Printf () & lt; BUG & gt;
Configuration and use of controllers and routes in nestjs
Force buckle 209 Minimum length subarray
Unity3d get screen width and height