当前位置:网站首页>New features of ES6
New features of ES6
2022-07-03 12:09:00 【Norxia 57】
One .let、const、var The difference between
(1) Block level Scope : Block scope is defined by { } Include ,let and const Has block level scope ,var There is no block level scope . Block level Scope It's solved ES5 Two questions in :
- Inner variables may override outer variables
- The loop variable used to count is leaked as Global variables
(2) Variable Promotion : var There is variable promotion ,let and const No variable promotion , That is, variables can only be used after declaration , No error will be reported .
(3) Add properties to the global : The global object of the browser is window,Node The global object of is global.var The declared variable is Global variables , And the variable will be added as the attribute of the global object , however let and const Can't .
(4) Repeat statement : var When variables are declared , Variables can be declared repeatedly , The variable with the same name declared after will overwrite the previously declared traversal .const and let Duplicate declaration of variables... Is not allowed .
(5) Temporary dead zone : In the use of let、const Before a command declares a variable , This variable is not available . This is in grammar , It's called a temporary dead zone . Use var The declared variable has no temporary deadband .
(6) Initial value setting : When variables are declared ,var and let You don't have to set the initial value . and const The declaration variable must have an initial value set .
(7) Pointer to : let and const All are ES6 New syntax for creating variables . let The created variable can change the pointer to ( You can reassign ). but const Declared variables are not allowed to change the pointer to .
const Can the properties of an object be modified const Can the properties of an object be modified
| difference | var | let | const |
|---|---|---|---|
| Whether there is scope level | × | ️ | ️ |
| Whether there is variable Promotion | ️ | × | × |
| Whether to add global attributes | ️ | × | × |
| Whether the variable can be declared repeatedly | ️ | × | × |
| Whether there is a temporary dead zone | × | ️ | ️ |
| Whether the initial value must be set | × | × | ️ |
| Can you change the pointer to | ️ | ️ | × |
const Can the properties of an object be modified
const It is not guaranteed that the value of the variable cannot be changed , But the memory address that the variable points to cannot be changed . For basic types of data ( The number 、 character string 、 Boolean value ), Its value is stored in the memory address pointed to by the variable , So it's equivalent to a constant .
But for reference type data ( Mainly objects and arrays ) Come on , The variable points to the memory address of the data , It's just a pointer ,const We can only guarantee that this pointer is fixed , As for whether the data structure it points to is variable , It's totally out of control .
Two . Structure expression
// Array
let arr=[1,2,3];
let [a,b,c]=[1,2,3];
console.log(a,b,c);
// 1 2 3
// object
let person={
name:"zhangsan",
age:21,
language:['java','js','vue']
}
let {name:abc,age,language}=person;
console.log(abc,age,language); //zhangsan 21 Array(3)3、 ... and . String extension
let a='qqqabacssscs';
console.log(a.startsWith('qq')); //true
console.log(a.endsWith('s'))//true
console.log(a.includes('z'));//false
String template
let a=`
<div>hello</div>
`Nested expressions
let name='zhangsan';
let age=21;
console.log(` I am a ${name}, This year, ${age+10} year , I want to say ${fun()}`); // I am a zhangsan, This year, 31 year , I want to say that this is a function
function fun(){
return ' This is a function ';
}Four . Arrow function
// Function default
function fun1(a,b=1){
return a+b;
}
console.log(fun1(1));
// Uncertain parameters
function fun2(...values){ //values Is an array of parameters
return values;
}
console.log(fun2(1,2,3));
// Arrow function
// let fun=function(a){
// console.log(a);
// }
// One parameter One line of function body
let fn=a=>console.log(a);
fn("hello");
// Multiple parameters One line of function body
let fn2=(a,b)=>a+b;
console.log( fn2(1,2));
// Multiple parameters Function body multiline
let fn3=(a,b)=>{c=a+b;
return a+c;
};
console.log(fn3(1,2));
// Object parameters
let fn4=(person)=>console.log('hello,'+person.name); // The parameter passed is person object
let person={
name:'wangzhen'
}
fn4(person);
// Object parameters 2
let fn5=({name})=>console.log('hello,'+name); // The parameters passed are name Belong to
The value of sex
fn4(person);5、 ... and . Object optimization
let person={
name:"zhangsan",
age:21,
language:['java','js','vue']
}
console.log(Object.keys(person)); // Print key
console.log(Object.values(person)); // Print value
console.log(Object.entries(person)); // Print key value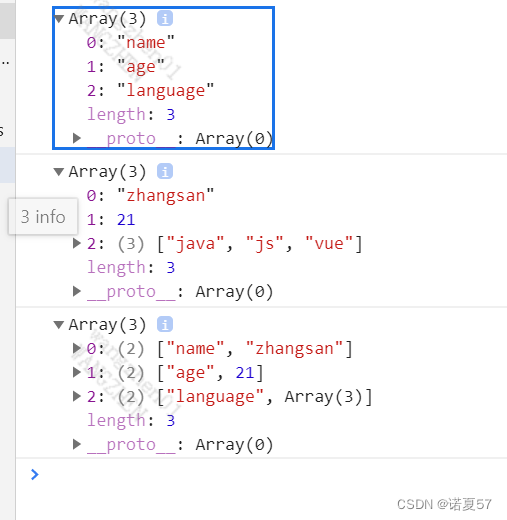
Object to merge
let target1={a:1};
let target2={b:2};
let target3={c:3};
// Object to merge
Object.assign(target1,target2,target3);
console.log(target1);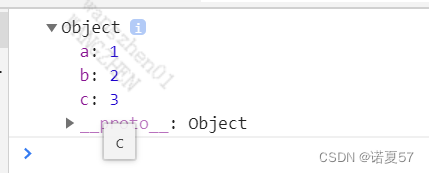
Declaration object abbreviation
const person1 = { age: age, name: name } console.log(person1)
// ES6: The property name is the same as the property value variable name , It can be omitted
const person2 = { age, name }
console.log(person2) //{age: 23, name: " Zhang San "}Object function attribute abbreviation
let person = {
name: "jack", // before :
eat: function (food) {
console.log(this.name + " Eating " + food);
},
// Arrow function version : I can't get it here this You must use the object point attribute
eat2: food => console.log(person.name + " Eating " + food),
// A simplified version :
eat3(food) {
console.log(this.name + " Eating " + food);
}
}
person.eat("apple");Object extension operators
// 1、 Copy the object ( Deep copy )
let person1 = { name: "Amy", age: 15 }
let someone = { ...person1 }
console.log(someone) //{name: "Amy", age: 15}
// 2、 Merge objects
let age = { age: 15 ,name:'Tom'}
let name = { name: "Amy" }
let person2 = { ...age, ...name }
// If the field names of two objects duplicate , The following object word The segment value overwrites the field value of the previous object
console.log(person2) //{age: 15, name: "Amy"} 6、 ... and .map and reduce
//map(): Receive a function , All elements in the original array are processed with this function and put into the new array to return .
let arr = ['1', '20', '-5', '3'];
console.log(arr)
arr = arr.map(s => parseInt(s)); //s For members in the array
console.log(arr)reduce
grammar : arr.reduce(callback,[initialValue]) reduce Execute the callback function for each element in the array in turn , Does not include elements in the array that have been deleted or have never been assigned plain , Accept four parameters : Initial value ( Or the return value of the last callback function ), Current element value , Current index , transfer use reduce Array of .
callback ( Functions that execute each value in the array , There are four parameters )
1、previousValue ( The value returned by the last call callback , Or the initial value provided (initialValue))
2、currentValue ( Elements currently being processed in the array )
3、index ( The index of the current element in the array )
4、array ( call reduce Array of ) initialValue ( As the first call callback The first parameter of .)
const arr = [1,20,-5,3];
// There is no initial value :
console.log(arr.reduce((a,b)=>a+b)); //19
console.log(arr.reduce((a,b)=>a*b));//-300
// Specify the initial value :
console.log(arr.reduce((a,b)=>a+b,1)7、 ... and .promise
// grammar
const promise = new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
// Perform asynchronous operations
if (/* Asynchronous operation succeeded */) {
resolve(value);// call resolve, representative Promise Will return a successful result
} else { reject(error);// call reject, representative Promise Will return a failed result
}
});
// The way the arrow function works
const promise = new Promise( (resolve, reject)=> {
// Perform asynchronous operations
if (/* Asynchronous operation succeeded */) {
resolve(value);// call resolve, representative Promise Will return a successful result
} else { reject(error);// call reject, representative Promise Will return a failed result
}
});
// Processing asynchronous results
promise.then(function (value) {
// Callback after successful asynchronous execution })
.catch(function (error) {
// Callback after asynchronous execution failure
})
})
//------------------------
// Arrowhead function
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.ajax({ url: "mock/user.json",
success(data) {
console.log(" Query the user :", data);
resolve(data.id);
},
error(error) {
console.log(" Something is wrong :" + error);
}
});
}).then((userId) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.ajax({ url: `mock/user_corse_${userId}.json`,
success(data) {
console.log(" Find the course :", data);
resolve(data.id);
},error(error) {
console.log(" Something is wrong :" + error);
}
});
});
}).then((corseId) => {
console.log(corseId);
$.ajax({
url: `mock/corse_score_${corseId}.json`,
success(data) {
console.log(" Query the score :", data);
},error(error) {
console.log(" Something is wrong :" + error);
}
});
});
// Optimize processing
let get = function (url, data) { // In the actual development, it will be placed separately common.js in
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.ajax({ url: url, type: "GET", data: data,
success(result) {
resolve(result);
},error(error) {
reject(error);
}
});
})
}
// Use encapsulated get Method , Realize query score
get("mock/user.json").then((result) => {
console.log(" Query the user :", result);
return get(`mock/user_corse_${result.id}.json`);
}).then((result) => {
console.log(" Find the course :", result);
return get(`mock/corse_score_${result.id}.json`)
}).then((result) => {
console.log(" Query the score :", result);
}).catch(() => {
console.log(" Something is wrong :" + error);
});8、 ... and . Import and export
export
const util = {
sum(a,b){
return a + b;
}
}
export {util};
// Abbreviation
export const util = {
sum(a,b){
return a + b;
}
}
// `export` Not only can you export objects , everything JS Variables can be exported . such as : Basic type variables 、 function 、 Array 、 object . When you want to export multiple values , It can also be abbreviated . For example, I have a file :user.js:
var name = "jack"
var age = 21
export {name,age}
// There is no need to declare the name of the object
export default {
sum(a,b){
return a + b;
}
} import
import util from 'hello.js'
// call util Properties in
util.sum(1,2)
import {name, age} from 'user.js'
console.log(name + " , This year, "+ age +" Year old ")Be careful : No variable name is declared when exporting , After importing, you can choose any name
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
PHP導出word方法(一mht)

(构造笔记)ADT与OOP

Is BigDecimal safe to calculate the amount? Look at these five pits~~
![Capturing and sorting out external Fiddler -- Conversation bar and filter [2]](/img/04/e9cc027d753e7049f273d866eefdce.png)
Capturing and sorting out external Fiddler -- Conversation bar and filter [2]
STL Tutorial 9 deep copy and shallow copy of container elements
Vulnhub's presidential
rxjs Observable filter Operator 的实现原理介绍

Qt OpenGL 旋转、平移、缩放

Xiaopeng P7 hit the guardrail and the airbag did not pop up. The official responded that the impact strength did not meet the ejection requirements

网络通讯之Socket-Tcp(一)
随机推荐
STL tutorial 10 container commonalities and usage scenarios
Solution to the second weekly test of ACM intensive training of Hunan Institute of technology in 2022
Redis notes 01: Introduction
Optimize interface performance
STL tutorial 8-map
ArcGIS application (XXI) ArcMap method of deleting layer specified features
Ripper of vulnhub
Experience container in libvirt
DEJA_VU3D - Cesium功能集 之 054-模拟火箭发射全过程
Sheet1$. Output [excel source output] Error in column [xxx]. The returned column status is: "the text is truncated, or one or more characters have no matches in the target code page.".
Shutter: overview of shutter architecture (excerpt)
[official MySQL document] deadlock
MCDF实验1
DEJA_ Vu3d - 054 of cesium feature set - simulate the whole process of rocket launch
Introduction to the implementation principle of rxjs observable filter operator
Redis 笔记 01:入门篇
安装electron失败的解决办法
Simple factory and factory method mode
DNS multi-point deployment IP anycast+bgp actual combat analysis
php 获取文件夹下面的文件列表和文件夹列表