1. The difference between program and process
Let's start with a story :
A Usually because of busy work , They eat in the company canteen or take out food . But one day, the class suddenly wanted to cook by themselves , therefore A Go shopping in the supermarket , He bought some ingredients to make a scrambled egg with tomatoes . When you get home ,A Took out a book that was placed in the deepest part of the bookshelf 《 Recipes for home cooked dishes 》, Follow the above method , He began to prepare the dishes : First wash the tomatoes and cut them into pieces , Stir the eggs into egg liquid , Boiling hot oil ........ Finally in the A Under the scornful efforts of , A tomato scrambled egg with all the colors, flavors and flavors is finished .
In the above story , We can abstract out a simple computing processing model :
【 Program 】 That's the recipe ( Stored on the shelf , A kind of Physics There is , Describe the process and method of cooking in a specific form )
notes :
Famous computer scientist Niklaus Wirth Put forward : Program = data structure + Algorithm
Think of recipes as programs , It is in the form of pictures and texts ( data structure ) Vividly show the readers how to cook each dish ( Algorithm )- 【 process 】 This is a series of activities for cooking ( dynamic On going ), Including washing vegetables 、 Chopping vegetables 、 Stir fry and so on
- 【CPU】 Namely A I am , He is the executor of all operations
- 【 data 】 It's all kinds of raw materials for scrambled eggs with tomatoes , Including tomatoes 、 egg ...( Pass a series of data through CPU Processing becomes different data )
2. process
2.1 State of process
A process is a sequence of programs on a data set Activities .
The process has three states , Namely :
- Running state 【running】(actually using the CPU at that instant)
- The ready state 【ready】(runnable; temporarily stopped to let another process run)
- Blocking state 【blocked】(unable to run until some external event happens)

From the above , We can clearly see the transformation process between the three states :
- Happen when IO In operation , The current process will be blocked until IO Operation is completed
- When the scheduler interrupts the current process and executes another process , The original process will be ready
- When the scheduler selects the process , It will change from ready state to running state , enjoy CPU resources
- When IO After completion , The blocked process becomes ready , Waiting for the operating system to schedule
2.2 Process context switch
When a process interrupts from one process to another (interrupt) Or system call (system call) Context switching occurs 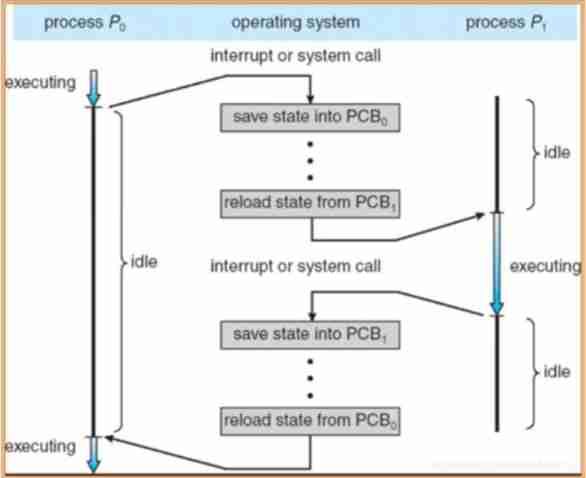
- Process in progress P0 Because the terminal or system call will cpu The right to use is returned to os
- os preservation P0 Of PCB Information , And reload from memory P1 Process pcb Content , And implement P1
- P1 After execution , Given to by an interrupt or system call os( Scheduler scheduler / Dispatcher scheduler)
- Come back and execute P0( load P0 Of PCB Information )
The cost of context switching is actually very high , Requires a lot of processor time ( So we usually use assembly complete ), occasionally 1 Context switching can be performed thousands of times in seconds 【CONTEXT SWITCH】
Even modern computers are reducing the amount of context switching CPU Time , But that is only in CPU Clock cycles decrease , Faster processing , Instead of improving the efficiency of context switching
3. Why introduce the concept of threads ?
Now that we have a process , So why did computer scientists come up with the concept of a thread ?
- In the system, multiple applications will be carried out at the same time , They often switch states , By splitting a process into multiple threads , achieve Quasi parallel 【quasi-parallel】, The program model will be simpler ( These threads <u> Share address space and data resources </u>, These capabilities are exactly what multiple processes cannot do ( Address space is different ))
- More lightweight . Compared to process , It's easier ( Fast ) Create and destroy ( In some systems , Faster than process creation 10-100 times )
- Better performance . When there are a lot of calculations and I/O When dealing with , Threads have the ability to overlap these activities , Speed up the program
- More useful for multi-core processors .
【 notes 】
because process Is the owner of resources , So in creating 、 revoke 、 The switching operation requires large space-time overhead , Limits the further improvement of concurrency .
by Reduce the overhead of process switching , Treat the process as Resource allocation unit and Dispatching unit These two properties <u> Separate the </u>, That is, the process is the basic unit of resource allocation , But not as the basic unit of scheduling ( Rarely scheduled or switched ), Assign the responsibility of scheduling execution and switching to “ Threads ”.
The benefits of doing so can not only Improve the concurrency of the system , It can also adapt to the new symmetric multiprocessor (SMP) The operation of the environment , Give full play to its performance
3.1 Some defects of threads
Although the thread runs very fast , But it is not perfect
Mainly in the Security Problems in : We know , The threads in the process share data and address space , If An error occurred in one of the threads ( For example, a variable is rewritten by mistake ), Other threads will also have problems , Errors that lead to the final whole process
therefore , We say that the current use of processes and threads is also separate , Not blindly pursuing threads :
- stay High performance computing ( Like the weather forecast 、 Water conservancy 、 Aerodynamics, etc ), This category needs to pursue high-performance computing , At the same time, the program is not error prone , Just fit Using threads
- And for example browser This application , Because the operation of the browser page is performed by the user , Sometimes data security is considered , So recommend Use process , A process opens a web page
3.2 Implementation of threads
3.2.1 User space implementation

Create in user space Thread library , Provides a set of procedures for managing threads by
Runtime system 【run-time system】 To complete thread management
The kernel manages processes , The kernel is unaware of the existence of threads
Thread switching There's no need to get into the kernel
Such as Unix、Linux
| advantage | shortcoming |
|---|---|
| Fast switching speed | A process has only one thread running on the processor |
| The scheduling algorithm can be set by the application | If a thread of the a process calls a blocked system call , Then all threads of the process will also be blocked , Page invalidation can have the same problem |
| User level threads can run on any operating system , Including unsupported threaded operating systems |
3.2.2 Kernel space implementation

The kernel manages all thread management , establish , Revocation and dispatch **, And provide... To the application API
The kernel maintains the process and thread context
Thread switching Need kernel support
Thread based To schedule
| advantage | shortcoming |
|---|---|
| Scheduled by the kernel , When there are multiple processors , Multiple threads of a process can execute simultaneously on multiple processors | Created by the kernel , revoke , Dispatch , More overhead |
| Blocking of one thread of a process does not cause blocking of other threads , The same goes for page invalidation |
3.3.3 Hybrid implementation

Threads establish stay —— User space
Threads Dispatch stay —— Kernel space
4. The relationship between processes and threads that have resources ?
【 process 】 yes Resource allocation The unit of ——————【 Threads 】 yes CPU Dispatch The unit of
Threads Also known as “ Lightweight process ”【lightweight processes】
it ( All threads of the same process ) Shared process address space , At the same time, there are some unique information :

The process information shared by each thread is shown on the left side of the above figure
but , Every Threads also have their own <u>PC、 register 、 Stack 、 State information </u>
( Because each thread may call different steps ,
therefore Each thread has its own stack 、PC、 register , This prevents exceptions from occurring during execution )
【 notes 】
- Multiple threads within a process coexist
- Share information with each other , It is even possible for one thread to create or delete another thread
- Although there is a hierarchical relationship between processes , But there are no threads ( All threads are Equal )
5. Reference material
《 Modern operating system 》
《Operating Systems》
operating system _ Tsinghua University ( Xiang Yong 、 Chen Yu )








![[project training] wechat official account to obtain user openid](/img/54/0a77e4441ee87e6ff04f3f07baa965.png)
