当前位置:网站首页>Detailed explanation of multithreading
Detailed explanation of multithreading
2022-07-03 13:12:00 【Tolerance speech】
1. Threads , process , Multithreading
1. Definition
multitasking : Play with your cell phone while eating .
Multithreading (Thread): There are many roads in one road ; Everyone in the game has an account ; Programming main Main function and sub function run at the same time .
process (Process): stay Programs running in the operating system Is the process ( A process can have multiple threads , If you hear sound in the video at the same time , Look at the image , Watch the barrage, etc ).
2. Relationship
Program It's an ordered collection of instructions and data , It has no operational meaning in itself , It's a static concept .
process It's a process of executing a program , It's a dynamic concept , Is the unit of system resource allocation .
Threads In the process , Usually a process has at least one thread , Or it doesn't make sense , Thread is CPU The unit of scheduling and execution .
Be careful :
A lot of multithreading is simulated , True multithreading means having more than one cpu, I.e. multi-core , Server, such as . Simulate multithreading in a cpu Under the circumstances , At the same time ,cpu Only one code can be executed , Because switching is fast , So there's the illusion of simultaneous execution .
2. Thread creation
| Thread class
Three ways to create | Runnable Interface
| Callable Interface
1.Thread
1. Definition
package Thread;
// Inherit Thread class ; rewrite run() Method ; call start() Open thread .
public class TestThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//run Method thread body
for (int i = 0; i <20 ; i++) {
System.out.println(" I'm looking at the code ---"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//main Threads , The main thread
// Create a thread object
TestThread1 testThread1 = new TestThread1();
// call start() Method to open the thread , The sub thread and the main thread execute at the same time , Sub threads do not necessarily execute immediately , from CPU Scheduling .
testThread1.start();
for (int i = 0; i <20 ; i++) {
System.out.println(" I'm learning multithreading ---"+i);
}
}
}
2. practice : Download Network Diagram
You need to import external packages commons IO, And add as library .


package Thread;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
// practice Thread, Realize multi thread synchronous download picture
public class TestThread2 extends Thread{
private String url; // Network file address
private String name; // Saved file name
public TestThread2(String url,String name){
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
// Download the execution of the image thread
@Override
public void run() {
Webdownloader webdownloader = new Webdownloader();
webdownloader.downloader(url,name);
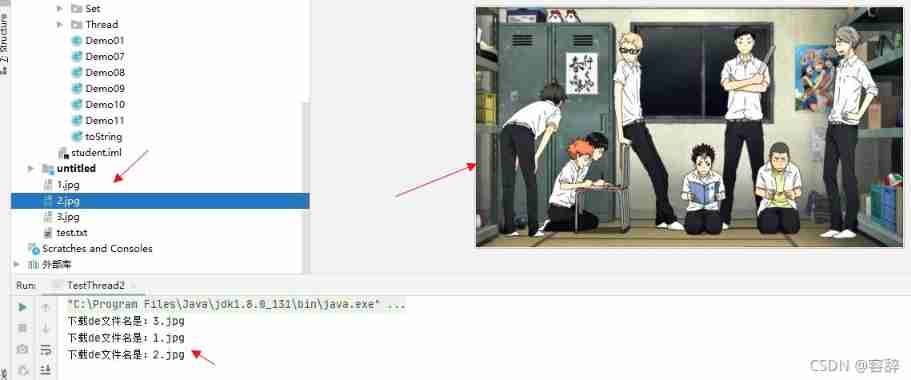
System.out.println(" download de The file name is :"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread2 t1 = new TestThread2("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=124374093,66469564&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=120&f=JPEG?w=500&h=500","1.jpg");
TestThread2 t2 = new TestThread2("https://img1.baidu.com/it/u=1456800335,2916237912&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg","2.jpg");
TestThread2 t3 = new TestThread2("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=97064133,754709681&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg","3.jpg");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
// Downloader
class Webdownloader{
// Download method
public void downloader(String url,String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("IO abnormal ,downloader Method exception ");
}
}
}
Running results :
2.Runnable
1. Definition
package Thread;
// Create method two : Realization runnable Interface : rewrite run() Method ; The execution thread needs to drop in runnable Interface implementation class ; call strat() Method .
public class TestThread3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//run Method thread body
for (int i = 0; i <20 ; i++) {
System.out.println(" I'm looking at the code ---"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// establish runnable Implementation class object of interface
TestThread3 testThread3 = new TestThread3();
// Creating thread objects , Open our thread through thread object , The meaning of agency
/*Thread thread = new Thread(testThread3); thread.start();*/
new Thread(testThread3).start();
for (int i = 0; i <20 ; i++) {
System.out.println(" I'm learning multithreading ---"+i);
}
}
}
2. practice 1: Buy train tickets
Multiple threads operate on an object at the same time .
package Thread;
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable {
// Number of votes
private int ticketnums = 10;
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if (ticketnums<=0){
break;
}
// Analog delay
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Got the number "+ticketnums--+" ticket ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread4 ticket = new TestThread4();
new Thread(ticket,"xi").start();
new Thread(ticket," teacher ").start();
new Thread(ticket," Cattle ").start();
}
}
Multiple threads operate on an object , There will be data insecurity , Data disorder , For example, two people grab the same ticket , Create concurrency problems .
3. practice 2: Tortoise and the hare
package Thread;
public class Race implements Runnable{
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {
// Rabbit rest , Analog delay
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals(" The rabbit ") && i%10 == 0){
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Judge whether the game is over
boolean flag = Gameover(i);
if (flag){
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ran "+i+" Step ");
}
}
// Judge whether to finish the game
private boolean Gameover(int sleeps){
if (winner != null){
return true;
}{
if (sleeps >= 100){
winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("winner is"+winner);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race = new Race();
new Thread(race," The rabbit ").start();
new Thread(race," Tortoise ").start();
}
}
3.callable
You can define the return value
You can throw an exception
package Thread;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
// Thread creation method 3 : Realization callable Interface , rewrite call() Method .
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String url; // Network file address
private String name; // Saved file name
public TestCallable(String url,String name){
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
// Download the execution of the image thread
@Override
public Boolean call() {
Webdownloader1 webdownloader = new Webdownloader1();
webdownloader.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println(" download de The file name is :"+name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t1 = new TestCallable("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=124374093,66469564&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=120&f=JPEG?w=500&h=500","1.jpg");
TestCallable t2 = new TestCallable("https://img1.baidu.com/it/u=1456800335,2916237912&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg","2.jpg");
TestCallable t3 = new TestCallable("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=97064133,754709681&fm=26&fmt=auto&gp=0.jpg","3.jpg");
// Create execution tasks
ExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
// Submit for execution
Future<Boolean> result1 = ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> result2 = ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> result3 = ser.submit(t3);
// To get the results
boolean r1 = result1.get();
boolean r2 = result2.get();
boolean r3 = result3.get();
// Close the service
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
// Downloader
class Webdownloader1 {
// Download method
public void downloader(String url,String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("IO abnormal ,downloader Method exception ");
}
}
}
3. Static proxy pattern
Real objects and proxy objects should implement the same interface .
benefits : Proxy objects can do a lot of things that real objects can't
Real objects focus on doing their own things
package Thread;
public class StaticAgent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Wedding wedding = new Wedding(new You());
wedding.happyMarry();
}
}
// Common interface
interface Marry{
void happyMarry();
}
// Real role
class You implements Marry{
@Override
public void happyMarry() {
System.out.println(" Married ");
}
}
// delegable role
class Wedding implements Marry{
// The real target character
private Marry target;
public Wedding(Marry target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public void happyMarry() {
before();
this.target.happyMarry();
after();
}
private void after() {
System.out.println(" Closing payment ");
}
private void before() {
System.out.println(" Site layout ");
}
}
4.Lamda expression
1. Definition
Lamda It is the eleventh letter of the Greek alphabet ,Lamda It is the function of simplifying the procedure .
Functional interface : Any interface if Contains only one abstract class , It's a functional interface .
public interface Runnable{
public abstract void run();
}
With a functional interface, you can use Lamda Expression to create the object of the interface .
2. deduction lamda expression
package Thread;
public class TestLamda1 {
// Static inner class
static class like1 implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lamda() {
System.out.println("I like lamda1");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ilike like = new like();
like.lamda();
like = new like1();
like.lamda();
// Local inner classes
class like2 implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lamda() {
System.out.println("I like lamda2");
}
}
like =new like2();
like.lamda();
// Anonymous inner class : There is no class name , You must use the interface or parent class of the class
like = new Ilike() {
@Override
public void lamda() {
System.out.println("I like lamda3");
}
};
like.lamda();
// use lamda simplify
like = () ->{
System.out.println("I like lamda4");
};
like.lamda();
}
}
// Functional interface
interface Ilike{
void lamda();
}
// Implementation class
class like implements Ilike{
@Override
public void lamda() {
System.out.println("I like lamda");
}
}
3. practice
package Thread;
public class TestLamda2 {
static class Love implements Ilove{
@Override
public void love(int a) {
System.out.println("i love you----"+a);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Ilove love = new Love();
love.love(1);
Ilove love1 = new Love();
love1.love(2);
class Love implements Ilove{
@Override
public void love(int a) {
System.out.println("i love you----"+a);
}
}
Ilove love2 = new Love();
love.love(3);
love = new Ilove(){
@Override
public void love(int a) {
System.out.println("i love you----"+a);
}
};
love.love(4);
love = (a)-> {
System.out.println("i love you----" + a);
};
love.love(5);
// simplify : Remove brackets
love = a-> {
System.out.println("i love you----" + a);
};
love.love(6);
// simplify : Remove the curly braces ( You can't simplify curly braces with multiple lines )
love = a-> System.out.println("i love you----" + a);;
love.love(7);
}
}
interface Ilove{
void love(int a);
}
class Love implements Ilove{
@Override
public void love(int a) {
System.out.println("i love you----"+a);
}
}
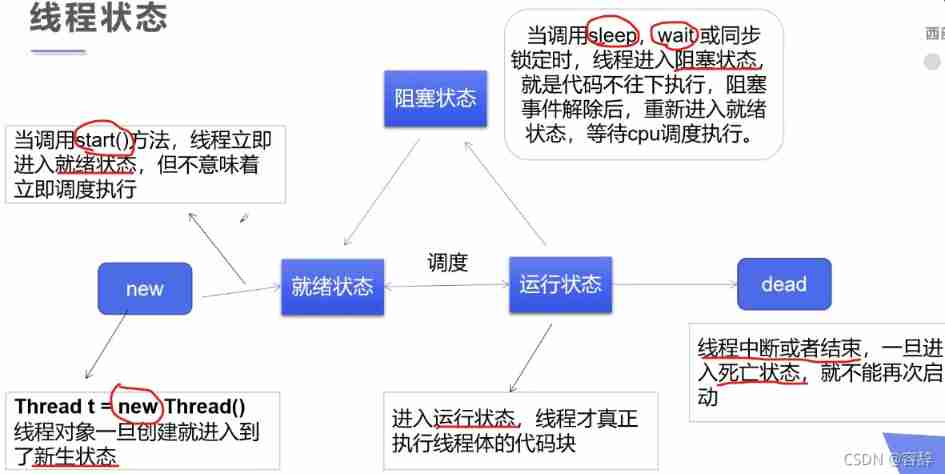
5. The five states of a thread
1. Thread stop (stop)
It is not recommended to use JDK Provided stop(),destroy() Method .【 obsolete 】
It is recommended to let the thread stop itself ----- Utilization times , Dead cycle is not recommended
It is recommended to use a flag bit to terminate the variable , When flag=flase, Then terminate the thread
package Thread;
public class TestStop implements Runnable {
//1. Set a flag bit
private Boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag){
System.out.println("Tread...run"+i++);
}
}
//2. Set an exposed method to stop the thread , Conversion flag bit
public void Stop(){
this.flag= false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop testStop = new TestStop();
new Thread(testStop).start();
for (int i = 0; i <1000 ; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
if (i==600){
testStop.Stop();
System.out.println(" It's time for the thread to stop ");
}
}
}
}
2. Thread to sleep (sleep)
sleep( Time ) Specifies the number of milliseconds the current thread is blocking ;
sleep There is abnormal InterruptedException;
sleep When time is up , The thread enters the ready state ;
Every object has a lock ,sleep It won't release the lock .
effect :
1. Analog network delay ---- Magnify the occurrence of the problem ; Avoid multiple threads operating on an object , For example, buy the ten tickets Xiao Ming took away , Everyone else has no tickets .
2. Analog countdown :
package Thread;
public class Sleep {
public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {
int num = 10;
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if (num<=0){
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tenDown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. Get system time
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());// Get the current time
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());// Update current time
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3. Thread comity (yield)
Comity is to suspend the currently executing thread , But not blocking , The thread From running state to ready state .
Comity is to re compete , Give Way CPU Rescheduling ,** Comity is not necessarily a success !** see CPU Mood .
package Thread;
public class Yield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield = new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" Thread start execution ");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" The thread stops executing ");
}
}
Comity is the result of success 
4. Thread enforcement (join)
Join Merge threads , It can be imagined as Jump the queue , After this thread is executed , While executing other threads , Other threads are blocking .
package Thread;
public class Join implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
System.out.println("vip coming "+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Join join = new Join();
Thread thread = new Thread(join);
thread.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (i==40){
thread.join();
}
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
5. Observe thread state (state)
package Thread;
public class State {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("/");
});
// Observation state
Thread.State state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//NEW
// Observe after starting the thread
thread.start();
state = thread.getState();
System.out.println(state);//RUNNABLE
// Determine thread state
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){
// As long as the thread does not terminate , Just keep outputting the state
thread.sleep(1010);
state = thread.getState();// Constantly update thread status
System.out.println(state);
}
}
}
6. Thread priority (Priority)
The thread scheduler determines which thread should be scheduled to execute according to the priority ( High priority does not necessarily lead to execution ,, But the weight will increase , Get more resources ).
The priority of a thread is expressed in numbers , Range from 1~10
Method : obtain getPriority, change setPriority(int xxx)
package Thread;
public class Priority {
// The default priority of the main thread 5
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();
Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority);
// Set the priority first , Restart
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(3);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(6);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);// Maximum priority 10
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);// Minimum priority 1
t5.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
7. The guardian thread (daemon)
Threads are divided into user threads (main()) And daemons (gc() Garbage collection )
The virtual machine must make sure that the user thread is finished
The virtual machine doesn't have to wait for the daemons to finish executing
package Thread;
public class Daemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
You1 you = new You1();
Thread thread = new Thread(god);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(you);
thread.setDaemon(true);// The default is false Represents the user thread , Normal threads are user threads
thread.start(); // The guardian thread
thread1.start(); // User threads
}
}
// lord
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println(" God is watching over you ");
}
}
}
class You1 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 356; i++) {
System.out.println(" Happy every day ");
}
System.out.println("==========goodbye world!==========");
}
}
Running results : The daemon thread will continue to run for a while 
6. Thread synchronization ()
1. Definition
Concurrent : The same object is operated by multiple threads at the same time
When dealing with multithreading , Multiple threads access the same object , And some threads also want to modify this object , At this point we need thread synchronization , Thread synchronization is actually a kind of Waiting mechanism , Multiple threads that need to access this object at the same time enter this *** Object's waiting pool *** Form a line .
need queue + lock Guarantee safety , Locking mechanism :synchronized.
2. There are the following problems :
A thread with a lock will cause other threads that need this lock to hang ;
Lock , Releasing lock will lead to more context switching and scheduling delay , Cause performance problems ;
A high priority thread waiting for a low priority thread to release the lock will cause priority inversion , Cause performance problems .
3. Three major insecurity
1. It's not safe to buy tickets , There are negative numbers and the same tickets
package Sys;
public class UnsafeBuyTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Buy buy = new Buy();
new Thread(buy," Li Qiang ").start();
new Thread(buy," Liu Yi ").start();
new Thread(buy," Xiao Ming ").start();
}
}
class Buy implements Runnable{
private int ticketnums=10;
boolean flag = true;
@Override
public void run() {
while (flag){
try {
buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// Use synchronized Method synchronization
public synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
// Judge whether there is a ticket
if (ticketnums<=0){
flag = false;
return;
}
// Analog delay
Thread.sleep(100);
// Buy tickets
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ticketnums--);
}
}
2. Unsafe bank
package Sys;
// Two people go to the bank to get money , Account
public class UnsafeBank {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account account = new Account(100000," Marriage Fund ");
Drawing you = new Drawing(account,50000,"you");
Drawing boyFriend = new Drawing(account,60000,"boyFriend");
you.start();
boyFriend.start();
}
}
// Account
class Account{
int money;// balance
String name;// Card name
public Account(int money, String name) {
this.money = money;
this.name = name;
}
}
// Bank : Simulated withdrawal
class Drawing extends Thread{
Account account;// Account
int drawingMoney;// How much money did you withdraw
int nowMoney;// How much money do you have now
public Drawing(Account account,int drawingMoney,String name){
super(name);
this.account=account;
this.drawingMoney=drawingMoney;
}
//synchronized The default lock is this It itself
// Withdraw money
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (account) {
// Judge whether there is money
if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Insufficient account balance , I can't take it ");
return;
}
//sleep Can magnify the occurrence of the problem
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Card balance = The account balance - The money taken
account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;
// Money in hand
nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;
System.out.println(account.name + " The balance is :" + account.money);
//this.getName()=Thread.currentThread().getName()
System.out.println(this.getName() + " The money in hand is :" + nowMoney);
}
}
}
3. Unsafe list
package Sys;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread (()->{
synchronized (list){
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());// Add two numbers to the same position in an instant
}
}
Expand :
package Sys;
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;
// test ·JUC A collection of security types , Concurrency issues
public class TestJUC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CopyOnWriteArrayList<String> list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
4. Sync
1. Synchronization method :public synchronized viod method(int args){ }
Synchronization code block :synchronized(Obj){ }
- Obj It's called a synchronous monitor :Obj It could be anything , But it is recommended to use shared resources ( The amount of change to modify , Which one did Additions and deletions Which lock ) As a synchronization monitor ;
- The synchronization monitor does not need to be specified in the synchronization method , Because the synchronization monitor of the synchronization method is this, It's the object itself , perhaps class.
2.synchronized Method control right “ object ” The interview of , Each object corresponds to a lock , Every synchronized Method must obtain the lock of the object calling the method to execute , Otherwise, the thread will block , Once the method is implemented , It's the lock , The lock is not released until the method returns , Only the blocked thread can obtain the lock , Carry on .
3. shortcoming : If a large method is stated as synchronized will Affect efficiency .
4. Three unsafe problems can be corrected by using the synchronization method , The result of the modification is directly written in the three unsafe codes .
5. Deadlock
Definition :
Multiple threads own some shared resources , And wait for each other's resources to run , As a result, two or more threads are waiting for each other to release resources , The situation in which both of them stop executing . A synchronization block has “ Locks for more than two objects ” when , It could happen “ Deadlock ” problem .
package Sys;
// Multiple threads hold the resources needed by each other at the same time , And then form an impasse
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup g1 = new Makeup(0," Cinderella ");
Makeup g2 = new Makeup(1," Snow White ");
g1.start();
g2.start();
}
}
// Lipstick
class Lipstick{
}
// Mirror
class Mirror{
}
// Make up
class Makeup extends Thread{
// There is only one thing , use static To guarantee
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;// choice
String girlname;// People who use cosmetics
Makeup(int choice,String girlname){
this.choice=choice;
this.girlname=girlname;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Make up
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Makeup holds each other's locks , You need to get the other person's resources
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0){
synchronized (lipstick){
// Get lipstick
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of lipstick ");
Thread.sleep(1000);
// Get the mirror in a second
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of the mirror ");
}
}
}else {
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of the mirror ");
Thread.sleep(2000);
//2 Get lipstick after seconds
synchronized (lipstick){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of lipstick ");
}
}
}
}
}
Running results 
Deadlock Relieving : You can't hold two locks
package Sys;
// Multiple threads hold the resources needed by each other at the same time , And then form an impasse
public class DeadLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Makeup g1 = new Makeup(0," Cinderella ");
Makeup g2 = new Makeup(1," Snow White ");
g1.start();
g2.start();
}
}
// Lipstick
class Lipstick{
}
// Mirror
class Mirror{
}
// Make up
class Makeup extends Thread{
// There is only one thing , use static To guarantee
static Lipstick lipstick = new Lipstick();
static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();
int choice;// choice
String girlname;// People who use cosmetics
Makeup(int choice,String girlname){
this.choice=choice;
this.girlname=girlname;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Make up
try {
makeup();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// Makeup holds each other's locks , You need to get the other person's resources
private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {
if (choice == 0){
synchronized (lipstick){
// Get lipstick
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of lipstick ");
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
// Get the mirror in a second
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of the mirror ");
}
}else {
synchronized (mirror){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of the mirror ");
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
//2 Get lipstick after seconds
synchronized (lipstick){
System.out.println(this.girlname+" Get the lock of lipstick ");
}
}
}
}
Running results :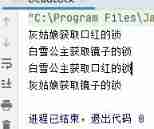
6.Lock lock
ReentrantLock class ( Repeatable lock ) Realized Lock Interface
package Sys;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class TestLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
new Thread(testLock2).start();
}
}
class TestLock2 implements Runnable{
int ticketnums = 10;
// Definition lock lock
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
try {
// Lock
lock.lock();
if (ticketnums > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(ticketnums--);
} else {
break;
}
}finally {
// Unlock
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
synchronized And Lock contrast :
- Lock It's an explicit lock ( Manually open and close the lock ),synchronized It is an implicit lock that is automatically released when it is out of scope ;
- Lock Only code block locks ,synchronized There are code block locks and method locks ;
- Use Lock lock ,JVM It will take less time to schedule threads , Better performance ; And it has better scalability , You can provide more subclasses (ReentrantLock);
- Priority of use :Lock> Synchronization code block > Synchronization method ;
7. Thread collaboration
1. Definition
Producer consumer issues : This is a thread synchronization , Producers and consumers share the same resource , And producers and consumers depend on each other , Mutually conditional . Only synchroned It can prevent concurrent updating of the same resource , But it can't be the message passing of different threads in Xi'an .
2.Java It provides several methods to solve the communication problem between threads :
wait() Indicates that the thread has been waiting , Wait for other threads to notify , And sleep Different ,wait Can release the lock
notify() Wake up a waiting thread
notifyAll() Wake up all calls on the same object wait() Method thread , High priority thread priority scheduling
Use buffer to solve ( Tube method ): Producers put data , Consumers take out the data
Concurrent collaboration : Signal lamp , The flag bit solves
3. Tube method
package Sys;
// producer , consumer , product , buffer
public class TestPc {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Syncontainer container = new Syncontainer();
new Productor(container).start();
new Consumer(container).start();
}
}
// producer
class Productor extends Thread{
Syncontainer container;
public Productor(Syncontainer container){
this.container = container;
}
// production
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(" Produced "+i+" chicken ");
container.Push(new Chicken(i));
}
}
}
// consumer
class Consumer extends Thread{
Syncontainer container;
public Consumer(Syncontainer container){
this.container = container;
}
// consumption
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println(" The consumption "+container.pop().id+" only ");
}
}
}
// product
class Chicken{
int id;// Product number
public Chicken(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
// buffer
class Syncontainer{
// Container counter
int count = 0;
// Need a container size
Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];
// Producers put in products
public synchronized void Push(Chicken chicken){
// If the goods are full , Need to wait for consumers to buy
if (count == chickens.length){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// If the goods are not enough , Producers add goods
chickens[count] = chicken;
count++;
// Consumers can be informed to spend
this.notifyAll();
}
// Consumers consume products
public synchronized Chicken pop(){
if (count == 0){
// Inform the producer to produce , Consumer waiting
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
count--;
Chicken chicken = chickens[count];
// It's gone , Inform the producer to produce
this.notifyAll();
return chicken;
}
}
4. Signal lamp method
package Sys;
public class TestPc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Tv tv = new Tv();
new Player(tv).start();
new Watcher(tv).start();
}
}
// producer --- actor
class Player extends Thread {
Tv tv;
public Player(Tv tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
tv.play(" The flash book is playing ");
} else {
tv.play(" Tiktok playing ");
}
}
}
}
// consumer --- The audience
class Watcher extends Thread{
Tv tv;
public Watcher(Tv tv){
this.tv=tv;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
tv.watch();
}
}
}
// product --- show
class Tv{
// Actors perform , The audience waited T
// The audience watched , The actor waits F
String voice;// The show
boolean flag = true;
// perform
public synchronized void play(String voice){
if (!flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(" The actors performed "+voice);
// Inform the audience to watch
this.notifyAll();
this.voice = voice;
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
// watch
public synchronized void watch(){
if (flag){
try {
this.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(" The audience watched "+voice);
// Tell the actors to perform
this.notifyAll();
this.flag = !this.flag;
}
}
8. Thread pool
Ideas : Create many threads ahead of time , Put it in the thread pool , Get it directly when you use it , Put it back into the pool after use . It can avoid frequent creation and destruction , Improve performance .
ExecutorService: Thread pool interface
void execute(Runnable command): Carry out orders
void shutdown(): Close thread pool
Executors: Used to create and return different types of thread pools
package Sys;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class Pool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. Create services , Creating a thread pool
//newFixedThreadPool The parameter is the thread pool size
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//2. perform
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
service.execute(new MyThread());
//3. The pool is closed
service.shutdown();
}
}
class MyThread implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
边栏推荐
- Flink SQL knows why (7): haven't you even seen the ETL and group AGG scenarios that are most suitable for Flink SQL?
- Will Huawei be the next one to fall
- 【習題七】【數據庫原理】
- Flink SQL knows why (XV): changed the source code and realized a batch lookup join (with source code attached)
- 我的创作纪念日:五周年
- 【历史上的今天】7 月 3 日:人体工程学标准法案;消费电子领域先驱诞生;育碧发布 Uplay
- [exercice 7] [principe de la base de données]
- Flink SQL knows why (12): is it difficult to join streams? (top)
- Tencent cloud tdsql database delivery and operation and maintenance Junior Engineer - some questions of Tencent cloud cloudlite certification (TCA) examination
- Logback 日志框架
猜你喜欢
Method overloading and rewriting
![[review questions of database principles]](/img/c3/81d192a40bcc4f5d72fcbe76c708bb.png)
[review questions of database principles]

How to get user location in wechat applet?
![[combinatorics] permutation and combination (the combination number of multiple sets | the repetition of all elements is greater than the combination number | the derivation of the combination number](/img/9d/6118b699c0d90810638f9b08d4f80a.jpg)
[combinatorics] permutation and combination (the combination number of multiple sets | the repetition of all elements is greater than the combination number | the derivation of the combination number

Sword finger offer14 the easiest way to cut rope

2022-02-09 survey of incluxdb cluster

February 14, 2022, incluxdb survey - mind map
(first) the most complete way to become God of Flink SQL in history (full text 180000 words, 138 cases, 42 pictures)

Huffman coding experiment report
![[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 6 exercises]](/img/c0/92e9e52f1f643b66720697523a1794.png)
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 6 exercises]
随机推荐
Seven habits of highly effective people
Sitescms v3.1.0 release, launch wechat applet
【習題七】【數據庫原理】
Differences and connections between final and static
My creation anniversary: the fifth anniversary
剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
2022-01-27 use liquibase to manage MySQL execution version
Sword finger offer 12 Path in matrix
C graphical tutorial (Fourth Edition)_ Chapter 20 asynchronous programming: examples - using asynchronous
Fabric.js 更换图片的3种方法(包括更换分组内的图片,以及存在缓存的情况)
35道MySQL面试必问题图解,这样也太好理解了吧
关于CPU缓冲行的理解
Fabric. JS three methods of changing pictures (including changing pictures in the group and caching)
正则表达式
(first) the most complete way to become God of Flink SQL in history (full text 180000 words, 138 cases, 42 pictures)
In the promotion season, how to reduce the preparation time of defense materials by 50% and adjust the mentality (personal experience summary)
【历史上的今天】7 月 3 日:人体工程学标准法案;消费电子领域先驱诞生;育碧发布 Uplay
Useful blog links
The foreground uses RSA asymmetric security to encrypt user information
Reptile