当前位置:网站首页>(p15-p16) optimization of the right angle bracket of the template and the default template parameters of the function template
(p15-p16) optimization of the right angle bracket of the template and the default template parameters of the function template
2022-06-12 08:26:00 【Ordinary people who like playing basketball】
List of articles
1. The right angle bracket of the template
In generic programming , Template instantiation has a very cumbersome place , That's two consecutive right angle brackets (>>) Will be parsed by the compiler into a shift right operator , Instead of the end of the template parameter table .
- Let's first look at a piece of code about container traversal , In the class template created Base The operation function of traversing the container is provided in traversal():
- eg: Traverse the container , There are two kinds of containers : Relational and non relational , Relational containers are key value pairs
// test.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class Base
{
public:
void traversal(T& t)
{
auto it = t.begin();
for (; it != t.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
vector<int> v{
1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
Base<vector<int>> b;
b.traversal(v);
return 0;
}
test :

according to 03 Standard compilation , Method :
g++ test.cpp -std=c++03 -o app
You will get the following error prompt :
test.cpp:25:20: error: '>>' should be '> >' within a nested template argument list
Base<vector<int>> b;
According to the error prompt, you need to add a space between the two right corners of the template , It is very troublesome to write in this way ,C++11 Improved the parsing rules of the compiler , As many right angle brackets as possible (>) Resolve to template parameter Terminator , It is convenient for us to write template related code .
- The code above , In support of C++11 There is no problem compiling in the compiler of , If you use g++ Direct compilation requires adding parameters -std=c++11:
g++ test.cpp -std=c++11 -o app
2. Default template parameters
stay C++98/03 In the standard , Class template You can have default template parameters :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T=int, T t=520>
class Test
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << "current value: " << t << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Test<> t;
t.print();
Test<int, 1024> t1;
t1.print();
return 0;
}
- test :

however 03 Default template parameters for functions are not supported , stay C++11 Added support for function template default parameters in :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T=int> // C++98/03 This is not supported , C++11 This writing method is supported in
void func(T t)
{
cout << "current value: " << t << endl;
}
int main()
{
func(100);
return 0;
}
test :
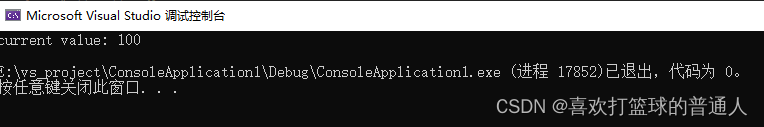
Conclusion :
From the above example, we can draw the following conclusions : When all template parameters have default parameters , The call of a function template is like a normal function . But for class templates , Even if all parameters have default parameters , In use, you must also follow the template name with <> To instantiate .
in addition : The default template parameters of function template are different from other default parameters in usage rules , There is no limit to the parameters that must be written at the end of the table . In this way, when the default template parameters are combined with the automatic derivation of template parameters , Writing is very flexible .
- We can specify some template parameters in the function template and use the default parameters , The other part uses automatic derivation , Take the following example :
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
template <typename R = int, typename N>
R func(N arg)
{
return arg;
}
int main()
{
// The function return value type uses the default template parameter , The parameter type of the function is automatically derived as int type .
auto ret1 = func(520);
cout << "return value-1: " << ret1 << endl;
// The return value of the function is specified as double type , Function parameters are derived from real parameters , by double type
auto ret2 = func<double>(52.134);
cout << "return value-2: " << ret2 << endl;
// The return value of the function is specified as int type , Function parameters are derived from real parameters , by double type
auto ret3 = func<int>(52.134);
cout << "return value-3: " << ret3 << endl;
// The arguments to the function are specified as int type , The return value of the function is specified as char type , There is no need to deduce
auto ret4 = func<char, int>(100);
cout << "return value-4: " << ret4 << endl;
return 0;
}
- test :

- When Default template parameters and Template parameter When automatic derivation is used at the same time ( Priority from high to low ):
If the parameter type can be derived, use the derived type
If the function template cannot deduce the parameter type , Then the compiler will use the default template parameters
If the template parameter type cannot be derived and the default template parameter is not set , The compiler will report an error .
- eg:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// Function template definition
template <typename T, typename U = char>
void func(T arg1 = 100, U arg2 = 100)
{
cout << "arg1: " << arg1 << ", arg2: " << arg2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
// Template function call
//func('a'): Parameters T Automatically derived as char type ,U The default template parameters used are char type
func('a');
//func(97, 'a');: Parameters T Automatically derived as int type ,U Use the derived type as char
func(97, 'a');
//func();: Parameters T No default template type specified , And can't automatically deduce , The compiler will directly report an error
/* The automatic derivation of template parameter types is based on the actual parameters specified during template function calls , You cannot derive without arguments Automatic derivation of template parameter types does not refer to the default parameters specified in the function template . */
// func(); // Compiler error
return 0;
}
- test :

author : Su Bingyu
link : https://subingwen.cn/cpp/template/#2-%E9%BB%98%E8%AE%A4%E6%A8%A1%E6%9D%BF%E5%8F%82%E6%95%B0
source : Da C who loves programming
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .
author : Su Bingyu
link : https://subingwen.cn/cpp/template/#1-%E6%A8%A1%E6%9D%BF%E7%9A%84%E5%8F%B3%E5%B0%96%E6%8B%AC%E5%8F%B7
source : Da C who loves programming
The copyright belongs to the author . Commercial reprint please contact the author for authorization , Non-commercial reprint please indicate the source .
- Reference resources : Template optimization
边栏推荐
- (P33-P35)lambda表达式语法,lambda表达式注意事项,lambda表达式本质
- Face recognition using BP neural network of NNET in R language
- (P15-P16)对模板右尖括号的优化、函数模板的默认模板参数
- call方法和apply方法
- (p36-p39) right value and right value reference, role and use of right value reference, derivation of undetermined reference type, and transfer of right value reference
- Hands on learning and deep learning -- simple implementation of linear regression
- 只把MES当做工具?看来你错过了最重要的东西
- Vins technical route and code explanation
- MES系统是什么?MES系统的操作流程是怎样?
- How to understand the production scheduling of APS system?
猜你喜欢

X64dbg debugging exception_ ACCESS_ VIOLATION C0000005

Prediction of COVID-19 by RNN network
(p36-p39) right value and right value reference, role and use of right value reference, derivation of undetermined reference type, and transfer of right value reference

In the era of intelligent manufacturing, how do enterprises carry out digital transformation

Hands on deep learning -- weight decay and code implementation

Why should enterprises implement MES? What are the specific operating procedures?

Database foundation -- normalization and relational schema

The Three Kingdoms kill the surrounding areas -------- explanation of the pig Kingdom kill problem

MATLAB image processing - cosine noise removal in image (with code)

Installation series of ROS system (I): installation steps
随机推荐
js中的正则表达式
Vscode download slow solution
MES系统质量追溯功能,到底在追什么?
Installation series of ROS system (I): installation steps
Where does the driving force of MES system come from? What problems should be paid attention to in model selection?
FPGA to flip video up and down (SRAM is61wv102416bll)
A brief summary of C language printf output integer formatter
Instructions spéciales pour l'utilisation du mode nat dans les machines virtuelles VM
(P15-P16)对模板右尖括号的优化、函数模板的默认模板参数
工厂的生产效益,MES系统如何提供?
Prediction of COVID-19 by RNN network
ctfshow web4
Hands on learning and deep learning -- Realization of linear regression from scratch
Record the treading pit of grain Mall (I)
Gtest/gmock introduction and Practice
At present, MES is widely used. Why are there few APS scheduling systems? Why?
call方法和apply方法
Hands on learning and deep learning -- simple implementation of softmax regression
The era of post MES system has come gradually
What is the MES system? What is the operation process of MES system?