当前位置:网站首页>Basic knowledge of lists
Basic knowledge of lists
2022-07-06 20:17:00 【Programming is too difficult】
Catalog
Definition list
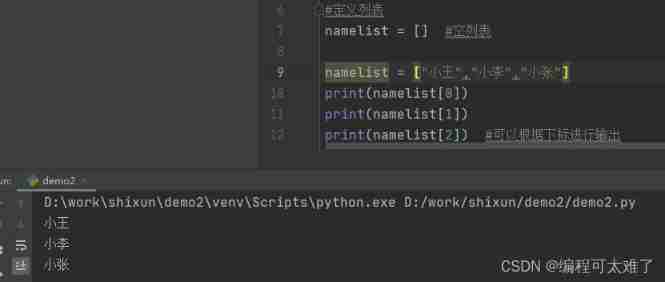
namelist = [ ] Define an empty list .
You can add content to the list , And search and output according to the subscript .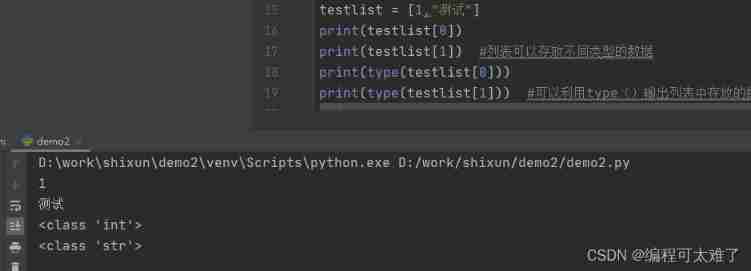
Different types of data can be defined in the same list , For example, you can add both integer and string types
You can use type() Function prints out the type of the element .
Traverse the list
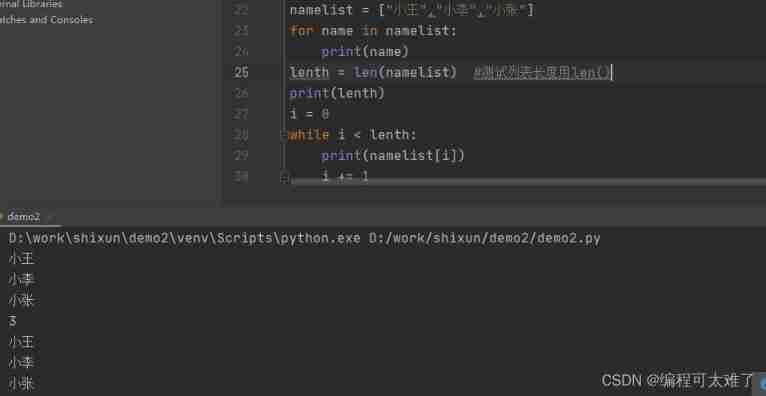
The traversal of the list can be done with for loop , It can also be used. while.
In the use of while when , It can be used len() The length of the test list , Then set a variable count to end the loop by increasing itself .
Pay attention to while Add subscript when .
General operation of list
increase
The first way :append(): Add an element at the end .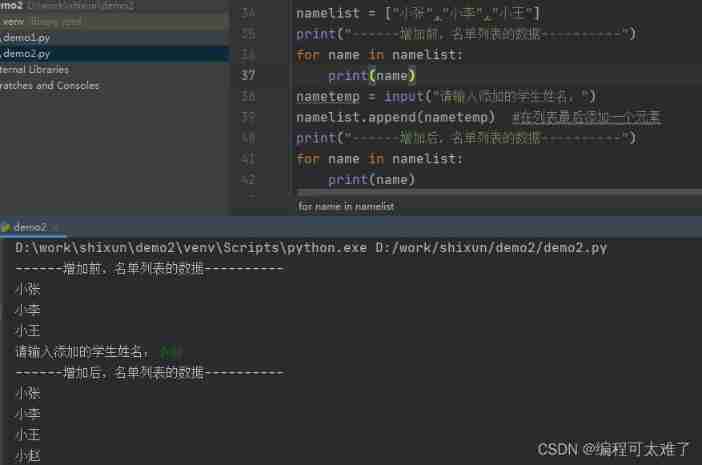
The second way :extend(): You can add the elements in the list to the new list in turn .
In the use of append when , If you want to fill in a list ,append You can only add the whole list to the end as an element , While using extend You can split the list , Add the elements in the list in turn .
Use append Methods :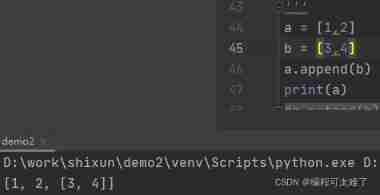
Use extend Methods :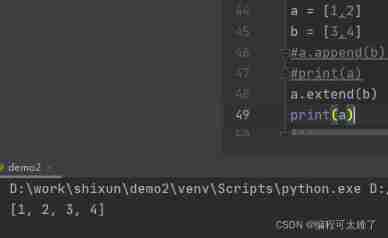
The third method :insert(): Insert the element into the specified position .
insert(1,3) The first variable represents the subscript , The second variable represents the value to be inserted .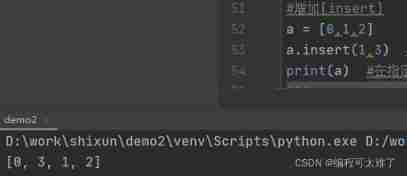
Delete
The first way :del: Used to delete the value of the specified subscript 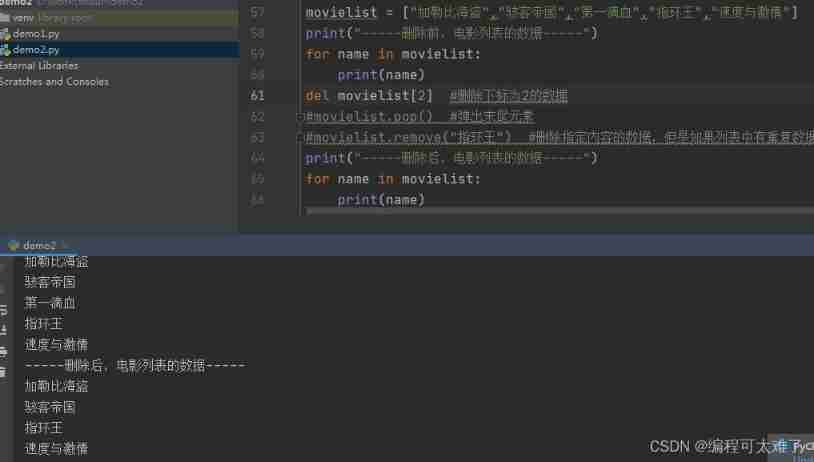
The second way :pop: Pop up the value at the end 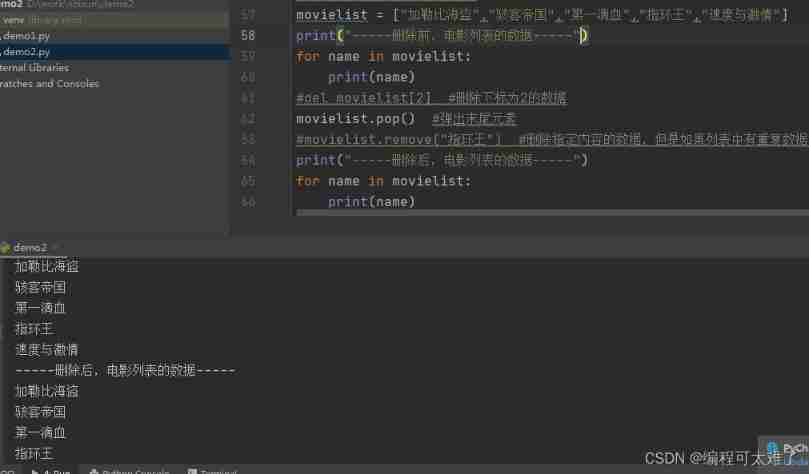
The third way :remove: Delete the data of the specified content .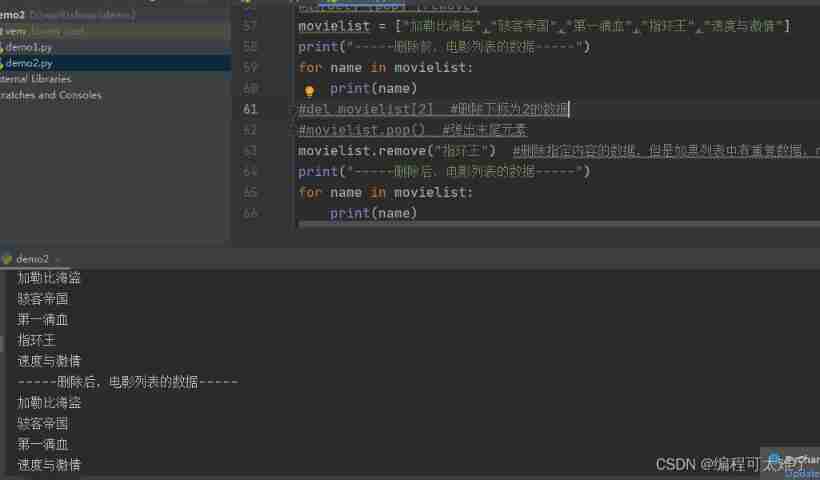
But when there are multiple identical values in the list ,remove You can only traverse to the first value that matches the deleted content and delete it , The duplicate in the back will not be deleted .
modify
Directly modify the value you want to modify .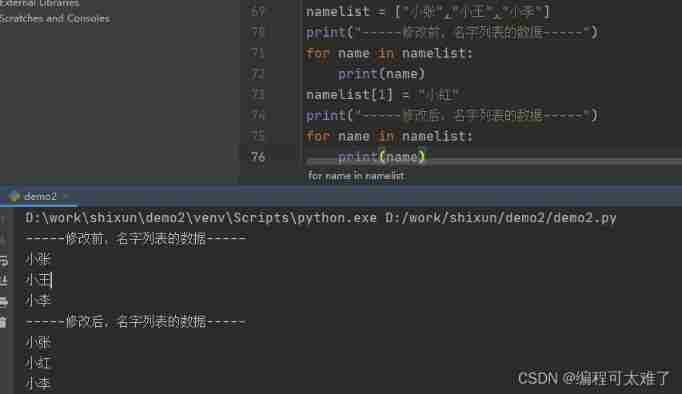
check
in perhaps not in Used to check whether the content to be found is in the list .
use if To determine whether the content to be searched is in the list .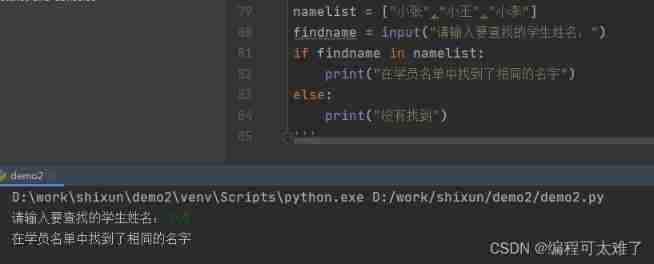
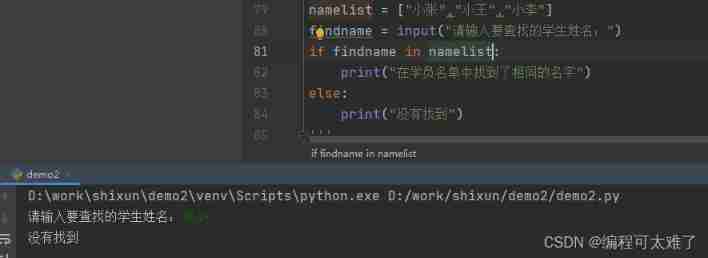
It can be used at the same time index() Find out whether there is a value you need to find in the specified range . When it is found, it will return the subscript of the found value , If it cannot be found, an error will be reported .
Note that the range of variables is left open and right closed , Include the value on the left , Excluding the value on the right .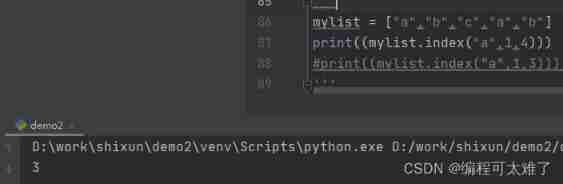
Count the number of values to be found in the list
Use functions count()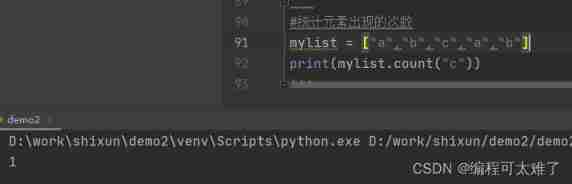
Sort and invert
The inversion of the list is used reverse, Indicates that the elements in the list are flashed out .
For sorting lists sort(), Sort the list in ascending order by default , If you need to sort flashbacks , Need to be in sort() Put reverse=True.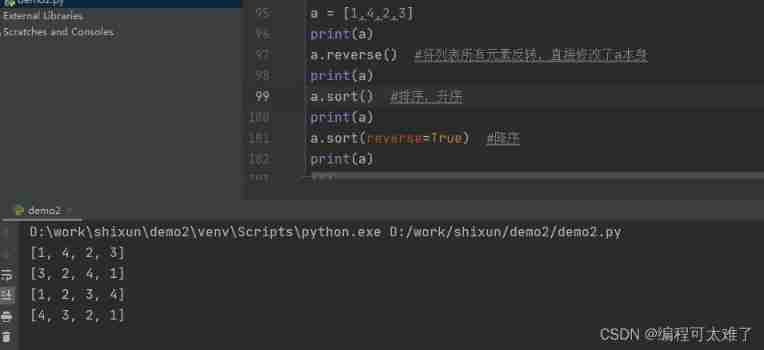
List nesting
You can continue to include the list in the list , And the number of data in each list is not unique .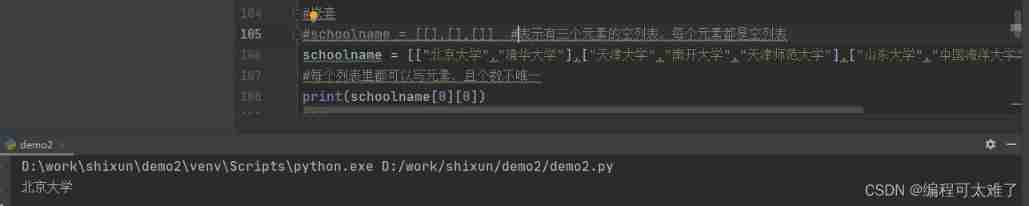
Example : Assign offices to teachers
There are three offices , Eight teachers , Eight teachers were randomly assigned to three offices , Finally, print the number of people in each office and the name of the teacher .
Ideas : You need to generate random numbers 、 Add... To the list .
Name the three offices 0、1、2, Then let the random number from 0、1、2 Randomly generated in . Traverse the teacher list , And combine the read teacher name with the randomly generated number , Insert , It means inserting into an office , Repeat until all teachers are assigned . Then output the distribution of each office through circulation .
import random # Introduce random numbers
offices = [[],[],[]] # Three offices
teachers = ["A","B","C","D","E","F","G","H"] # Eight teachers
for name in teachers:
index = random.randint(0,2) #index From 0 To 2 Randomly generated number , Subscript representing the office
offices[index].append(name) # Assign the traversed teachers to the office
i = 1 # Used to mark which office
for office in offices:
print(" The office %d Yes %d Famous teachers "%(i,len(office)))
for teacher in office:
print(teacher,end="\t")
print("\n")
print("-"*20)
i += 1
``
practice : Print product information
products = [[“iphone”,6888],[“MacPro”,14800],[“ millet 6”,2499],[“Coffee”,31],[“Book”,60],[“Nike”,699]], You need to print out the following format :
----- List of goods -----
0 iphone 6888
1 MacPro 14800
2 millet 6 2499
3 Coffee 31
4 Book 60
5 Nike 699
Record the products added by the user , If input q The exit , Print the information added by the user .
Ideas : The serial number in front of the commodity corresponds to the subscript of the commodity stored in the list , Double loop access list , You can output the product name and price separately . Don't wrap lines when printing , Put a placeholder directly , Change lines when you read the next item .
When recording user additions , use while The cycle keeps recording , Until user input q Jump out of the loop as the end . When storing items entered by users , Create a new list to store product names , In storage , Only read the product name for storage , The amount of goods is calculated separately . And then when outputting , Read the stored product name and output the total amount .
products = [["iphone",6888],["MacPro",14800],[" millet 6",2499],["Coffee",31],["Book",60],["Nike",699]]
print("----- List of goods -----")
i = 0
for product in products:
print(i,end="\t")
for information in product:
print(information,end="\t")
print("\n")
i += 1
buylist = []
sum = 0
while 1:
buy = input(" Please enter the item number to be purchased ( With q ending ):")
if buy == "q":
break
if buy != "q":
buy = int(buy)
buylist.append(products[buy][0]) # Only add the product name
sum += products[buy][1] # Only calculate the total amount
print(" The product you want to buy is :")
for list in buylist:
print(list)
print(" The total amount is %d"%sum)
边栏推荐
- PHP与EXCEL PHPExcel
- 【计网】第三章 数据链路层(4)局域网、以太网、无线局域网、VLAN
- 【云原生与5G】微服务加持5G核心网
- [network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (4) LAN, Ethernet, WLAN, VLAN
- B-杰哥的树(状压树形dp)
- Special topic of rotor position estimation of permanent magnet synchronous motor -- Summary of position estimation of fundamental wave model
- 枚举根据参数获取值
- Tips for web development: skillfully use ThreadLocal to avoid layer by layer value transmission
- 腾讯架构师首发,2022Android面试笔试总结
- Technology sharing | packet capturing analysis TCP protocol
猜你喜欢

【Yann LeCun点赞B站UP主使用Minecraft制作的红石神经网络】

【GET-4】
01 基础入门-概念名词
Learn to punch in Web
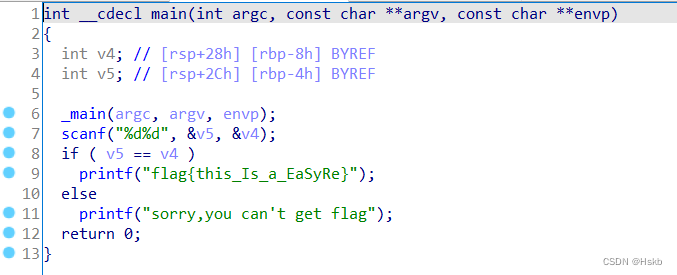
BUUCTF---Reverse---easyre
![[cloud native and 5g] micro services support 5g core network](/img/c9/4ccacd1e70285c2ceb50c324e5018c.png)
[cloud native and 5g] micro services support 5g core network
Transformer model (pytorch code explanation)

Digital triangle model acwing 1018 Minimum toll
New generation garbage collector ZGC
PowerPivot - DAX (first time)
随机推荐
PHP and excel phpexcel
Jupyter launch didn't respond after Anaconda was installed & the web page was opened and ran without execution
爬虫(14) - Scrapy-Redis分布式爬虫(1) | 详解
PowerPivot——DAX(初识)
Speech recognition (ASR) paper selection: talcs: an open source Mandarin English code switching corps and a speech
Digital triangle model acwing 1018 Minimum toll
Period compression filter
数字三角形模型 AcWing 1018. 最低通行费
Crawler (14) - scrape redis distributed crawler (1) | detailed explanation
PowerPivot - DAX (first time)
【GET-4】
Monthly report of speech synthesis (TTS) and speech recognition (ASR) papers in June 2022
系统与应用监控的思路和方法
范式的数据库具体解释
[cloud native and 5g] micro services support 5g core network
Tencent byte and other big companies interview real questions summary, Netease architects in-depth explanation of Android Development
Extraction rules and test objectives of performance test points
新一代垃圾回收器—ZGC
logstash高速入口
[network planning] Chapter 3 data link layer (3) channel division medium access control