当前位置:网站首页>Do you know how data is stored? (C integer and floating point)
Do you know how data is stored? (C integer and floating point)
2022-07-01 08:37:00 【Stir fried rice with lotus root】
Generally, ordinary programmers will not understand these lower level things , Because for the time being, knowing these things will not help a lot , But for me who loves programming , If you love it, you should understand it from the inside out , Moreover, every day we learn a little new knowledge that others don't want to learn, so we can draw a little distance from others , Over time, the boss formed , Come on, young man , This is an era of struggle !

The key points of this blog are as follows :
1. Data type introduction
2. Integer primitive , back , Complement code
3. Introduction and judgment of byte order at large and small ends
4. Storage solution of floating-point type in memory
Catalog
2. Basic classification of types
Two . The storage of integers in memory
1. Understand the original , back , Complement code
2. Introduce unsigned Unsigned sum signed There are symbolic differences
One . Data type introduction
1. Basic built-in type
char // Character data type
short // Short
int // integer
long // Long integer
long long // Longer integer
float // Single precision floating point
double // Double precision floating point
The meaning of type :
1. Type determines the size of the used space , Size determines the range of use
2. Type determines how memory space is viewed ( Integer and floating-point storage methods are different )
2. Basic classification of types
The integer family
char:
unsigned char
signed char
short:
unsigned short
signed short
int:
unsigned int
signed int
long:
unsigend long
signed long
except char Other types are divided into unsigend( Unsigned ) and sigend( A signed ) type , What we usually write int n = 10; there int The default is equivalent to sigend int type , But for char The standard of what type it belongs to is undefined , Depends on the implementation of the compiler ;
Floating point family
float // Single precision floating point
double // Double precision floating point
Construction type
An array type
Type of structure struct
Enumeration type enum
Joint type union
Pointer types
int *pi
char *pc
float *pd
void *pv
Two . The storage of integers in memory
1. Understand the original , back , Complement code
There are three binary expressions for computer integers , The original , back , Complement code ;
There are three ways Sign bit and Value bits , Sign bit 0 Express positive ,1 Negative ; The numeric bits of positive numbers are the same as the original inverse complement ;
The digit of a negative number :
Original code : The original code can be obtained by directly translating the numerical value into binary in the form of positive and negative numbers .
Inverse code : Change the sign bit of the original code , The reverse code can be obtained by inverting other bits in turn .
Complement code : Inverse code +1 You get the complement .
* For integers , The data stored in memory is the complement , What we see is the original code ;
ask : Why bother to create 3 Two binary expressions , Can't you save the original code directly ?
* In computer system , All values are represented and stored by complements . The reason lies in , Use complement , You can combine sign bits and numeric fields One processing ; meanwhile , Addition and subtraction can also be handled in a unified way (CPU Only adders ) Besides , Complement code and original code are converted to each other , Its operation process It's the same , No need for additional hardware circuits .
in other words CPU Only addition can be calculated , So how to calculate the subtraction ? We can convert it :
1-1 ------> 1+(-1)
But here you can find that if we store data in the form of original code for 1+(-1):
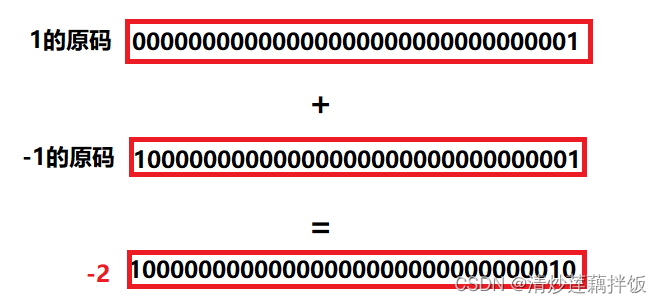
The result is equal to the -2 了 , This is totally unreasonable ; So scientists have invented the form of complement for storage , Just can calculate :

Isn't that amazing , This is the meaning of complement !
2. Introduce unsigned Unsigned sum signed There are symbolic differences
Before we introduce it, let's take a look at a piece of code , What does this code output ?
#include <stdio.h> int main() { char a= -1; signed char b=-1; unsigned char c=-1; printf("a=%d,b=%d,c=%d",a,b,c); return 0; }
Topic ideas :
We have learned about signed and unsigned types , Then we will infer their results according to their characteristics , A signed As the name suggests, its The highest bit of binary is the sign bit , Sign bit No participation Numerical calculation ; Unsigned It's in binary The highest bit is not a sign bit , Yes, it will directly Participate in To numerical calculations ; So do you have a new understanding of the above code ?( The picture below shows a chestnut )
️ Answer key :
a Value : We said earlier char A special , Whether it is signed or unsigned depends on the compiler ;
b Value :b It is clearly indicated in the title that it is signed , So it's a negative number , According to the law of original inverse complement, its original code is -1, therefore b The value of is -1;
c Value :c Is an unsigned type , So here we focus on c Value ;
1. First of all, will -1 The assignment of to unsigned char c, There's an integer boost ;
2. Because the complement is stored in the memory , So we convert
3. because c yes char type , There is not enough space for truncation
4. because c It's an unsigned integer , therefore 11111111 Is its value , Please have a computer :
therefore c The value should be 255 ;
At this point, you should know the difference between signed and unsigned , Although it is only a little knowledge , But when you encounter similar problems in the future, you can solve them at the first time. I think these are worth it , Our efforts will not be in vain
3. Large and small end
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 20;
int b = -10;
return 0;
}a Hexadecimal representation of ( Complement code ):0x 00 00 00 14 ( a pair 00 Size represents a byte )
b Hexadecimal representation of ( Complement code ):0x f f f f f f f 6
With this code, let's look at the memory storage :

The storage mode here is small end storage ;
Introduction to big and small end :
Big end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the high address of memory , And the high end of the data , Low address saved in memory in ;
The small end ( Storage ) Pattern , The low bit of data is stored in the low address of memory , And the high end of the data ,, Stored in memory Address .
Why are there big and small end storage methods :
Why are there big and small end patterns ? This is because in a computer system , We are in bytes , Each address unit Each corresponds to a byte , A byte is 8 bit. But in C In language, except 8 bit Of char outside , also 16 bit Of short type ,32 bit Of long type ( It depends on the compiler ), in addition , For digits greater than 8 Bit processor , for example 16 Bits or 32 Bit processor , Because the register width is larger than one byte , So there must be a problem of how to arrange multiple bytes . because This leads to the big end storage mode and the small end storage mode . for example : One 16bit Of short type x , The address in memory is 0x0010 , x The value of is 0x1122 , that 0x11 by High byte , 0x22 Is low byte . For big end mode , will 0x11 Put it in the low address , namely 0x0010 in , 0x22 Put it high In the address , namely 0x0011 in . The small end model , Just the opposite . That we use a lot X86 The structure is small end mode , and KEIL C51 be For big end mode . A great deal of ARM,DSP It's all small end mode . There are some ARM The processor can also be selected by hardware, which is the big end mode Or small end mode .
️ topic : Write a program to determine the current system size ;
Ideas : Judging the size side means that we want to judge how a number is stored in memory , for example int n = 1 Its first address should be 0 perhaps 1, We just need to take out the first byte and judge ; The code is as follows :
#include <stdio.h> int check_sys() { int i = 1; return (*(char *)&i); } int main() { int ret = check_sys(); if(ret == 1) { printf(" The small end \n"); } else { printf(" Big end \n"); } return 0; }
3、 ... and . Floating point storage in memory
Floating point storage code example :
int main()
{
int n = 9;
float *pFloat = (float *)&n;
printf("n The value of is :%d\n",n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat);
*pFloat = 9.0;
printf("num The value of is :%d\n",n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat);
return 0;
}Output results :
After reading the code and output results, are you confused again ? Don't worry , Let me explain the storage rules of floating point numbers ;
international standard IEEE 754 Regulations , Any binary floating point number V Can be expressed in the following form :
The formula ------ (-1)^S * M * 2^E
(-1)^S The sign bit , When S=0,V Is a positive number ; When S=1,V It's a negative number .
M Represents a significant number , Greater than or equal to 1, Less than 2.
2^E Indicates the index bit .
Take a chestnut :
chestnuts 1: Decimal 5.0 Binary for yes 101.0, In binary, that is 1.01 * 2^2( Power ), According to the above IEEE Standard we can know S = 0,M = 1.01, Index E = 2;
chestnuts 2: Decimal -5.0 Binary for yes -101.0, In binary, that is -1.01 * 2^2( Power ), According to the above IEEE Standard we can know S = 1,M = 1.01, Index E = 2;
For the rules that floating-point numbers are stored in single precision and double precision respectively :


IEEE 754 For significant figures M And the index E, There are some special rules .
As I said before , 1≤M<2 , in other words ,M It can be written. 1.xxxxxx In the form of , among xxxxxx Represents the fractional part . IEEE 754 Regulations , Keep it in the computer M when , By default, the first digit of this number is always 1, So it can be discarded , Save only the back xxxxxx part . For example preservation 1.01 When the Hou , Save only 01, Wait until you read , Put the first 1 Add . The purpose of this , It's saving 1 Significant digits . With 32 position Floating point numbers, for example , Leave to M Only 23 position , Will come first 1 After giving up , It's equivalent to being able to save 24 Significant digits .
As for the index E, The situation is more complicated .
First ,E For an unsigned integer (unsigned int) It means , If E by 8 position , Its value range is 0~255; If E by 11 position , Its value range is 0~2047. however , We know , In scientific counting E Yes, you can Now negative , therefore IEEE 754 Regulations , In memory E The true value of must be added with an intermediate number , about 8 Bit E, This middle number yes 127; about 11 Bit E, In the middle The number is 1023. such as ,2^10 Of E yes 10, So save it as 32 When floating-point numbers are in place , Must be saved as 10+127=137, namely 10001001.
then , Index E Fetching from memory can be further divided into three cases :
1.E Not all for 0 Or not all of them 1
At this time , Floating point numbers are represented by the following rules , The index E The calculated value of minus 127( or 1023), Get the real value , then Significant figures M Add the first 1.
such as : 0.5(1/2) The binary form of is 0.1, Since it is stipulated that the positive part must be 1, That is to move the decimal point to the right 1 position , Then for 1.0*2^(-1), Its order code is -1+127=126, Expressed as 01111110, And the mantissa 1.0 Remove the integer part and make it 0, A filling 0 To 23 position 00000000000000000000000, Then the second goes The system is expressed as :
0 01111110 00000000000000000000000
2.E All for 0
At this time , The exponent of a floating point number E be equal to 1-127( perhaps 1-1023) That's the true value , Significant figures M No more first 1, It's reduced to 0.xxxxxx Decimals of . This is to show that ±0, And close to 0 A very small number of .
3. E All for 1
At this time , If the significant number M All for 0, Express ± infinity ( It depends on the sign bit s);
️ Let's return to the topic :
int main()
{
int n = 9;
float *pFloat = (float *)&n;
printf("n The value of is :%d\n",n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat);
*pFloat = 9.0;
printf("num The value of is :%d\n",n);
printf("*pFloat The value of is :%f\n",*pFloat);
return 0;
}Ideas :
First print :
Print directly as an integer n therefore n The value is 9;
Second print :
take n The value of is accessed and printed as a floating-point number , Then he would think 9 The binary expression of is a floating point number , So according to the formula (-1)^S * M * 2^E obtain :
+ 0.00000000000000000001001 * 2 ^ -126
This is an infinitely close 0 Floating point number , But our space is limited, so print 0.000000
The third print :
take n The contents of are stored as floating-point numbers 9.0, Then print as an integer :
1.001 * 2 ^ 3 S = 0, E = 3, M = 1.001 Get binary :
01000001000100000000000000000000
Print in integer :
Print for the fourth time :
n The contents of are stored in floating-point numbers 9.0, Then print as a floating point number : Save as floating-point number and fetch as floating-point number , The result must be 9.0 了 ;
️ In the process of learning, you should also pay attention to your body , Only a healthy body can support our ideals ; If you like this blog , Support bloggers for the third time
边栏推荐
- P4 installation bmv2 detailed tutorial
- yolov5训练可视化指标的含义
- 为什么LTD独立站就是Web3.0网站!
- 分享2022上半年我读过的7本书
- What is 1cr0.5mo (H) material? 1cr0.5mo (H) tensile yield strength
- 01 numpy introduction
- DID的使用指南,原理
- Intelligent constant pressure irrigation system
- How to use OKR as the leadership framework of marketing department
- 5mo3 UHI HII HII 17mn4 19Mn6 executive standard
猜你喜欢

华为机试真题专栏订阅指引

SPL installation and basic use (II)

Agrometeorological environment monitoring system

机动目标跟踪——当前统计模型(CS模型)扩展卡尔曼滤波/无迹卡尔曼滤波 matlab实现

避免按钮重复点击的小工具bimianchongfu.queren()

2022.2.15

Suivi des cibles de manoeuvre - - mise en oeuvre du modèle statistique actuel (modèle CS) filtre Kalman étendu / filtre Kalman sans trace par MATLAB
![Matlab [functions and images]](/img/8a/d2f68b5a7ed396ad20234c0aa24953.jpg)
Matlab [functions and images]

Centos7 shell脚本一键安装jdk、mongo、kafka、ftp、postgresql、postgis、pgrouting

On several key issues of digital transformation
随机推荐
截图小妙招
栈实现计算器
Leetcode T34: 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
"Analysis of 43 cases of MATLAB neural network": Chapter 30 design of combined classifier based on random forest idea - breast cancer diagnosis
Using settoolkit to forge sites to steal user information
MATLAB【函数和图像】
Principle and application of single chip microcomputer - principle of parallel IO port
Suivi des cibles de manoeuvre - - mise en oeuvre du modèle statistique actuel (modèle CS) filtre Kalman étendu / filtre Kalman sans trace par MATLAB
When using charts to display data, the time field in the database is repeated. How to display the value at this time?
Adding color blocks to Seaborn clustermap matrix
一文纵览主流 NFT 市场平台版税、服务费设计
Hijacking a user's browser with beef
[untitled]
华为机试真题专栏订阅指引
Leetcode T29: 两数相除
Share 7 books I read in the first half of 2022
SPL-安装与基本使用(二)
毕业论文中word的使用1-代码域标公式
Conception et mise en service du processeur - chapitre 4 tâches pratiques
Leetcode T39: 组合总和







