当前位置:网站首页>Task6: using transformer for emotion analysis
Task6: using transformer for emotion analysis
2022-07-03 13:14:00 【Levi Bebe】
# Data preparation
import torch
import random
import numpy as np
SEED = 1234
random.seed(SEED)
np.random.seed(SEED)
torch.manual_seed(SEED)
torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
# Load pre training model
from transformers import BertTokenizer
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
# Define the length
def tokenize_and_cut(sentence):
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(sentence)
tokens = tokens[:max_input_length-2]
return tokens
from torchtext.legacy import data
TEXT = data.Field(batch_first = True,
use_vocab = False,
tokenize = tokenize_and_cut,
preprocessing = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids,
init_token = init_token_idx,
eos_token = eos_token_idx,
pad_token = pad_token_idx,
unk_token = unk_token_idx)
LABEL = data.LabelField(dtype = torch.float)
# Load data
from torchtext.legacy import datasets
train_data, test_data = datasets.IMDB.splits(TEXT, LABEL)
train_data, valid_data = train_data.split(random_state = random.seed(SEED))
# Set up the device
BATCH_SIZE = 128
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
train_iterator, valid_iterator, test_iterator = data.BucketIterator.splits(
(train_data, valid_data, test_data),
batch_size = BATCH_SIZE,
device = device)
# Build the model
from transformers import BertTokenizer, BertModel
bert = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
import torch.nn as nn
class BERTGRUSentiment(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
bert,
hidden_dim,
output_dim,
n_layers,
bidirectional,
dropout):
super().__init__()
self.bert = bert
embedding_dim = bert.config.to_dict()['hidden_size']
self.rnn = nn.GRU(embedding_dim,
hidden_dim,
num_layers = n_layers,
bidirectional = bidirectional,
batch_first = True,
dropout = 0 if n_layers < 2 else dropout)
self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_dim * 2 if bidirectional else hidden_dim, output_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, text):
#text = [batch size, sent len]
with torch.no_grad():
embedded = self.bert(text)[0]
#embedded = [batch size, sent len, emb dim]
_, hidden = self.rnn(embedded)
#hidden = [n layers * n directions, batch size, emb dim]
if self.rnn.bidirectional:
hidden = self.dropout(torch.cat((hidden[-2,:,:], hidden[-1,:,:]), dim = 1))
else:
hidden = self.dropout(hidden[-1,:,:])
#hidden = [batch size, hid dim]
output = self.out(hidden)
#output = [batch size, out dim]
return output
HIDDEN_DIM = 256
OUTPUT_DIM = 1
N_LAYERS = 2
BIDIRECTIONAL = True
DROPOUT = 0.25
model = BERTGRUSentiment(bert,
HIDDEN_DIM,
OUTPUT_DIM,
N_LAYERS,
BIDIRECTIONAL,
DROPOUT)
def count_parameters(model):
return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f'The model has {
count_parameters(model):,} trainable parameters')
for name, param in model.named_parameters():
if name.startswith('bert'):
param.requires_grad = False
def count_parameters(model):
return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
print(f'The model has {
count_parameters(model):,} trainable parameters')
# Training models
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters())
criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
model = model.to(device)
criterion = criterion.to(device)
def binary_accuracy(preds, y):
""" Returns accuracy per batch, i.e. if you get 8/10 right, this returns 0.8, NOT 8 """
#round predictions to the closest integer
rounded_preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds))
correct = (rounded_preds == y).float() #convert into float for division
acc = correct.sum() / len(correct)
return acc
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.train()
for batch in iterator:
optimizer.zero_grad()
predictions = model(batch.text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
acc = binary_accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc.item()
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
def evaluate(model, iterator, criterion):
epoch_loss = 0
epoch_acc = 0
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in iterator:
predictions = model(batch.text).squeeze(1)
loss = criterion(predictions, batch.label)
acc = binary_accuracy(predictions, batch.label)
epoch_loss += loss.item()
epoch_acc += acc.item()
return epoch_loss / len(iterator), epoch_acc / len(iterator)
import time
def epoch_time(start_time, end_time):
elapsed_time = end_time - start_time
elapsed_mins = int(elapsed_time / 60)
elapsed_secs = int(elapsed_time - (elapsed_mins * 60))
return elapsed_mins, elapsed_secs
# Training
N_EPOCHS = 5
best_valid_loss = float('inf')
for epoch in range(N_EPOCHS):
start_time = time.time()
train_loss, train_acc = train(model, train_iterator, optimizer, criterion)
valid_loss, valid_acc = evaluate(model, valid_iterator, criterion)
end_time = time.time()
epoch_mins, epoch_secs = epoch_time(start_time, end_time)
if valid_loss < best_valid_loss:
best_valid_loss = valid_loss
torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'tut6-model.pt')
print(f'Epoch: {
epoch+1:02} | Epoch Time: {
epoch_mins}m {
epoch_secs}s')
print(f'\tTrain Loss: {
train_loss:.3f} | Train Acc: {
train_acc*100:.2f}%')
print(f'\t Val. Loss: {
valid_loss:.3f} | Val. Acc: {
valid_acc*100:.2f}%')
# We will load the parameters that provide us with the best loss value on the validation set , And apply these parameters to the test set - And achieved the best results on the test set
model.load_state_dict(torch.load('tut6-model.pt'))
test_loss, test_acc = evaluate(model, test_iterator, criterion)
print(f'Test Loss: {
test_loss:.3f} | Test Acc: {
test_acc*100:.2f}%')
def predict_sentiment(model, tokenizer, sentence):
model.eval()
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(sentence)
tokens = tokens[:max_input_length-2]
indexed = [init_token_idx] + tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens) + [eos_token_idx]
tensor = torch.LongTensor(indexed).to(device)
tensor = tensor.unsqueeze(0)
prediction = torch.sigmoid(model(tensor))
return prediction.item()
predict_sentiment(model, tokenizer, "This film is terrible")
predict_sentiment(model, tokenizer, "This film is great")
边栏推荐
- Finite State Machine FSM
- Logback 日志框架
- Leetcode234 palindrome linked list
- Sword finger offer 17 Print from 1 to the maximum n digits
- Four problems and isolation level of MySQL concurrency
- [Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter III exercises]
- 关于CPU缓冲行的理解
- [Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 7 exercises]
- 解决 System has not been booted with systemd as init system (PID 1). Can‘t operate.
- Image component in ETS development mode of openharmony application development
猜你喜欢
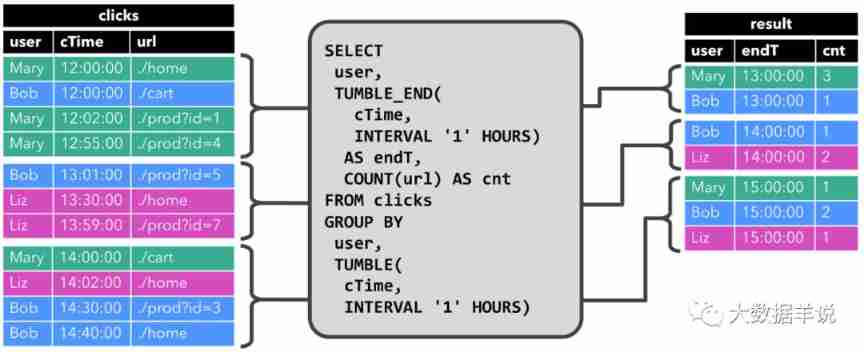
(first) the most complete way to become God of Flink SQL in history (full text 180000 words, 138 cases, 42 pictures)
When the R language output rmarkdown is in other formats (such as PDF), an error is reported, latex failed to compile stocks Tex. solution

Flick SQL knows why (10): everyone uses accumulate window to calculate cumulative indicators

Integer case study of packaging
![[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 6 exercises]](/img/c0/92e9e52f1f643b66720697523a1794.png)
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 6 exercises]

【数据库原理及应用教程(第4版|微课版)陈志泊】【第三章习题】

剑指 Offer 12. 矩阵中的路径
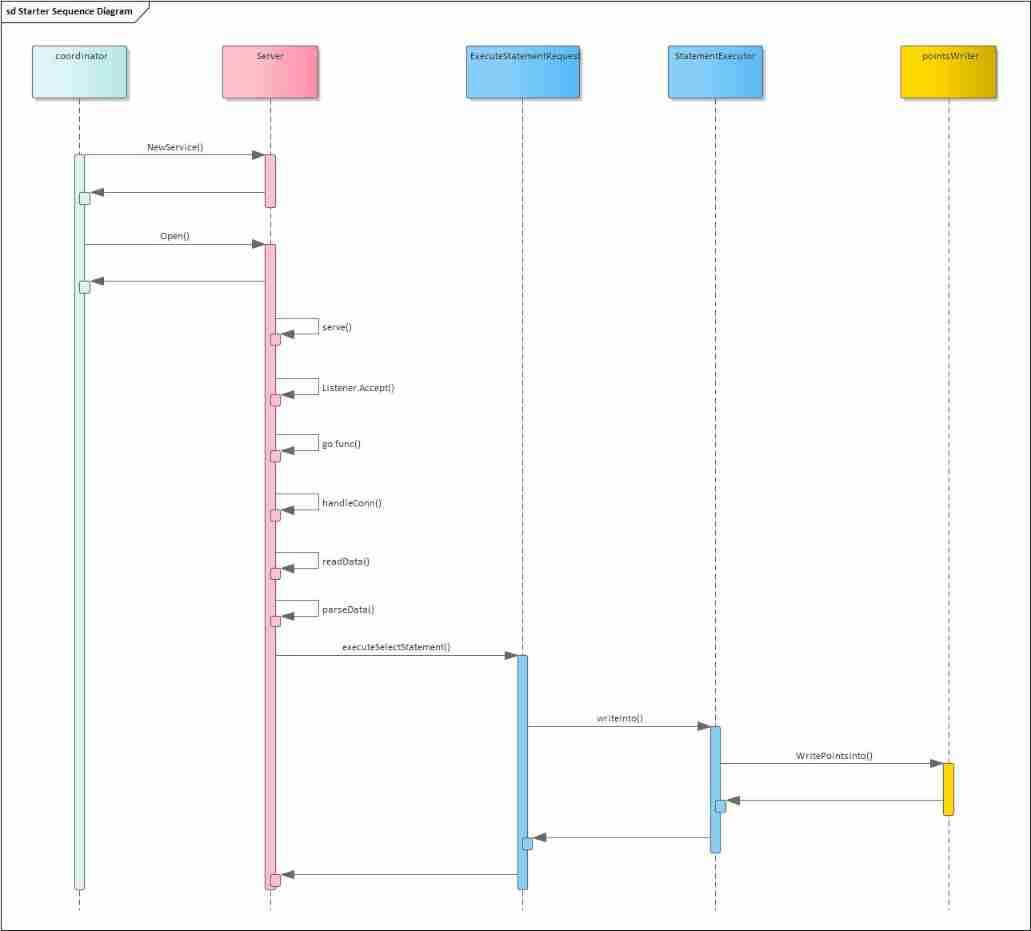
2022-02-14 analysis of the startup and request processing process of the incluxdb cluster Coordinator
![[data mining review questions]](/img/96/00f866135e06c4cc0d765c6e499b29.png)
[data mining review questions]

【数据挖掘复习题】
随机推荐
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter IV exercises]
Some thoughts on business
【习题五】【数据库原理】
C graphical tutorial (Fourth Edition)_ Chapter 13 entrustment: delegatesamplep245
我的创作纪念日:五周年
The difference between session and cookie
Sword finger offer 11 Rotate the minimum number of the array
mysqlbetween实现选取介于两个值之间的数据范围
2022-01-27 redis cluster technology research
Kotlin - improved decorator mode
How to get user location in wechat applet?
解决 System has not been booted with systemd as init system (PID 1). Can‘t operate.
【习题七】【数据库原理】
Cache penetration and bloom filter
阿南的疑惑
对业务的一些思考
剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
Node. Js: use of express + MySQL
[Database Principle and Application Tutorial (4th Edition | wechat Edition) Chen Zhibo] [Chapter 7 exercises]
2022-02-09 survey of incluxdb cluster