当前位置:网站首页>[introduction to information retrieval] Chapter 1 Boolean retrieval
[introduction to information retrieval] Chapter 1 Boolean retrieval
2022-07-02 07:21:00 【lwgkzl】
The overview
The first chapter mainly introduces information retrieval , The concept of Boolean retrieval and some basic definitions of retrieval , Such as inverted index, etc .
1.1 An example of information retrieval
Information retrieval (information retrieval): From large-scale unstructured corpus ( It's usually text ) Find out the process of meeting users' information needs .
Ad hoc retrieval: This is an application scenario of information retrieval , Generally speaking, the whole information retrieval is divided into two kinds , One is Ad hoc retrieval, That is, the corpus is basically fixed , Use this corpus to meet users' arbitrary queries , The scene is IR The most common , For example, search engine , Library retrieval system , Can be seen as Ad hoc retrieval. The other is filtering retrieval, This kind of demand will not change much , But the corpus will be in iteration at any time , This demand is less , A less appropriate example is the search of sports news websites , User query Probably fixed ( ball-game star , league ), News is dynamically updated .
Indexes (index): The usual search is linear search , Such as linear scanning text , Find the desired field, etc . If there is a tag, it can mark the document where the field is located , Then you can make this tag an index , Such as the number of the Library .
Term (term): In Text Retrieval , The term will be used as the index unit . Segment a sentence , The resulting sub unit is the word item . Such as “ I'm Chinese ” After the participle [“ I ”,“ yes ”,“ Chinese ”], There are three words in the list .
file (document): In the retrieval system , The retrieved object , It could be books , Journalism , Chapter, etc . Of course, we need to assign a number to each document (01,02,03…).
Term - Document correlation matrix (term-document incidence matrix): The basic structure of simple Boolean retrieval , It is a two-dimensional matrix composed of words and documents C, Value taken by 0,1 form , C i j = 1 C_{ij}=1 Cij=1 A word item i In the document j There has been , On the contrary, it means that there is no . The example is as follows :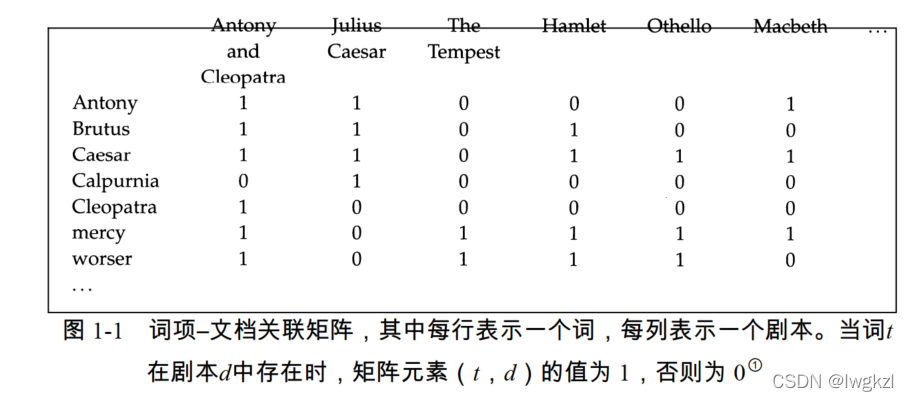
Boolean retrieval model (bool retrieval model): Boolean search is to search all documents containing the word according to keywords . And it supports multiple keywords “AND”,“OR”,"NOT" operation .
According to the above words - Document correlation matrix , We can do this easily .
If the search also includes “Antony” and “Brutus” Documents , Will “Antony” Corresponding document vector “110001” And “Brutus” Document vector "110100" Just do and operate
110001 & 110100 => 110000
And the first two answers obtained by operation are 1, Explain that one document and the second document are the answers to the search ( It also includes the above two words ). The same can be achieved “OR” and “NOT” operation
Inverted index (inverted index):
Why do we need inverted index : By word item - Document incidence matrix construction of the relationship between terms and documents takes up too much space , Because in real life , There are tens of thousands of words , Documents are at the level of hundreds of billions , Multiplying the two is the volume that no machine can store . Because of the word - In the document matrix , A large number of locations are 0, In fact, it can be used in graph theory ** Adjacency list ** To store , That is, for each word , Save only the document number containing the word .
What is inverted index : That is, the adjacency table with word items as keys , Each line stores an idea of the document number containing the word item .
Inverted record sheet (posting list): Use inverted index to store word items - Adjacency table of the association relationship between documents , As shown in the figure below : On the left is the word column , On the right is a linked list , Store the document number containing the word item 
For more efficient retrieval , The words on the left are arranged in order according to the dictionary order , The document numbers on the right are arranged from small to large
1.2 Preliminary construction of inverted index table
It is mainly divided into four steps
- collecting data

- Word segmentation of text data , Construct lexical items
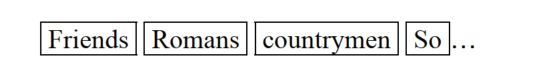
- Normalize the word items .( In English , Remove lexical tenses , etc. )
- Merge the documents corresponding to the word items , And store them in order , You can also count the frequency of vocabulary .

1.3 Handle Boolean search queries
Reverse table merge (posting merge): Because each word item corresponds to an adjacency table ( chart 1-3), Then the previous requirements of Boolean retrieval ,“AND”,“OR”,"NOT" The implementation of is not a simple and or non operation of vectors . Instead, you need to merge multiple linked lists , Find its common elements . The public elements of the linked list can be found in O ( n ) O(n) O(n) In time to complete ( Based on the premise that the document number of the same word is orderly ):
More complex operations have corresponding optimizations , I'm not going to go into details here
1.4 Expand Boolean retrieval
Boolean search can find all documents that meet the conditions , But you can't grade and sort documents , That is, all documents have the same weight , Therefore, it leads to :
Lexical proximity index (term proxlmity): Its main idea is : The two terms used to specify the query should be close to each other in the document , The proximity depends on whether the two words are in the same institutional unit ( The same paragraph , The same sentence )
This provides additional functionality for Boolean retrieval ( not only “AND”“OR”,“NOT”):
“/s”,"/p","/k" It means that two words are in the same sentence , The same paragraph , as well as K Within a word .
limitations : Use “AND” In operation , Will cause high precision, low recall The circumstances of , While using “OR” During operation , Will cause high recall, low precision The situation of , It is difficult to weigh the relationship between the two by constructing query rules .
summary
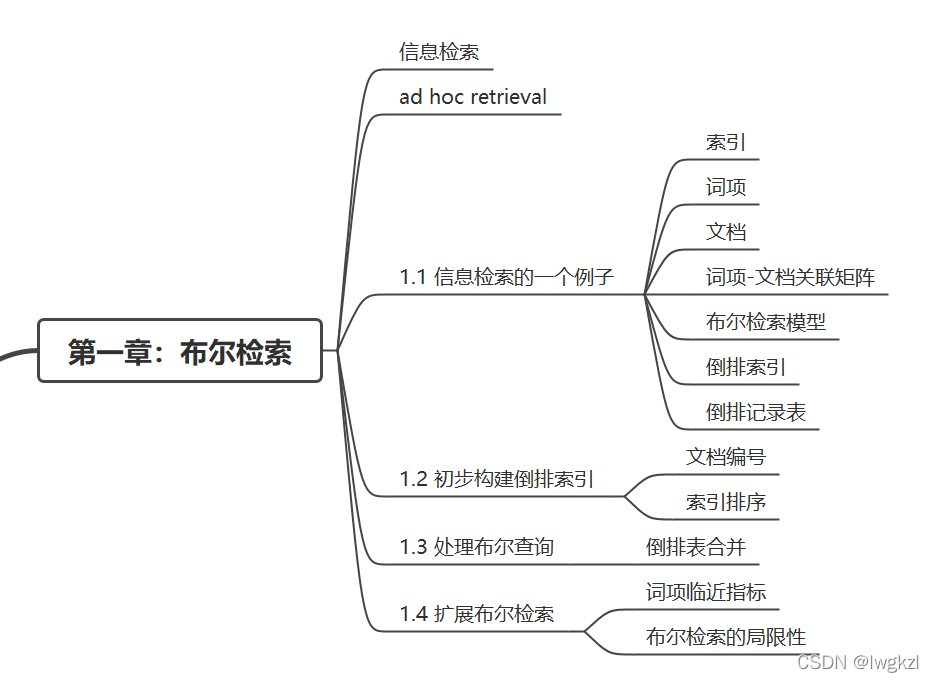
This chapter mainly introduces :
- The concept and construction of inverted index
- The concept of Boolean retrieval model
- Some basic concepts of information retrieval
Knowledge map in this chapter
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
华为机试题
mapreduce概念和案例(尚硅谷学习笔记)
2021-07-05c /cad secondary development create arc (4)
php中计算树状结构数据中的合计
php中计算两个日期之前相差多少天、月、年
離線數倉和bi開發的實踐和思考
SSM garbage classification management system
数仓模型事实表模型设计
Oracle RMAN semi automatic recovery script restore phase
oracle apex ajax process + dy 校验
Oracle general ledger balance table GL for foreign currency bookkeeping_ Balance change (Part 1)
Pratique et réflexion sur l'entrepôt de données hors ligne et le développement Bi
MySQL has no collation factor of order by
The boss said: whoever wants to use double to define the amount of goods, just pack up and go
Message queue fnd in Oracle EBS_ msg_ pub、fnd_ Application of message in pl/sql
架构设计三原则
CSRF attack
User login function: simple but difficult
parser.parse_args 布尔值类型将False解析为True
Oracle RMAN automatic recovery script (migration of production data to test)