当前位置:网站首页>[set theory] relationship properties (common relationship properties | relationship properties examples | relationship operation properties)
[set theory] relationship properties (common relationship properties | relationship properties examples | relationship operation properties)
2022-07-03 04:57:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 The nature of common relationships
- Two 、 Examples of the nature of relationships
- 3、 ... and 、 Relation operation properties
One 、 The nature of common relationships
stay Set of natural numbers
N
=
{
0
,
1
,
2
,
⋯
}
N=\{ 0, 1,2, \cdots \}
N={ 0,1,2,⋯} On , The nature of the following relationship :
1. Less than or equal to :
Less than or equal to :
Symbolic description :
≤
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
≤
y
}
\leq = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x \leq y \}
≤={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x≤y}
The nature of the relationship : introspect , antisymmetric , Pass on
2. Relationship greater than or equal to :
Relationship greater than or equal to :
Symbolic description :
≥
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
≥
y
}
\geq = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x \geq y \}
≥={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x≥y}
The nature of the relationship : introspect , antisymmetric , Pass on
3. Less than relationship :
Less than relationship :
Symbolic description :
<
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
<
y
}
< = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x < y \}
<={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x<y}
The nature of the relationship : Reflexion , antisymmetric , Pass on
4. Greater than the relationship :
Greater than the relationship :
Symbolic description :
>
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
>
y
}
> = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x > y \}
>={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x>y}
The nature of the relationship : Reflexion , antisymmetric , Pass on
5. Division relations :
Division relations :
Symbolic description :
∣
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
∣
y
}
| = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x | y \}
∣={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x∣y}
The nature of the relationship : antisymmetric , Pass on
x
∣
y
x|y
x∣y Medium
∣
|
∣ The symbol means division ,
x
x
x to be divisible by
y
y
y ;
x
x
x to be divisible by
y
y
y ,
x
x
x It's a divisor ( molecular ) ,
y
y
y It's a dividend ( The denominator ) ;
y
x
\dfrac{y}{x}
xy
y
y
y Can be
x
x
x to be divisible by ,
x
x
x It's a divisor ( molecular ) ,
y
y
y It's a dividend ( The denominator ) ;
y
x
\dfrac{y}{x}
xy
In the divisible relationship , Be sure to pay attention to , Only non
0
0
0 to be divisible by
0
0
0 ,
0
0
0 Cannot divide non
0
0
0 , namely
0
0
0 Can only be divisor , Cannot divide ;
Reference resources : 【 Set theory 】 Binary relationship ( Special relationship types | Empty relation | Identity | Global relations | Division relations | Size relationship ) 3、 ... and 、 Division relations
6. Identity :
Identity :
Symbolic description :
I
N
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
∧
x
=
y
}
I_N = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \land x = y \}
IN={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N∧x=y}
The nature of the relationship : introspect , symmetry , antisymmetric , Pass on
7. Global relations :
Global relations :
Symbolic description :
E
N
=
{
<
x
,
y
>
∣
x
∈
N
∧
y
∈
N
}
=
N
×
N
E_N = \{ <x, y> | x \in N \land y \in N \} = N \times N
EN={ <x,y>∣x∈N∧y∈N}=N×N
The nature of the relationship : introspect , symmetry , Pass on
introspect , Antisymmetric relation , It is called partial order relation ;
Two 、 Examples of the nature of relationships
Relationship diagram relationship determination :
- ① introspect : All vertices in the graph They all have rings ;
- ② Reflexion : All vertices in the graph There is no ring ;
- ③ symmetry : Between two vertices Yes
0
0
0 Or
2
2
2 A directed edge ;
- ④ antisymmetric : Between two vertices Yes
0
0
0 Or
1
1
1 A directed edge ;
- ⑤ Pass on : Premise
a
→
b
,
b
→
c
a \to b , b\to c
a→b,b→c Don't set up Default delivery , Premise
a
→
b
,
b
→
c
a \to b , b\to c
a→b,b→c establish Must satisfy
a
→
c
a \to c
a→c There is ;
1.
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
}
R_1 = \{ <a, a> , <a, b> , <b , c> , <a,c> \}
R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,c>,<a,c>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : antisymmetric , Pass on 
introspect / Reflexion : Some vertices have rings , Some vertices have no rings , Neither reflexivity nor reflexivity is tenable ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
1
1
1 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
1
0/1
0/1 side , yes antisymmetric Of ;
Pass on :
a
→
b
,
b
→
c
a\to b, b \to c
a→b,b→c establish ,
a
→
c
a \to c
a→c There is , Transitivity establish ;
2.
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
,
<
c
,
a
>
}
R_2 = \{ <a, a> , <a, b> , <b , c> , <c,a> \}
R2={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,c>,<c,a>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : antisymmetric

introspect / Reflexion : Some vertices have rings , Some vertices have no rings , Neither reflexivity nor reflexivity is tenable ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
1
1
1 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
1
0/1
0/1 side , yes antisymmetric Of ;
Pass on :
a
→
b
,
b
→
c
a\to b, b \to c
a→b,b→c establish ,
a
→
c
a \to c
a→c non-existent , Transitivity Don't set up ;
3.
R
3
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
c
>
}
R_3 = \{ <a, a> , <b, b> , <a,b> , <b,a> , <c,c> \}
R3={ <a,a>,<b,b>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<c,c>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : introspect , symmetry , Pass on
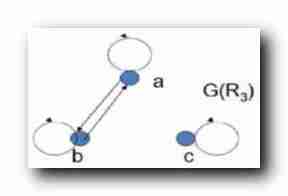
introspect / Reflexion : All vertices have rings , reflexivity establish ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
0
0
0 or
2
2
2 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
2
0/2
0/2 side , yes symmetry Of ;
Pass on : Transitivity establish ;
- Premise
a
→
b
,
b
→
a
a \to b , b\to a
a→b,b→a , Correspondence exists
a
→
a
a \to a
a→a
- Premise
b
→
a
,
a
→
b
b \to a , a\to b
b→a,a→b , Correspondence exists
b
→
b
b \to b
b→b
4.
R
4
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
c
>
}
R_4 = \{ <a, a> , <a,b> , <b,a> , <c,c> \}
R4={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<c,c>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : symmetry

introspect / Reflexion : Some vertices have rings , Some vertices have no rings , Neither reflexivity nor reflexivity is tenable ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
0
0
0 or
2
2
2 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
2
0/2
0/2 side , yes symmetry Of ;
Pass on : Transitivity Don't set up ;
- Premise
a
→
b
,
b
→
a
a \to b , b\to a
a→b,b→a , Correspondence exists
a
→
a
a \to a
a→a
- Premise
b
→
a
,
a
→
b
b \to a , a\to b
b→a,a→b , There is no corresponding
b
→
b
b \to b
b→b , Here transitivity does not hold ;
5.
R
5
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
b
>
,
<
c
,
c
>
}
R_5 = \{ <a, a> , <a,b> , <b,b> , <c,c> \}
R5={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,b>,<c,c>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : introspect , antisymmetric , Pass on
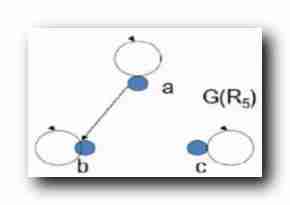
introspect / Reflexion : All vertices have rings , reflexivity establish ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
0
0
0 or
1
1
1 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
1
0/1
0/1 side , yes antisymmetric Of ;
Pass on : The premise doesn't hold , Transitivity establish ;
6.
R
6
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
,
<
a
,
a
>
}
R_6 = \{ <a, a> , <b,a> , <b,c> , <a,a> \}
R6={ <a,a>,<b,a>,<b,c>,<a,a>} :
Draw a diagram of the above relationship : It doesn't matter
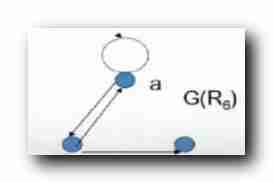
introspect / Reflexion : Some vertices have rings , Some vertices have no rings , Neither reflexivity nor reflexivity is tenable ;
symmetry / antisymmetric : Between the vertices are
1
1
1 or
2
2
2 The strip has a directed edge , There is only
0
/
1
0/1
0/1 The edge is antisymmetric , There is only
0
/
2
0/2
0/2 The edges are symmetrical , The above symmetry / The objection is not tenable ;
Pass on : Premise
a
→
b
,
b
→
c
a \to b , b \to c
a→b,b→c , There is no corresponding
a
→
c
a \to c
a→c , Here transitivity does not hold ;
3、 ... and 、 Relation operation properties
discuss a problem : Specify the nature of the relationship Between them , The nature of the result ; Such as Two relations of reflexivity Perform the reverse order synthesis operation , The result is reflexive ;
The meaning of the table in the following figure is : Such as Second column “ introspect ” And The third column “
R
1
∪
R
2
R_1 \cup R_2
R1∪R2” , Cross table position , representative Relationship
R
1
R_1
R1 And relationships
R
2
R_2
R2 It's reflexive , Whether the intersection of its ordered pairs is reflexive , If it is
1
1
1 , The explanation is reflexive , If there is no value , The explanation is not reflexive ;
| introspect | Reflexion | symmetry | antisymmetric | Pass on | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
R 1 − 1 , R 2 − 1 R_1^{-1}, R_2^{-1} R1−1,R2−1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 |
R 1 ∪ R 2 − 1 R_1 \cup R_2^{-1} R1∪R2−1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | ||
R 1 ∩ R 2 R_1 \cap R_2 R1∩R2 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 |
R 1 ∘ R 2 , R 2 ∘ R 1 R_1 \circ R_2 , R_2 \circ R_1 R1∘R2,R2∘R1 | 1 1 1 | ||||
R 1 − R 2 , R 2 − R 1 R_1 - R_2 , R_2 - R_1 R1−R2,R2−R1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | 1 1 1 | ||
∼ R 1 , ∼ R 2 \sim R_1, \sim R_2 ∼R1,∼R2 | 1 1 1 |
边栏推荐
- 第十九届浙江省 I. Barbecue
- [SQL injection point] location and judgment of the injection point
- M1 Pro install redis
- Interface frequency limit access
- Literature reading_ Research on the usefulness identification of tourism online comments based on semantic fusion of multimodal data (Chinese Literature)
- Notes | numpy-10 Iterative array
- Day 51 - tree problem
- Market status and development prospect prediction of global neutral silicone sealant industry in 2022
- ZABBIX monitoring of lamp architecture (3): zabbix+mysql (to be continued)
- Market status and development prospect prediction of the global fire alarm sensor industry in 2022
猜你喜欢
Silent authorization login and registration of wechat applet

Truncated sentences of leetcode simple questions

The least operation of leetcode simple problem makes the array increment

Leetcode simple question: the key with the longest key duration

I stepped on a foundation pit today
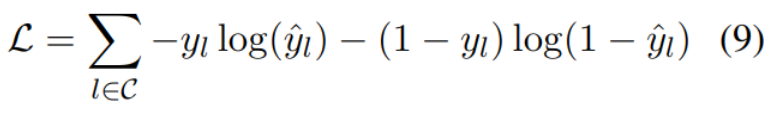
Thesis reading_ ICD code_ MSMN
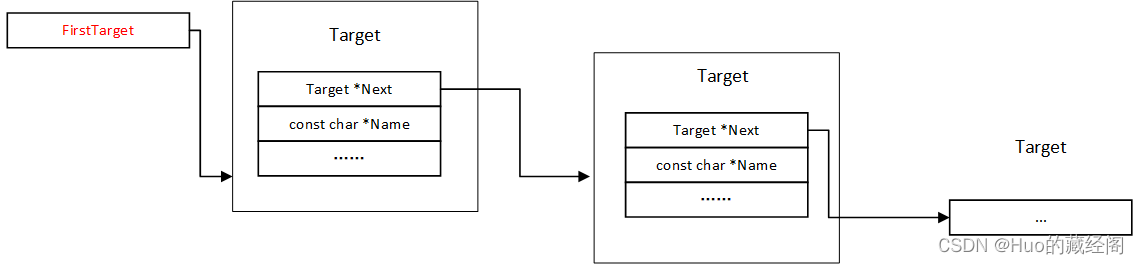
MC Layer Target

Automatic voltage rise and fall 5-40v multi string super capacitor charging chip and solution

Number of uniform strings of leetcode simple problem
Mobile terminal - uniapp development record (public request encapsulation)
随机推荐
Review the old and know the new: Notes on Data Science
Market status and development prospects of the global autonomous marine glider industry in 2022
移动端——uniapp开发记录(公共请求request封装)
Wechat applet distance and map
[tools run SQL blind note]
Shuttle + Alluxio 加速内存Shuffle起飞
Basic use of Metasploit penetration testing framework
5-36v input automatic voltage rise and fall PD fast charging scheme drawing 30W low-cost chip
Use Sqlalchemy module to obtain the table name and field name of the existing table in the database
联发科技2023届提前批IC笔试(题目)
Thesis reading_ ICD code_ MSMN
UiPath实战(08) - 选取器(Selector)
Handler understands the record
On typescript and grammar
Blog building tool recommendation (text book delivery)
The principle is simple, but I don't know how to use it? Understand "contemporaneous group model" in one article
Retirement plan fails, 64 year old programmer starts work again
Market status and development prospects of the global IOT active infrared sensor industry in 2022
document. The problem of missing parameters of referer is solved
2022-02-11 daily clock in: problem fine brush