当前位置:网站首页>Recursion: depth first search
Recursion: depth first search
2022-07-03 03:32:00 【My family Dabao is the cutest】
The maximum depth of a binary tree
The problem of binary tree usually gives priority to recursion , We want to ask for the depth of a tree , When we know the depth of the left subtree and the right subtree , that root The depth of the node is the maximum value of the left and right subtrees plus 1
d e p t h ( r o o t ) = m a x ( d e p t h ( r o o t . l e f t ) , d e p t h ( r o o t . r i g h t ) ) + 1 depth(root)=max(depth(root.left),depth(root.right))+1 depth(root)=max(depth(root.left),depth(root.right))+1
Obviously, this is also a recursive formula , So you can use recursion directly
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
if not root: # base case
return 0
l = dfs(root.left) # First find the depth of the left subtree
r = dfs(root.right) # Then find the depth of the right subtree
return max(l,r)+1 # The lion , And then add root The node is +1
return dfs(root)
Minimum depth of binary tree
At first, I felt that the minimum depth was the same as the maximum depth , But find it written directly min There is a problem .
The most important question is , The minimum depth is from the leaf node , therefore base case There are two kinds of , One is head==None, The other way is head.right is None and head.left is None. It must start from the leaf node .
Wrong writing , You can see a node ,a The left subtree depth of the node is 0, The depth of the right subtree is 2, Then according to the recursive formula of this error, we can get a The minimum depth of the node is min(0,2)=0, But obviously ,a Node is not a leaf node , So we can't find the minimum depth . But the maximum depth will not have such a problem .
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
return min(self.minDepth(root.right),self.minDepth(root.left))+1

To write correctly, you need to consider that a subtree is None The situation of , At this time, we need to recurse the subtree on the other side as the minimum depth .
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def minDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
elif root.left is None and root.right is None:
return 1
elif root.left is None:
return self.minDepth(root.right)+1
elif root.right is None:
return self.minDepth(root.left) + 1
else:
return min(self.minDepth(root.right),self.minDepth(root.left))+1
Balanced binary trees
Given a binary tree , Determine if it's a highly balanced binary tree .
In this question , A height balanced binary tree is defined as :
Every node of a binary tree The absolute value of the height difference between the left and right subtrees is not more than 1
The essence of this problem is to solve the depth of the tree , It is only required that the depth difference between the left and right subtrees should not exceed 1, If it exceeds one, it will return directly False. The same understanding , We want to know root Nodes are balanced , Then we need to calculate the height of the left and right subtrees , After calculating the height , We also need to judge whether the left and right subtrees are also balanced binary trees , If one is not , that root Certainly not
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
def dfs(root):
if not root:
return 0,True
l,lf = dfs(root.left)
r,rf = dfs(root.right)
if abs(l-r) <= 1 and lf and rf:
return max(l,r)+1,True
else:
return max(l,r)+1,False
_,f = dfs(root)
return f
The number of nodes in a complete binary tree
Counting numbers is also very simple , We count the number of left subtrees and then add the number of right subtrees , Then add the root node to get the total number of nodes .
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def countNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
if root is None:
return 0
return self.countNodes(root.left) + self.countNodes(root.right) + 1
边栏推荐
- Hutool动态添加定时任务
- numpy之 警告VisibleDeprecationWarning: Creating an ndarray from ragged nested sequences
- Elsevier latex submitted the article pdftex def Error: File `thumbnails/cas-email. jpeg‘ not found: using draf
- Mongodb replication set [master-slave replication]
- [AI practice] Application xgboost Xgbregressor builds air quality prediction model (I)
- Solve high and send system Currenttimemillis Caton
- The XML file generated by labelimg is converted to VOC format
- VS 2019 配置tensorRT生成engine
- Unity3d RPG implementation (medium)
- Bid farewell to artificial mental retardation: Mengzi open source project team received RMB 100 million financing to help NLP develop
猜你喜欢

Summary of electromagnetic spectrum

Positioning (relative positioning, absolute positioning, fixed positioning, Z-index) 2022-2-11

Summary of determinant knowledge points in Chapter 1 of Linear Algebra (Jeff's self perception)

npm : 无法将“npm”项识别为 cmdlet、函数、脚本文件或可运行程序的名称。请检查名称的拼写,如果包括路径,请确保路径正确,然后再试一次。

ffmpeg录制屏幕和截屏
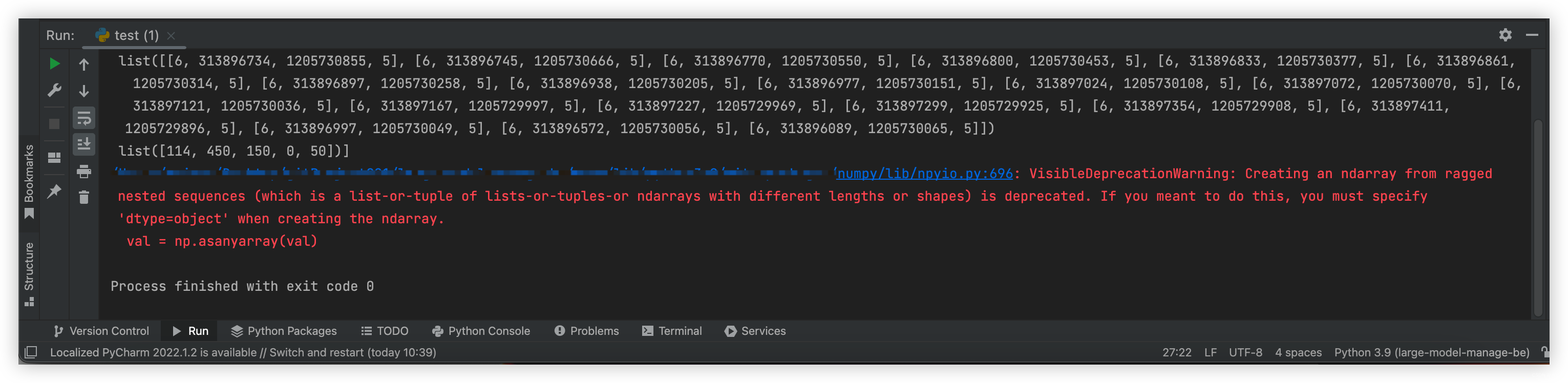
numpy之 警告VisibleDeprecationWarning: Creating an ndarray from ragged nested sequences

Pytorch轻量级可视化工具wandb(local)
Pytorch multi card distributed training distributeddataparallel usage
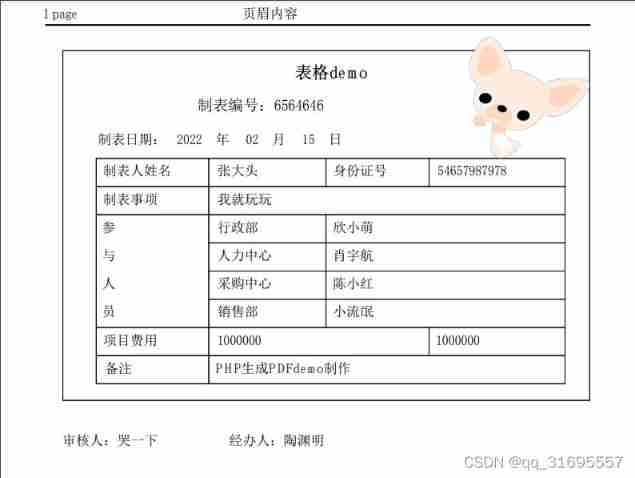
PHP generates PDF tcpdf

Pytoch lightweight visualization tool wandb (local)
随机推荐
File rename
动态规划:最长公共子串和最长公共子序列
VS 2019 配置tensorRT生成engine
Model transformation onnx2engine
The XML file generated by labelimg is converted to VOC format
node 开启服务器
Applet get user avatar and nickname
Use of El tree search method
PAT乙级常用函数用法总结
FileZilla Client下载安装
使用InputFilter限制EditText时踩坑及解决方案
Advanced redis applications [password protection, data persistence, master-slave synchronization, sentinel mode, transactions] [not completed yet (semi-finished products)]
UMI route interception (simple and rough)
redis高级应用【密码防护、数据持久化、主从同步、哨兵模式、事务】【暂未完成(半成品)】
MongoDB基本操作【增、删、改、查】
Spark on yarn resource optimization ideas notes
900W+ 数据,从 17s 到 300ms,如何操作
基于Qt的yolov5工程
Mysql Mac版下载安装教程
[mathematical logic] predicate logic (individual word | individual domain | predicate | full name quantifier | existence quantifier | predicate formula | exercise)