当前位置:网站首页>[set theory] relational representation (relational matrix | examples of relational matrix | properties of relational matrix | operations of relational matrix | relational graph | examples of relationa
[set theory] relational representation (relational matrix | examples of relational matrix | properties of relational matrix | operations of relational matrix | relational graph | examples of relationa
2022-07-03 04:37:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 The relational matrix
- Two 、 Example of relational matrix
- 3、 ... and 、 Properties of relation matrix
- Four 、 Relational matrix operation
- 5、 ... and 、 The diagram
- 6、 ... and 、 Diagram example
- 7、 ... and 、 Relationships represent related properties
One 、 The relational matrix
A
=
{
a
1
,
a
2
,
⋯
,
a
n
}
,
R
⊆
A
×
A
A = \{ a_1, a_2 , \cdots , a_n \} , R \subseteq A \times A
A={ a1,a2,⋯,an},R⊆A×A
R
R
R Use The relational matrix Express :
M
(
R
)
=
(
r
i
j
)
n
×
n
M(R) = (r_{ij})_{n\times n}
M(R)=(rij)n×n
Relation matrix value :
M
(
R
)
(
i
,
j
)
=
r
i
j
=
{
1
,
a
i
R
a
j
0
,
nothing
Turn off
system
M(R)(i, j) = r_{ij} =\begin{cases} 1, & a_i R a_j \\ 0, & It doesn't matter \end{cases}
M(R)(i,j)=rij={ 1,0,aiRaj nothing Turn off system
Description of relation matrix definition :
A
A
A It's a
n
n
n Meta set ( There are
n
n
n Elements ) ,
R
R
R yes
A
A
A The binary relationship on ,
R
R
R The relation matrix of is
n
×
n
n \times n
n×n Matrix of , The first
i
i
i Xing di
j
j
j Element at column position
r
i
j
r_{ij}
rij The value can only be
0
0
0 or
1
1
1 ;
Description of relation matrix value :
If
r
i
j
=
1
r_{ij} = 1
rij=1 , shows
A
A
A Collection The first
i
i
i Elements and
j
j
j Elements have relationships
R
R
R , Write it down as :
a
i
R
a
j
a_i R a_j
aiRaj ;
If
r
i
j
=
0
r_{ij} = 0
rij=0 , shows
A
A
A Collection The first
i
i
i Elements and
j
j
j Elements don't matter
R
R
R ;
The essence of relational matrix : In the relation matrix , Each line corresponds to
A
A
A The elements in the collection , Each column also corresponds to
A
A
A The elements in the collection , The value of the position where the rows intersect (
0
0
0 or
1
1
1 ) Express
A
A
A In the set
i
i
i Elements and
j
j
j Whether there is a relationship between the ordered pairs of elements
R
R
R ;
Two 、 Example of relational matrix
A
=
{
a
,
b
,
c
}
A = \{ a, b, c \}
A={ a,b,c}
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_1 = \{ <a, a>, <a,b> , <b,a> , <b,c> \}
R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>}
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_2 = \{ <a,b> , <a,c> , <b,c> \}
R2={ <a,b>,<a,c>,<b,c>}
Use the relation matrix to express the above
R
1
,
R
2
R_1 , R_2
R1,R2 Two relationships :
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_1 = \{ <a, a>, <a,b> , <b,a> , <b,c> \}
R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>} among :
<
a
,
a
>
<a, a>
<a,a> :
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements ,
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements , The first
1
1
1 Xing di
1
1
1 The column elements are
1
1
1
<
a
,
b
>
<a, b>
<a,b> :
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements ,
b
b
b It's No
2
2
2 Elements , The first
1
1
1 Xing di
2
2
2 The column elements are
1
1
1
<
b
,
a
>
<b, a>
<b,a> :
b
b
b It's No
2
2
2 Elements ,
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements , The first
2
2
2 Xing di
1
1
1 The column elements are
1
1
1
<
b
,
c
>
<b, c>
<b,c> :
b
b
b It's No
2
2
2 Elements ,
c
c
c It's No
3
3
3 Elements , The first
2
2
2 Xing di
3
3
3 The column elements are
1
1
1
- The rest are all
0
0
0
M
(
R
1
)
=
[
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
]
M(R_1) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R1)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110100010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_2 = \{ <a,b> , <a,c> , <b,c> \}
R2={ <a,b>,<a,c>,<b,c>} among :
<
a
,
b
>
<a, b>
<a,b> :
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements ,
b
b
b It's No
2
2
2 Elements , The first
1
1
1 Xing di
2
2
2 The column elements are
1
1
1
<
a
,
c
>
<a, c>
<a,c> :
a
a
a It's No
1
1
1 Elements ,
c
c
c It's No
3
3
3 Elements , The first
1
1
1 Xing di
3
3
3 The column elements are
1
1
1
<
b
,
c
>
<b, c>
<b,c> :
b
b
b It's No
2
2
2 Elements ,
c
c
c It's No
3
3
3 Elements , The first
2
2
2 Xing di
3
3
3 The column elements are
1
1
1
- The rest are all
0
0
0
M
(
R
2
)
=
[
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
]
M(R_2) = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R2)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡000100110⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
3、 ... and 、 Properties of relation matrix
Ordered pair set expression And The relational matrix Can only be mutually determined
Property one : Inverse operation related properties
M
(
R
−
1
)
=
(
M
(
R
)
)
T
M(R^{-1}) = (M(R))^T
M(R−1)=(M(R))T
M
(
R
−
1
)
M(R^{-1})
M(R−1) The inverse of the relationship Of The relational matrix
And
(
M
(
R
)
)
T
(M(R))^T
(M(R))T The relational matrix Of The inverse
These two matrices are equal ;
Property two : Properties related to composition operation
M
(
R
1
∘
R
2
)
=
M
(
R
2
)
∙
M
(
R
1
)
M(R_1 \circ R_2) = M(R_2) \bullet M(R_1)
M(R1∘R2)=M(R2)∙M(R1)
∙
\bullet
∙ It's matrix Logical multiplication , Calculation matrix
r
i
j
r_{ij}
rij Value The first
i
i
i That's ok multiply The first
j
j
j Column , Bit by bit Logical multiplication , Then multiply the logic and the result is Logical addition ;
Above Logical multiplication uses
∧
\land
∧ operation , Logical addition uses
∨
\lor
∨ operation ;
Four 、 Relational matrix operation
A
=
{
a
,
b
,
c
}
A = \{ a, b, c \}
A={ a,b,c}
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_1 = \{ <a, a>, <a,b> , <b,a> , <b,c> \}
R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>}
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_2 = \{ <a,b> , <a,c> , <b,c> \}
R2={ <a,b>,<a,c>,<b,c>}
In the example above , Two relational matrices have been found ;
M
(
R
1
)
=
[
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
]
M(R_1) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R1)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110100010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤ ,
M
(
R
2
)
=
[
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
]
M(R_2) = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R2)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡000100110⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
1. seek
M
(
R
−
1
)
,
M
(
R
2
−
1
)
M(R^{-1}) , M(R_2^{-1})
M(R−1),M(R2−1)
Directly transpose the matrix , Can get Inverse relation matrix of relation ;
M
(
R
1
−
1
)
=
(
M
(
R
1
)
)
T
=
[
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
]
M(R_1^{-1}) = (M(R_1))^T = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R1−1)=(M(R1))T=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110101000⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
M
(
R
2
−
1
)
=
(
M
(
R
2
)
)
T
=
[
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
]
M(R_2^{-1}) = (M(R_2))^T = \begin{bmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 1 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R2−1)=(M(R2))T=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡011001000⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
R
1
−
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
b
>
}
R_1^{-1} = \{ <a, a> , <a, b> , <b,a> , <c,b> \}
R1−1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<c,b>}
R
2
−
1
=
{
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
b
>
}
R_2^{-1} = \{ <b, a> , <c,a> , <c,b> \}
R2−1={ <b,a>,<c,a>,<c,b>}
2. seek
M
(
R
1
∘
R
1
)
M( R_1 \circ R_1 )
M(R1∘R1)
M
(
R
1
∘
R
1
)
=
M
(
R
1
)
∙
M
(
R
1
)
M( R_1 \circ R_1 ) = M(R_1) \bullet M(R_1)
M(R1∘R1)=M(R1)∙M(R1)
Among them
∙
\bullet
∙ Is the logical multiplication of two matrices , Addition uses
∨
\lor
∨ , Multiplication uses
∧
\land
∧
M
(
R
1
)
∙
M
(
R
1
)
=
[
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
]
∙
[
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
]
=
[
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
]
M(R_1) \bullet M(R_1) = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \bullet \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R1)∙M(R1)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110100010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∙⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110100010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110110100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Logical multiplication of matrices : The second of the result matrix
i
i
i That's ok , The first
j
j
j The value of the column element is , The first
i
i
i The three elements of a row Respectively with the previous
j
j
j The three elements of the column , Then the three results are or calculated , The end result is The order of the matrix
i
i
i That's ok , The first
j
j
j Value of column element ;
R
1
∘
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
b
>
}
R_1 \circ R_1 = \{ <a,a> , <a,b> , <a,c> , <b,a>, <b,b> \}
R1∘R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<a,c>,<b,a>,<b,b>}
3. seek
M
(
R
1
∘
R
2
)
M( R_1 \circ R_2 )
M(R1∘R2)
M
(
R
1
∘
R
2
)
=
M
(
R
2
)
∙
M
(
R
1
)
M( R_1 \circ R_2 ) = M(R_2) \bullet M(R_1)
M(R1∘R2)=M(R2)∙M(R1)
Among them
∙
\bullet
∙ Is the logical multiplication of two matrices , Addition uses
∨
\lor
∨ , Multiplication uses
∧
\land
∧
Particular attention , The order of synthesis is reverse synthesis , The latter relation matrix comes first , The former relation matrix is later
M
(
R
1
)
∙
M
(
R
2
)
=
[
0
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
]
∙
[
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
]
=
[
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
]
M(R_1) \bullet M(R_2) =\begin{bmatrix} 0 & 1 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} \bullet \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 1 & 0 \\\\ 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 & 0 & 1 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\\\ 0 & 0 & 0 \end{bmatrix}
M(R1)∙M(R2)=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡000100110⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∙⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡110100010⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡100000100⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤
Logical multiplication of matrices : The second of the result matrix
i
i
i That's ok , The first
j
j
j The value of the column element is , The first
i
i
i The three elements of a row Respectively with the previous
j
j
j The three elements of the column , Then the three results are or calculated , The end result is The order of the matrix
i
i
i That's ok , The first
j
j
j Value of column element ;
R
1
∘
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
}
R_1 \circ R_2 = \{ <a,a>, <a,c> \}
R1∘R2={ <a,a>,<a,c>}
5、 ... and 、 The diagram
A
=
{
a
1
,
a
2
,
⋯
,
a
n
}
,
R
⊆
A
×
A
A = \{ a_1, a_2 , \cdots , a_n \} , R \subseteq A \times A
A={ a1,a2,⋯,an},R⊆A×A
R
R
R Diagram for :
- The vertices :
∘
\circ
∘ Express
A
A
A The elements in the collection ;
- There is a directional side :
→
\rightarrow
→ Express
R
R
R The elements in ;
a
i
R
a
j
a_i R a_j
aiRaj It's from the apex
a
i
a_i
ai To The vertices
a
j
a_j
aj The directed side of
<
a
i
,
a
j
>
<a_i , a_j>
<ai,aj> ;
6、 ... and 、 Diagram example
A
=
{
a
,
b
,
c
}
A = \{ a, b, c \}
A={ a,b,c}
R
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_1 = \{ <a, a> , <a,b> , <b,a> , <b,c> \}
R1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<b,c>} Diagram representation :
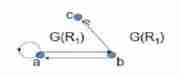
R
2
=
{
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
a
,
c
>
,
<
b
,
c
>
}
R_2 = \{ <a,b>, <a,c>, <b,c> \}
R2={ <a,b>,<a,c>,<b,c>} Use diagrams to represent :

R
1
−
1
=
{
<
a
,
a
>
,
<
a
,
b
>
,
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
b
>
}
R_1^{-1} = \{ <a,a>, <a,b>, <b,a> , <c,b> \}
R1−1={ <a,a>,<a,b>,<b,a>,<c,b>}
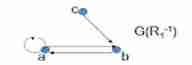
R
2
−
1
=
{
<
b
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
a
>
,
<
c
,
b
>
}
R_2^{-1} = \{ <b,a> , <c,a> , <c,b> \}
R2−1={ <b,a>,<c,a>,<c,b>}
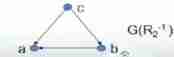
7、 ... and 、 Relationships represent related properties
A
A
A The elements in the collection , After calibration sequence , That is, the
A
A
A Relationship on ,
R
⊆
A
×
A
R \subseteq A \times A
R⊆A×A , It has the following properties :
- The diagram
G
(
R
)
G(R)
R
R
R Set expression of ( Ordered pair set ) , Sure Sole determination ;
G(R) And Relational
- Relationship
R
R
R Set expression of , The relational matrix
M
(
R
)
M(R)
M(R) , The diagram
G
(
R
)
G(R)
G(R) , They all correspond to each other ;
R
⊆
A
×
B
R \subseteq A \times B
R⊆A×B
- aggregate
A
A
A There is
n
n
n Elements ,
∣
A
∣
=
n
|A| = n
∣A∣=n
- aggregate
B
B
B There is
m
m
m Elements ,
∣
B
∣
=
m
|B| = m
∣B∣=m
- The relational matrix
M
(
R
)
M(R)
M(R) yes
n
×
m
n \times m
n×m Order matrix ;
- The diagram
G
(
R
)
G(R)
G(R) All directional edges are from
A
A
A The elements in the collection Point to
B
B
B The elements in the collection
边栏推荐
- Design and implementation of JSP logistics center storage information management system
- Integration of Android high-frequency interview questions (including reference answers)
- Priv-app permission异常
- 使用BENCHMARKSQL工具对kingbaseES执行灌数据提示无法找到JDBC driver
- STM32 reverse entry
- Joint set search: merge intervals and ask whether two numbers are in the same set
- [fairseq] error: typeerror:_ broadcast_ coalesced(): incompatible function arguments
- Symbol of array element product of leetcode simple problem
- P35-P41 fourth_ context
- Internationalization and localization, dark mode and dark mode in compose
猜你喜欢
UiPath实战(08) - 选取器(Selector)

P35-P41 fourth_ context

Joint search set: the number of points in connected blocks (the number of points in a set)

Preliminary cognition of C language pointer
2022 P cylinder filling test content and P cylinder filling simulation test questions

有道云笔记

Truncated sentences of leetcode simple questions

After job hopping at the end of the year, I interviewed more than 30 companies in two weeks and finally landed
vulnhub HA: Natraj

4 years of experience to interview test development, 10 minutes to end, ask too
随机推荐
Network security textual research recommendation
General undergraduate college life pit avoidance Guide
Solve BP Chinese garbled code
The simple problem of leetcode: dismantling bombs
一名外包仔的2022年中总结
[BMZCTF-pwn] 18-RCTF-2017-Recho
GFS distributed file system (it's nice to meet it alone)
Bugku CTF daily question baby_ flag. txt
JS multidimensional array to one-dimensional array
Joint search set: the number of points in connected blocks (the number of points in a set)
[set theory] binary relationship (binary relationship notation | binary relationship from a to B | number of binary relationships | example of binary relationship)
Introduction to JVM principle
Leetcode simple question: check whether two string arrays are equal
[set theory] binary relationship (definition field | value field | inverse operation | inverse synthesis operation | restriction | image | single root | single value | nature of synthesis operation)
Why should programmers learn microservice architecture if they want to enter a large factory?
Jincang KFS data bidirectional synchronization scenario deployment
2022-02-12 (338. Bit count)
What are the Bluetooth headsets with good sound quality in 2022? Inventory of four high-quality Bluetooth headsets
【XSS绕过-防护策略】理解防护策略,更好的绕过
Use the benchmarksql tool to perform a data prompt on kingbases. The jdbc driver cannot be found