当前位置:网站首页>POJ3250「Bad Hair Day」
POJ3250「Bad Hair Day」
2022-06-11 09:35:00 【hotarugali】
1. subject
Topic link :POJ3250「Bad Hair Day」 .
Description
Some of Farmer John’s NNN cows (1 ≤ NNN ≤ 80,000) are having a bad hair day! Since each cow is self-conscious about her messy hairstyle, FJ wants to count the number of other cows that can see the top of other cows’ heads.
Each cow i has a specified height hih_ihi (1 ≤ hih_ihi ≤ 1,000,000,000) and is standing in a line of cows all facing east (to the right in our diagrams). Therefore, cow iii can see the tops of the heads of cows in front of her (namely cows iii+1, iii+2, and so on), for as long as these cows are strictly shorter than cow iii.
Consider this example:
= = = = = = Cows facing right --> = = = = = = = = = = = = = = 1 2 3 4 5 6
- Cow#1 can see the hairstyle of cows #2, 3, 4
- Cow#2 can see no cow’s hairstyle
- Cow#3 can see the hairstyle of cow #4
- Cow#4 can see no cow’s hairstyle
- Cow#5 can see the hairstyle of cow 6
- Cow#6 can see no cows at all!
Let cic_ici denote the number of cows whose hairstyle is visible from cow iii; please compute the sum of c1c_1c1 through cNc_NcN. For this example, the desired is answer 3+0+1+0+1+0=53 + 0 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 = 53+0+1+0+1+0=5.
Input
Line 111: The number of cows, NNN. Lines 2..N+12..N+12..N+1: Line i+1i+1i+1 contains a single integer that is the height of cow iii.
Output
Line 111: A single integer that is the sum of c1c_1c1 through cNc_NcN.
Sample Input
6 10 3 7 4 12 2
Sample Output
5
2. Answer key
analysis
The topic is to ask for the total number of other cattle hairstyles that all cattle can see , It is equivalent to finding the sum of the times that all cows are seen by other cows . That is, for the current cow iii Come on , notice iii A cow with a hairstyle should be iii The height on the left side of cattle is strictly increasing from right to left and greater than iii The height of those cows , And the increasing height sequence is relative to iii It is the first increasing sequence from right to left ( That is, the first strictly increasing sequence ).
First increment sequence For the sequence a_1,a_2,\cdots,a_N, Define from left to right a_i The first increasing sequence of is a_{b_0}=a_i,a_{b_1},a_{b_2},\cdots,a_{b_m}, Satisfy \forall j \in (0, m] , There are \forall 1 \leq k \lt b_j, a_{b_{j-1}} \geq a_k \wedge a_k \lt a_{b_j}
For the first increment sequence , We can easily solve this problem by using the monotone stack . Monotonic incremental stack is used to save the first incremental sequence of the current top element of the stack , The sequence formed from the top element of the stack to the bottom element of the stack is the first increasing sequence of the top element in the original sequence . Because we process data from left to right and the stack satisfies the property of last in first out , Therefore, the first increment sequence formed is the first increment sequence of stack top elements from right to left .
【 notes 】N \leq 80000, so {N(N-1) \over 2} It will go beyond int Representation range of , So the answer needs to be long long Type representation .
Code
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
// #include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Compare elements
template < typename T >
struct Compare {
bool operator () (const T & a, const T & b) {
return a > b;
}
};
// Monotonic stack
template < typename T, typename F = Compare<T> >
struct MStack{
#ifndef _MSTACK_
#define ll int
#define MAXN 100005
#endif
ll depth; // Stack depth
T stack[MAXN]; // Single increment stack
F cmp;
MStack():depth(0) {}
// Two points search
ll find(T x, ll l, ll r) {
if(l == r) return l;
ll m = (l+r) >> 1;
if(cmp(stack[m], x)) {
return find(x, m+1, r);
} else {
return find(x, l, m);
}
}
// Pressing stack
T push(T x) {
// // Method 1
// // Sequence play stack O(n), whole O(2n)
// while(depth && !cmp(stack[depth-1], x)) --depth;
// stack[depth++] = x;
// return x;
// Method 2
// Two points search O(lg(n)), whole O(nlg(n))
if(!depth || cmp(stack[depth-1], x)) {
stack[depth++] = x;
return x;
}
ll pos = find(x, 0, depth-1);
T t = stack[pos];
stack[pos] = x;
depth = pos + 1;
return t;
}
// Bomb stack
T pop() {
return stack[--depth];
}
};
int main()
{
ll n;
ll a[MAXN];
MStack <ll> ms;
scanf("%d", &n);
for(ll i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", a+i);
}
long long ans = 0;
for(ll i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ms.push(a[i]);
ans += ms.depth - 1;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
return 0;
}边栏推荐
- Why is it difficult to implement informatization in manufacturing industry?
- Do you know these advantages of ERP system?
- The mobile terminal page uses REM for adaptation
- 报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer
- Modularnotfounderror: no module named 'find_ version’
- Clothing ERP: how do enterprises carry out implementation planning?
- 【软件】ERP体系价值最大化的十点技巧
- 【方案开发】血压计方案压力传感器SIC160
- Device = depthai Device(““, False) TypeError: _init_(): incompatible constructor arguments.
- Technical practice of dolphin dispatching in kubernetes system
猜你喜欢
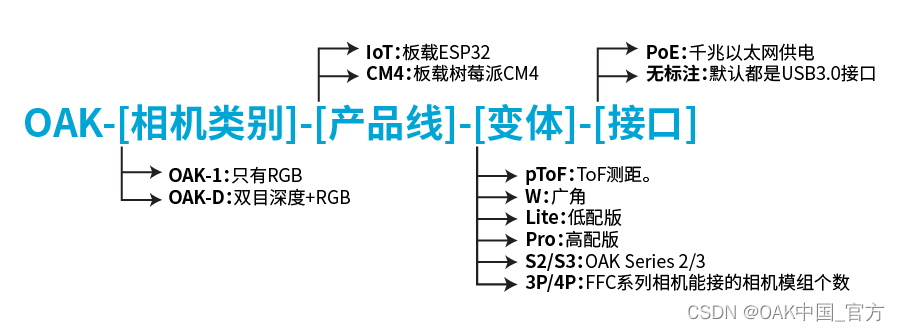
OpenCV OAK相机对比及介绍

Runtimeerror: blobreader error:the version of imported blob doesn't match graph_ transformer

Video review pulsar summit Asia 2021, cases, operation and maintenance, ecological dry goods

Install jupyter in the specified environment

MSF adds back door to normal program

报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer
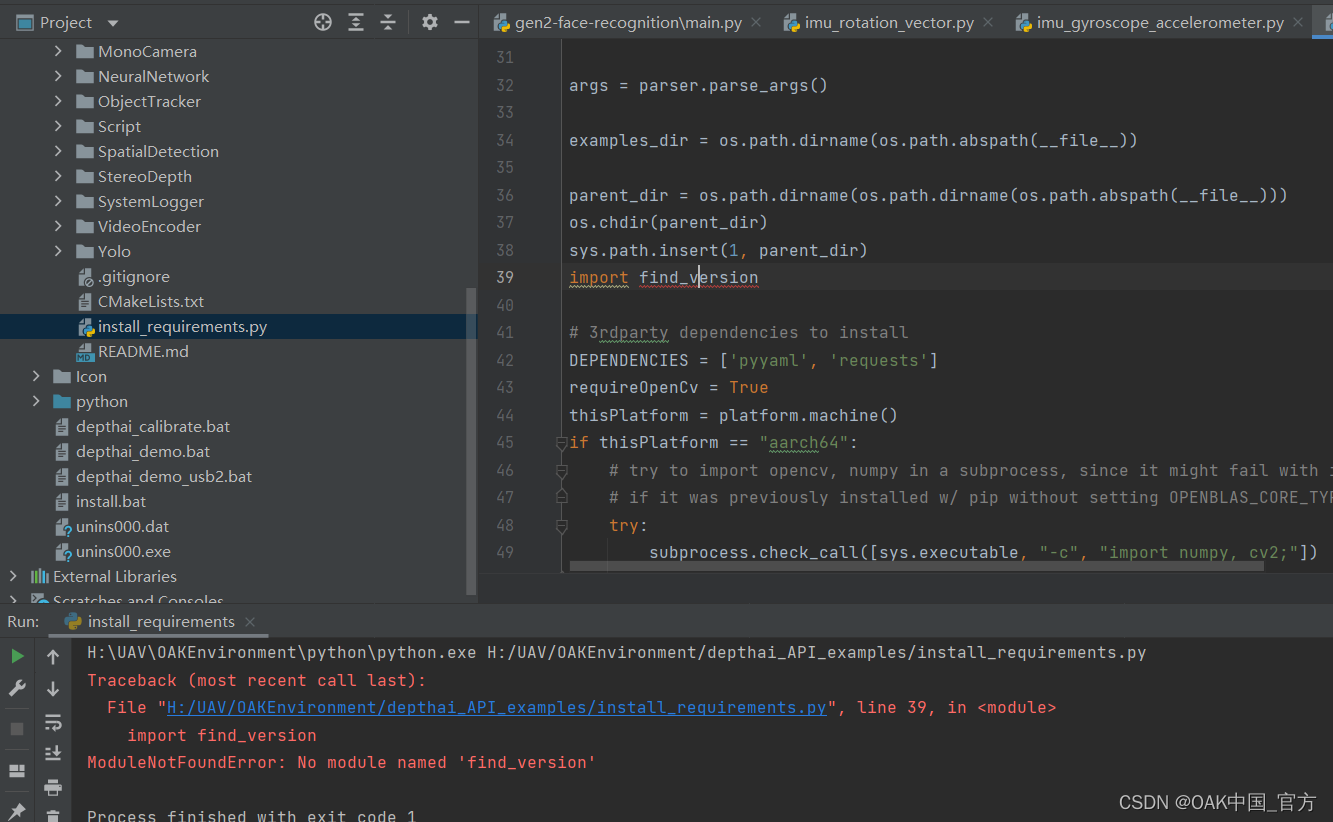
报错ModularNotFoundError: No module named ‘find_version’

Machine learning notes - convolutional neural network memo list

Detailed explanation of the difference between construction method and method

MySQL:Got a packet bigger than ‘max_ allowed_ packet‘ bytes
随机推荐
Video review pulsar summit Asia 2021, cases, operation and maintenance, ecological dry goods
山东大学项目实训(四)—— 微信小程序扫描web端二维码实现web端登录
基于SIC32F911RET6设计的腕式血压计方案
Install jupyter in the specified environment
Opencv CEO teaches you to use oak (V): anti deception face recognition system based on oak-d and depthai
Day41 process pool and thread pool
Pytorch installation for getting started with deep learning
Award winning survey streamnational sponsored 2022 Apache pulsar user questionnaire
1493. 删掉一个元素以后全为 1 的最长子数组
Why is it difficult to implement informatization in manufacturing industry?
机器学习笔记 - 卷积神经网络备忘清单
ERP体系的这些优势,你知道吗?
制作业信息化为什么难施行?
Fabric.js 動態設置字號大小
报错Output image is bigger(1228800B) than maximum frame size specified in properties(1048576B)
PD chip ga670-10 for OTG while charging
Design of wrist sphygmomanometer based on sic32f911ret6
[ERP system] how much do you know about the professional and technical evaluation?
Type-C蓝牙音箱单口可充可OTG方案
Strength and appearance Coexist -- an exclusive interview with Liu Yu, a member of Apache pulsar PMC