当前位置:网站首页>Finally understand what dynamic planning is
Finally understand what dynamic planning is
2022-07-05 22:49:00 【Thousands of miles in all directions】
Catalog
1.1 Warm up : How to say 10000 times “ I love you! ”
First gun : Basic questions : Count the total number of paths
Second gun : Optimize recursion using two-dimensional arrays
The third shot : Scrolling array : Replace two-dimensional array with one dimension
The fourth shot : Topic development : Minimum path sum
Fifth shot : Topic development : The minimum path of a triangle and
3 Understanding dynamic programming
DP The problem in the whole algorithm belongs to the upper middle , Most people may have been exposed for ten years and have not understood DP What is it . It doesn't seem to be used at work . Why should we always examine this , And more and more investigations ? Mainly because the Internet began to roll , Algorithm is the best tool to brush people , Let who go , No one has anything to say .
In this chapter, we will start from the basic problems and gradually expand , Fully explain several key issues related to dynamic planning , Let you really feel ” Dynamic programming , nothing more than this “. Then we will summarize the template of dynamic planning , Yes , Dynamic has problem-solving templates .
1.DP What the hell is that?
Although everyone knows dynamic programming (Dynamic Programming, abbreviation DP) difficult , But few people can tell what it is DP. And even if DP Few people understand the meaning of the concept of .
Now let's take a simple example to gradually disassemble this complex explanation .
1.1 Warm up : How to say 10000 times “ I love you! ”
First of all, let's feel what is double counting and memorized search .
Once participated in an online activity , See who says more “ I love you! ”, I wrote such a piece of code at that time :
public class FibonacciTest {
public static int count = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
fibonacci(20);
System.out.println("count:" + count);
}
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
System.out.println(" I love you! ");
count++;
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
}
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
return n;
else {
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
}
}This is the Fibonacci sequence , When n by 20 when ,count yes 21891 Time . And when n=30 It turns out that 2692537, That is, to be close to 270 ten thousand . If it's just Fibonacci series , We can cycle directly :
public static int count_2 = 0;
public int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 2) {
count_2++;
return n;
}
int f1 = 1;
int f2 = 2;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
count_2++;
sum = f1 + f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = sum;
}
return sum;
}n by 30 Time is only the accumulation of more than 20 numbers , But why is recursion as high as 270 Wan? ? Because there are a lot of repeated calculations , The bigger the number , The more you repeat . For example, when n=8 When , We can see that there are many repeated calculations in the following structure diagram :
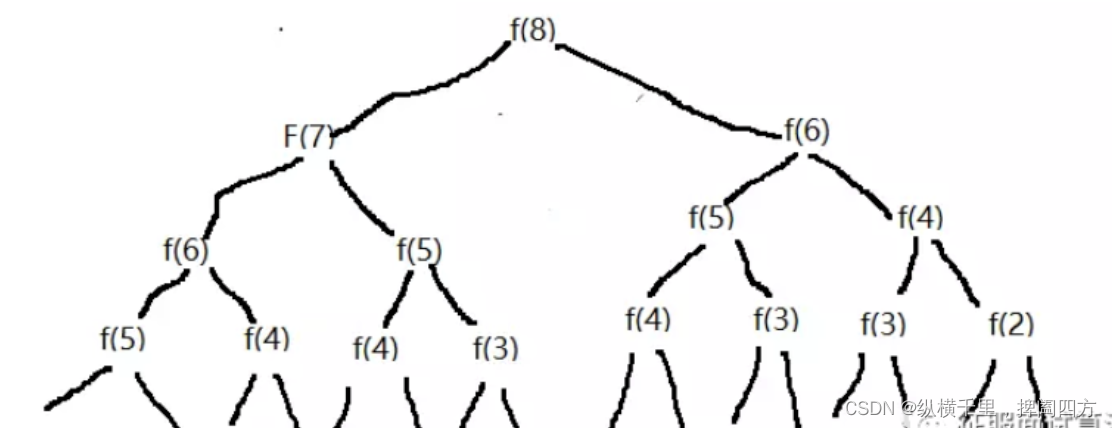
Above we are calculating f(8) when , You can see f(6)、f(5) And so on all need to calculate , This is the overlapping subproblem . How to optimize it ? You can see that the main problem here is that many data will be calculated frequently , If you save the calculation results to a one-dimensional array . hold n As our array subscript ,f(n) As value , That is to say arr[n] = f(n). When executing, if a certain position has been calculated, update the array value of the corresponding position , for example f(4) It's over , Save it to arr[4] in , When we need to calculate again f(4) When , We can judge f(4) Calculated , So read directly f(4) Value , No more recursive calculations . The code is as follows :
public static int[] arr = new int[50];
public static int count_3 = 0;
Arrays.fill(arr, -1);
arr[0] = 1;
int fibonacci(int n){
if (n == 2 || n == 1) {
count_3++;
arr[n] = n;
return n;
}
if (arr[n] != -1) {
count_3++;
return arr[n];
} else {
count_3++;
arr[n] = fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
return arr[n];
}
}In the code above , Check the array to see if it has been calculated before recursion , If the calculation is repeated , Just read it directly , This is called ” Memory search “, It's that simple .
2 Path cannon
Explain clearly DP, We should also analyze it with some examples , In this part, we analyze the problems related to multiple paths . The path problem itself is a hot topic , At the same time, it is easy to draw , Easy to understand , Can show step by step DP The connotation of .
First gun : Basic questions : Count the total number of paths
LeetCode62: A robot is in a m x n The top left corner of the grid ( The starting point is marked as “Start” ). The robot can only move down or right one step at a time . The robot tries to reach the bottom right corner of the grid ( In the figure below, it is marked as “Finish” ), Ask how many different paths there are in total ?
Example 1:
Input :m = 3, n = 7
Output :28
Example 2:
Input :m = 3, n = 2
Output :3
explain :
From the top left corner , All in all 3 Path to the bottom right .
1. towards the right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> towards the right
3. Down -> towards the right -> Down 
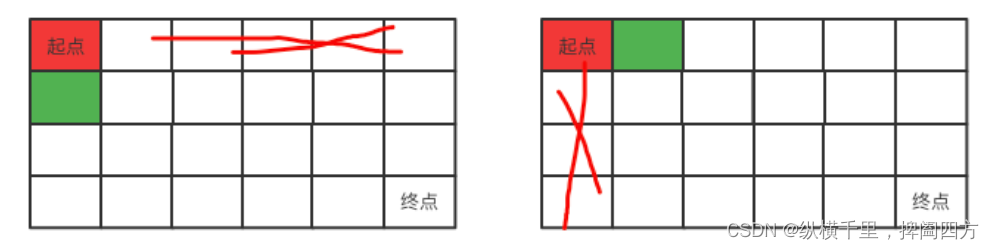
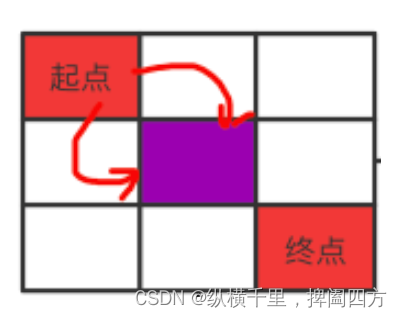
This problem is a classic recursive problem , First gun , Let's study how to solve this problem by recursion . As shown in the figure below , Every position from the starting point , Or to the right , Or down . Each will result in the reduction of the remaining interval by one row or column , Form two different intervals . Each interval can continue the above operations starting from the red dot , So this is a recursive process .
Red in the figure indicates the starting and ending points , Green indicates where to go next , Grey means you can't go anymore .
Let's start with one 3x2 To analyze :
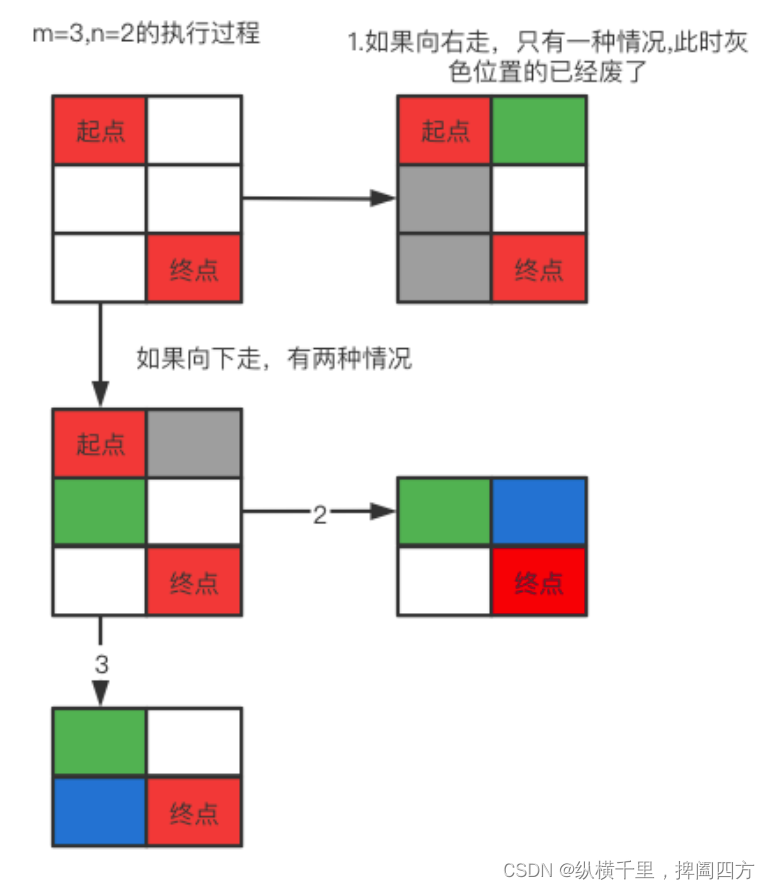
Our goal is from the beginning to the end , Because it can only be right or down , You can see from the figure :
1. If you go right , Is the figure 1 The situation of , There's a 3x1 Matrix , At this point, the two gray positions below the starting point will no longer be visited , Only go straight down from the green position , There is only one path .
2. If it's down , We can see that the one on the right of the original starting point can no longer be accessed , And the rest is another 2X2 Matrix , That is, from the green position to the red position in the figure , At this time, you can still choose right or down , There are two paths .
So the above situation adds up to a total 3 Kind of .
We can see from above , For one 3X2 Matrix , The total number of paths is counted separately from the starting point arr One 2X2 Array and a 1X3 Array of , Then add it up . If it's a little more complicated , It's a 3X3 The matrix of ? Let's just look at the picture :
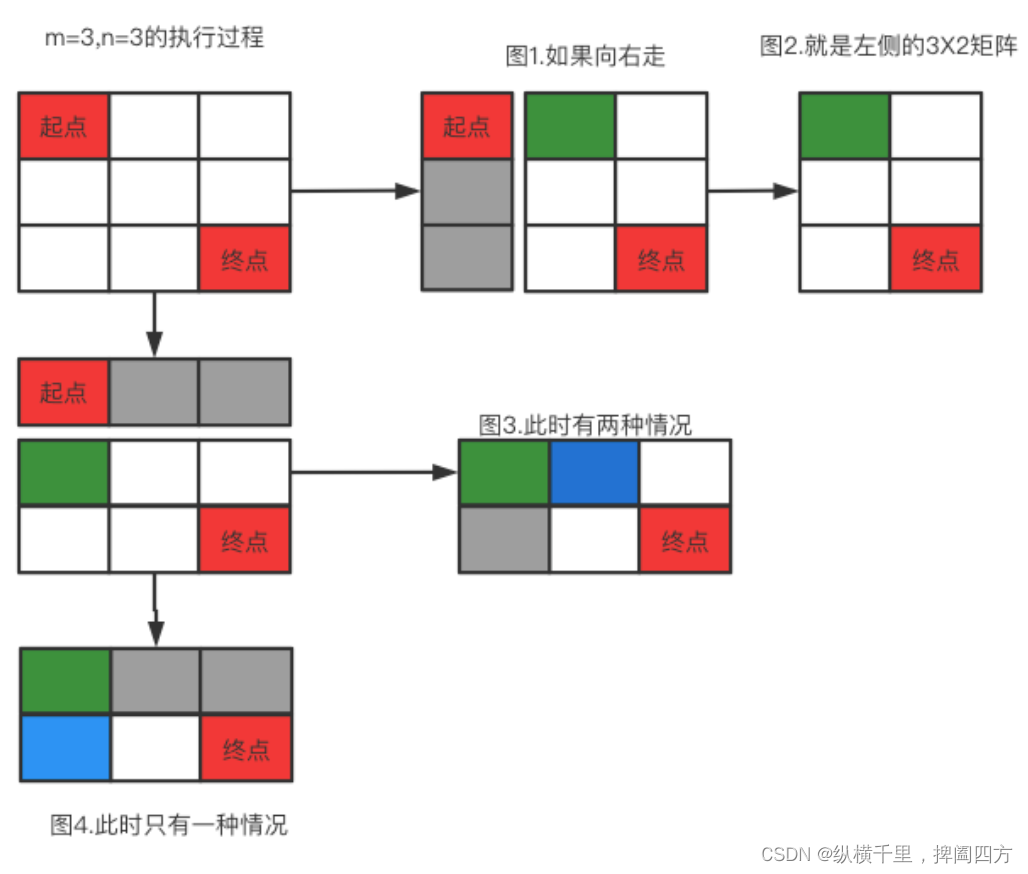
You can see , One 3X3 The next step of the matrix becomes a 3X2 perhaps 2X3 Matrix , And the total number of paths , It is also the sum of their respective paths .
therefore , For one mxn Matrix , The way to find the path search(m,n) Namely :
search(m-1,n)+search(m,n-1);Recursion means that the processing method remains unchanged , But the scale of the problem has decreased , So the code here is :
public class Solution {
public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) {
return search(m,n);
}
public int search(int m,int n){
if(m==1 || n==1){
return 1;
}
return search(m-1,n)+search(m,n-1);
}
}The above process , We can also express it with binary tree :
For example, for 3X3 Matrix , The process diagram is :
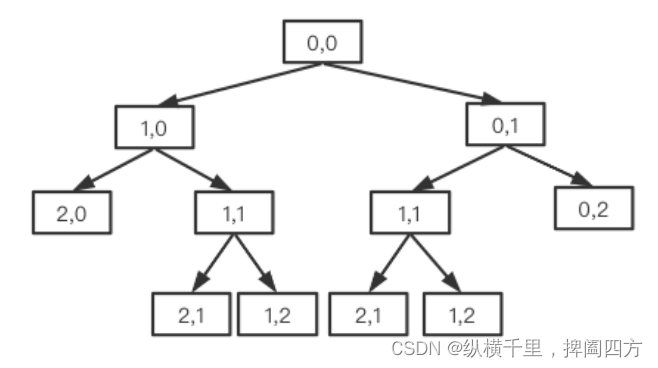
The total number of paths is the number of leaf nodes , In the picture is 6 individual , This is essentially the same as recursive traversal of binary trees .
Second gun : Optimize recursion using two-dimensional arrays
Second gun , Let's optimize the problem of recursion , Study how to combine two-dimensional array to realize memory search .
From the tree above, we can also see that there are repeated calculations in the process of recursion , for example {1,1} It appears twice , If it's a NXN Space , that {1,0} and {0,1} The subsequent calculation of is the same .
From the perspective of two-dimensional array , For example, in location (1,1) It's about , No matter from (0,1) still (1,0) arrival , Then there will be 2 Seed walking method , So you don't have to iterate every time to get the result .
So , We can use a two-dimensional array to carry out memory search , The calculated ones are recorded in the array , That's what it looks like :
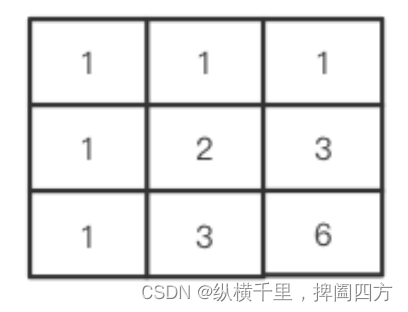
The number of each grid indicates that there are several ways to reach the current position from the starting point , So that we When calculating the total path, you can check whether the two-dimensional array has records , If there is a record, read it directly , No more calculations , In this way, double counting can be largely avoided , This is memory search .
Based on the above analysis , We can get two laws :
1. The first row and the first column are 1.
2. The value of other grids is the sum of the left and upper grids . For others m,n Lattice of , This conclusion is equally applicable , for example :
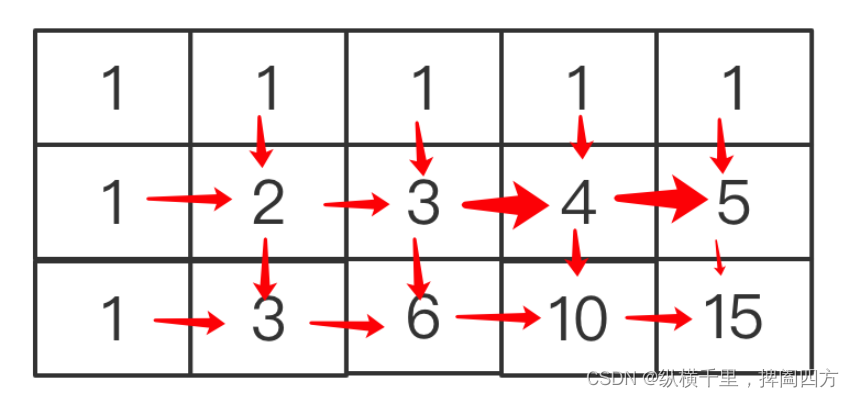
Like in the picture 4, There is something above 1 And on the left 3 Come by calculation ,15 It's on the top 5 And on the left 10 Come by calculation . If it's expressed in a formula, it's :
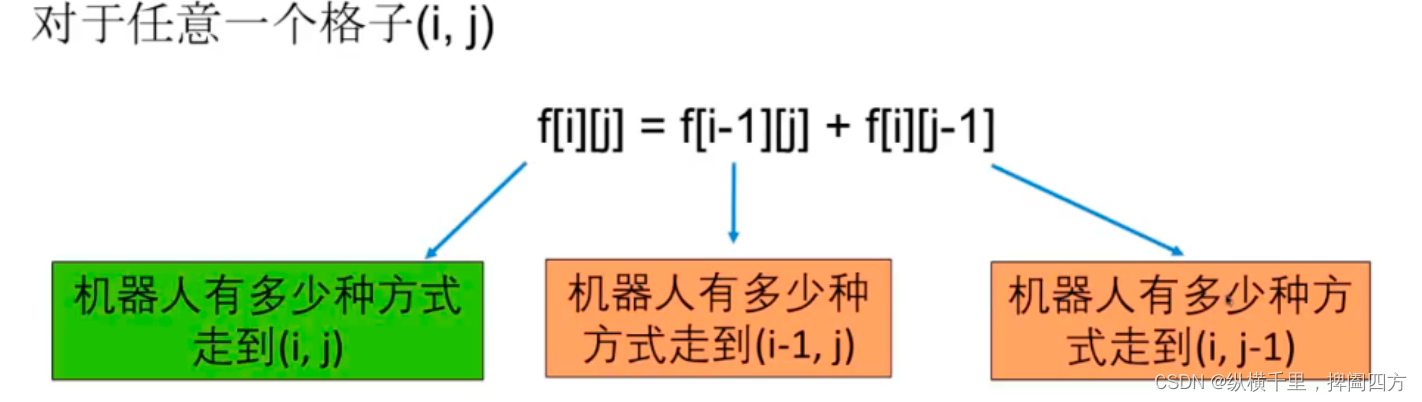
We can write the following code directly :
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[][] f = new int[m][n];
f[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j] + f[i][j - 1];
} else if (i > 0) {
f[i][j] = f[i - 1][j];
} else if (j > 0) {
f[i][j] = f[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return f[m - 1][n - 1];
}The third shot : Scrolling array : Replace two-dimensional array with one dimension
The third shot , We optimize this problem by scrolling the array . The above cache space uses a two-dimensional array , This takes up too much space , Can it be further optimized ?
Let's take a look at the above calculation process :
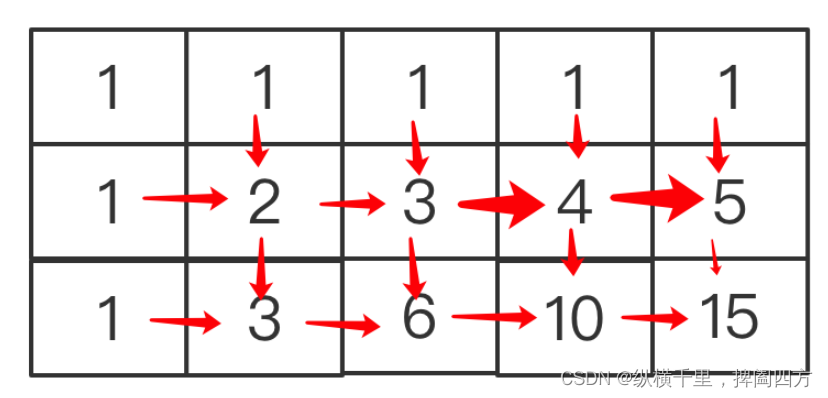
In the above figure, except for the first row and the first column 1 Outside , Each position is the sum of its left side and the petitioning grid , Then I can use a size of n One dimensional array of :
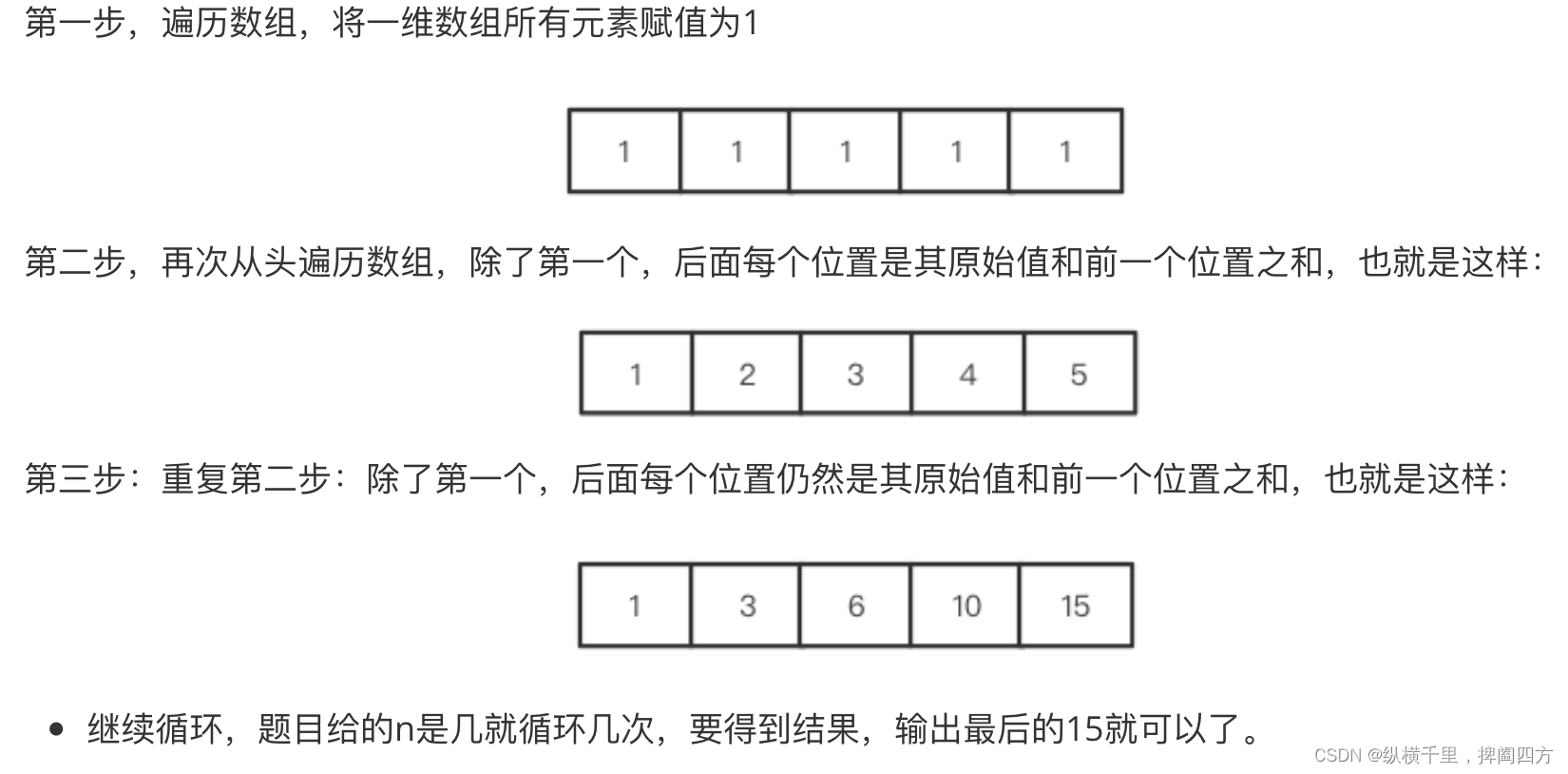
The above one-dimensional arrays are spliced together , Is it found that it is exactly the same as the two-dimensional array above ? Here we use a one-dimensional array to solve , This strategy of updating arrays repeatedly is Scrolling array . The formula is :
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1]That's what happened , The code is as follows :
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1);
for(int i = 1; i < m; ++i) {
for(int j = 1; j < n; ++j) {
// On the right side of the equation dp[j] It's from the last calculation , Add the one on the left dp[j-1] This is the current result
dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
} This topic covers DP Many aspects of , For example, repeat the sub problem 、 Memory search 、 Scrolling arrays, and so on . This is the simplest dynamic programming , But our plan here is dp[j] = dp[j] + dp[j - 1]; No complicated comparison and calculation .
This question is very important , Learn to understand recursion behind 、 Algorithms such as dynamic programming play a very important role .
The fourth shot : Topic development : Minimum path sum
There are two other important issues in the above topic that are not obvious : Optimal substructure , Let's combine another example to study .
LeetCode64. Given a... That contains a nonnegative integer m x n grid grid , Please find a path from the top left corner to the bottom right corner , Make the sum of the numbers on the path the smallest .
explain : You can only move down or right one step at a time . Example :
Input :grid = [[1,3,1],[1,5,1],[4,2,1]]
Output :7
explain : Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 The sum of is the smallest .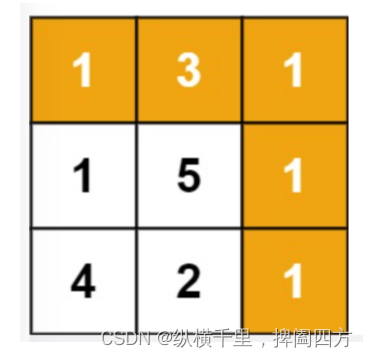
This question is based on the above question , Added the concept of path cost . Because of the limitation of the topic, we can only 「 Down 」 perhaps 「 To the right 」 Move , So we can transfer according to the current position Analyze :
The current position can only be accessed through 「 Down 」 Move to , That is to say
f[i][j] = f[i-1][j] + grid[i][j]The current position can only be accessed through 「 To the right 」 Move to , That is to say
f[i][j] = f[i][j-1] + grid[i][j]The current position can pass through 「 Down 」 Can also 「 To the right 」 Move , That is to say
f[i][j] = min(f[i][j-1],f[i-1][j]) + grid[i][j]
Update process of two-dimensional array , We can illustrate :
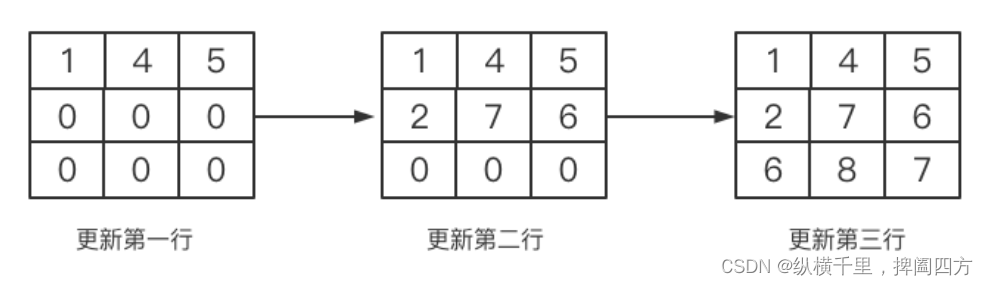
We can now introduce another conceptual state : The so-called status is to update the following table to the last two-dimensional array , The formula for calculating the back lattice through the front lattice is called the state transition equation . If expressed in mathematics, it is :
Definition f[i][j] For from (0,0) Start to reach the position (i,j) The minimum sum of . that f[m-1][n-1] That's our final answer ,f[0][0]=grid[0][0] It's an obvious starting point .
If you make f[i][j] From f(0,0) Go to the grid (i,j) The sum of the number of paths , Then use an expression to express the above relationship is :
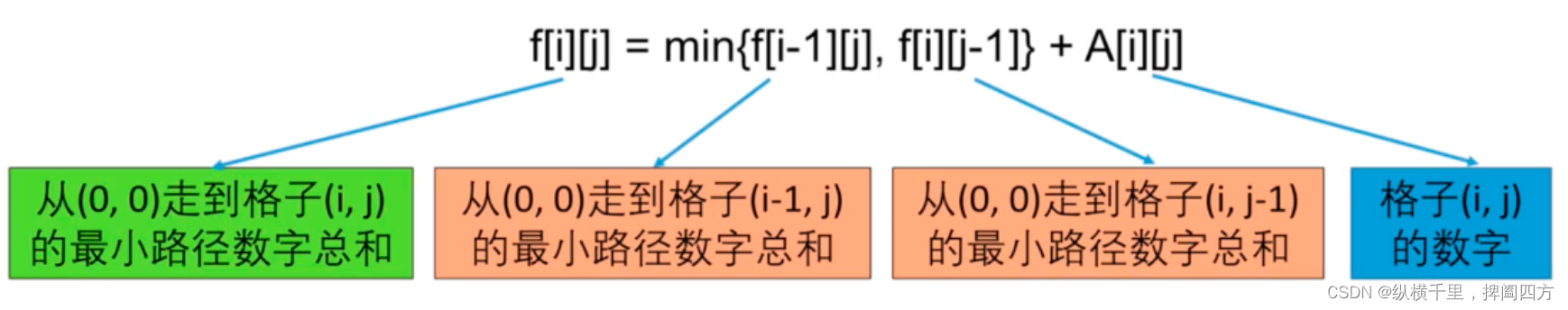
The so-called deterministic state transition equation is to find the recursive relationship , Usually we will start with the analysis of the change law at both ends , We will continue to analyze the following topics .
The code implementation of this problem is :
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] f = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0) {
f[i][j] = grid[i][j];
} else {
int top = i - 1 >= 0 ? f[i - 1][j] + grid[i][j] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int left = j - 1 >= 0 ? f[i][j - 1] + grid[i][j] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
f[i][j] = Math.min(top, left);
}
}
}
return f[m - 1][n - 1];
}Fifth shot : Topic development : The minimum path of a triangle and
This question is a simple variant of the above one ,LeetCode120. Given a triangle triangle , Find the smallest sum from the top down . Each step can only move to adjacent nodes in the next row . Adjacent nodes What I mean here is Subscript And The upper node subscript Equal to or equal to The upper node subscript + 1 Two nodes of . in other words , If it is in the subscript of the current line i , So the next step is to move to the subscript of the next line i or i + 1 .
Example 1:
Input :triangle = [[2],[3,4],[6,5,7],[4,1,8,3]]
Output :11
explain : As shown in the diagram below :
2
3 4
6 5 7
4 1 8 3
The minimum path sum from the top down is zero 11( namely 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11).Before looking at parsing , Let's see what this question means first . The question is 1.2 Simple transformation of the minimum path sum in ,
For the convenience of handling , We can deal with diagonal structure first .
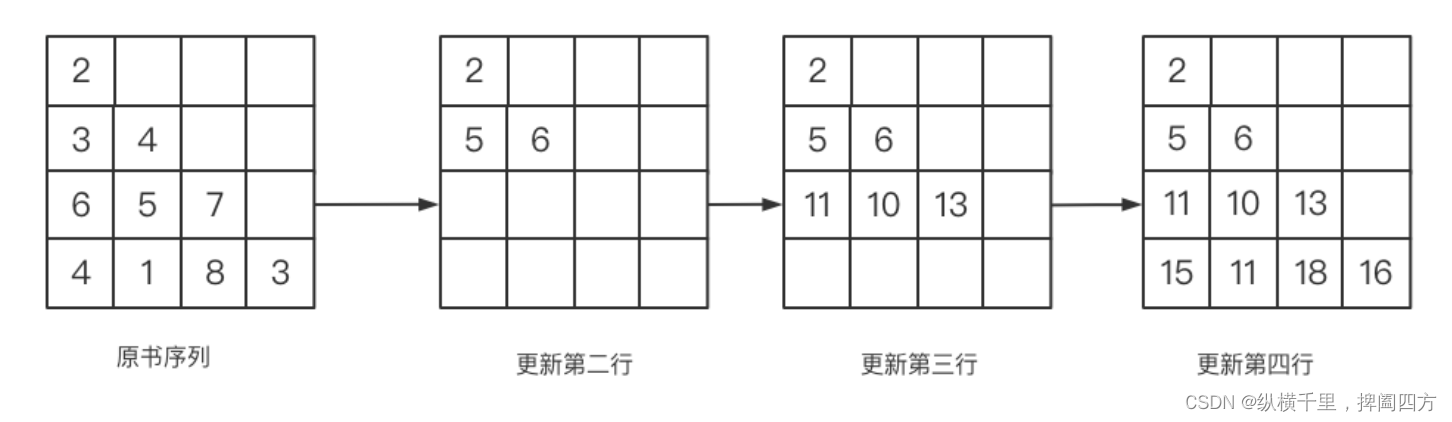
If you can figure out the picture above , You can write code directly , But we want to understand another concept through this topic ” No aftereffect “, Determine whether a topic can be used DP solve , We should analyze whether there is aftereffect . So-called No aftereffect is that we need to use a certain value to transfer a certain state , But I don't care how the value comes from . Add more * The expression of is : After the current state is determined , The subsequent state transition has nothing to do with the previous decision , So we can decide to use DP To solve the .
In the subject , Since it is the path from top to bottom , Then the last point must fall on the last line . For the value of a certain position in the last line , According to the meaning of the question, it can only be transferred from one position or one of the two positions in the previous line . meanwhile , We only focus on the cumulative value of the previous digit , In particular, what is the minimum cumulative value , It doesn't care what path the cumulative value result comes from , This is enough 「 No aftereffect 」 The definition of .
The next question is how to determine 「 State definition 」 Well ? This is to find a recursive relationship , We usually start with the change law at both ends . For this question , We can guess one by combining the two DP state :f[i][j] Represents the minimum path to a point and , that min(f[n-1][i])( The minimum value of the path sum of each column in the last row ) That's the answer. .
The following properties can be found through observation ( Make i For row coordinates ,j Column coordinates ):
Every line i have i+1 A digital (i from 0 Start )
As long as it's not the first column (j!=0) The number in position , Can pass. 「 upper left 」 Turn around
As long as it is not the last column of each row (j!=i) The number in position , Can pass. 「 upper 」 Transfer from
This process can promote and cover all locations , thus , The state transition equation can also enumerate every path without repetition , So the DP Status definitions are available , Code :
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> tri) {
int n = tri.size();
int ans = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[][] f = new int[n][n];
f[0][0] = tri.get(0).get(0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i + 1; j++) {
int val = tri.get(i).get(j);
f[i][j] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (j != 0) {
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j - 1] + val);
}
if (j != i){
f[i][j] = Math.min(f[i][j], f[i - 1][j] + val);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
ans = Math.min(ans, f[n - 1][i]);
}
return ans;
}There are other topics very similar to this one LeetCode931 topic ” The descent path is the smallest and “, as well as LeetCode1289 topic ” The descent path is the smallest and II“, Interested students can study .
3 Understanding dynamic programming
After so many examples above , We can finally completely analyze what is dynamic planning .
First ,DP What kind of problems can be solved ? Intuitively ,DP Generally, it is for you to find the most valuable , For example, the longest common subsequence , But the key is DP The subproblems of the problem are not independent , If recursive decomposition is used, direct decomposition will lead to exponential growth of repeated calculation ( Think about the warm-up question above ). and DP The greatest value is for Eliminate redundant , Accelerate Computing .
secondly , Strictly speaking ,DP To meet the 「 Whether there is aftereffect 」, That is, it can “ A bear breaks a stick , Just be present , No matter before ”, For a state , We can only focus on the value of the state , Without paying attention to how the state is transferred , Those meeting this requirement can consider using DP solve . To understand this , Let's take a look at this problem :
The problem of the above path , Go from the top left corner to the bottom right corner , We set two questions , Which is the dynamic programming problem :
A Ask how many ways to walk B Output all moves
We say that dynamic programming is non backward , Only record the quantity , Anyway , therefore A yes DP problem , and B Out-of-service DP. If you understand the principle of backtracking in the previous chapter , I know that backtracking can record all paths , therefore B It's a question of backtracking .
to flash back : Can solve , But the solution efficiency is not high
DP: High calculation efficiency , But we can't find a path that meets the requirements .
Therefore, the most important thing to distinguish between dynamic planning and backtracking is : Dynamic programming only cares about the current results , It doesn't matter how it came , Therefore, dynamic planning cannot obtain a complete path , This is different from backtracking , Backtracking can obtain one or even all complete paths that meet the requirements .
DP The basic idea of is to decompose the problem to be solved into several sub problems , Let's start with the subproblem , Then we can get the solution of the original problem from these sub problems . Since you're looking for “ most ” What must be done is to look for all the possibilities , And then choose “ most ” the , Is that why DP A lot of judgment logic in the code will be covered min() perhaps max(), And that's why DP One of the reasons that seems difficult .
Next , Since it is exhausting , Why should there be DP The concept of ? This is because there are a lot of repeated calculations in the process of enumeration , inefficiency , So we should use memory search and other methods to eliminate unnecessary calculation , The so-called memory search is to store the calculated results in the array first , If you read directly later, you will not repeat the calculation .
Next , Since memorization can solve the problem , Why? DP It's so hard , because DP The problem must have “ Optimal substructure ”, Only in this way can we get accurate results in memory . As for what is the optimal substructure , We still have to wait for the specific issues later .
Next , With the optimal substructure , We also need to write the correct “ State transition equation ”, In order to correctly exhaust . That is, recursive relation , But in DP in , Most recursion can be achieved through arrays , Therefore, the code structure is generally like this for loop , This is it. DP Basic template of code :
// initialization base case, That is, the first few scenes , There are several enumerations
dp[0][0][...]=base case
// Make a state transition
for state 1 state 1 All values of
for state 2 in state 2 All values of
for ....
dp[ state 1][ state 2][...]= Find the maximum value Max( choice 1, choice 2,...)
}We usually write dynamic planning with only oneortwo layers , It's not too deep , Therefore, you will find that the code of dynamic planning is particularly concise .
There are many common types of Dynamic Planning , In form , There are coordinate types 、 Sequence type 、 Division type 、 Interval type 、 Knapsack type, game type and so on . However, there is no need to deliberately study what these types mean , Because the basic idea of solving problems is the same . As a general rule , There are three basic types of dynamic programming problems :
1. Count related , For example, find out how many ways to go to the lower right corner , How many ways to choose K The number makes *** wait , And don't care about the specific path .
2. Find the maximum and minimum , At most, at least, wait , For example, the maximum number and 、 The longest ascending subsequence 、 Longest common subsequence 、 The longest palindrome sequence and so on .
3. Seeking existence , For example, the game of taking stones , Whether the first is sure to win ; Can you choose K The number makes ** wait .
But no matter what kind of problem-solving template is also similar , All are :
First step : Determine the status and sub problems , That is to say, all the possibilities of a certain position , about DP, The last step of most topic analysis is easier , Get the recurrence relation , At the same time, the problem is transformed into a sub problem .
The second step : Determine the state transfer equation , That is, what the array should store . Many times, after the state is determined , The state transition equation is also determined , Therefore, we can also take the first and second steps as a step .
The third step : Determine initial conditions and boundary conditions , Be careful , Try to be considerate .
Step four : Calculate from small to large :
f[0]、f[1]、f[2]...
Although we calculate from f[0] Start , But for most DP problem , Analyzing the last one first is often more conducive to finding the state expression , Therefore, the following questions are basically
Find recursion from right to left , Calculate from left to right This is also our analysis DP The core template of the problem .
The template above , In vernacular, it means : We should do it from beginning to end , You have to put an array in your brain , It depends on the meaning of each element of this array , It depends on who calculates the position of each array , Then fill the array from small to large , Finally, let's see which position is the result we want .
Explain in more detail :
We should do it from beginning to end , You have to put an array in your brain ( It may be one dimension , It may also be two-dimensional ), Look at what each element of this array represents What does it mean ( That is the state ), It depends on who calculates the position of each array ( State transition equation ), Then fill the array from small to large ( From small to large , Realize memory search ), Finally, let's see which position is the result we want .
边栏推荐
- Unity Max and min constraint adjustment
- Paddy serving v0.9.0 heavy release multi machine multi card distributed reasoning framework
- 鏈錶之雙指針(快慢指針,先後指針,首尾指針)
- Distributed solution selection
- 一文搞定JVM常见工具和优化策略
- [error record] file search strategy in groovy project (src/main/groovy/script.groovy needs to be used in the main function | groovy script directly uses the relative path of code)
- 第一讲:蛇形矩阵
- Distance entre les points et les lignes
- Metaverse Ape上线倒计时,推荐活动火爆进行
- Nacos installation and service registration
猜你喜欢
d3dx9_ What if 29.dll is missing? System missing d3dx9_ Solution of 29.dll file
How can easycvr cluster deployment solve the massive video access and concurrency requirements in the project?

Google Maps case
傅里叶分析概述
Arduino 测量交流电流
![[speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on MATLAB low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1709]](/img/f4/4d09dc05f5789b980ebd23cc352f8b.jpg)
[speech processing] speech signal denoising and denoising based on MATLAB low-pass filter [including Matlab source code 1709]

谷歌地图案例
【无标题】
![[error record] groovy function parameter dynamic type error (guess: groovy.lang.missingmethodexception: no signature of method)](/img/3e/34b45cd14f0302bb381efd244bc68f.jpg)
[error record] groovy function parameter dynamic type error (guess: groovy.lang.missingmethodexception: no signature of method)
鏈錶之雙指針(快慢指針,先後指針,首尾指針)
随机推荐
Global and Chinese market of water treatment technology 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Evolution of APK reinforcement technology, APK reinforcement technology and shortcomings
Hcip day 16
Binary tree (II) -- code implementation of heap
[error record] file search strategy in groovy project (src/main/groovy/script.groovy needs to be used in the main function | groovy script directly uses the relative path of code)
Metasploit (MSF) uses MS17_ 010 (eternal blue) encoding:: undefined conversionerror problem
Google Maps case
50. Pow(x, n). O(logN) Sol
2022软件测试工程师涨薪攻略,3年如何达到30K
[secretly kill little buddy pytorch20 days] - [Day2] - [example of picture data modeling process]
Record several frequently asked questions (202207)
从 1.5 开始搭建一个微服务框架——日志追踪 traceId
Overview of Fourier analysis
All expansion and collapse of a-tree
Global and Chinese markets for reciprocating seal compressors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
FBO and RBO disappeared in webgpu
如何快速体验OneOS
Codeforces Global Round 19
The code generator has deoptimised the styling of xx/typescript.js as it exceeds the max of 500kb
a-tree 树的全部展开和收起