当前位置:网站首页>牛客网——华为题库(51~60)
牛客网——华为题库(51~60)
2022-07-02 01:37:00 【wrdoct】
华为题库
51.输出单向链表中倒数第k个结点
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{
int m_nKey;
ListNode* m_pNext;
ListNode() : m_nKey(0), m_pNext(nullptr){
};
ListNode(int x) : m_nKey(x), m_pNext(nullptr){
};
};
ListNode* findNode(ListNode* head, int k){
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while(k--){
fast = fast->m_pNext;
}
//fast = fast->m_pNext;
while(fast != nullptr){
slow = slow->m_pNext;
fast = fast->m_pNext;
}
return slow;
}
int main(){
int num = 0;
while(cin >> num){
//构建链表
ListNode* head = new ListNode();
ListNode* dummyHead = head;
while(num--){
int nodeNum = 0;
cin >> nodeNum;
ListNode* next = new ListNode(nodeNum);
head->m_pNext = next; //
head = next; //
}
//寻找倒数第k个节点
int k = 0;
cin >> k;
ListNode* res = findNode(dummyHead->m_pNext, k); //
if(res != nullptr){
cout << res->m_nKey << endl;
}
else{
cout << "0" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
52.计算字符串的编辑距离
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//动态规划
int minDistance(string s1, string s2){
//本质不同的操作实际上只有三种:
//在单词 A 中插入一个字符;
//在单词 B 中插入一个字符;
//修改单词 A 的一个字符。
//字符串 A 为空,如从 转换到 ro,显然编辑距离为字符串 B 的长度,这里是 2;
//字符串 B 为空,如从 horse 转换到 ,显然编辑距离为字符串 A 的长度。
//可以使用动态规划来解决这个问题了。
//我们用 D[i][j] 表示 A 的前 i 个字母和 B 的前 j 个字母之间的编辑距离。
int n = s1.size(); int m = s2.size();
if(n * m == 0) return n + m; //有一个为空
vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(m + 1, 0));
//边界初始化
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j = 0; j <= m; j++){
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
if(s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]){
//
//A 的第 i 个字符和 B 的第 j 个字符原本就相同,不需要进行修改操作
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1), dp[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
else{
dp[i][j] = min(min(dp[i - 1][j] + 1, dp[i][j - 1] + 1), dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[n][m];
}
int main(){
string s1 = "";
string s2 = "";
while(cin >> s1 >>s2){
cout << minDistance(s1, s2) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
53.杨辉三角的变形
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
//找规律
//分析思路:
// 1
// 1 1 1
// 1 2 3 2 1
// 1 3 6 7 6 3 1
// 1 4 10 16 19 16 10 4 1
// 1 5 15 30 45 51 45 30 15 5 1
// 1 6 21 50 90 126 141 126 90 50 21 6 1
// 1 7 28 77
// 1 8 36 112
// 1 9 51 156
// 10
//通过以上的数据分析规律为 {-1,-1,2,3,2,4,2,3,2,4,...}
void process(int n, int& res){
if(n == 1 || n == 2) {
res = -1;
return;
}
/*//构建普通的杨辉三角 vector<vector<int>> matrix(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0)); // //二维数组 for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){ matrix[i].resize(i + 1); //第i行共有i+1个元素 matrix[i][0] = 1; matrix[i][i] = 1; //首尾都是1 for(int j = 1; j < i; j++){ // matrix[i][j] = matrix[i - 1][j - 1] + matrix[i - 1][j]; } }*/
int myInt[]={
4, 2, 3, 2};
res=myInt[(n - 2) % 4]; //
return;
}
int main(){
int n = 0;
while(cin >> n){
int res = 0;
process(n, res);
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
54.表达式求值
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int calculate(int a, int b, char sym){
switch(sym){
case '+':
return a + b;
break;
case '-':
return a - b;
break;
case '*':
return a * b;
break;
case '/':
return a / b;
break;
default:
return 0;
break;
}
}
int process(string s){
int flag = 0; //0无符号,1为正号,2为负号
stack<int> numst;
stack<char> symbolst;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
if(isdigit(s[i])){
int j = i; int num = 0;
while(i + 1 < s.size() && isdigit(s[i + 1])) i++;
string tmp = s.substr(j, i - j + 1);
for(int k = 0; k < tmp.size(); k++){
num = num * 10 + (tmp[k] - '0');
}
if(flag == 2) num = 0 - num;
flag = 0;
numst.push(num);
}
else if(s[i] == '*' || s[i] == '/' || s[i] == '('){
symbolst.push(s[i]);
}
else if(s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-'){
if(i == 0 || s[i - 1] == '('){
if(s[i] == '+') flag = 1;
else flag = 2;
}
while(!flag && !symbolst.empty() && symbolst.top() != '('){
int b = 0, a = 0;
char sym_tmp;
b = numst.top(); numst.pop();
a = numst.top(); numst.pop();
sym_tmp = symbolst.top(); symbolst.pop();
numst.push(calculate(a, b, sym_tmp));
}
if(!flag) symbolst.push(s[i]); //
}
else if(s[i] == ')'){
while(symbolst.top() != '('){
int b = 0, a = 0;
char sym_tmp;
b = numst.top(); numst.pop();
a = numst.top(); numst.pop();
sym_tmp = symbolst.top(); symbolst.pop();
numst.push(calculate(a, b, sym_tmp));
}
symbolst.pop();
}
else{
cout << "error!" << endl;
}
}
while(!symbolst.empty()){
int b = 0, a = 0;
char sym_tmp;
b = numst.top(); numst.pop();
a = numst.top(); numst.pop();
sym_tmp = symbolst.top(); symbolst.pop();
numst.push(calculate(a, b, sym_tmp));
}
return numst.top();
}
int main(){
string str = "";
while(cin >> str){
int res = process(str);
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
55.挑7
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool is_7_beishu(int num){
if(num % 7 == 0){
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool bao_han_7(int num){
string tmp = to_string(num);
for(char c : tmp){
if(c == '7'){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
void process(int n, int& res){
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(is_7_beishu(i) || bao_han_7(i)){
res++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n = 0;
cin >> n;
int res = 0;
process(n, res);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}
56.完全数计算
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isAllNum(int num){
int tmp = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < num; i++){
if(num % i == 0){
tmp += i;
}
}
if(tmp == num){
//cout << num<<"是完全数。"<<endl;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int num = 0;
while(cin>>num){
int res = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++){
if(isAllNum(i)) res++;
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
57.高精度整数加法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long str2int(string s){
long res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
res = res * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
//cout << " " << res << endl;
}
//cout << res << endl;
return res;
}
int main(){
string A = "";
string B = "";
while(cin >> A >> B){
/*long s1Num = str2int(s1); long s2Num = str2int(s2); cout << s1Num + s2Num << endl; //会超出范围*/
int i = A.size() - 1; int j = B.size() - 1;
string res = "";
int carry = 0; //进位
while(i >= 0 || j >= 0){
int digitA = i >= 0 ? A[i--] - '0' : 0;
int digitB = j >= 0 ? B[j--] - '0' : 0;
int sum = digitA + digitB + carry;
carry = sum / 10; //是否有进位
sum = sum % 10; //当前的非进位和
res += to_string(sum);
}
if(carry == 1) res += "1"; //最后的进位 //
reverse(res.begin(), res.end()); //
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}
58.输入n个整数,输出其中最小的k个
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n = 0, k = 0;
while(cin>>n>>k){
vector<int> vec(n, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int num = 0;
cin>>num;
vec[i] = num;
}
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end());
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
59.找出字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void process(string s, char& c){
unordered_map<char, int> m;
for(char ch : s){
m[ch]++;
}
for(char ch : s){
if(m[ch] == 1){
c = ch;
break;
}
}
}
int main(){
string str = "";
getline(cin, str);
char res;
process(str, res);
if(res)
cout << res << endl;
else
cout << "-1" << endl;
return 0;
}
60.查找组成一个偶数最接近的两个素数
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool isSuShu(int num){
for(int i = 2; i < num; i++){
if(num % i == 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int main(){
int num = 0;
while(cin >> num){
if(num <= 2 || num % 2 != 0){
break;
}
vector<int> res;
int minSub = INT_MAX; //保存最小的差值
unordered_map<int, pair<int, int>> m; //键为差值,值为firstNum和secondNum
for(int i = num; i >= num / 2; i--){
int secondNum = i;
int firstNum = num - i;
//判断两个数字是否是素数 并且计算差值 保存进哈希表
if(isSuShu(secondNum) && isSuShu(firstNum)){
int sub = secondNum - firstNum;
//cout << sub << endl;
m[sub] = make_pair(firstNum, secondNum);
minSub = min(minSub, sub);
}
}
for(auto item = m.begin(); item != m.end(); item++){
if(minSub == item->first){
//遍历寻找最小差值在哈希表中对应的位置
res.push_back(item->second.first);
res.push_back(item->second.second);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < res.size(); i++){
cout << res[i] << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- SAP ui5 beginner tutorial 20 - explanation of expression binding usage of SAP ui5
- 卷積神經網絡(包含代碼與相應圖解)
- Have you stepped on the nine common pits in the e-commerce system?
- 现货黄金分析的技巧有什么呢?
- Learning note 24 - multi sensor post fusion technology
- 电子协会 C语言 1级 33 、奇偶数判断
- 6-2 vulnerability exploitation - inevitable problems of FTP
- What are the affordable Bluetooth headsets? Student party parity Bluetooth headset recommendation
- [IVX junior engineer training course 10 papers to get certificates] 01 learn about IVX and complete the New Year greeting card
- Modeling essays series 124 a simple coding method
猜你喜欢
Self drawing of menu items and CListBox items
![[IVX junior engineer training course 10 papers] 02 numerical binding and adaptive website production](/img/b7/aecb815ca9545981563a1e16cfa19e.jpg)
[IVX junior engineer training course 10 papers] 02 numerical binding and adaptive website production

This is the form of the K-line diagram (pithy formula)

卷积神经网络(包含代码与相应图解)

SAP ui5 beginner tutorial XXI - trial version of custom formatter of SAP ui5

Day 13 of hcip (relevant contents of BGP agreement)

技术大佬准备就绪,话题C位由你决定
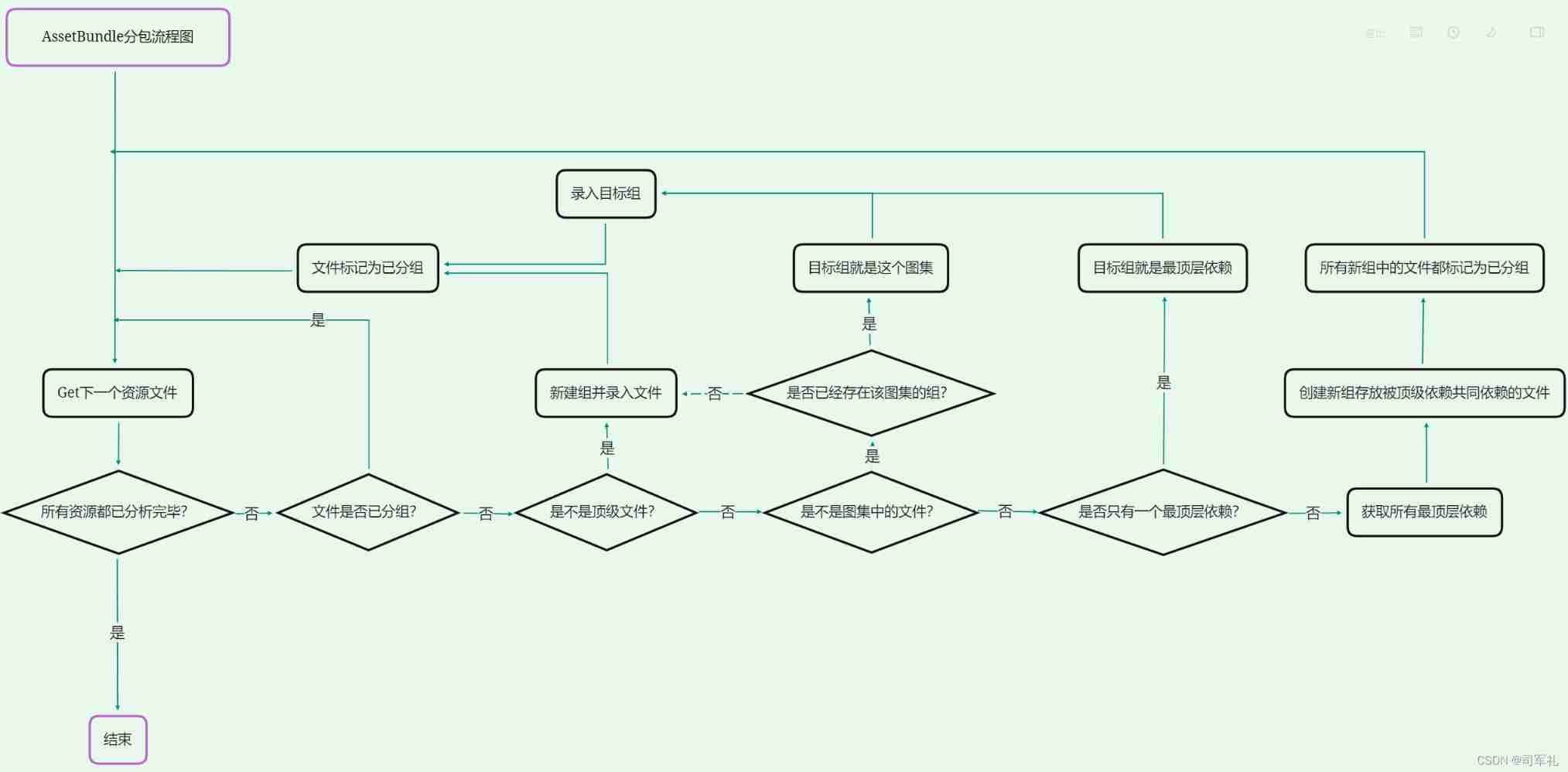
Unity AssetBundle subcontracting

Learn C language from scratch day 025 (maze)
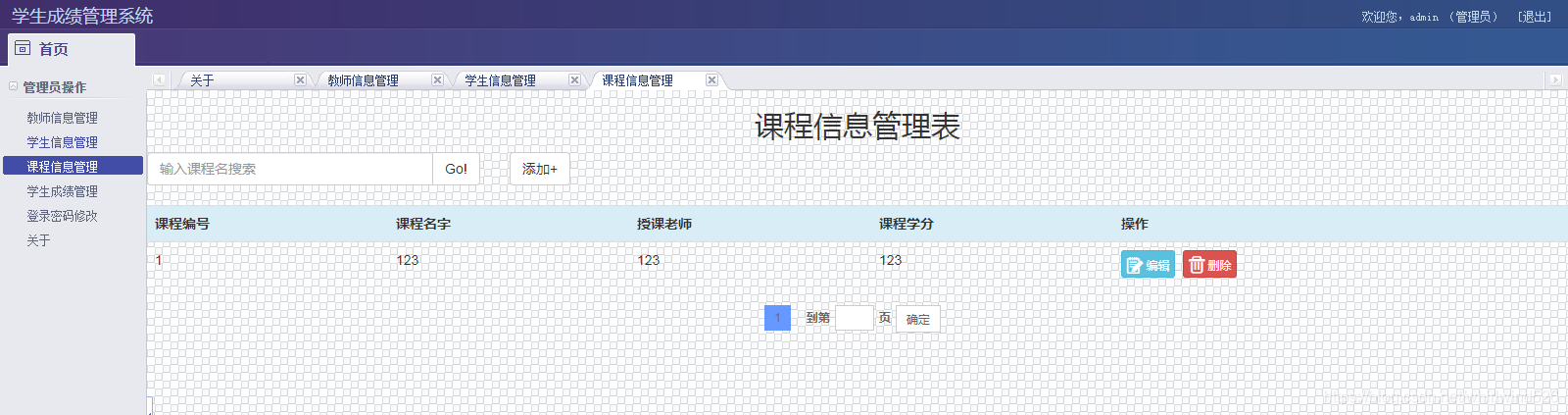
KS006基于SSM实现学生成绩管理系统
随机推荐
Six lessons to be learned for the successful implementation of edge coding
6-2漏洞利用-ftp不可避免的问题
Look at the industrial Internet from a new perspective and seek the correct ways and methods of industrial Internet
Matlab uses resample to complete resampling
Design and control of multi rotor aircraft (VII) -- sensor calibration and measurement model
matlab 实现语音信号重采样和归一化,并播放比对效果
Altium designer measure distance (ctrl+m)
Part 29 supplement (XXIX) basis of ECMAScript
机器学习基本概念
MySQL application day02
电子协会 C语言 1级 32、计算2的幂
遊戲思考15:全區全服和分區分服的思考
Ks006 student achievement management system based on SSM
Pyldavis installation and use | attributeerror: module 'pyldavis' has no attribute' gensim '| visual results are exported as separate web pages
[IVX junior engineer training course 10 papers to get certificates] 0708 news page production
Three core problems of concurrent programming
电子协会 C语言 1级 33 、奇偶数判断
Docker安装Oracle_11g
Game thinking 15: thinking about the whole region and sub region Services
Matlab uses audiorecorder and recordblocking to record sound, play to play sound, and audiobook to save sound