当前位置:网站首页>Source code analysis and practical testing openfeign load balancing
Source code analysis and practical testing openfeign load balancing
2022-06-10 19:17:00 【Natural player】
1 origin
Make up lessons .
I have been in a hurry to catch up with the progress ,
It only combs the micro service architecture and how to use the components in these architectures ,
However , Don't know how it works ,
I am still too weak , Can't stand the storm ,
therefore , Want to make yourself stronger , Continue to study the source code .
There's another reason , Recently saw K8S, And practice K8S Deploy SpringBoot service ,
Find out , You can use it directly K8S Load balancing ,
therefore , I think of ,Spring I also have load balancing , How is it realized ?
therefore , With this article .
2 Source code analysis
2.1 How to find the entrance
We know ,
When development students use SpringBoot In development ,
Some... Are not configured Bean, however , You can use these directly Bean,
Just explain ,SpringBoot These are automatically assembled at startup Bean,
OpenFeign The same goes for load balancing ,
The developer did not configure the load balancing policy , however , Use OpenFeign It can be balanced automatically ,
therefore ,OpenFeign The load balancing of is accomplished automatically through automatic assembly ,
therefore , Find the automatic assembly class for load balancing ,
Get into OpenFeign Source code , Found LoadBalancer Automatic assembly class , The source code is shown in the figure below .
Location :org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.loadbalancer.FeignLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration
This class is an automatic assembly , Instantiation is based on LoadBalancerClient Of Client Realization ,
LoadBalancerClient It's the interface , I.e. implementation LoadBalancerClient.
2.2 Look for load balancing strategies
Through the load balancing entry class FeignLoadBalancerAutoConfiguration, We see a lot of annotations in the logo ,
What we need to pay attention to LoadBalancerClientFactory Load balancing factory ,
How do I know ?
Go in one by one .
2.2.1 Load balancing client factory
What does this factory do ?
Guess from the name of the factory , It should be equipped with a load balancing client .
below , Put on your work clothes , Enter the load balancing factory !
First, let's look at what's in the factory ?
The source code is shown in the figure below , It can be seen from the notes , This factory is the production client 、 Load balancing and client configuration instances .
He creates a for each client name Spring Application context , And extract as needed .
Location :org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.support.LoadBalancerClientFactory
2.2.2 Load balancing client configuration
Pass the above figure , Read... Carefully , It's not hard to find out ,
The constructor of the factory LoadBalancerClientFactory()
By inheritance NamedContextFactory<LoadBalancerClientSpecification> instantiate ,
and LoadBalancerClientSpecification Specify the load balancing client ,
therefore , You can take a look at the classes used :LoadBalancerClientConfiguration.class,
guess , This class specifies the load balancing policy .( Actually , You can't know until you click in , belated effort )
Location :org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClientConfiguration
The source code of this class is shown in the following figure , We can know from the source code ,
Created Bean:reactorServiceInstanceLoadBalancer The load balancing strategy used is “ polling ” The way ,
RoundRobinLoadBalancer.
2.3 “ polled ” Load balancing strategy
Old rules , Enter the source code to view the implementation ,
Look at this. “ polling ” How to implement the load balancing strategy of ?
Location :org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.RoundRobinLoadBalancer#RoundRobinLoadBalancer(org.springframework.beans.factory.ObjectProvider<org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.ServiceInstanceListSupplier>, java.lang.String)
The method of the first layer is shown in the figure below ,
Here we focus on the third parameter :new Random().nextInt(1000)
The randomly generated value range is [1, 1000] Seeds , Used to balance clients , Instead of polling sequentially .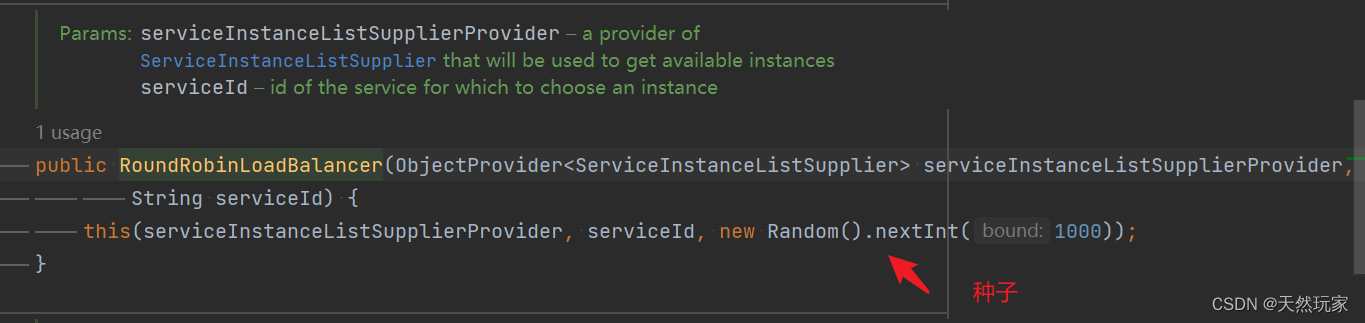
The instantiated parameters are shown in the following figure ,
position As a seed .
Next , See how this seed is used for balancing ,
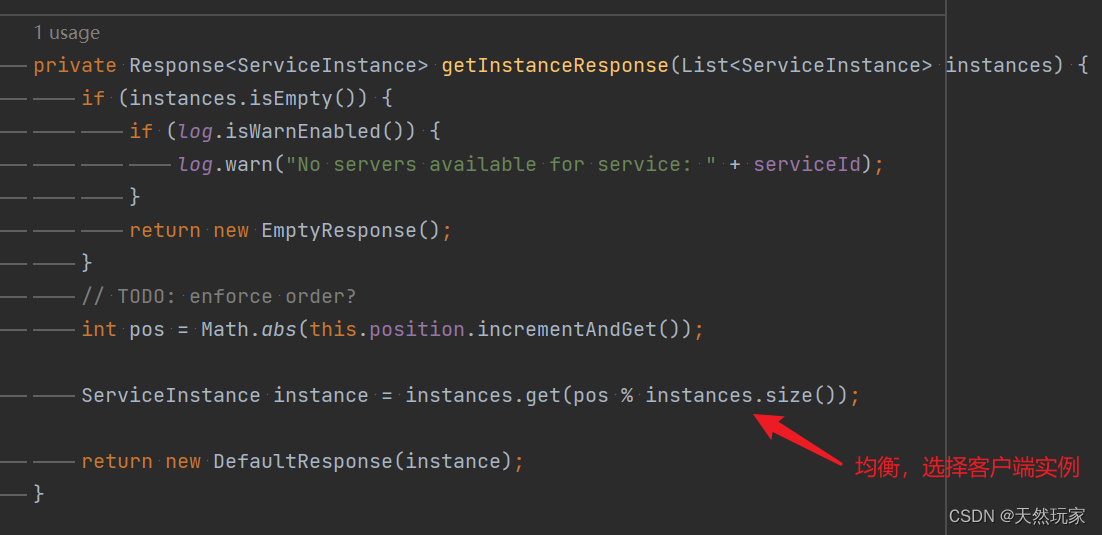
Method call path :choose-》processInstanceResponse-》getInstanceResponse,
therefore , The final equilibrium logic is :getInstanceResponse
Location :org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.RoundRobinLoadBalancer#getInstanceResponse
In equilibrium logic , There is one TODO: enforce order? Whether to force equilibrium order ?
The equilibrium used here , It's not sequential equilibrium ,
Instead, we use random seed and service quantity to get the remainder (pos%servcie.size), To decide which service to balance requests to .
Come here , complete OpenFeign Load balancing exploration .
Let's verify OpenFeign Load balancing of .
3 practice
The service architecture of this experiment is shown in the figure below .
There are three modules : Registry Center (Eureka)、 consumer (tutorial) And producers (spring-boot-template, Three ).
| Serial number | modular | describe |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Registry Center | What is drawn here is Eureka colony , however , Actual experimental process , With only one Eureka service |
| 2 | consumer | Through integration OpenFeign and LoadBalancer Call producer , verification LoadBalancer Load balancing function of |
| 3 | producer | Provide external interface , Sign up to Eureka, Other services can be provided through OpenFeign call |

3.1 rely on
SpingCloud edition :2020.0.3
therefore , Integrate Eureka after , You need to change the default Ribbon remove ,
add to SpringCloud Load balancing of .
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
<version>2.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-loadbalancer</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2020.0.3</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
3.2 Configure consumers (Consumer)FeignClient: service A
service A You need to call the same registry (Eureka For experiment ) Service for B,
therefore , Need to be in service A(tutorial) Configure service in B Of Feigin client , To invoke the service B(spring-boot-template),
service A(tutorial) Configured in FeiginClient As shown below ,
adopt @FeignClient(value = “spring-boot-template”) Specify the producer (Provider).
package com.monkey.tutorial.common.rpc;
import com.monkey.tutorial.common.constant.MicroServiceApiConstant;
import com.monkey.tutorial.common.constant.MicroServiceNameConstant;
import com.monkey.tutorial.common.response.Response;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
/** * FeignTemplate The service call . * * @author xindaqi * @date 2021-12-22 10:01 */
@FeignClient(value = "spring-boot-template")
public interface IFeignTemplateService {
/** * Test interface . * * @return test result */
@RequestMapping(MicroServiceApiConstant.API_GET_TEST)
Response<String> feign1Test(@RequestParam("msg") String msg);
@RequestMapping(MicroServiceApiConstant.API_FEIGN_TEST)
String feign2Test();
}
3.3 Enable FeignClient
package com.monkey.tutorial;
import com.monkey.tutorial.common.constant.MicroServiceNameConstant;
import io.micrometer.core.instrument.MeterRegistry;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.actuate.autoconfigure.metrics.MeterRegistryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.annotation.LoadBalancerClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.loadbalancer.core.RandomLoadBalancer;
import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.EnableFeignClients;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
@EnableFeignClients
@ServletComponentScan
public class TutorialApplication {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TutorialApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TutorialApplication.class, args);
logger.info("Tutorial Successful startup ");
}
}
3.4 Configure producers (Provider): service B
here , Running services from multiple producers on a single machine ,
Use 3 A producer :p1,p2 and p3
3.4.1 The configuration file
- application.yml
spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
application:
name: spring-boot-template
profiles:
active: dev
web:
resources:
static-locations: classpath:/resources/
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:/config/mybatis-config.xml
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
logging:
config: classpath:config/logback.xml
Many configurations have been streamlined in each producer ,
Only necessary configurations are given : port ( Used to differentiate services )、Eureka( Sign up to Eureka)
- application-p1.yml
server:
port: 9321
servlet:
session:
timeout: PT10S
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8001/eureka/eureka
- application-p2.yml
server:
port: 9322
servlet:
session:
timeout: PT10S
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8001/eureka/eureka
- application-p3.yml
server:
port: 9323
servlet:
session:
timeout: PT10S
eureka:
client:
fetch-registry: true
register-with-eureka: true
service-url:
defaultZone: http://localhost:8001/eureka/eureka
3.4.2 Producer interface
package com.monkey.springboottemplate.api;
import com.monkey.springboottemplate.common.enms.BizExceptionResponseCodeEnums;
import com.monkey.springboottemplate.common.exception.BizException;
import com.monkey.springboottemplate.common.response.Response;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import static com.monkey.springboottemplate.common.constant.DigitalConstant.ONE;
/** * Test interface . * * @author xindaqi * @date 2021-04-30 18:01 */
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1")
public class TestApi {
@GetMapping("/get/test")
public Response<String> getTest(@RequestParam("msg") String msg, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
int localPort = httpServletRequest.getLocalPort();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(msg).append(",LocalPort:").append(localPort);
return Response.success(sb.toString());
}
@GetMapping("/feign")
public String feignTest() {
return "feign";
}
}
4 IDEA To configure
IDEA Specify profile , Start producers separately .
stay Configuration Configure the main function to be started in , As shown in the figure below .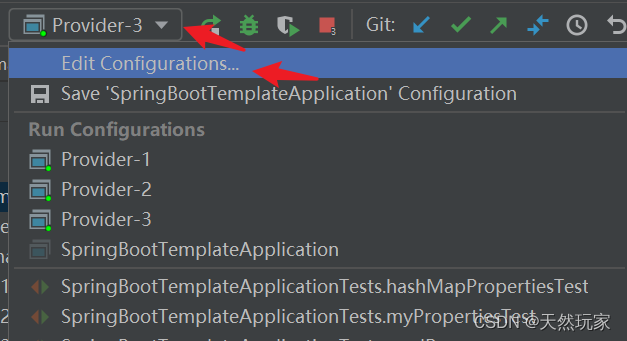
Three producers are used here (Provider), So create three new Application,
Respectively Provider-1、Provider-2 and Provider-3,
Add operating parameters , Specify the profile to be activated at run time , As shown in the figure below .
--spring.profiles.active

Start three producers respectively , After successful startup , stay IDEA Three are opened in Provider,
As shown in the figure below .
5 Registry Center
Start the registry Eureka,
Then start the consumer and 3 A producer ,
All in all 4 Services registered to Eureka,
Sign in Eureka, As shown in the figure below , You can see .
6 test
Call the consumer through the consumer interface ,
Each call will be balanced to different consumers .
The following tests were conducted three times , The results are shown in the following figure ,
Determine which consumer is requesting through different interfaces .


7 Summary
(1)SpringCloud:2020.0.3, Abandoned Netflix Of Ribbon,
Use own components spring-cloud-loadbalancer Load balancing , therefore , Integrate Eureka Need to be removed when ribbon;
(2)spring-cloud-loadbalancer The default load balancing policy used is : Random “ polling ” The way , By random seed and service quantity , Choose a balanced service ;
(3) Consumers do not need to choose a load balancing strategy ,OpenFeign Startup time , Automatically assemble the load balancer ;
(4)spring-cloud-loadbalancer There are two kinds of load balancing : Pure random and random polling .
边栏推荐
- 腾讯云数据库TDSQL-大咖论道 | 基础软件的过去、现在、未来
- APICloud可视化开发丨一键生成专业级源码
- c指针(面试经典题目练习)
- Leecode27977 double finger needling
- Wireshark learning notes (II) detailed explanation of forensics analysis cases
- AEC: analysis of echo generation causes and echo cancellation principle
- 调试的技巧
- SQL statement to view the basic table structure and constraint fields, primary codes and foreign codes in the table (simple and effective)
- 第四章 数据类型(三)
- 单纯形法代码求解(含超详细代码注释和整个流程图)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
数据治理经典6大痛点?这本书教你解决
Chapter 6 relational data theory exercise
Introduction to DB2 SQL pl
【数据库语言SPL】写着简单跑得又快的数据库语言 SPL
Beam pattern analysis based on spectral weighting
【web】个人主页web大作业「课表」「相册」「留言板」
Chapter II data type (I)
第一章 SQL操作符
2022.05.29(LC_6079_价格减免)
Wireshark learning notes (II) detailed explanation of forensics analysis cases
Openssl1.1.1 vs2013 compilation tutorial
Analysis of optical storage direct flexible power distribution system
Openssl1.1.1 compilation error can't locate win32/console pm in @INC
Adobe Premiere基础-介绍,配置,快捷键,创建项目,创建序列(一)
基于谱加权的波束方向图分析
[Code] neural symbol generation machine
libcurl 7.61.0 VS2013 编译教程
Jsp基于ssm项目实验室管理系统设计与现实.doc
Chapter 161 SQL function year
端午“沉浸式云旅游”怎么玩?即构助力“直播+”新场景落地