当前位置:网站首页>多线程并发之CountDownLatch阻塞等待
多线程并发之CountDownLatch阻塞等待
2022-07-01 16:33:00 【鱼找水需要时间】
1. 简介
CountDownLatch中count down是倒数的意思,latch则是门闩、锁住的含义。整体含义可以理解为倒数的门栓。CountDownLatch的作用也是如此,在构造CountDownLatch的时候需要传入一个整数n(必须>0),在这个整数“倒数”到0之前,主线程需要等待在门口,而这个“倒数”过程则是由各个执行线程驱动的,每个线程执行完一个任务“倒数”一次。总结来说,CountDownLatch的作用就是等待其他的线程都执行完任务,必要时可以对各个任务的执行结果进行汇总,然后主线程才继续往下执行。
CountDownLatch主要有两个方法:countDown()和await()。countDown()方法用于使计数器减一,其一般是执行任务的线程调用,await()方法则使调用该方法的线程处于等待状态,其一般是主线程调用。这里需要注意的是,countDown()方法并没有规定一个线程只能调用一次,当同一个线程调用多次countDown()方法时,每次都会使计数器减一;另外,await()方法也并没有规定只能有一个线程执行该方法,如果多个线程同时执行await()方法,那么这几个线程都将处于等待状态,并且以共享模式享有同一个锁。
2. 方法API
方法:
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| await() | 使当前线程进入同步队列进行等待,直到latch的值被减到0或者当前线程被中断,当前线程就会被唤醒。 |
| await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 等待timeout时间后,count的值还不是0,不再等待,那么将继续执行 |
| countDown() | 使latch的值减1,如果减到了0,则会唤醒所有等待在这个latch上的线程。 |
| getCount() | 获得latch的数值。 |
3. 使用
3.1 await()
示例:
CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(3);
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务1
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown();//确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务2
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown();//确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t2").start();
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务3
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); } catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown(); //确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t3").start();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
count.await(); // 等待任务执行
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务执行完成,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
结果:

3.2 boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
boolean await(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)示例:
CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(3);
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务1
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("task1 over");} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown();//确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务2
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println("task2 over");} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown();//确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t2").start();
new Thread(()->{
//处理业务3
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println("task3 over");} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); } finally {
count.countDown(); //确保每个任务执行完递减
}
}, "t3").start();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean await = count.await(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);// 指定等待时间,如果当前有任务未执行完成则返回false
System.out.println("所有任务是否执行完成:" + (await ? "是" : "否"));
System.out.println("计数器值为:" + count.getCount());
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("任务执行完成,耗时:" + (endTime - startTime) + "毫秒");
分析:
开启三个线程去执行任务,任务1、任务2、任务3耗时依次为1s、2s、3s
计数器await等待2s,如果2s后计数器值不为0(即三个任务中有任务未执行完成),那么就返回false。可以用在一些比较耗时长的任务上,例如调用第三方接口、业务线比较长,当超过指定时间后就当作失败处理,避免服务一直处于等待阻塞状态。
结果:

4. CountDownLatch和Thread.join()方法的区别
1、
CountDownLatch的作用就是允许一个或多个线程等待其他线程完成操作,看起来有点类似join()方法,但其提供了比join()更加灵活的API。2、
CountDownLatch可以手动控制在n个线程里调用n次countDown()方法使计数器进行减一操作,也可以在一个线程里调用n次执行减一操作。 而join()的实现原理是不停检查join线程是否存活,如果join线程存活则让当前线程永远等待。所以两者之间相对来说还是CountDownLatch使用起来较为灵活。
5. CountDownLatch的不足
CountDownLatch是一次性的,计算器的值只能在构造方法中初始化一次,之后没有任何机制再次对其设置值,当CountDownLatch使用完毕后,它不能再次被使用。
6. 扩展
如果采用多线程异步任务Future,通过CompletableFuture.allOf也可以实现同样的效果,阻塞等待任务执行结果,参考文章多线程Future,CompletableFuture
边栏推荐
- String类
- How to solve the problem that the battery icon of notebook computer does not display
- Zabbix2.2 monitoring system and application log monitoring alarm
- Today, at 14:00, 15 ICLR speakers from Hong Kong University, Beihang, Yale, Tsinghua University, Canada, etc. continue!
- 机器学习11-聚类,孤立点判别
- 剑指 Offer II 015. 字符串中的所有变位词
- Tutorial on the principle and application of database system (003) -- MySQL installation and configuration: manually configure MySQL (Windows Environment)
- Redis6.0 new features
- Advantages, values and risks of chain games compared with traditional games
- Basic use of MySQL
猜你喜欢

Redis Distributed Lock

Tutorial on principles and applications of database system (006) -- compiling and installing MySQL 5.7 (Linux Environment)
![[flask introduction series] cookies and session](/img/2e/d50e0a032c4ec48935cb5df206a29b.png)
[flask introduction series] cookies and session

Redis 分布式鎖
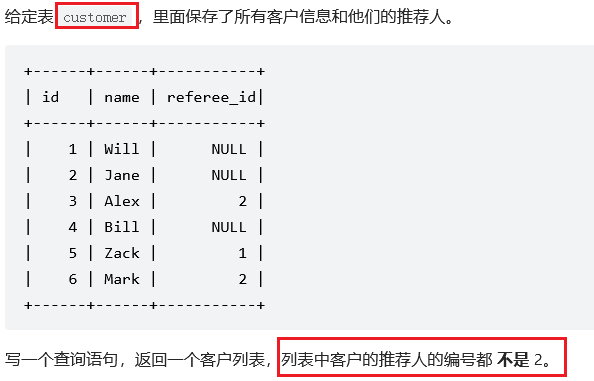
sql刷题584. 寻找用户推荐人
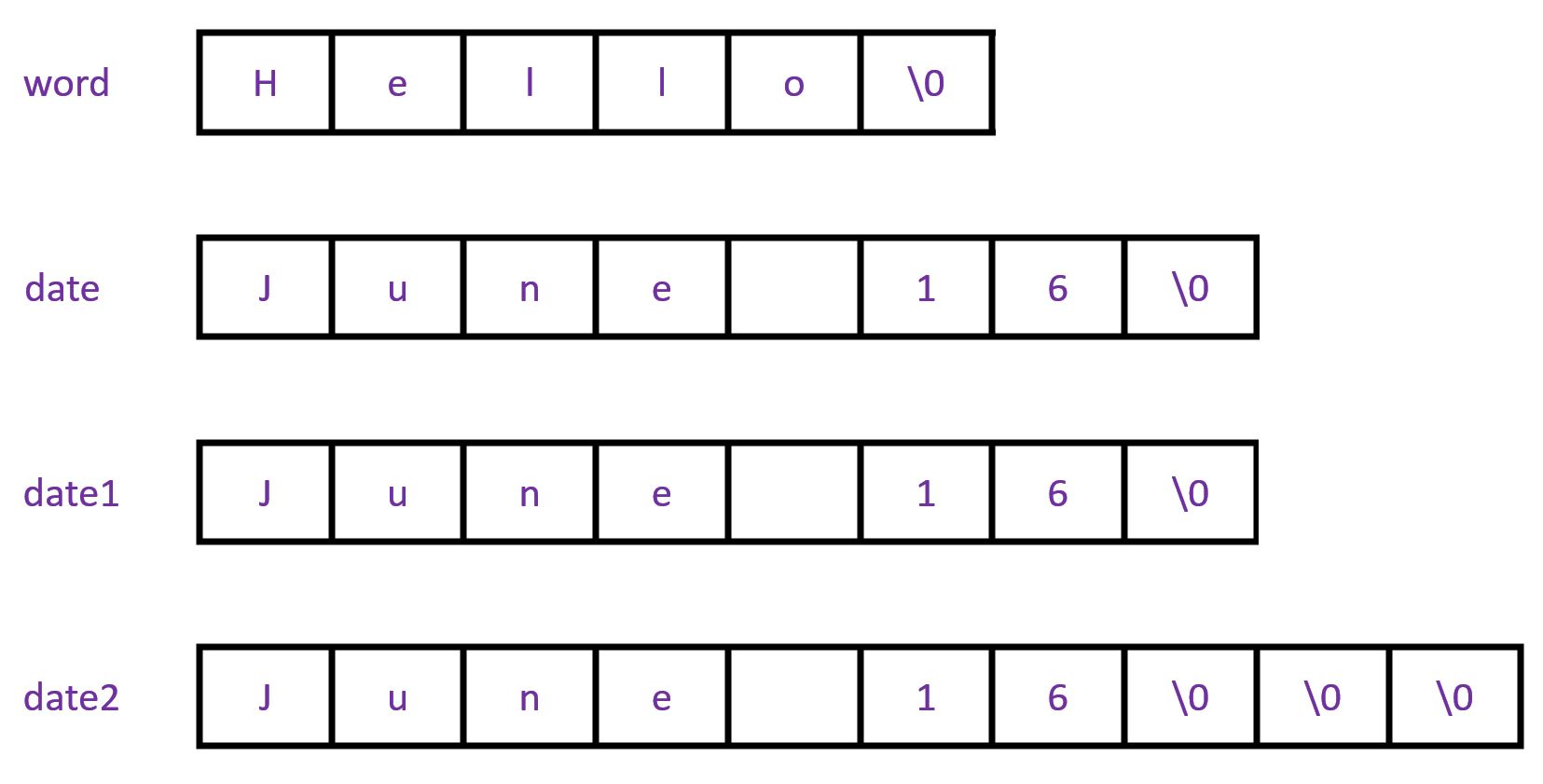
【C语言基础】12 字符串
巴比特 | 元宇宙每日必读:奈雪币、元宇宙乐园、虚拟股票游戏...奈雪的茶这波“操作拉满”的营销活动你看懂了吗?...

How to use etcd to realize distributed /etc directory
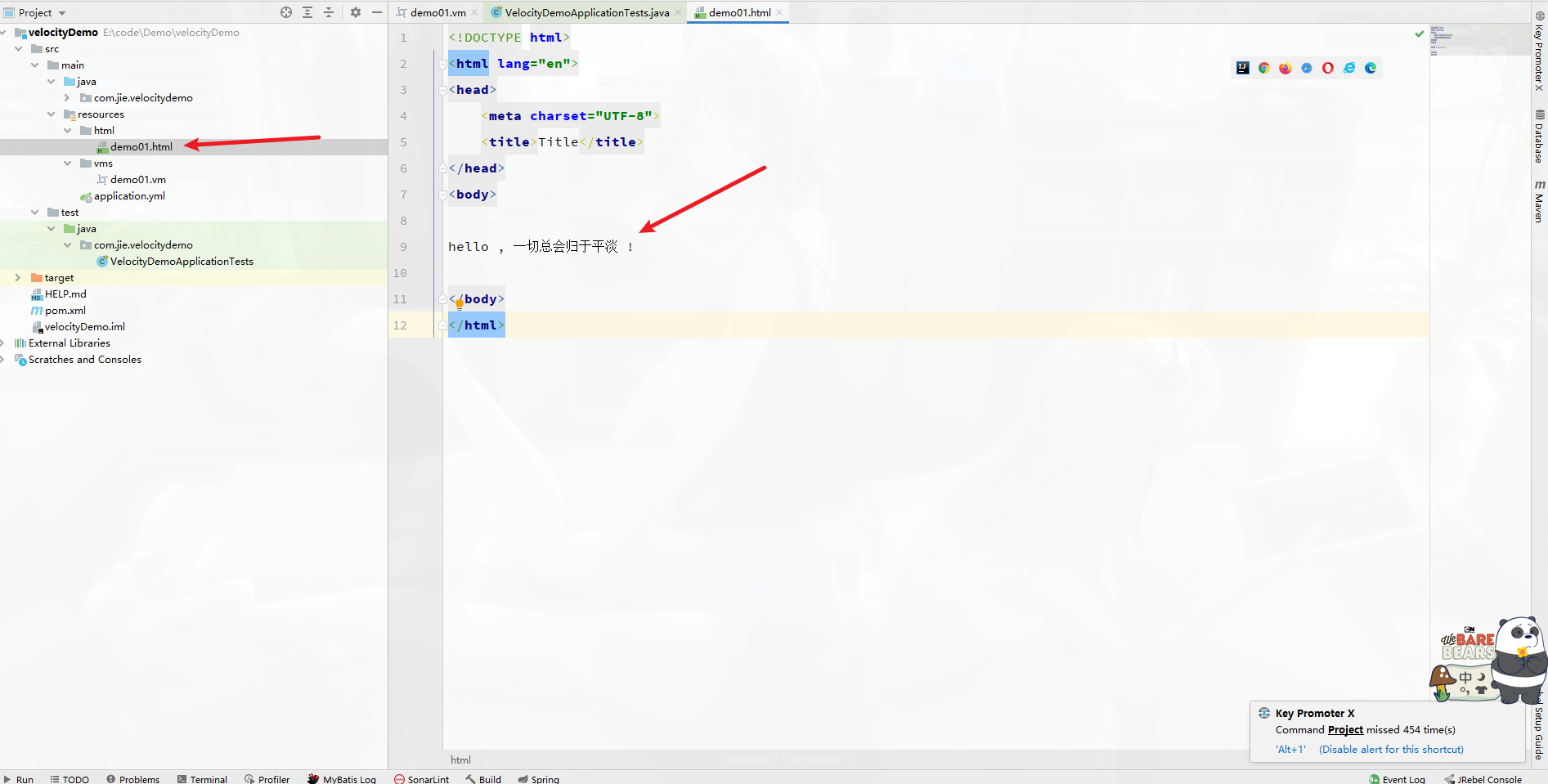
模板引擎Velocity 基础

Tutorial on the principle and application of database system (002) -- MySQL installation and configuration: MySQL software uninstallation (Windows Environment)
随机推荐
美国国家安全局(NSA)“酸狐狸”漏洞攻击武器平台技术分析报告
[kotlin] Introduction to higher-order functions
Redis distributed lock
为国产数据库添砖加瓦,StoneDB 一体化实时 HTAP 数据库正式开源!
剑指 Offer II 105. 岛屿的最大面积
判断链表是否是回文链表
How to maintain the laptop battery
China nylon 11 industry research and future forecast report (2022 Edition)
Mlperf training v2.0 list released, with the same GPU configuration, the performance of Baidu PaddlePaddle ranks first in the world
Jojogan practice
String类
GaussDB(for MySQL) :Partial Result Cache,通过缓存中间结果对算子进行加速
China BMS battery management system Market Research Report (2022 Edition)
How to solve the keyboard key failure of notebook computer
Rhcsa Road
String class
模板引擎Velocity 基础
sql刷题586. 订单最多的客户
What are the differences between PHP and DW
6月刊 | AntDB数据库参与编写《数据库发展研究报告》 亮相信创产业榜单