当前位置:网站首页>C language (high level) program environment and preprocessing
C language (high level) program environment and preprocessing
2022-07-25 23:48:00 【ℳ white ℳ night ℳ】
Program environment and preprocessing
Program translation environment and execution environment
stay ANSI C In any implementation of , There are two different environments .
The first 1 One is the translation environment , In this environment, source code is converted into executable machine instructions .
The first 2 One is the execution environment , It's used to actually execute code .
Translation environment :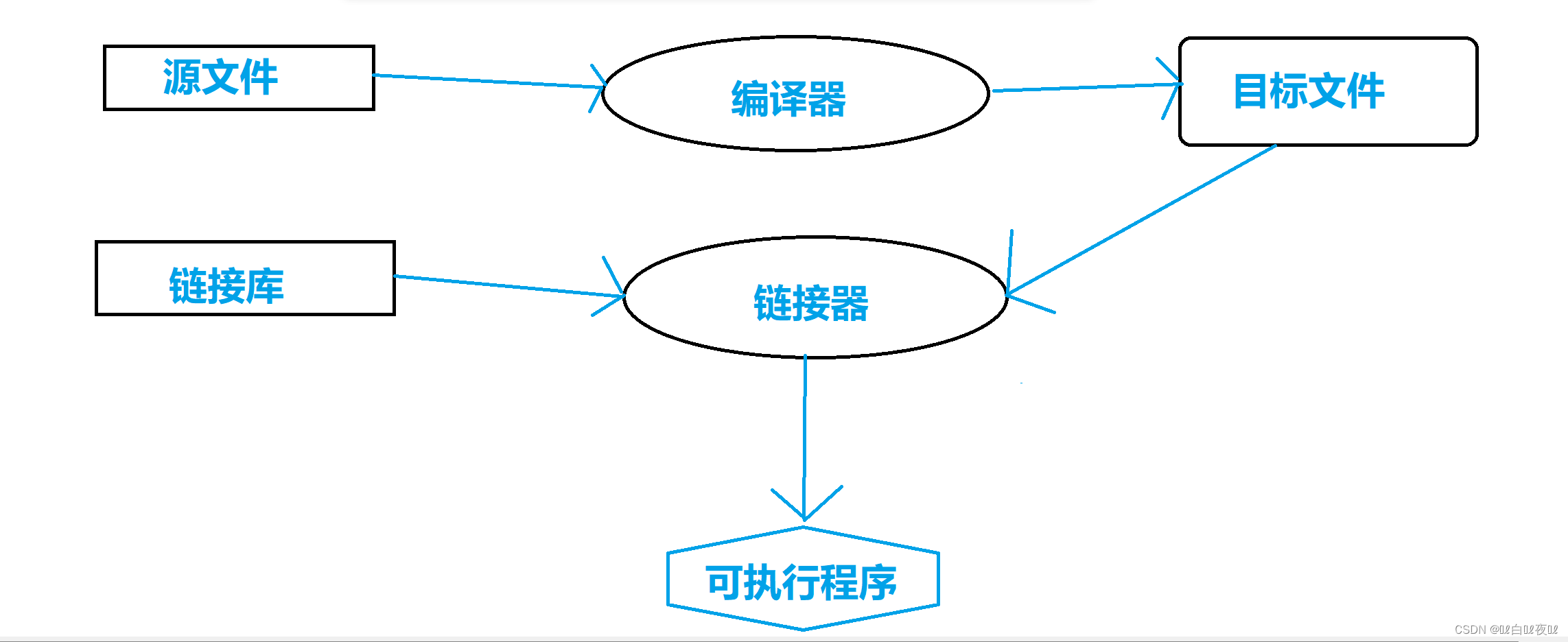
Each source file constituting a program is converted into object code through the compilation process (object code).
Each target file is linked by a linker (linker) Tied together , Form a single and complete executable program .
Linkers also introduce standards C Any function in the function library used by the program , And it can search the programmer's personal library , Link the functions it needs to the program .
Translation stage 
The order is from left to right , use gcc The compiler can observe :
- Preprocessing Options gcc -E test.c -o test.i
Stop after the pretreatment is complete , All the results after pretreatment are put in test.i In file . - compile Options gcc -S test.c
Stop when the compilation is complete , The results are stored in test.s in . - assembly gcc -c test.c
Stop when the assembly is finished , The results are stored in test.o in .
Running environment
The process of program execution :
- The program must be loaded into memory . In an operating system environment : This is usually done by the operating system . In an independent environment , The loading of the program must be arranged manually , It can also be done by putting executable code into read-only memory .
- The execution of the procedure begins . And then I call main function .
- Start executing program code . At this point, the program will use a runtime stack (stack), Store function local variables and return address . Programs can also use static (static) Memory , Variables stored in static memory retain their values throughout the execution of the program .
- To terminate the program . Normal termination main function ; It could be an accidental termination .
Preprocessing
Predefined symbols
__FILE__ // Source files to compile
__LINE__ // The current line number of the file
__DATE__ // The date the file was compiled
__TIME__ // When the file was compiled
__STDC__ // If the compiler follows ANSI C, Its value is 1, Otherwise, it is not defined
These predefined symbols are built into the language .
#define Defining macro
#define The mechanism includes a provision , Allow parameters to be replaced with text , This implementation is often referred to as (macro) Or define macro (define macro).
Here's how the macro is declared :
#define name( parament-list ) stuff
Among them parament-list It's a list of symbols separated by commas , They may appear in stuff in .
Be careful :
The left parenthesis of the argument list must be the same as name Next door neighbor .
If there is any gap between the two , The parameter list will be interpreted as stuff Part of .
The defined macro runs in the preprocessing , It means that some data has been replaced before the compilation stage .
example :
#include <stdio.h>
#define QWE(x) x + x
int main()
{
int x = 10;
printf("%d", 10 * QWE(x));
return 0;
}
The result is 110, Because this is what happens after text replacement :
printf(“%d”, 10 * 10+10));
Tips :
So the macro definitions used to evaluate numeric expressions should be bracketed in this way , Avoid unexpected interactions between operators in parameters or adjacent operators when using macros .
Replacement rules
Extend... In a program #define When defining symbols and macros , There are several steps involved .
- When calling a macro , First, check the parameters , See if it contains any information from #define Defined symbols . If it is , They are replaced first .
- The replacement text is then inserted into the program at the location of the original text . For macros , Parameter names are replaced by their values .
- Last , Scan the result file again , See if it contains any information from #define Defined symbols . If it is , Repeat the above process .
Be careful :
4. Macro parameters and #define Other... Can appear in the definition #define Defined symbols . But for macros , No recursion .
5. When the preprocessor searches #define When defining symbols , The contents of string constants are not searched .
## The role of
Here we will talk about the relationship between escape characters and macro definitions :
You can find it here , If it doesn't work after changing lines , This is because there is a carriage return after our macro definition , If we use \ Transfer carriage return to define multiple lines :
#
Use # , Change a macro parameter into the corresponding string .
for example :
#include <stdio.h>
int i = 1;
#define PRINT(FORMAT, VALUE) printf("the value of " #VALUE "is "FORMAT "\n",VALUE);
int main()
{
PRINT("%d", i + 3);
return 0;
}
In code #VALUE Will preprocess to :“VALUE” .
##
You can combine the symbols on both sides of it into one symbol .
It allows macro definitions to create identifiers from detached pieces of text .
#define ADD(num, value) \ sum##num += value;
ADD(5, 10);// Role is : to sum5 increase 10.
notes : Such a connection must produce a legal identifier . Otherwise the result is undefined .
Macro and function comparison
| attribute | #define Defining macro | function |
|---|---|---|
| Code length | Every time I use it , Macro code is inserted into the program . Except for very small macros , The length of the program will increase significantly | Function code only appears in one place ; Every time you use this function , Call the same code in that place |
| Execution speed | faster | There is an extra cost of calling and returning functions , So it's relatively slow |
| Operator priority | Macro parameters are evaluated in the context of all surrounding expressions , Unless you put parentheses , Otherwise, the priority of adjacent operators may have unpredictable consequences , Therefore, it is recommended that macros be written with more parentheses | Function parameters are evaluated only once when the function is called , Its result value is passed to the function . The evaluation of expressions is easier to predict |
| Functions with side effects | Parameters may be replaced at multiple locations in the macro body , Therefore, parameter evaluation with side effects may produce unpredictable results | Function parameters are evaluated only once when passing parameters , The result is easier to control |
| Parameter type | Macro parameters are type independent , As long as the operation on parameters is legal , It can be used for any parameter type | The arguments to the function are type dependent , If the type of parameter is different , You need different functions , Even if they perform different tasks |
| debugging | Macros are inconvenient to debug | Functions can be debugged statement by statement |
| recursive | Macros cannot be recursive | Functions can be recursive |
Naming conventions
Generally speaking, the syntax of function macro is very similar . So language itself can't help us distinguish the two .
Well, one of our usual habits is :
Capitalize all macro names
Do not capitalize all function names
**#undef **
This instruction is used to remove a macro definition .
Command line definition
many C Our compiler provides a capability , Allows symbols to be defined on the command line . Used to start the compilation process .
for example : When we compile different versions of a program according to the same source file , This feature is useful .( Suppose an array of a certain length is declared in a program , If the machine memory is limited , We need a very small array , But the other machine's memory is uppercase , We need an array that can be capitalized .)
Conditional compilation
When compiling a program, if we want to translate a statement ( A set of statements ) It's convenient to compile or discard . Because we have conditional compilation instructions .
for instance :
Debugging code , It's a pity , Reservation is in the way , So we can selectively compile .
Common conditional compilation instructions :
//1.
#if Constant expression
//...
#endif
// Constant expressions are evaluated by the preprocessor .
//2. Conditional compilation of multiple branches
#if Constant expression
//...
#elif Constant expression
//...
#else
//...
#endif
//3. Judge whether it is defined
#if defined(symbol)
#ifdef symbol
#if !defined(symbol)
#ifndef symbol
//4. Nested instruction
#if defined(OS_UNIX)
#ifdef OPTION1
unix_version_option1();
#endif
#ifdef OPTION2
unix_version_option2();
#endif
#elif defined(OS_MSDOS)
#ifdef OPTION2
msdos_version_option2();
#endif
#endif
These are the same as before if Statement type , If the condition is true , The following preprocessing instruction will trigger , The rest will not trigger .
Such as :
File contains
We already know , #include Instruction can cause another file to be compiled . It's like it actually appears in #include It's the same place as the command .
It's a simple alternative :
The preprocessor first removes this instruction , And replace... With the contents of the containing file .
Such a source file is contained 10 Time , So it's actually compiled 10 Time .
This takes up a lot of memory , So don't repeat including header files .
Nested files contain 
comm.h and comm.c It's a common module .
test1.h and test1.c Using common modules .
test2.h and test2.c Using common modules .
test.h and test.c Used test1 Module and test2 modular .
So there will be two copies in the final program comm.h The content of . In this way, the content of the file is duplicated .
This problem can be solved by conditional compilation , Or put all the header files together and reference them , Just like the address book written before , Mine clearance , Like three piece chess .
边栏推荐
- Inheritance (the child constructor inherits the attributes in the parent constructor)
- Which securities company should a novice choose to open an account? Is it safe?
- 红娘的话
- How does JS judge whether the current date is within a certain range
- Storage of data in memory
- ABAP 代码中读取会计科目的字段状态(隐藏、可选、必输)
- Three board axe! Help you become an excellent software engineer
- A long detailed explanation of C language operators
- Redis basic data type (string/list/set/hash/zset)
- Good news under the epidemic
猜你喜欢

反射之类加载过程

Bubble sort idea and Implementation

What is the difference between'1 and'b1 when assigning values
LeetCode 0919. 完全二叉树插入器:完全二叉树的数组表示
![[Muduo] EventLoop event cycle](/img/80/824c7061d58796d454be0c438e257c.png)
[Muduo] EventLoop event cycle

Read the field status of account in ABAP code (hidden, optional, required)
VSCode格式化Json文件

Ratio of learning_ add,ratio_ subtract,ratio_ multiply,ratio_ Use of divide

抽丝剥茧C语言(高阶)程序环境和预处理

Get the data of Mafeng Hotel
随机推荐
结对编程实践心得
S4/HANA ME21N创建PO 输出控制消息按钮丢失解决方法(切换EDI 输出模式BRF+至NAST模式)
死信队列 和消息TTL过期代码
Promise asynchronous callback function
[intelligence question] interview intelligence question
Docker 安装 Redis-5.0.12(远程访问)
程序环境和预处理
Programmer interview Golden Classic 4.12 summation path
Why are there many snapshot tables in the BI system?
A long detailed explanation of C language operators
1913. 两个数对之间的最大乘积差-无需排序法
Graph traversal DFS, BFS (code explanation)
Part 66: monocular 3D reconstruction point cloud
意向不到的Dubug妙招
SAP Message No. VG202 IDoc E1EDK18 中付款条款已经转移:检查数据
TS union type
Anti shake and throttling
R language installation tutorial | graphic introduction is super detailed
Get the data of Mafeng Hotel
152. 乘积最大子数组-动态规划