当前位置:网站首页>Matlab tips (23) matrix analysis -- simulated annealing
Matlab tips (23) matrix analysis -- simulated annealing
2022-07-01 08:35:00 【mozun2020】
MATLAB Tips (23) matrix analysis -- Simulated annealing
Preface
MATLAB Learning about image processing is very friendly , You can start from scratch , There are many encapsulated functions that can be called directly for basic image processing , This series of articles is mainly to introduce some of you in MATLAB Some concept functions are commonly used in routine demonstration !
Simulated annealing algorithm (Simulate Anneal Arithmetic,SAA) It's a general probability algorithm , It is used to find the optimal solution of a proposition in a large search space . Simulated annealing is S.Kirkpatrick, C.D.Gelatt and M.P.Vecchi stay 1983 Invented in . and V.Černý stay 1985 The algorithm was also independently invented in . Simulated annealing algorithm is to solve TSP One of the effective ways to solve the problem .
One . Simulated annealing basis
Simulated annealing comes from the term annealing in metallurgy . Annealing is the process of heating a material and then cooling it at a specific rate , The purpose is to increase the volume of grains , And reduce defects in the lattice . The atoms in the material will stay at the position where the internal energy has a local minimum , Heating increases energy , The atom will leave its original position , And random moves in other places . Annealing cooling is slower , It makes it possible for atoms to find positions with lower internal energy than before .
The principle of simulated annealing is similar to that of metal annealing : Apply the theory of thermodynamics to statistics , Think of searching every point in space as a molecule in the air ; Molecular energy , It's the kinetic energy of itself ; And search every point in space , It's also like air molecules with “ energy ”, To show the suitability of the point to the proposition . The algorithm starts by searching for an arbitrary point in space : Choose one at each step “ neighbor ”, And then calculate how to get from the existing position to “ neighbor ” Probability .
Simulated annealing algorithm can be decomposed into solution space 、 Objective function and initial solution .
The basic idea of simulated annealing :
(1) initialization : initial temperature T( Big enough ), The initial solution state S( It's the starting point of algorithm iteration ), Every T The number of iterations of the value L;
(2) Yes k=1,……,L Do the first (3) To 6 Step ;
(3) New solutions S′;
(4) Calculate increment Δt′=C(S′)-C(S), among C(S) Is the evaluation function ;
(5) if Δt′<0 received S′ As a new current solution , Otherwise, with probability exp(-Δt′/T) To take over S′ As a new current solution ;
(6) If the termination condition is satisfied, the current solution is output as the optimal solution , End procedure . The termination condition is usually taken as terminating the algorithm when several new solutions are not accepted ;
(7) T Gradually reduce , And T->0, And then turn to 2 Step ;
The generation and acceptance of the new solution of simulated annealing algorithm can be divided into the following four steps :
First step : A generating function generates a new solution in the solution space from the current solution ; For the convenience of subsequent calculation and acceptance , Reduce algorithm time , In general, the method of generating a new solution by simply transforming the current solution is chosen , For example, replace all or part of the elements constituting the previous solution 、 Swap, etc , Note that the transformation method of generating the new solution determines the neighborhood structure of the current new solution , Therefore, it has a certain influence on the selection of cooling schedule .
The second step : Calculate the difference between the objective function corresponding to the new solution . Because the objective function difference is only generated by the transformation part , So it's better to calculate the difference of objective function by increment . It turns out that , For most applications , This is the fastest way to calculate the difference of the objective function .
The third step : Judge whether the new solution is accepted , The basis of judgment is an acceptance criterion , The most common acceptance criteria are Metropolis Rules : if Δt′<0 received S′ As a new current solution S, Otherwise, with probability exp(-Δt′/T) Accept S′ As a new current solution S.
Step four : When the new solution is determined to be accepted , Replace the current solution with a new one , This only needs to realize the transformation part of the current solution corresponding to the new solution , At the same time, the objective function value can be modified . here , The current solution implements an iteration . On this basis, we can start the next round of tests . And when the new solution is judged to be abandoned , On the basis of the original current solution, the next round of test is continued .
The example encountered when searching for data , Here to share ,MATLAB Version is MATLAB2015b.
Two . MATLAB Fake one
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% function : matrix analysis -- Simulated annealing
% Environmental Science :Win7,Matlab2015b
%Modi: C.S
% Time :2022-06-27
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% I. Clear environment variables
clear all
clc
tic
%% II. Unary function optimization
x = 1:0.01:2;
y = sin(10*pi*x) ./ x;
figure
plot(x,y,'linewidth',1.5)
ylim([-1.5, 1.5])
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
title('y = sin(10*pi*x) / x')
hold on
%%
% 1. Mark the maximum point
[maxVal,maxIndex] = max(y);
plot(x(maxIndex), maxVal, 'r*','linewidth',2)
text(x(maxIndex), maxVal, {
[' X: ' num2str(x(maxIndex))];[' Y: ' num2str(maxVal)]})
hold on
%%
% 2. Mark the minimum point
[minVal,minIndex] = min(y);
plot(x(minIndex), minVal, 'ks','linewidth',2)
text(x(minIndex), minVal, {
[' X: ' num2str(x(minIndex))];[' Y: ' num2str(minVal)]})
%% III. Bivariate function optimization
[x,y] = meshgrid(-5:0.1:5,-5:0.1:5);
z = x.^2 + y.^2 - 10*cos(2*pi*x) - 10*cos(2*pi*y) + 20;
figure
mesh(x,y,z)
hold on
xlabel('x')
ylabel('y')
zlabel('z')
title('z = x^2 + y^2 - 10*cos(2*pi*x) - 10*cos(2*pi*y) + 20')
%%
% 1. Mark the maximum point
maxVal = max(z(:));
[maxIndexX,maxIndexY] = find(z == maxVal);
for i = 1:length(maxIndexX)
plot3(x(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)),y(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)), maxVal, 'r*','linewidth',2)
text(x(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)),y(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)), maxVal, {
[' X: ' num2str(x(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)))];[' Y: ' num2str(y(maxIndexX(i),maxIndexY(i)))];[' Z: ' num2str(maxVal)]})
hold on
end
toc
Click on “ function ”, The results are as follows :

3、 ... and . MATLAB Simulation II
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% function : matrix analysis -- Simulated annealing
% Environmental Science :Win7,Matlab2015b
%Modi: C.S
% Time :2022-06-27
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% I. Clear environment variables
clear all
clc
tic
%% II. Import city location data
X = [16.4700 96.1000
16.4700 94.4400
20.0900 92.5400
22.3900 93.3700
25.2300 97.2400
22.0000 96.0500
20.4700 97.0200
17.2000 96.2900
16.3000 97.3800
14.0500 98.1200
16.5300 97.3800
21.5200 95.5900
19.4100 97.1300
20.0900 92.5500];
%% III. Calculate distance matrix
D = Distance(X); % Calculate distance matrix
N = size(D,1); % Number of cities
%% IV. Initialize parameters
T0 = 1e10; % initial temperature
Tend = 1e-30; % Termination temperature
L = 2; % Number of iterations at each temperature
q = 0.9; % Cooling rate
Time = ceil(double(solve([num2str(T0) '*(0.9)^x = ',num2str(Tend)]))); % Calculate the number of iterations
% Time = 132;
count = 0; % Iteration count
Obj = zeros(Time,1); % Initialization of target value matrix
track = zeros(Time,N); % The optimal route matrix of each generation is initialized
%% V. Randomly generate an initial route
S1 = randperm(N);
DrawPath(S1,X)
disp(' A random value in the initial population :')
OutputPath(S1);
Rlength = PathLength(D,S1);
disp([' Total distance :',num2str(Rlength)]);
%% VI. Iterative optimization
while T0 > Tend
count = count + 1; % Update iterations
temp = zeros(L,N+1);
%%
% 1. New solutions
S2 = NewAnswer(S1);
%%
% 2. Metropolis The law determines whether to accept the new solution
[S1,R] = Metropolis(S1,S2,D,T0); %Metropolis Sampling algorithm
%%
% 3. Record the best route for each iteration
if count == 1 || R < Obj(count-1)
Obj(count) = R; % If the optimal distance at the current temperature is less than the previous distance, record the current distance
else
Obj(count) = Obj(count-1);% If the optimal distance at the current temperature is greater than the previous distance, record the previous distance
end
track(count,:) = S1;
T0 = q * T0; % cool
end
%% VII. Iteration diagram of optimization process
figure
plot(1:count,Obj)
xlabel(' The number of iterations ')
ylabel(' distance ')
title(' The optimization process ')
%% VIII. Draw the optimal path map
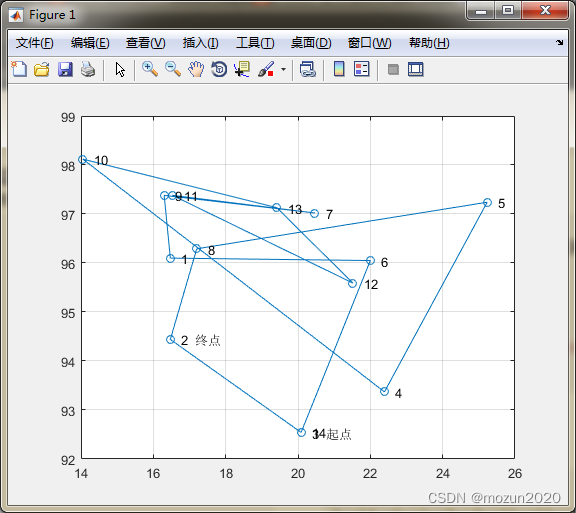
DrawPath(track(end,:),X)
%% IX. The route and total distance of the output optimal solution
disp(' Optimal solution :')
S = track(end,:);
p = OutputPath(S);
disp([' Total distance :',num2str(PathLength(D,S))]);
toc
Click on “ function ”, The results are as follows :
A random value in the initial population :
3—>14—>6—>1—>9—>7—>11—>12—>13—>10—>4—>5—>8—>2—>3
Total distance :60.8861
Optimal solution :
11—>9—>10—>2—>14—>3—>4—>5—>6—>12—>7—>13—>8—>1—>11
Total distance :29.6889
Time has passed 1.465166 second .


Four . Summary
Simulated annealing algorithm is widely used , It can solve the maximum cut problem with high efficiency (Max Cut Problem)、0-1 knapsack problem (Zero One Knapsack Problem)、 Graph coloring problem (Graph Colouring Problem)、 Scheduling problem (Scheduling Problem) wait . This example , It may be used later , Take a note . Learn one every day MATLAB Little knowledge , Let's learn and make progress together !
边栏推荐
- [JS reverse] MD5 encryption parameter cracking
- Stack implementation calculator
- win7 pyinstaller打包exe 后报错 DLL load failed while importing _socket:参数错误
- Leetcode T34: 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置
- Data analysis notes 11
- Leetcode t40: combined sum II
- 避免按钮重复点击的小工具bimianchongfu.queren()
- Download jackson codehaus. org jar - downloading jackson. codehaus. org jar
- Leetcode t34: find the first and last positions of elements in a sorted array
- MATLAB小技巧(23)矩阵分析--模拟退火
猜你喜欢

明明设计的是高带宽,差点加工成开路?

What is the material of 15CrMoR, mechanical properties and chemical analysis of 15CrMoR

机动目标跟踪——当前统计模型(CS模型)扩展卡尔曼滤波/无迹卡尔曼滤波 matlab实现

Intelligent water supply system solution

公网集群对讲+GPS可视追踪|助力物流行业智能化管理调度

使用 setoolkit 伪造站点窃取用户信息
![Matlab [function derivation]](/img/ba/9fb9da8a458d0c74b29b21a17328fc.png)
Matlab [function derivation]

Manually dig XSS vulnerabilities

SPL-安装与基本使用(二)

《单片机原理与应用》——并行IO口原理
随机推荐
Glitch Free时钟切换技术
2022 Chinese cook (technician) simulation test and Chinese cook (technician) practice test video
机动目标跟踪——当前统计模型(CS模型)扩展卡尔曼滤波/无迹卡尔曼滤波 matlab实现
The use of word in graduation thesis
AES简单介绍
MATLAB小技巧(23)矩阵分析--模拟退火
What is the material of 16MnDR, the minimum service temperature of 16MnDR, and the chemical composition of 16MnDR
截图小妙招
How to recruit Taobao anchor suitable for your own store
[deep analysis of C language] - data storage in memory
How to use OKR as the leadership framework of marketing department
3、Modbus通讯协议详解
Audio audiorecord create (I)
[untitled]
How to prevent the other party from saying that he has no money after winning the lawsuit?
XX攻击——反射型 XSS 攻击劫持用户浏览器
CPU設計實戰-第四章實踐任務一簡單CPU參考設計調試
Rumtime 1200 upgrade: London upgrade support, pledge function update and more
Using settoolkit to forge sites to steal user information
Mavros sends a custom topic message to Px4