当前位置:网站首页>AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.11)
AGCO AI frontier promotion (6.11)
2022-06-11 11:42:00 【Zhiyuan community】
LG - machine learning CV - Computer vision CL - Computing and language AS - Audio and voice RO - robot
Turn from love to a lovely life
Abstract : Beyond imitation game benchmarks (BIG-bench)、 Efficient self supervised visual pre training based on local mask reconstruction 、 Mask guided layered depth refinement 、 Mobile terminal vision Transformer Separable self attention 、 oriented 3D Scene manipulated volume unwrapping 、 Cross domain aligned sample generation based on learned deformable graph 、 Based on context RQ-Transformer Efficient image generation 、 High resolution image synthesis based on fractional generation model 、 Explicit regularization of overparameterized model based on noise injection
1、[CL] Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models
A Srivastava, A Rastogi, A Rao, A A M Shoeb, A Abid, A Fisch...
Beyond imitation game benchmarks (BIG-bench): Quantification and inference of language model capabilities . With the expansion of the scale , The language model shows some improvement in quantity and new qualitative ability . Despite their potentially transformative impact , But these new capabilities have not been well described . In order to provide information for future research , Prepare for disruptive new model capabilities , And improve the harmful effects in society , We must understand the current and future capabilities and limitations of the language model . To meet this challenge , This paper proposes Beyond the Imitation Game The benchmark (BIG-bench).BIG-bench At present by 204 A task consists of , from 132 Institutional 442 Famous authors contributed . Task themes are diverse , From linguistics 、 Child development 、 mathematics 、 Commonsense reasoning 、 biology 、 physics 、 Social prejudice 、 Learn from problems in software development, etc .BIG-bench Focus on tasks that are considered beyond the capabilities of the current language model . In this paper BIG-bench On the assessment OpenAI Of GPT Model 、Google-internal dense transformer The architecture and Switch-style sparse transformer act , The scale of the model spans millions to hundreds of billions of parameters . Besides , A team of human expert reviewers performed all the tasks , To provide a strong baseline . The findings include : Model performance and calibration are improved with the expansion of scale , But the absolute value is poor ( The same is true when compared with the performance of the reviewers ); The performance of each model category is very similar , Despite the benefits of sparsity ; Gradually improving and predictable tasks usually involve a large number of knowledge or memory components , And on the key scale " breakthrough " The task of behavior usually involves multiple steps or components , Or indicators of vulnerability ; In the case of a blurred background , Social prejudice usually increases with size , But this can be improved by prompting .
Language models demonstrate both quantitative improvement and new qualitative capabilities with increasing scale. Despite their potentially transformative impact, these new capabilities are as yet poorly characterized. In order to inform future research, prepare for disruptive new model capabilities, and ameliorate socially harmful effects, it is vital that we understand the present and near-future capabilities and limitations of language models. To address this challenge, we introduce the Beyond the Imitation Game benchmark (BIG-bench). BIG-bench currently consists of 204 tasks, contributed by 442 authors across 132 institutions. Task topics are diverse, drawing problems from linguistics, childhood development, math, common-sense reasoning, biology, physics, social bias, software development, and beyond. BIG-bench focuses on tasks that are believed to be beyond the capabilities of current language models. We evaluate the behavior of OpenAI’s GPT models, Google-internal dense transformer architectures, and Switch-style sparse transformers on BIG-bench, across model sizes spanning millions to hundreds of billions of parameters. In addition, a team of human expert raters performed all tasks in order to provide a strong baseline. Findings include: model performance and calibration both improve with scale, but are poor in absolute terms (and when compared with rater performance); performance is remarkably similar across model classes, though with benefits from sparsity; tasks that improve gradually and predictably commonly involve a large knowledge or memorization component, whereas tasks that exhibit “breakthrough” behavior at a critical scale often involve multiple steps or components, or brittle metrics; social bias typically increases with scale in settings with ambiguous context, but this can be improved with prompting.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04615
2、[CV] Efficient Self-supervised Vision Pretraining with Local Masked Reconstruction
J Chen, M Hu, B Li, M Elhoseiny
[King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) & Nanyang Technological University]
Efficient self supervised visual pre training based on local mask reconstruction . The self supervised learning of computer vision has made great progress , Improved many downstream visual tasks , Such as image classification 、 Semantic segmentation and target detection . among , Generative self supervised visual learning method , Such as MAE and BEiT, Show good performance . However , Its global mask reconstruction mechanism is computationally demanding . To solve this problem , This paper proposes local mask reconstruction (LoMaR), A simple and effective way , In a simple Transformer On the encoder 7×7 Mask reconstruction in a small window , Compared with the global mask reconstruction of the whole image , Improved trade-off between efficiency and accuracy . Extensive experiments show that ,LoMaR stay ImageNet-1K The classification has reached 84.1% The highest accuracy of , Than MAE Higher than 0.5%. stay 384×384 Pre training on the image LoMaR After fine tuning , The highest accuracy can be achieved 85.4%, Than MAE Higher than 0.6%. stay MS COCO On ,LoMaR More than... In object detection MAE 0.5 AP, More than... On instance segmentation 0.5 AP.LoMaR The computational efficiency is especially high on pre training high-resolution images , for example , In pre training 448×448 On the image of , Than MAE fast 3.1 times , High classification accuracy 0.2%. This local mask reconstruction learning mechanism can be easily integrated into any other generative self supervised learning method .
Self-supervised learning for computer vision has achieved tremendous progress and improved many downstream vision tasks such as image classification, semantic segmentation, and object detection. Among these, generative self-supervised vision learning approaches such as MAE and BEiT show promising performance. However, their global masked reconstruction mechanism is computationally demanding. To address this issue, we propose local masked reconstruction (LoMaR), a simple yet effective approach that performs masked reconstruction within a small window of 7×7 patches on a simple Transformer encoder, improving the trade-off between efficiency and accuracy compared to global masked reconstruction over the entire image. Extensive experiments show that LoMaR reaches 84.1% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K classification, outperforming MAE by 0.5%. After finetuning the pretrained LoMaR on 384×384 images, it can reach 85.4% top-1 accuracy, surpassing MAE by 0.6%. On MS COCO, LoMaR outperforms MAE by 0.5 AP on object detection and 0.5 AP on instance segmentation. LoMaR is especially more computation-efficient on pretraining high-resolution images, e.g., it is 3.1× faster than MAE with 0.2% higher classification accuracy on pretraining 448×448 images. This local masked reconstruction learning mechanism can be easily integrated into any other generative self-supervised learning approach. Our code will be publicly available.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00790
3、[CV] Layered Depth Refinement with Mask Guidance
S Y Kim, J Zhang, S Niklaus, Y Fan, S Chen, Z Lin, M Kim
[KAIST & Adobe]
Mask guided layered depth refinement . Depth maps are widely used from 3D Render to 2D Image effects ( Such as emptiness ) In a variety of applications . However , Those estimated from a single image depth (SIDE) The depth map predicted by the model can not capture the isolated holes and / Or there are inaccurate boundary areas . meanwhile , High quality masks are easier to obtain , Use commercial automated masking tools or off the shelf segmentation and matting methods , Even through manual editing . This paper constructs a new mask guided depth refinement problem , Refine with a generic mask SIDE Depth prediction of the model . The framework performs hierarchical refinement and inpainting/outpainting, Decompose the depth map into two separate layers , It is represented by mask and unmask respectively . Because there are very few datasets with depth and mask annotations , This paper presents a self supervised learning scheme , Use any mask and RGB-D Data sets . Experience shows that , The proposed method is robust to different types of mask and initial depth prediction , It can accurately improve the depth value of the inner and outer boundary areas of the mask . The proposed model is further analyzed with an ablation study , The results are shown in practical application .
Depth maps are used in a wide range of applications from 3D rendering to 2D image effects such as Bokeh. However, those predicted by single image depth estimation (SIDE) models often fail to capture isolated holes in objects and/or have inaccurate boundary regions. Meanwhile, high-quality masks are much easier to obtain, using commercial automasking tools or off-the-shelf methods of segmentation and matting or even by manual editing. Hence, in this paper, we formulate a novel problem of mask-guided depth refinement that utilizes a generic mask to refine the depth prediction of SIDE models. Our framework performs layered refinement and inpainting/outpainting, decomposing the depth map into two separate layers signified by the mask and the inverse mask. As datasets with both depth and mask annotations are scarce, we propose a self-supervised learning scheme that uses arbitrary masks and RGB-D datasets. We empirically show that our method is robust to different types of masks and initial depth predictions, accurately refining depth values in inner and outer mask boundary regions. We further analyze our model with an ablation study and demonstrate results on real applications. More information can be found on our project page.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.03048
4、[CV] Separable Self-attention for Mobile Vision Transformers
S Mehta, M Rastegari
[Apple]
Mobile terminal vision Transformer Separable self attention . Mobile terminal vision Transformer(MobileViT) It can achieve the most advanced performance in several mobile terminal visual tasks , Including classification and detection . Although these models have fewer parameters , But compared with the model based on convolutional neural network , They have high latency .MobileViT The main efficiency bottleneck is Transformer The bulls in the pay attention to themselves (MHA), need O(k) Time complexity of , And token( Or block ) The number of k of . Besides ,MHA Expensive operation required ( for example , Batch matrix multiplication ) To calculate self attention , This affects latency on resource limited devices . In this paper, we propose a new algorithm with linear complexity , namely O(k) Separable self attention method . A simple and effective feature of the proposed method is , Use element level operations to calculate self attention , Make it a good choice for resource constrained devices . The improved model ,MobileViTv2, It is the most advanced in several mobile terminal visual tasks , Include ImageNet Object classification and MS-COCO object detection . On loan 300 All the parameters ,MobileViTv2 stay ImageNet Reached on dataset 75.6% The highest accuracy of , Than MobileViT Above the limit 1%, At the same time, it runs fast on mobile devices 3.2 times .
Mobile vision transformers (MobileViT) can achieve state-of-the-art performance across several mobile vision tasks, including classification and detection. Though these models have fewer parameters, they have high latency as compared to convolutional neural network-based models. The main efficiency bottleneck in MobileViT is the multi-headed self-attention (MHA) in transformers, which requires O(k) time complexity with respect to the number of tokens (or patches) k. Moreover, MHA requires costly operations (e.g., batch-wise matrix multiplication) for computing self-attention, impacting latency on resource-constrained devices. This paper introduces a separable self-attention method with linear complexity, i.e. O(k). A simple yet effective characteristic of the proposed method is that it uses element-wise operations for computing self-attention, making it a good choice for resource-constrained devices. The improved model, MobileViTv2, is state-of-the-art on several mobile vision tasks, including ImageNet object classification and MS-COCO object detection. With about three million parameters, MobileViTv2 achieves a top-1 accuracy of 75.6% on the ImageNet dataset, outperforming MobileViT by about 1% while running 3.2× faster on a mobile device. Our source code is available at: https://github.com/apple/ml-cvnets
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02680
5、[CV] Volumetric Disentanglement for 3D Scene Manipulation
S Benaim, F Warburg, P E Christensen, S Belongie
[University of Copenhagen & Technical University of Denmark]
oriented 3D Scene manipulated volume unwrapping . lately , The development of differential volume rendering makes it complicated 3D A major breakthrough has been made in the photo realistic and refined reconstruction of scenes , This is the key to many virtual reality applications . However , In the context of augmented reality , People may also want to perform semantic operations or enhance the objects in the scene . So , This paper proposes an individual framework , be used for (i) Separate the volume representation of a given foreground object from the background , as well as (ii) Semantic manipulation of foreground objects and backgrounds . The framework assigns a set of foreground objects required by the training view 2D Mask and related 2D View and pose as input , And generate a 、 Reflections and partially occluded foreground - Background separation , Available for training and new views . The proposed method can control the pixel color and depth separately , And foreground and background objects 3D Similarity transformation . This article shows the applicability of the framework to some downstream operational tasks , Including object camouflage 、 non-negative 3D Object complement 、3D Objects change 、3D Object completion and based on 3D Object manipulation of text .
Recently, advances in differential volumetric rendering enabled significant breakthroughs in the photo-realistic and fine-detailed reconstruction of complex 3D scenes, which is key for many virtual reality applications. However, in the context of augmented reality, one may also wish to effect semantic manipulations or augmentations of objects within a scene. To this end, we propose a volumetric framework for (i) disentangling or separating, the volumetric representation of a given foreground object from the background, and (ii) semantically manipulating the foreground object, as well as the background. Our framework takes as input a set of 2D masks specifying the desired foreground object for training views, together with the associated 2D views and poses, and produces a foreground-background disentanglement that respects the surrounding illumination, reflections, and partial occlusions, which can be applied to both training and novel views. Our method enables the separate control of pixel color and depth as well as 3D similarity transformations of both the foreground and background objects. We subsequently demonstrate the applicability of our framework on a number of downstream manipulation tasks including object camouflage, non-negative 3D object inpainting, 3D object translation, 3D object inpainting, and 3D text-based object manipulation. Full results are given in our project webpage at https: //sagiebenaim.github.io/volumetric-disentanglement/
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02776
Several other papers worthy of attention :
[CV] Polymorphic-GAN: Generating Aligned Samples across Multiple Domains with Learned Morph Maps
polymorphic GAN: Cross domain aligned sample generation based on learned deformable graph
S W Kim, K Kreis, D Li, A Torralba, S Fidler
[NVIDIA & MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02903
[CV] Draft-and-Revise: Effective Image Generation with Contextual RQ-Transformer
Draft-and-Revise: Based on context RQ-Transformer Efficient image generation
D Lee, C Kim, S Kim, M Cho, W Han
[POSTECH & Kakao Brain]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04452
[CV] Accelerating Score-based Generative Models for High-Resolution Image Synthesis
High resolution image synthesis based on fractional generation model
H Ma, L Zhang, X Zhu, J Zhang, J Feng
[Fudan University & University of Surrey & RIKEN]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04029
[LG] Explicit Regularization in Overparametrized Models via Noise Injection
An over parameterized model based on noise injection is presented type Regularization
A Orvieto, A Raj, H Kersting, F Bach
[ETH Zürich & University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign & PSL Research University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.04613
边栏推荐
- [issue 30] shopee golang development experience
- 2020-07 学习笔记整理
- Command mode - attack, secret weapon
- [fragmentary thoughts] thoughts on wavelength, wave velocity and period
- Network protocol of yyds dry goods inventory: datagram socket for detailed explanation of socket protocol
- 实用WordPress插件收集(更新中)
- Gerber文件在PCB制造中的作用
- P2580 "so he started the wrong roll call"
- arguments.callee 实现函数递归调用
- WordPress登录页面定制插件推荐
猜你喜欢
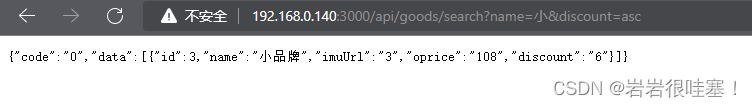
Node连接MySql数据库写模糊查询接口

Web development model selection, who graduated from web development

李飞飞:我更像物理学界的科学家,而不是工程师|深度学习崛起十年

Intl.numberformat set number format
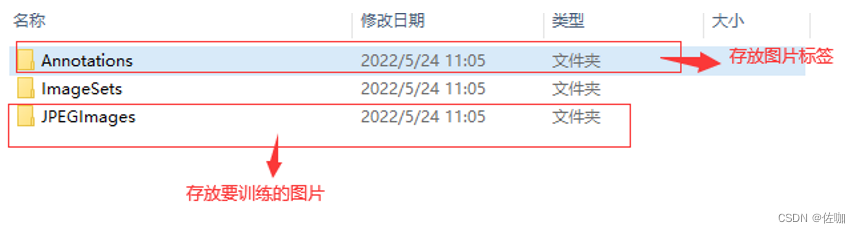
Use yolov3 to train yourself to make datasets and get started quickly

01_ Description object_ Class diagram

Use yolov5 to train your own data set and get started quickly

Uncaught TypeError: Cannot set property ‘next‘ of undefined 报错解决

JS to realize the rotation chart (riding light). Pictures can be switched left and right. Moving the mouse will stop the rotation

Intl.NumberFormat 设置数字格式
随机推荐
Set the default receiving address [project mall]
JS 加法乘法错误解决 number-precision
木瓜移动CFO刘凡 释放数字时代女性创新力量
李飞飞:我更像物理学界的科学家,而不是工程师|深度学习崛起十年
【Go】Gin源码解读
Let WordPress support registered users to upload custom avatars
推荐几款Gravatar头像缓存插件
The no category parents plug-in helps you remove the category prefix from the category link
AcWing 1944. Record keeping (hash, STL)
JVM class loading process
How to form a good habit? By perseverance? By determination? None of them!
修改 WordPress 管理账号名称插件:Admin renamer extended
WordPress数据库缓存插件:DB Cache Reloaded
01_ Description object_ Class diagram
文件excel导出
Maximum water container
广东市政安全施工资料管理软件2022新表格来啦
Display of receiving address list 【 project mall 】
AcWing 1944. 记录保存(哈希,STL)
Liufan, CFO of papaya mobile, unleashes women's innovative power in the digital age