当前位置:网站首页>树结构---二叉树2非递归遍历
树结构---二叉树2非递归遍历
2022-07-01 09:05:00 【遨游的laugh哥】
目录
完整代码(binTree.h)
#include"seqQueue.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class binTree{
friend void printTree(const binTree<T>& t,T flag){
//由于要输出值,所以队列存值
//为了检验函数功能,直接调用已实现函数
if(t.root==NULL) return;
seqQueue<T> s;
s.enQueue(t.root->data);//值
T tmp,lc,rc;
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.deQueue();
//调用左右孩子
lc=t.lchild(tmp,flag);
rc=t.rchild(tmp,flag);
cout<<"("<<tmp<<" "<<lc<<" "<<rc<<")"<<endl;
if(lc!=flag) s.enQueue(lc);
if(rc!=flag) s.enQueue(rc);}
}
private:
struct node{
T data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
node():lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
node(const T& x,node* p=NULL,node* q=NULL):data(x),lchild(p),rchild(q){}
~node(){}
};
node* root;
//为公有无参函数传参
void preTraverse(node* t) const;
void midTraverse(node* t) const;
void postTraverse(node* t) const;
int nodeSize(node* t) const;
int treeHigh(node* t) const;
void clear(node* &t);
//辅助函数---找给定结点值的结点指针
node* find(T x,node* t) const{//传值x和要返回的指针t
node* tmp;
if(t==NULL) return NULL;
//根左右
if(t->data==x) return t;
tmp=find(x,t->lchild);
if(tmp) return tmp;
else return find(x,t->rchild);
}
public:
/*构造函数*/
binTree(){ root=NULL;}
/*层次遍历创建树+层次遍历已有树*/
void createTree(T flag);//用flag表示空结点
void levelTraverse() const;//层次遍历
/*递归实现前中后序遍历*/
void preTraverse() const;
void midTraverse() const;
void postTraverse() const;
/*求树的高度+叶子结点个数*/
int nodeSize() const;
int treeHigh() const;
/*求左右孩子结点值---传参x和表示空的flag*/
T lchild(T x,T flag) const;
T rchild(T x,T flag) const;
//清空+剪枝
void clear();
void defLeft(T x);
void defRight(T x);
};
//创建树+层次遍历
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::createTree(T flag){
seqQueue<node*> s;//创建装有结点指针的队列
//输入根节点并入队
T x;
cout<<"输入根节点:";
cin>>x;
s.enQueue(root=new node(x));
//访问结点,并将非空左右孩子入队
node* tmp;
T ldata,rdata;
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.deQueue();
cout<<"输入结点"<<tmp->data<<"的左右孩子:";
cin>>ldata>>rdata;
if(ldata!=flag) s.enQueue(tmp->lchild=new node(ldata));
if(rdata!=flag) s.enQueue(tmp->rchild=new node(rdata));
}
cout<<"create successful!\n";
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::levelTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n层次遍历:";
if(root==NULL) return;
seqQueue<node*> s;
s.enQueue(root);
while(!s.is_empty()){
node* tmp=s.deQueue();
cout<<tmp->data<<" ";//输出
if(tmp->lchild) s.enQueue(tmp->lchild);
if(tmp->rchild) s.enQueue(tmp->rchild);
}
}
//递归实现前中后序遍历
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::preTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
cout<<t->data<<" ";
preTraverse(t->lchild);
preTraverse(t->rchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::preTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n前序遍历:";
preTraverse(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::midTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
midTraverse(t->lchild);
cout<<t->data<<" ";
midTraverse(t->rchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::midTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n中序遍历:";
midTraverse(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::postTraverse(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return;
postTraverse(t->lchild);
postTraverse(t->rchild);
cout<<t->data<<" ";
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::postTraverse() const{
cout<<"\n后序遍历:";
postTraverse(root);
}
//求结点数+树高
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::nodeSize(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return 0;
//结点数=根+左子树+右子树
else return nodeSize(t->lchild)+nodeSize(t->rchild)+1;
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::nodeSize() const{
return nodeSize(root);
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::treeHigh(node* t) const{
if(t==NULL) return 0;
int L,R;
L=treeHigh(t->lchild);
R=treeHigh(t->rchild);
return 1+(L>R?L:R);//根+max(左子树高度,右子树高度)
}
template<class T>
int binTree<T>::treeHigh() const{
return treeHigh(root);
}
//求左右孩子
template<class T>
T binTree<T>::lchild(T x,T flag) const{
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL||tmp->lchild==NULL) return flag;
else return tmp->lchild->data;
}
template<class T>
T binTree<T>::rchild(T x,T flag) const{
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL||tmp->rchild==NULL) return flag;
else return tmp->rchild->data;
}
//清空+剪枝
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::clear(node* &t){
if(t==NULL) return;
clear(t->lchild);
clear(t->rchild);
delete t;
t=NULL;//把根节点置空
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::clear(){
clear(root);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::defLeft(T x){
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL) return;
clear(tmp->lchild);
}
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::defRight(T x){
node* tmp=find(x,root);
if(tmp==NULL) return;
clear(tmp->rchild);
}主函数测试

#include"binTree.h"
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
binTree<char> bt;
bt.createTree('#');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
bt.defLeft('D');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<endl;
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
bt.defRight('B');
printTree(bt,'#');
cout<<endl;
cout<<bt.nodeSize()<<" "<<bt.treeHigh()<<endl;
return 0;
}

非递归的前中后遍历
引入栈文件----stack.h
template<class elemType>
class seqStack{
private:
elemType* data;
int maxsize;
int top_s;
void doublespace();//扩容
public:
//构造+析构
seqStack(int initszie=10){
data=new elemType[initszie];
maxsize=initszie;
top_s=-1;
}
~seqStack(){ delete[] data;}
//函数操作
bool is_empty() const{ return top_s==-1;}
elemType top() const{ return data[top_s];}
elemType pop(){
return data[top_s--];
}
void push(const elemType& x){
data[++top_s]=x;
}
};
//扩容
template<class elemType>
void seqStack<elemType>::doublespace(){
elemType* tmp;
maxsize*=2;
data=new elemType[maxsize];
for(int i=0;i<=top_s;i++){
data[i]=tmp[i];
}
delete[] tmp;
}前序实现:
void preTraverse() const{ seqStack<node*> s; if(root==NULL) return; cout<<"前序遍历:"; s.push(root); node* tmp; while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); cout<<tmp->data<<" "; //由于栈后进先出,一定要先右后左 if(tmp->rchild) s.push(tmp->rchild); if(tmp->lchild) s.push(tmp->lchild); } }比较简单,类似层次遍历,只是一定要先右孩子进栈,然后左孩子进栈
中序
void midTraverse() const{//非递归中序 /*由于要记录出栈次数,所以引入结构elem*/ if(root==NULL) return; struct elem{ node* cur; int time; elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//构造函数 }; cout<<"非递归中序遍历:"; //初始化---装有elem的栈和elem变量 seqStack<elem> s; elem bt(root); s.push(bt); elem tmp;//记录出栈 while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); if(tmp.time==1){ //表明已经出栈过一次了,也就是左结点访问结束 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; //接下来访问右孩子节点 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(tmp.cur->rchild); } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己是第一次访问,入栈,time+1 //左孩子进栈 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(tmp.cur->lchild); } } cout<<endl; }注意:elem(tmp.cur->lchild)-----是elem类型,没有指定变量名,类似临时变量
注意:如果出栈过一次,那么time+1,而且在访问左结点,一定要:再进栈push一次
后序
void postTraverse() const{//非递归后序 /*由于要记录出栈次数,所以引入结构elem*/ if(root==NULL) return; struct elem{ node* cur; int time; elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//构造函数 }; cout<<"非递归后序遍历:"; //初始化---装有elem的栈和elem变量 seqStack<elem> s; elem bt(root); s.push(bt); elem tmp;//记录出栈 //以上和中序遍历代码一致 while(!s.is_empty()){ tmp=s.pop(); if(tmp.time==2){ //已访问两次,也就是左右孩子都遍历了,输出结果 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; } else{ if(tmp.time==1){ //左孩子已访问,右孩子进栈 tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//一定别忘了,右孩子进栈时,自己再进一次栈 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意类型 } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己进栈,然后遍历左孩子 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild)); } } } }与中序区别只在:
while(!s.is_empty()){
//区别
}
if(tmp.time==2){ //已访问两次,也就是左右孩子都遍历了,输出结果 cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" "; } else{ if(tmp.time==1){ //左孩子已访问,右孩子进栈 tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//一定别忘了,右孩子进栈时,自己再进一次栈 if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意类型 } else{ tmp.time+=1; s.push(tmp);//自己进栈,然后遍历左孩子 if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild)); } }注意这个根左右过程:
if 访问根
else if 第一次---左孩子
else 第二次---右孩子
完整程序
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"seqStack.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class binTree{
private:
struct node{
T data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
node():lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
node(const T& x,node* p=NULL,node* q=NULL):data(x),lchild(p),rchild(q){}
~node(){}
};
node* root;
public:
binTree(){ root=NULL;}
void createTree();//静态初始化树
void preTraverse() const{//非递归前序
if(root==NULL) return;
cout<<"非递归前序遍历:";
//将根节点入栈
seqStack<node*> s;//栈的元素类型是--node*
s.push(root);
node* tmp;//记录出栈元素
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();//栈顶元素出栈
cout<<tmp->data<<" ";//前序遍历--先访问根
//由于栈的后进先出,右孩子先于左孩子进栈
if(tmp->rchild) s.push(tmp->rchild);
if(tmp->lchild) s.push(tmp->lchild);
}
cout<<endl;
}
void midTraverse() const{//非递归中序
/*由于要记录出栈次数,所以引入结构elem*/
if(root==NULL) return;
struct elem{
node* cur;
int time;
elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//构造函数
};
cout<<"非递归中序遍历:";
//初始化---装有elem的栈和elem变量
seqStack<elem> s;
elem bt(root);
s.push(bt);
elem tmp;//记录出栈
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();
if(tmp.time==1){
//表明已经出栈过一次了,也就是左结点访问结束
cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" ";
//接下来访问右孩子节点
if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(tmp.cur->rchild);
}
else{
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//自己是第一次访问,入栈,time+1
//左孩子进栈
if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(tmp.cur->lchild);
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
void postTraverse() const{//非递归后序
/*由于要记录出栈次数,所以引入结构elem*/
if(root==NULL) return;
struct elem{
node* cur;
int time;
elem(node* p=NULL):cur(p),time(0){ }//构造函数
};
cout<<"非递归后序遍历:";
//初始化---装有elem的栈和elem变量
seqStack<elem> s;
elem bt(root);
s.push(bt);
elem tmp;//记录出栈
//以上和中序遍历代码一致
while(!s.is_empty()){
tmp=s.pop();
if(tmp.time==2){
//已访问两次,也就是左右孩子都遍历了,输出结果
cout<<tmp.cur->data<<" ";
}
else{
if(tmp.time==1){
//左孩子已访问,右孩子进栈
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//一定别忘了,右孩子进栈时,自己再进一次栈
if(tmp.cur->rchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->rchild));//注意类型
}
else{
tmp.time+=1;
s.push(tmp);//自己进栈,然后遍历左孩子
if(tmp.cur->lchild) s.push(elem(tmp.cur->lchild));
}
}
}
}
};
template<class T>
void binTree<T>::createTree(){
node* f=new node('f');
node* g=new node('g');
node* k=new node('k');
node* h=new node('h');
node* e=new node('e',f,g);
node* j=new node('j',NULL,k);
node* d=new node('d',NULL,e);
node* i=new node('i',j,NULL);
node* b=new node('b',d,NULL);
node* c=new node('c',h,i);
root=new node('a',b,c);
}测试主函数
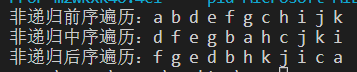
int main(){
binTree<char> bt;
bt.createTree();
bt.preTraverse();
bt.midTraverse();
bt.postTraverse();
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- Nacos - Configuration Management
- Insert mathematical formula in MD document and mathematical formula in typora
- Promise asynchronous programming
- Shell脚本-case in 和正则表达式
- Shell script case in and regular expressions
- 如何一站式高效管理固定资产?
- Pain points and solutions of fixed assets management of group companies
- 任务、线程、进程 区别
- How to solve the problem of fixed assets management and inventory?
- 【pytorch】transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
猜你喜欢

如何做好固定资产管理?易点易动提供智能化方案

动态代理

VSYNC+三重缓存机制+Choreographer

AVL树的理解和实现

2.3 【kaggle数据集 - dog breed 举例】数据预处理、重写Dataset、DataLoader读取数据

Nacos - gestion de la configuration
![[interview brush 101] linked list](/img/52/d159bc66c0dbc44c1282a96cf6b2fd.png)
[interview brush 101] linked list

Principles of Microcomputer - internal and external structure of microprocessor

足球篮球体育比赛比分直播平台源码/app开发建设项目

How to solve the problem of fixed assets management and inventory?
随机推荐
Software Engineer Interview Question brushing website and experience method
Shell脚本-位置参数(命令行参数)
How to solve the problem of fixed assets management and inventory?
中断与其他函数共享变量、临界资源的保护
3D printing Arduino four axis aircraft
【pytorch学习】torch.device
nacos简易实现负载均衡
An overview of the design of royalties and service fees of mainstream NFT market platforms
Shell脚本-if else语句
R language observation log (part24) -- initialization settings
[MFC development (17)] advanced list control list control
又到年中,固定资产管理该何去何从?
Dynamic proxy
Mysql 优化
R语言观察日志(part24)--初始化设置
pcl_ Viewer command
[ESP nanny level tutorial] crazy completion chapter - Case: ws2812 light control system based on Alibaba cloud, applet and Arduino
日常办公耗材管理解决方案
Football and basketball game score live broadcast platform source code /app development and construction project
Serialization, listening, custom annotation