当前位置:网站首页>[set theory] equivalence relation (concept of equivalence relation | examples of equivalence relation | equivalence relation and closure)
[set theory] equivalence relation (concept of equivalence relation | examples of equivalence relation | equivalence relation and closure)
2022-07-03 06:11:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 Equivalence relation
- Two 、 Examples of equivalence relationships
- 3、 ... and 、 Examples of equivalence relations and closures
One 、 Equivalence relation
Concept of equivalence relation :
A
A
A Set is a non empty set ,
A
≠
∅
A \not= \varnothing
A=∅ , also
R
R
R The relationship is
A
A
A Binary relations on sets ,
R
⊆
A
×
A
R \subseteq A\times A
R⊆A×A ;
If
R
R
R The relationship is introspect , symmetry , Pass on Of , So called
R
R
R The relationship is Equivalence relation ;
Two 、 Examples of equivalence relationships
1. Relationship
1
1
1 :
x
x
x And
y
y
y The same age ;
- introspect :
x
x
x And
x
x
x The same age ; introspect establish ;
- symmetry :
x
x
x And
y
y
y The same age ,
y
y
y And
x
x
x The same age ; symmetry establish ;
- Pass on :
x
x
x And
y
y
y The same age ,
y
y
y And
z
z
z The same age ,
x
x
x And
z
z
z The same age ; Pass on establish ;
- Equivalence relation : The relationship is introspect , symmetry , Pass on Of , So the relationship yes Equivalence relation ;
It can be seen from the above , Equivalence relations are used for classification , People born in the same year can be divided into an equivalent class ;
2. Relationship
2
2
2 :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Same last name ;
- introspect :
x
x
x And
x
x
x Same last name ; introspect establish ;
- symmetry :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Same last name ,
y
y
y And
x
x
x Same last name ; symmetry establish ;
- Pass on :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Same last name ,
y
y
y And
z
z
z Same last name ,
x
x
x And
z
z
z Same last name ; Pass on establish ;
- Equivalence relation : The relationship is introspect , symmetry , Pass on Of , So the relationship It's equivalence ;
3. Relationship
3
3
3 :
x
x
x Older than or equal to
y
y
y ;
- introspect :
x
x
x Older than or equal to
x
x
x ; introspect establish ;
- symmetry :
x
x
x Older than or equal to
y
y
y ,
y
y
y Older than or equal to
x
x
x ; symmetry Don't set up ;
- Pass on :
x
x
x Older than or equal to
y
y
y ,
y
y
y Older than or equal to
z
z
z ,
x
x
x Older than or equal to
z
z
z ; Pass on establish ;
- Equivalence relation : The relationship is introspect , Pass on Of , It's not symmetrical , So the relationship It's not equivalent ;
4. Relationship
4
4
4 :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Take the same course ;
- introspect :
x
x
x And
x
x
x Take the same course ; introspect establish ;
- symmetry :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Take the same course ,
y
y
y And
x
x
x Take the same course ; symmetry establish ;
- Pass on :
x
x
x And
y
y
y Take the same course ,
y
y
y And
z
z
z Take the same course ,
x
x
x And
z
z
z Take the same course ; The above situation is not necessarily true ,
x
,
y
x,y
x,y May also choose music ,
y
,
z
y,z
y,z At the same time, take history ,
x
,
z
x,z
x,z Not taking the same course ; Pass on Don't set up ;
- Equivalence relation : The relationship is introspect , symmetry Of , Not transitive , So the relationship It's not equivalent ;
5. Relationship
5
5
5 :
x
x
x Weight greater than
y
y
y ;
- introspect :
x
x
x Weight greater than
x
x
x ; introspect Don't set up ;
- symmetry :
x
x
x Weight greater than
y
y
y ,
y
y
y Weight greater than
x
x
x ; symmetry Don't set up ;
- Pass on :
x
x
x Weight greater than
y
y
y ,
y
y
y Weight greater than
z
z
z ,
x
x
x Weight greater than
z
z
z ; Pass on establish ;
- Equivalence relation : The relationship is Pass on Of , No introspect , symmetry Of , So the relationship It's not equivalent ;
3、 ... and 、 Examples of equivalence relations and closures
A
A
A Set is a non empty set ,
A
≠
∅
A \not= \varnothing
A=∅ , also
R
R
R The relationship is
A
A
A Binary relations on sets ,
R
⊆
A
×
A
R \subseteq A\times A
R⊆A×A ;
Yes
R
R
R Three closures of relation , Yes
6
6
6 In a different order , Discuss the properties of these closure results ;
6
6
6 A property of finding closures :
r
t
s
(
R
)
rts(R)
rts(R) : First find the symmetric closure , Ask again Pass closures , Finally, find the reflexive closure ;
t
r
s
(
R
)
trs(R)
trs(R) : First find the symmetric closure , Then find the reflexive closure , Finally, ask for Pass closures ;
t
s
r
(
R
)
tsr(R)
tsr(R) : First find the reflexive closure , Then find the symmetric closure , Finally, ask for Pass closures ;
r
s
t
(
R
)
rst(R)
rst(R) : First seek Pass closures , Then find the symmetric closure , Finally, find the reflexive closure ;
s
r
t
(
R
)
srt(R)
srt(R) : First seek Pass closures , Then find the reflexive closure , Finally, find the symmetric closure ;
s
t
r
(
R
)
str(R)
str(R) : First find the reflexive closure , Ask again Pass closures , Finally, find the symmetric closure ;
Reference resources : 【 Set theory 】 Relational closure ( Relational closure method | Find closure of relation graph | Find closure of relation matrix | Closure operation and relation properties | Closure compound operation ) 5、 ... and 、 Closure compound operation
r
s
(
R
)
=
s
r
(
R
)
rs(R) = sr(R)
rs(R)=sr(R) : Symmetric closure And Reflexive closure Compound operation of , Whatever the order , It's the same to ask for first ;
r
t
(
R
)
=
t
r
(
R
)
rt(R) = tr(R)
rt(R)=tr(R) : Pass closures And Reflexive closure Compound operation of , Whatever the order , It's the same to ask for first ;
s
t
(
R
)
⊆
t
s
(
R
)
st(R) \subseteq ts(R)
st(R)⊆ts(R) : Pass closures And Symmetric closure Coincidence operation of , Different order , The calculation results are different ;
Therefore, there are two categories
- ① Transitive closure first , Then find the symmetric closure
- ② First find the symmetric closure , Then find the transitive closure
First find the symmetric closure , Then find the transitive closure :
r
t
s
(
R
)
rts(R)
rts(R) : First find the symmetric closure , Ask again Pass closures , Finally, find the reflexive closure ;
t
r
s
(
R
)
trs(R)
trs(R) : First find the symmetric closure , Then find the reflexive closure , Finally, ask for Pass closures ;
t
s
r
(
R
)
tsr(R)
tsr(R) : First find the reflexive closure , Then find the symmetric closure , Finally, ask for Pass closures ;
Fix ts The order of operations , First t after s , r Operations can be placed anywhere ;
Reflexivity does not conflict with the other two closure operations , It can be anywhere ;
Symmetry and transmission , The transmission of subsequent requests , So the result is transitive ;
The result of the above three sequences is introspect , symmetry , Pass on Of , It satisfies the equivalence relation , The result is Equivalent closure ;
First ask for the transfer package , Then find the symmetric closure :
r
s
t
(
R
)
rst(R)
rst(R) : First seek Pass closures , Then find the symmetric closure , Finally, find the reflexive closure ;
s
r
t
(
R
)
srt(R)
srt(R) : First seek Pass closures , Then find the reflexive closure , Finally, find the symmetric closure ;
s
t
r
(
R
)
str(R)
str(R) : First find the reflexive closure , Ask again Pass closures , Finally, find the symmetric closure ;
Fix st The order of operations , First s ( Symmetric closure ) after t ( Pass closures ) , r ( Symmetric closure ) Operations can be placed anywhere ;
Reflexivity does not conflict with the other two closure operations , It can be anywhere ;
Symmetry and transmission , The transmission of the first request , Then find symmetry , Symmetry destroys transmission , Therefore, the result is not transitive ;
The result of the above three sequences is introspect , symmetry , Don't deliver Of , It does not satisfy the equivalence relation ;
r t s ( R ) = t r s ( R ) = = t s r ( R ) rts(R)=trs(R)==tsr(R) rts(R)=trs(R)==tsr(R) | r s t ( R ) = s r t ( R ) = s t r ( R ) rst(R) = srt(R) = str(R) rst(R)=srt(R)=str(R) | |
|---|---|---|
| introspect | establish | establish |
| symmetry | establish | establish |
| Pass on | establish | Don't set up |
| Equivalence relation | establish ( This closure is called an equivalent closure ) | Don't set up |
边栏推荐
- [teacher Zhao Yuqiang] the most detailed introduction to PostgreSQL architecture in history
- Oauth2.0 - use database to store client information and authorization code
- Simple handwritten ORM framework
- 1. Somme des deux nombres
- Cesium Click to obtain the longitude and latitude elevation coordinates (3D coordinates) of the model surface
- 表达式的动态解析和计算,Flee用起来真香
- 项目总结--04
- Kubernetes notes (VII) kuberetes scheduling
- What's the difference between using the Service Worker Cache API and regular browser cache?
- When PHP uses env to obtain file parameters, it gets strings
猜你喜欢
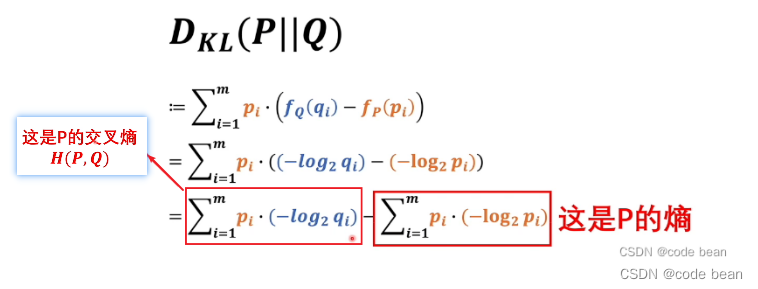
最大似然估计,散度,交叉熵
智牛股项目--05

ThreadLocal的简单理解
![[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] the most detailed introduction to PostgreSQL architecture in history](/img/18/f91d3d21a39743231d01f2e4015ef8.jpg)
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] the most detailed introduction to PostgreSQL architecture in history

.NET程序配置文件操作(ini,cfg,config)
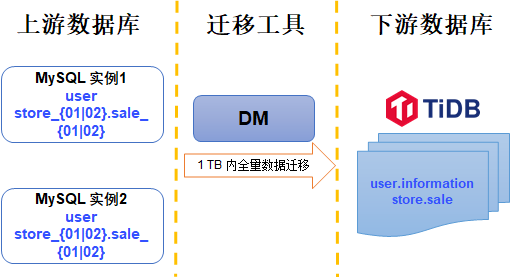
Merge and migrate data from small data volume, sub database and sub table Mysql to tidb
![[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] index in mongodb (Part 1)](/img/2d/277ec737f2a7065831a19d036e61e1.jpg)
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] index in mongodb (Part 1)
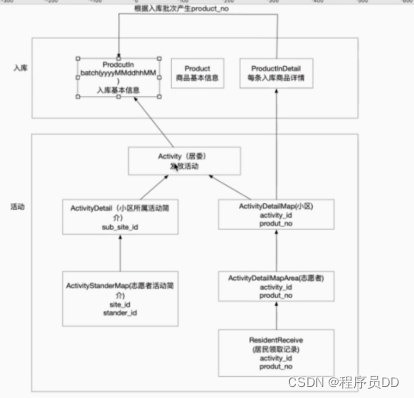
项目总结--01(接口的增删改查;多线程的使用)

Alibaba cloud OOS file upload
In depth analysis of kubernetes controller runtime
随机推荐
Deep learning, thinking from one dimensional input to multi-dimensional feature input
Kubernetes notes (VII) kuberetes scheduling
Kubernetes notes (V) configuration management
最大似然估计,散度,交叉熵
MySQL帶二進制的庫錶導出導入
Kubernetes notes (II) pod usage notes
Intel's new GPU patent shows that its graphics card products will use MCM Packaging Technology
MySQL带二进制的库表导出导入
Cesium entity(entities) 实体删除方法
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] MySQL high availability architecture: MHA
88. 合并两个有序数组
Method of converting GPS coordinates to Baidu map coordinates
. Net program configuration file operation (INI, CFG, config)
Sorry, this user does not exist!
Understand the first prediction stage of yolov1
理解 YOLOV1 第一篇 预测阶段
Clickhouse learning notes (I): Clickhouse installation, data type, table engine, SQL operation
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
[teacher Zhao Yuqiang] calculate aggregation using MapReduce in mongodb
Kubernetes notes (VIII) kubernetes security