当前位置:网站首页>ShardingJDBC usage summary
ShardingJDBC usage summary
2022-07-31 01:50:00 【xushiyu1996818】
目录
The implementation motivation of the configuration center
Implementation motivation of the registry
环境构建
1、创建一个springboot项目
2、导入如下依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.mashibing</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere_demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>shardingsphere_demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skipTests>true</skipTests>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>sharding-jdbc实现水平分表
1、创建sharding_sphere数据库
2、在数据库中创建两张表,orders_1和orders_2
3、分片规则:如果订单编号是偶数添加到orders_1,如果是奇数添加到orders_2
4、创建实体类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
public class Orders {
private Integer id;
private Integer orderType;
private Integer customerId;
private Double amount;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public Integer getOrderType() {
return orderType;
}
public void setOrderType(Integer orderType) {
this.orderType = orderType;
}
public Integer getCustomerId() {
return customerId;
}
public void setCustomerId(Integer customerId) {
this.customerId = customerId;
}
public Double getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(Double amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Orders{" +
"id=" + id +
", orderType=" + orderType +
", customerId=" + customerId +
", amount=" + amount +
'}';
}
}5、创建mapper类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface OrdersMapper {
@Insert("insert into orders(id,order_type,customer_id,amount) values(#{id},#{orderType},#{customerId},#{amount})")
public void insert(Orders orders);
@Select("select * from orders where id = #{id}")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "orderType",column = "order_type"),
@Result(property = "customerId",column = "customer_id"),
@Result(property = "amount",column = "amount")
})
public Orders selectOne(Integer id);
}6、创建配置文件
#整合mybatis
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.mashibing.mapper
#配置数据源的名称
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1
#配置数据源的具体内容,
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.111:3306/sharding_sphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
#指定orders表的分布情况,配置表在哪个数据库中,表名称是什么
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.actual-data-nodes=ds1.orders_$->{1..2}
#指定orders表里主键id生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#指定分片策略.根据id的奇偶性来判断插入到哪个表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=orders_${id%2+1}
#打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true7、创建测试类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.OrdersMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingsphereDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private OrdersMapper ordersMapper;
@Test
public void addOrders(){
for (int i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
Orders orders = new Orders();
orders.setId(i);
orders.setCustomerId(i);
orders.setOrderType(i);
orders.setAmount(1000.0*i);
ordersMapper.insert(orders);
}
}
@Test
public void queryOrders(){
Orders orders = ordersMapper.selectOne(1);
System.out.println(orders);
}
}sharding-jdbc实现水平分库
1、在不同的数据节点node01,node02上创建不同名称的数据库:sharding_sphere_1,sharding_sphere_2
2、在两个数据库上创建相同的表orders_1,orders_2
3、分片规则,按照customer_id的奇偶性来进行分库,然后按照id的奇偶性进行分表
4、修改配置文件
# 配置不同的数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
#配置ds1数据源的基本信息
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.111:3306/sharding_sphere_1?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
#配置ds2数据源的基本信息
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.112:3306/sharding_sphere_2?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456
#指定数据库的分布情况
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.actual-data-nodes=ds$->{1..2}.orders_$->{1..2}
#指定orders表的主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#指定表分片策略,根据id的奇偶性来添加到不同的表中
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=orders_$->{id%2+1}
#指定库分片策略,根据customer_id的奇偶性来添加到不同的库中
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=customer_id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.orders.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds$->{customer_id%2+1}
#打开sql输出日志
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true5、修改mapper类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface OrdersMapper {
@Insert("insert into orders(id,order_type,customer_id,amount) values(#{id},#{orderType},#{customerId},#{amount})")
public void insert(Orders orders);
@Select("select * from orders where id = #{id}")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "orderType",column = "order_type"),
@Result(property = "customerId",column = "customer_id"),
@Result(property = "amount",column = "amount")
})
public Orders selectOne(Integer id);
@Select("select * from orders where id = #{id} and customer_id=#{customerId}")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id"),
@Result(property = "orderType",column = "order_type"),
@Result(property = "customerId",column = "customer_id"),
@Result(property = "amount",column = "amount")
})
public Orders selectOneDB(Orders orders);
}6、编写测试类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.OrdersMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Random;
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingsphereDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private OrdersMapper ordersMapper;
@Test
public void addOrdersDB(){
for (int i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
Orders orders = new Orders();
orders.setId(i);
orders.setCustomerId(new Random().nextInt(10));
orders.setOrderType(i);
orders.setAmount(1000.0*i);
ordersMapper.insert(orders);
}
}
@Test
public void queryOrdersDB(){
Orders orders = new Orders();
orders.setCustomerId(7);
orders.setId(7);
Orders o = ordersMapper.selectOneDB(orders);
System.out.println(o);
}
}sharding-jdbc实现垂直分库
1、在不同的数据节点node01,node02创建相同的库sharding_sphere
2、在node01上创建orders表,在node02上创建customer表
3、分片规则:将不同的表插入到不同的库中
4、编写customer类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
public class Customer {
private Integer id;
private String name;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}5、编写customerMapper类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Customer;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface CustomerMapper {
@Insert("insert into customer(id,name) values(#{id},#{name})")
public void insertCustomer(Customer customer);
}6、修改配置文件
#配置数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
#配置第一个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.111:3306/sharding_sphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
#配置第二个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.112:3306/sharding_sphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456
#配置orders表所在的数据节点
#spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.order.actual-data-nodes=ds1.orders
#配置customer表所在的数据节点
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.customer.actual-data-nodes=ds2.customer
#customer表的主键生成策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.customer.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.customer.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE
#指定分片的策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.customer.table-strategy.inline.sharding-column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.customer.table-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=customer
#显示sql
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true
7、编写测试类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Customer;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.OrdersMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Random;
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingsphereDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private CustomerMapper customerMapper;
@Test
public void insertCustomer(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 10 ; i++) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(i);
customer.setName("zs"+i);
customerMapper.insertCustomer(customer);
}
}
}
sharding-jdbc公共表
之前我们在学习mycat的时候接触过字典表的概念,其实在shardingsphere中也有类似的概念,只不过名字叫做公共表,也就是需要在各个库中都存在的表,方便做某些关联查询.
1、在不同节点的库上创建相同的表
2、分片规则:公共表表示所有的库都具备相同的表
3、创建实体类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
public class DictOrderType {
private Integer id;
private String orderType;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getOrderType() {
return orderType;
}
public void setOrderType(String orderType) {
this.orderType = orderType;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DictOrderType{" +
"id=" + id +
", orderType='" + orderType + '\'' +
'}';
}
}4、创建DictOrderTypeMapper文件
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.DictOrderType;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface DictOrderTypeMapper {
@Insert("insert into dict_order_type(id,order_type) values(#{id},#{orderType})")
public void insertDictOrderType(DictOrderType dictOrderType);
@Delete("delete from dict_order_type where id = #{id}")
public void DeleteDictOrderType(Integer id);
}
5、修改配置文件
#配置数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
#配置第一个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.111:3306/sharding_sphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
#配置第二个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.112:3306/sharding_sphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456
#配置公共表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.broadcast-tables=dict_order_type
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.dict_order_type.key-generator.column=id
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.dict_order_type.key-generator.type=SNOWFLAKE6、编写测试类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Customer;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.DictOrderType;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.DictOrderTypeMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.OrdersMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Random;
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingsphereDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private DictOrderTypeMapper dictOrderTypeMapper;
@Test
public void insertDictOrderType(){
for (int i = 1; i <= 10 ; i++) {
DictOrderType dictOrderType = new DictOrderType();
dictOrderType.setOrderType("orderType"+i);
dictOrderTypeMapper.insertDictOrderType(dictOrderType);
}
}
@Test
public void deleteDictOrderType(){
dictOrderTypeMapper.DeleteDictOrderType(1);
}
}
sharding-jdbc绑定表
Configure as before2个表,Then configure the binding table
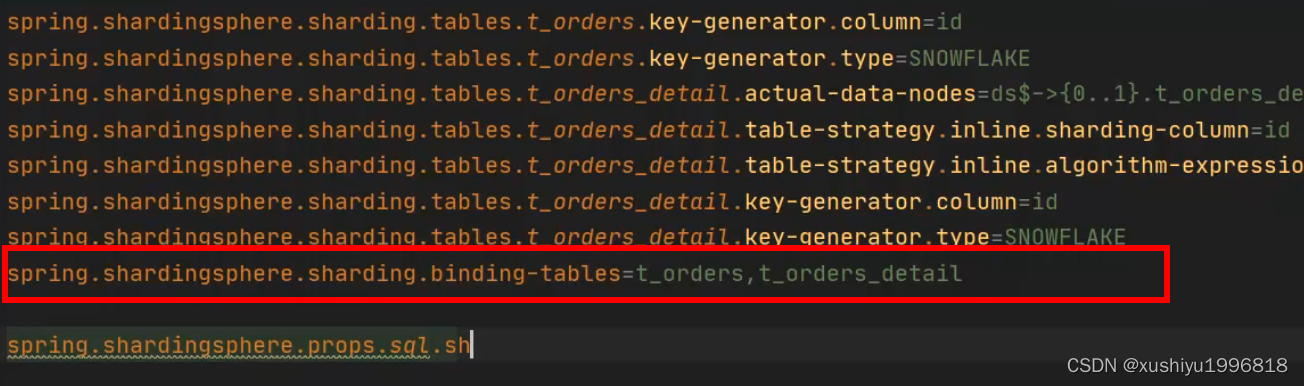
sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.binding-tables=t_order,t_order_item分片规则
Sharding-JDBC中的分片策略有两个维度:
数据源分片策略(DatabaseShardingStrategy):数据被分配的目标数据源
表分片策略(TableShardingStrategy):数据被分配的目标表
两种分片策略API完全相同,但是表分片策略是依赖于数据源分片策略的(即:先分库,然后才有分表)

Sharding分片策略继承自ShardingStrategy,提供了5种分片策略.
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.ShardingStrategy
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.standard.StandardShardingStrategy
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.standard.ComplexShardingStrategy
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.standard.InlineShardingStrategy
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.standard.HintShardingStrategy
io.shardingsphere.core.routing.strategy.standard.NoneShardingStrategy准备工作
先创建两个数据库 ds-0、ds-1,两个库中分别建表 t_order_0、t_order_1、t_order_2 、t_order_item_0、t_order_item_1、t_order_item_2 6张表,下边实操看看如何在不同场景下应用 sharding-jdbc 的 4种分片策略.
t_order_n 表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `t_order_0` (
`order_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL,
`order_no` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`user_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL,
`create_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`price` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`order_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC;
t_order_item_n 表结构如下:
CREATE TABLE `t_order_item_0` (
`item_id` bigint(100) NOT NULL,
`order_id` bigint(200) NOT NULL,
`order_no` varchar(200) NOT NULL,
`item_name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`price` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`item_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC;
The sharding strategy is divided into table sharding strategy and database sharding strategy,它们实现分片算法的方式基本相同,不同是一个对库ds-0、ds-1,一个对表 t_order_0 ··· t_order_n 等做处理.
标准分片策略
使用场景:SQL 语句中有>,>=, <=,<,=,IN 和 BETWEEN AND 操作符,都可以应用此分片策略.
标准分片策略(StandardShardingStrategy),它只支持对单个分片健(字段)为依据的分库分表,并提供了两种分片算法 PreciseShardingAlgorithm(精准分片)和 RangeShardingAlgorithm(范围分片).
在使用标准分片策略时,精准分片算法是必须实现的算法,用于 SQL 含有 = 和 IN 的分片处理;范围分片算法是非必选的,用于处理含有 BETWEEN AND 的分片处理.
一旦我们没配置范围分片算法,而 SQL 中又用到 BETWEEN AND 或者 like等,那么 SQL 将按全库、表路由的方式逐一执行,查询性能会很差需要特别注意.
接下来自定义实现 精准分片算法 和 范围分片算法.
精准分片算法
1 精准分库算法
实现自定义精准分库、分表算法的方式大致相同,都要实现 PreciseShardingAlgorithm 接口,并重写 doSharding() 方法,只是配置稍有不同,而且它只是个空方法,得我们自行处理分库、分表逻辑.其他分片策略亦如此.
SELECT * FROM t_order where order_id = 1 or order_id in (1,2,3);
下边我们实现精准分库策略,通过对分片健 order_id 取模的方式(怎么实现看自己喜欢)计算出 SQL 该路由到哪个库,计算出的分片库信息会存放在分片上下文中,方便后续分表中使用.
/**
* @author TianL
* @description 自定义标准分库策略
* @date 2020/10/30 13:48
*/
public class MyDBPreciseShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> databaseNames, PreciseShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
/**
* databaseNames 所有分片库的集合
* shardingValue 为分片属性,其中 logicTableName 为逻辑表,columnName 分片健(字段),value 为从 SQL 中解析出的分片健的值
*/
for (String databaseName : databaseNames) {
String value = shardingValue.getValue() % databaseNames.size() + "";
if (databaseName.endsWith(value)) {
return databaseName;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
其中 Collection<String> 参数在几种分片策略中使用一致,在分库时值为所有分片库的集合 databaseNames,分表时为对应分片库中所有分片表的集合 tablesNames;PreciseShardingValue 为分片属性,其中 logicTableName 为逻辑表,columnName 分片健(字段),value 为从 SQL 中解析出的分片健的值.

而 application.properties 配置文件中只需修改分库策略名 database-strategy 为标准模式 standard,分片算法 standard.precise-algorithm-class-name 为自定义的精准分库算法类路径.
### 分库策略
# 分库分片健
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=order_id
# 分库分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.dbAlgorithm.MyDBPreciseShardingAlgorithm
精准分表算法
精准分表算法同样实现 PreciseShardingAlgorithm 接口,并重写 doSharding() 方法.
/**
* @author TianL
* @description 自定义标准分表策略
* @date 2020/10/30 13:48
*/
public class MyTablePreciseShardingAlgorithm implements PreciseShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public String doSharding(Collection<String> tableNames, PreciseShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
/**
* tableNames 对应分片库中所有分片表的集合
* shardingValue 为分片属性,其中 logicTableName 为逻辑表,columnName 分片健(字段),value 为从 SQL 中解析出的分片健的值
*/
for (String tableName : tableNames) {
/**
* 取模算法,分片健 % 表数量
*/
String value = shardingValue.getValue() % tableNames.size() + "";
if (tableName.endsWith(value)) {
return tableName;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
}
分表时 Collection<String> 参数为上边计算出的分片库,对应的所有分片表的集合 tablesNames;PreciseShardingValue 为分片属性,其中 logicTableName 为逻辑表,columnName 分片健(字段),value 为从 SQL 中解析出的分片健的值.

application.properties 配置文件也只需修改分表策略名 database-strategy 为标准模式 standard,分片算法 standard.precise-algorithm-class-name 为自定义的精准分表算法类路径.
# 分表策略
# 分表分片健
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=order_id
# 分表算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.tableAlgorithm.MyTablePreciseShardingAlgorithm
看到这不难发现,自定义分库和分表算法的实现基本是一样的,所以后边我们只演示分库即可
范围分片算法
使用场景:当我们 SQL中的分片健字段用到 BETWEEN AND操作符会使用到此算法,会根据 SQL中给出的分片健值范围值处理分库、分表逻辑.
SELECT * FROM t_order where order_id BETWEEN 1 AND 100;
自定义范围分片算法需实现 RangeShardingAlgorithm 接口,重写 doSharding() 方法,下边我通过遍历分片健值区间,计算每一个分库、分表逻辑.
/**
* @author TianL
* @description 范围分库算法
* @date 2020/11/2 12:06
*/
public class MyDBRangeShardingAlgorithm implements RangeShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> databaseNames, RangeShardingValue<Integer> rangeShardingValue) {
Set<String> result = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// between and 的起始值
int lower = rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().lowerEndpoint();
int upper = rangeShardingValue.getValueRange().upperEndpoint();
// 循环范围计算分库逻辑
for (int i = lower; i <= upper; i++) {
for (String databaseName : databaseNames) {
if (databaseName.endsWith(i % databaseNames.size() + "")) {
result.add(databaseName);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
和上边的一样 Collection<String> 在分库、分表时分别代表分片库名和表名集合,RangeShardingValue 这里取值方式稍有不同, lowerEndpoint 表示起始值, upperEndpoint 表示截止值.

在配置上由于范围分片算法和精准分片算法,同在标准分片策略下使用,所以只需添加上 range-algorithm-class-name 自定义范围分片算法类路径即可.
# 精准分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.precise-algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.dbAlgorithm.MyDBPreciseShardingAlgorithm
# 范围分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.standard.range-algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.dbAlgorithm.MyDBRangeShardingAlgorithm
复合分片策略
使用场景:SQL 语句中有>,>=, <=,<,=,IN 和 BETWEEN AND 等操作符,不同的是复合分片策略支持对多个分片健操作.
下面我们实现同时以 order_id、user_id 两个字段作为分片健,自定义复合分片策略.
SELECT * FROM t_order where user_id =0 and order_id = 1;
我们先修改一下原配置,complex.sharding-column 切换成 complex.sharding-columns 复数,分片健上再加一个 user_id ,分片策略名变更为 complex ,complex.algorithm-class-name 替换成我们自定义的复合分片算法.
### 分库策略
# order_id,user_id 同时作为分库分片健
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.complex.sharding-column=order_id,user_id
# 复合分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.complex.algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.dbAlgorithm.MyDBComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm
自定义复合分片策略要实现 ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm 接口,重新 doSharding()方法.
/**
* @author xiaofu TianL
* @description 自定义复合分库策略
* @date 2020/10/30 13:48
*/
public class MyDBComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm implements ComplexKeysShardingAlgorithm<Integer> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> databaseNames, ComplexKeysShardingValue<Integer> complexKeysShardingValue) {
// 得到每个分片健对应的值
Collection<Integer> orderIdValues = this.getShardingValue(complexKeysShardingValue, "order_id");
Collection<Integer> userIdValues = this.getShardingValue(complexKeysShardingValue, "user_id");
List<String> shardingSuffix = new ArrayList<>();
// 对两个分片健同时取模的方式分库
for (Integer userId : userIdValues) {
for (Integer orderId : orderIdValues) {
String suffix = userId % 2 + "_" + orderId % 2;
for (String databaseName : databaseNames) {
if (databaseName.endsWith(suffix)) {
shardingSuffix.add(databaseName);
}
}
}
}
return shardingSuffix;
}
private Collection<Integer> getShardingValue(ComplexKeysShardingValue<Integer> shardingValues, final String key) {
Collection<Integer> valueSet = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, Collection<Integer>> columnNameAndShardingValuesMap = shardingValues.getColumnNameAndShardingValuesMap();
if (columnNameAndShardingValuesMap.containsKey(key)) {
valueSet.addAll(columnNameAndShardingValuesMap.get(key));
}
return valueSet;
}
}
Collection<String> 用法还是老样子,由于支持多分片健 ComplexKeysShardingValue 分片属性内用一个分片健为 key,分片健值为 value 的 map来存储分片键属性.

行表达式分片策略
行表达式分片策略(InlineShardingStrategy),在配置中使用 Groovy 表达式,提供对 SQL语句中的 = 和 IN 的分片操作支持,它只支持单分片健.
行表达式分片策略适用于做简单的分片算法,无需自定义分片算法,省去了繁琐的代码开发,是几种分片策略中最为简单的.
它的配置相当简洁,这种分片策略利用inline.algorithm-expression书写表达式.
比如:ds-$->{order_id % 2} 表示对 order_id 做取模计算,$ 是个通配符用来承接取模结果,最终计算出分库ds-0 ··· ds-n,整体来说比较简单.
# 行表达式分片键
sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.sharding-column=order_id
# 表达式算法
sharding.jdbc.config.sharding.tables.t_order.database-strategy.inline.algorithm-expression=ds-$->{order_id % 2}
Hint分片策略
Hint分片策略(HintShardingStrategy)相比于上面几种分片策略稍有不同,这种分片策略无需配置分片健,分片健值也不再从 SQL中解析,而是由外部指定分片信息,让 SQL在指定的分库、分表中执行.ShardingSphere 通过 Hint API实现指定操作,实际上就是把分片规则tablerule 、databaserule由集中配置变成了个性化配置.
举个例子,如果我们希望订单表t_order用 user_id 做分片健进行分库分表,但是 t_order 表中却没有 user_id 这个字段,这时可以通过 Hint API 在外部手动指定分片健或分片库.
下边我们这边给一条无分片条件的SQL,看如何指定分片健让它路由到指定库表.
SELECT * FROM t_order;
使用 Hint分片策略同样需要自定义,实现 HintShardingAlgorithm 接口并重写 doSharding()方法.
/**
* @author xinzhifu
* @description hit分表算法
* @date 2020/11/2 12:06
*/
public class MyTableHintShardingAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm<String> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(Collection<String> tableNames, HintShardingValue<String> hintShardingValue) {
Collection<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String tableName : tableNames) {
for (String shardingValue : hintShardingValue.getValues()) {
if (tableName.endsWith(String.valueOf(Long.valueOf(shardingValue) % tableNames.size()))) {
result.add(tableName);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
自定义完算法只实现了一部分,还需要在调用 SQL 前通过 HintManager 指定分库、分表信息.由于每次添加的规则都放在 ThreadLocal 内,所以要先执行 clear() 清除掉上一次的规则,否则会报错;addDatabaseShardingValue 设置分库分片健键值,addTableShardingValue设置分表分片健键值.setMasterRouteOnly 读写分离强制读主库,避免造成主从复制导致的延迟.
// 清除掉上一次的规则,否则会报错
HintManager.clear();
// HintManager API 工具类实例
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
// 直接指定对应具体的数据库
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue("ds",0);
// 设置表的分片健
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order" , 0);
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order" , 1);
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order" , 2);
// 在读写分离数据库中,Hint 可以强制读主库
hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly();
debug 调试看到,我们对 t_order 表设置分表分片健键值,可以在自定义的算法 HintShardingValue 参数中成功拿到.

properties 文件中配置无需再指定分片健,只需自定义的 Hint分片算法类路径即可.
# Hint分片算法
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.tables.t_order.table-strategy.hint.algorithm-class-name=com.xiaofu.sharding.algorithm.tableAlgorithm.MyTableHintShardingAlgorithm
sharding-jdbc实现读写分离
读写分离的概念大家应该已经很熟练了,此处不在赘述,下面我们通过sharding-jdbc来实现读写分离,其实大家应该已经发现了,所有的操作都是配置问题,下面我们来讲一下具体的配置,关于读写分离的原理,以及如何配置mysql的主从复制,我们就不在多聊了,直接看sharding-jdbc的配置.
1、我们规定ds1为写库,ds2为读库
2、创建person类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
public class Person {
private Long id;
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}3、创建personMapper类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Person;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface PersonMapper {
@Insert("insert into person(id,name) values(#{id},#{name})")
public void insertPerson(Person person);
@Select("select * from person where id = #{id}")
public Person queryPerson(Long id);
}4、修改配置文件
#配置数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
#配置第一个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.111:3306/shardingsphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.password=123456
#配置第二个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.112:3306/shardingsphere?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.username=root
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.password=123456
#主库从库逻辑定义
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.name=ms
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.master-data-source-name=ds1
spring.shardingsphere.masterslave.slave-data-source-names=ds2
#显示执行的sql
spring.shardingsphere.props.sql.show=true5、编写测试类
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Customer;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.DictOrderType;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Orders;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Person;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.CustomerMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.DictOrderTypeMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.OrdersMapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.PersonMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Order;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.Random;
@SpringBootTest
class ShardingsphereDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private PersonMapper personMapper;
@Test
public void insertPerson(){
Person person = new Person();
person.setId(1l);
person.setName("zhangsan");
personMapper.insertPerson(person);
}
@Test
public void queryPerson(){
Person person = personMapper.queryPerson(1l);
System.out.println(person);
}
}sharding-jdbc强制路由
ShardingSphere使用ThreadLocal管理分片键值进行Hint强制路由.可以通过编程的方式向HintManager中添加分片值,该分片值仅在当前线程内生效. Hint方式主要使用场景:
1.分片字段不存在SQL中、数据库表结构中,而存在于外部业务逻辑.
2.强制在主库进行某些数据操作.
具体操作:
order.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Order implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 661434701950670670L;
private long orderId;
private int userId;
private long addressId;
private String status;
public long getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(final long orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(final int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(final String status) {
this.status = status;
}
public long getAddressId() {
return addressId;
}
public void setAddressId(final long addressId) {
this.addressId = addressId;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("order_id: %s, user_id: %s, address_id: %s, status: %s", orderId, userId, addressId, status);
}
}orderItem.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class OrderItem implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 263434701950670170L;
private long orderItemId;
private long orderId;
private int userId;
private String status;
public long getOrderItemId() {
return orderItemId;
}
public void setOrderItemId(final long orderItemId) {
this.orderItemId = orderItemId;
}
public long getOrderId() {
return orderId;
}
public void setOrderId(final long orderId) {
this.orderId = orderId;
}
public int getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(final int userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(final String status) {
this.status = status;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("order_item_id:%s, order_id: %s, user_id: %s, status: %s", orderItemId, orderId, userId, status);
}
}Address.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean;
public class Address {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 661434701950670670L;
private Long addressId;
private String addressName;
public Long getAddressId() {
return addressId;
}
public void setAddressId(final Long addressId) {
this.addressId = addressId;
}
public String getAddressName() {
return addressName;
}
public void setAddressName(final String addressName) {
this.addressName = addressName;
}
}MyHintalgorithm.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingAlgorithm;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingValue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
@Component
public class MyHintAlgorithm implements HintShardingAlgorithm<Long> {
@Override
public Collection<String> doSharding(final Collection<String> availableTargetNames, final HintShardingValue<Long> shardingValue) {
Collection<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (String each : availableTargetNames) {
for (Long value : shardingValue.getValues()) {
if (each.endsWith(String.valueOf(value % 2))) {
result.add(each);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
HintType.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint;
public enum HintType {
DATABASE_ONLY, DATABASE_TABLES, MASTER_ONLY
}
HintMain.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.service.ExampleService;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.service.OrderServiceImpl;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.api.hint.HintManager;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.yaml.YamlMasterSlaveDataSourceFactory;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.yaml.YamlShardingDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class HintMain {
private static final HintType TYPE = HintType.DATABASE_TABLES;
// private static final HintType TYPE = HintType.DATABASE_ONLY;
// private static final HintType TYPE = HintType.MASTER_ONLY;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, SQLException {
DataSource dataSource = getDataSource();
ExampleService exampleService = getExampleService(dataSource);
exampleService.initEnvironment();
exampleService.processSuccess();
processWithHintValue(dataSource);
// exampleService.cleanEnvironment();
}
private static DataSource getDataSource() throws IOException, SQLException {
switch (TYPE) {
case DATABASE_TABLES:
return YamlShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(getFile("F:\\selfproject\\shardingsphere_demo\\src\\main\\resources\\hint-databases-tables.yaml"));
case DATABASE_ONLY:
return YamlShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(getFile("F:\\selfproject\\shardingsphere_demo\\src\\main\\resources\\hint-databases-only.yaml"));
case MASTER_ONLY:
return YamlMasterSlaveDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(getFile("F:\\selfproject\\shardingsphere_demo\\src\\main\\resources\\hint-master-only.yaml"));
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("unsupported type");
}
}
private static File getFile(final String configFile) {
return new File(configFile);
}
private static ExampleService getExampleService(final DataSource dataSource) {
return new OrderServiceImpl(dataSource);
}
private static void processWithHintValue(final DataSource dataSource) throws SQLException {
try (HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
setHintValue(hintManager);
statement.execute("select * from t_order");
statement.execute("SELECT i.* FROM t_order o, t_order_item i WHERE o.order_id = i.order_id");
statement.execute("select * from t_order_item");
statement.execute("INSERT INTO t_order (user_id, address_id, status) VALUES (1, 1, 'init')");
}
}
private static void setHintValue(final HintManager hintManager) {
switch (TYPE) {
case DATABASE_TABLES:
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue("t_order", 1L);
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order", 1L);
return;
case DATABASE_ONLY:
hintManager.setDatabaseShardingValue(1L);
return;
case MASTER_ONLY:
hintManager.setMasterRouteOnly();
return;
default:
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("unsupported type");
}
}
}
CommonMapper.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
public interface CommonMapper<T, P> {
/**
* Create table if not exist.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void createTableIfNotExists() throws SQLException;
/**
* Drop table.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void dropTable() throws SQLException;
/**
* Truncate table.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void truncateTable() throws SQLException;
/**
* insert data.
*
* @param entity entity
* @return generated primary key
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
P insert(T entity) throws SQLException;
/**
* Delete data.
*
* @param primaryKey primaryKey
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void delete(P primaryKey) throws SQLException;
/**
* Select all data.
*
* @return all data
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
List<T> selectAll() throws SQLException;
}
OrderMapper.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Order;
public interface OrderMapper extends CommonMapper<Order,Long>{
}
OrderMapperImpl.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Order;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class OrderMapperImpl implements OrderMapper {
private DataSource dataSource;
public OrderMapperImpl(final DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public void createTableIfNotExists() throws SQLException {
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_order (order_id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, user_id INT NOT NULL, address_id BIGINT NOT NULL, status VARCHAR(50), PRIMARY KEY (order_id))";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void dropTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "DROP TABLE t_order";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void truncateTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "TRUNCATE TABLE t_order";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public Long insert(final Order order) throws SQLException {
String sql = "INSERT INTO t_order (user_id, address_id, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS)) {
preparedStatement.setInt(1, order.getUserId());
preparedStatement.setLong(2, order.getAddressId());
preparedStatement.setString(3, order.getStatus());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
try (ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys()) {
if (resultSet.next()) {
order.setOrderId(resultSet.getLong(1));
}
}
}
return order.getOrderId();
}
@Override
public void delete(final Long orderId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "DELETE FROM t_order WHERE order_id=?";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setLong(1, orderId);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
}
@Override
public List<Order> selectAll() throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_order";
return getOrders(sql);
}
protected List<Order> getOrders(final String sql) throws SQLException {
List<Order> result = new LinkedList<>();
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (resultSet.next()) {
Order order = new Order();
order.setOrderId(resultSet.getLong(1));
order.setUserId(resultSet.getInt(2));
order.setAddressId(resultSet.getLong(3));
order.setStatus(resultSet.getString(4));
result.add(order);
}
}
return result;
}
}
OrderItemMapper.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.OrderItem;
public interface OrderItemMapper extends CommonMapper<OrderItem,Long> {
}
OrderItemMapperImpl.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.OrderItem;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class OrderItemMapperImpl implements OrderItemMapper{
private DataSource dataSource;
public OrderItemMapperImpl(final DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public void createTableIfNotExists() throws SQLException {
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_order_item "
+ "(order_item_id BIGINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, order_id BIGINT NOT NULL, user_id INT NOT NULL, status VARCHAR(50), PRIMARY KEY (order_item_id))";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void dropTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "DROP TABLE t_order_item";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void truncateTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "TRUNCATE TABLE t_order_item";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public Long insert(final OrderItem orderItem) throws SQLException {
String sql = "INSERT INTO t_order_item (order_id, user_id, status) VALUES (?, ?, ?)";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS)) {
preparedStatement.setLong(1, orderItem.getOrderId());
preparedStatement.setInt(2, orderItem.getUserId());
preparedStatement.setString(3, orderItem.getStatus());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
try (ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.getGeneratedKeys()) {
if (resultSet.next()) {
orderItem.setOrderItemId(resultSet.getLong(1));
}
}
}
return orderItem.getOrderItemId();
}
@Override
public void delete(final Long orderItemId) throws SQLException {
String sql = "DELETE FROM t_order_item WHERE order_item_id=?";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setLong(1, orderItemId);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
}
@Override
public List<OrderItem> selectAll() throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT i.* FROM t_order o, t_order_item i WHERE o.order_id = i.order_id";
return getOrderItems(sql);
}
protected List<OrderItem> getOrderItems(final String sql) throws SQLException {
List<OrderItem> result = new LinkedList<>();
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (resultSet.next()) {
OrderItem orderItem = new OrderItem();
orderItem.setOrderItemId(resultSet.getLong(1));
orderItem.setOrderId(resultSet.getLong(2));
orderItem.setUserId(resultSet.getInt(3));
orderItem.setStatus(resultSet.getString(4));
result.add(orderItem);
}
}
return result;
}
}
AddressMapper.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Address;
public interface AddressMapper extends CommonMapper<Address,Long> {
}AddressMapperImpl.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Address;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class AddressMapperImpl implements AddressMapper{
private DataSource dataSource;
public AddressMapperImpl(final DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
@Override
public void createTableIfNotExists() throws SQLException {
String sql = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_address "
+ "(address_id BIGINT NOT NULL, address_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (address_id))";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void dropTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "DROP TABLE t_address";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public void truncateTable() throws SQLException {
String sql = "TRUNCATE TABLE t_address";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
statement.executeUpdate(sql);
}
}
@Override
public Long insert(final Address entity) throws SQLException {
String sql = "INSERT INTO t_address (address_id, address_name) VALUES (?, ?)";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setLong(1, entity.getAddressId());
preparedStatement.setString(2, entity.getAddressName());
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
return entity.getAddressId();
}
@Override
public void delete(final Long primaryKey) throws SQLException {
String sql = "DELETE FROM t_address WHERE address_id=?";
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql)) {
preparedStatement.setLong(1, primaryKey);
preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
}
}
@Override
public List<Address> selectAll() throws SQLException {
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_address";
return getAddress(sql);
}
private List<Address> getAddress(final String sql) throws SQLException {
List<Address> result = new LinkedList<>();
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (resultSet.next()) {
Address address = new Address();
address.setAddressId(resultSet.getLong(1));
address.setAddressName(resultSet.getString(2));
result.add(address);
}
}
return result;
}
}ExampleService.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.service;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public interface ExampleService {
/**
* Initialize environment.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void initEnvironment() throws SQLException;
/**
* Clean environment.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void cleanEnvironment() throws SQLException;
/**
* Process success.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void processSuccess() throws SQLException;
/**
* Process failure.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void processFailure() throws SQLException;
/**
* Print data.
*
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
void printData() throws SQLException;
}
OrderServiceImpl.java
package com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.service;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Address;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.Order;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.bean.OrderItem;
import com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.mapper.*;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class OrderServiceImpl implements ExampleService{
private OrderMapperImpl orderMapperImpl;
private OrderItemMapperImpl orderItemMapperImpl;
private AddressMapperImpl addressMapperImpl;
public OrderServiceImpl(final DataSource dataSource) {
this.orderMapperImpl = new OrderMapperImpl(dataSource);
this.orderItemMapperImpl = new OrderItemMapperImpl(dataSource);
this.addressMapperImpl = new AddressMapperImpl(dataSource);
}
public OrderServiceImpl( OrderMapperImpl orderMapperImpl, OrderItemMapperImpl orderItemMapperImpl, AddressMapperImpl addressMapperImpl) {
this.orderMapperImpl = orderMapperImpl;
this.orderItemMapperImpl = orderItemMapperImpl;
this.addressMapperImpl = addressMapperImpl;
}
@Override
public void initEnvironment() throws SQLException {
orderMapperImpl.createTableIfNotExists();
orderItemMapperImpl.createTableIfNotExists();
orderMapperImpl.truncateTable();
orderItemMapperImpl.truncateTable();
initAddressTable();
}
private void initAddressTable() throws SQLException {
addressMapperImpl.createTableIfNotExists();
addressMapperImpl.truncateTable();
initAddressData();
}
private void initAddressData() throws SQLException {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
insertAddress(i);
}
}
private void insertAddress(final int i) throws SQLException {
Address address = new Address();
address.setAddressId((long) i);
address.setAddressName("address_" + i);
addressMapperImpl.insert(address);
}
@Override
public void cleanEnvironment() throws SQLException {
orderMapperImpl.dropTable();
orderItemMapperImpl.dropTable();
addressMapperImpl.dropTable();
}
@Override
public void processSuccess() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("-------------- Process Success Begin ---------------");
List<Long> orderIds = insertData();
printData();
// deleteData(orderIds);
printData();
System.out.println("-------------- Process Success Finish --------------");
}
@Override
public void processFailure() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("-------------- Process Failure Begin ---------------");
insertData();
System.out.println("-------------- Process Failure Finish --------------");
throw new RuntimeException("Exception occur for transaction test.");
}
private List<Long> insertData() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("---------------------------- Insert Data ----------------------------");
List<Long> result = new ArrayList<>(10);
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
Order order = insertOrder(i);
insertOrderItem(i, order);
result.add(order.getOrderId());
}
return result;
}
private Order insertOrder(final int i) throws SQLException {
Order order = new Order();
order.setUserId(i);
order.setAddressId(i);
order.setStatus("INSERT_TEST");
orderMapperImpl.insert(order);
return order;
}
private void insertOrderItem(final int i, final Order order) throws SQLException {
OrderItem item = new OrderItem();
item.setOrderId(order.getOrderId());
item.setUserId(i);
item.setStatus("INSERT_TEST");
orderItemMapperImpl.insert(item);
}
private void deleteData(final List<Long> orderIds) throws SQLException {
System.out.println("---------------------------- Delete Data ----------------------------");
for (Long each : orderIds) {
orderMapperImpl.delete(each);
orderItemMapperImpl.delete(each);
}
}
@Override
public void printData() throws SQLException {
System.out.println("---------------------------- Print Order Data -----------------------");
for (Object each : orderMapperImpl.selectAll()) {
System.out.println(each);
}
System.out.println("---------------------------- Print OrderItem Data -------------------");
for (Object each : orderItemMapperImpl.selectAll()) {
System.out.println(each);
}
}
}hint-databases-only.yaml
dataSources:
ds_0: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_0
username: root
password: 123456
ds_1: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_1
username: root
password: 123456
shardingRule:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item
bindingTables:
- t_order,t_order_item
broadcastTables:
- t_address
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint.MyHintAlgorithm
defaultTableStrategy:
none:
props:
sql.show: truehint-databases-tables.yaml
dataSources:
ds_0: !!com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_0
username: root
password: 123456
ds_1: !!com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_1
username: root
password: 123456
shardingRule:
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
databaseStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint.MyHintAlgorithm
tableStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: com.mashibing.shardingsphere_demo.hint.MyHintAlgorithm
keyGenerator:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
props:
worker.id: 123
t_order_item:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${0..1}
bindingTables:
- t_order,t_order_item
broadcastTables:
- t_address
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: user_id
algorithmExpression: ds_${user_id % 2}
defaultTableStrategy:
inline:
shardingColumn: order_id
algorithmExpression: t_order_item_${order_id % 2}
props:
sql.show: truehint-master-only.yaml
dataSources:
ds_master: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_0
username: root
password: 123456
ds_slave_0: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://192.168.85.113:3306/sharding_sphere_1
username: root
password: 123456
masterSlaveRule:
name: ds_ms
masterDataSourceName: ds_master
slaveDataSourceNames: [ds_slave_0]
props:
sql.show: truesharding-jdbc编排治理
编排治理模块提供配置中心/注册中心(以及规划中的元数据中心)、配置动态化、数据库熔断禁用、调用链路等治理能力.
The implementation motivation of the configuration center
1、配置集中化:越来越多的运行时实例,使得散落的配置难于管理,配置不同步导致的问题十分严重.将配置集中于配置中心,可以更加有效进行管理.
2、配置动态化:配置修改后的分发,是配置中心可以提供的另一个重要能力.它可支持数据源、表与分片及读写分离策略的动态切换.
Implementation motivation of the registry
1、相对于配置中心管理配置数据,注册中心存放运行时的动态/临时状态数据,比如可用的proxy的实例,需要禁用或熔断的datasource实例.
2、通过注册中心,可以提供熔断数据库访问程序对数据库的访问和禁用从库的访问的编排治理能力.治理仍然有大量未完成的功能(比如流控等).
支持的配置中心/注册中心
SPI
[Service Provider Interface (SPI)](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/sound/SPI-intro.html)是一种为了被第三方实现或扩展的API.它可以用于实现框架扩展或组件替换.
ShardingSphere在数据库治理模块使用SPI方式载入数据到配置中心/注册中心,进行实例熔断和数据库禁用. 目前,ShardingSphere内部支持Zookeeper和etcd这种常用的配置中心/注册中心. 此外,您可以使用其他第三方配置中心/注册中心,并通过SPI的方式注入到ShardingSphere,从而使用该配置中心/注册中心,实现数据库治理功能.
Zookeeper
ShardingSphere官方使用[Apache Curator](http://curator.apache.org/)作为Zookeeper的实现方案(Support configuration center and registration center). 请使用Zookeeper 3.4.6及其以上版本,详情请参见[官方网站](https://zookeeper.apache.org/).
Etcd
ShardingSphere官方使用[io.etcd/jetcd](https://github.com/etcd-io/jetcd)作为Etcd的实现方案(Support configuration center and registration center). 请使用Etcd v3以上版本,详情请参见[官方网站](https://etcd.io/).
Apollo
ShardingSphere官方使用[Apollo Client](https://github.com/ctripcorp/apollo)作为Apollo的实现方案(支持配置中心). 请使用Apollo Client 1.5.0及其以上版本,详情请参见[官方网站](https://github.com/ctripcorp/apollo).
Nacos
ShardingSphere官方使用[Nacos Client](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/sdk.html)作为Nacos的实现方案(支持配置中心). 请使用Nacos Client 1.0.0及其以上版本,详情请参见[官方网站](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/sdk.html).
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Software testing basic interface testing - getting started with Jmeter, you should pay attention to these things

GCC Rust获批将被纳入主线代码库,或将于GCC 13中与大家见面
coldfusion8后台计划任务拿shell

Teach you how to configure Jenkins automated email notifications

leetcode-1161: Maximum in-layer element sum

leetcode-1161:最大层内元素和
Between two orderly array of additive and Topk problem
C语言_结构体指针数组函数选票系统

ShardingJDBC使用总结
太阳能板最大面积 od js
随机推荐
VSCode Plugin: Nested Comments
leetcode-128: longest continuous sequence
软件测试报告有哪些内容?
程序员转正述职报告/总结
手把手教你配置Jenkins自动化邮件通知
最大路径和
leetcode-952: Calculate max component size by common factor
C语言小程序 -- 常见经典练习题
android的webview缓存相关知识收集
1.非类型模板参数 2.模板的特化 3.继承讲解
tkinter模块高级操作(二)—— 界面切换效果、立体阴影字效果及gif动图的实现
聚簇索引和非聚簇索引到底有什么区别
勾股数元组 od js
曼城推出可检测情绪的智能围巾,把球迷给整迷惑了
Google官方控件ShapeableImageView使用
Likou Daily Question - Day 46 - 704. Binary Search
【AcWing 第62场周赛】
Word/Excel 固定表格大小,填写内容时,表格不随单元格内容变化
汉诺塔问题
如何在 go 程序中暴露 Prometheus 指标