当前位置:网站首页>STL -- common function replication of string class
STL -- common function replication of string class
2022-07-08 00:49:00 【New Young】
List of articles
Preface :
string First knowledge of class
- string The essence is basic_string Rename the instantiated template class , It contains many member functions that handle strings : Replanted [],= etc.
typedef basic_string<char> string;
Namespace
I'm copying string Class time , because string Class is a built-in type in the standard library , To avoid naming pollution , You can name your own namespace
// complete string Add, delete, check, modify, duplicate
namespace My_Str // To prevent pollution std Namespace
{
class string
{
private:
char* _str;
int _size;// Number of valid characters
int _capacity;// The capacity of valid characters , It doesn't contain '\0', But because when opening up space, open up one more ,
// Therefore, one is reserved by default '\0', Easy to carry out C function
......
};
Data member
Here we use array form , Convenient operation
namespace My_Str // To prevent pollution std Namespace
{
class string
{
private:
char* _str;
int _size;// Number of valid characters
int _capacity;// The capacity of valid characters , It doesn't contain '\0', But because when opening up space, open up one more ,
// Therefore, one is reserved by default '\0', Easy to carry out C function
Constructors
string The standard cannot use a single character in initialization , You can only use strings or existing objects .
It is recommended to use Modern writing , It makes use of the automatic destruction of local variables after the frame of function stack and the flexible reuse of code
Custom constructors
- All default constructors , For empty strings ,_size by 0, Pay attention to when expanding
// All default constructors , For empty strings ,_size by 0, Pay attention to when expanding
//string(const char* str="");
My_Str::string::string(const char* str)
:_size(strlen(str)), _capacity( _size)
{
_str = new char[_capacity+1];//+1 It's for \0 Reserve space , prevent
strcpy(_str, str);
}
copy constructor
- Without reference , The transfer of arguments to formal parameters is also a copy
- When there are members who need dynamic management , Prevent shallow copy from causing multiple attacks on the same space delete problem
- Modern writing , The essence is the reuse of code and the post frame destruction of local variable function stack
// Copy structure , Be careful
// 1. Without reference , The transfer of arguments to formal parameters is also a copy
// 2. When there are members who need dynamic management , Prevent shallow copy from causing multiple attacks on the same space delete problem
My_Str::string::string(const string& s)
{
General writing
//_str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
//strcpy(_str, s._str);
//_size = s._size;
//_capacity = s._capacity;
Modern writing , The essence is the reuse of code and the post frame destruction of local variable function stack
string tmp(s._str);// A custom constructor was called
_str = nullptr;// This step must have , Otherwise, the random values are delete
swap(tmp);//string Under the swap function
//std::swap(_str,tmp._str);// Under the standard library swap template function
_size = tmp._size;
_capacity = tmp._capacity;
}
Assignment operator
Generally, we need to consider the problem of self assignment
Modern writing , Because the address of the copied object is different , Therefore, there is no need to consider the problem of self assignment and releasing the same space multiple times
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator=(const My_Str::string& s)
{
// Assignment of itself
//if (&s != this)
//{
// // General writing :
// char *tmp = new char[s._size + 1];// Prevent application failure ,C++ Of new Would throw exceptions , Not learned
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// delete[]_str;// Release the original space
// _str = tmp;// After the local variable is destroyed , Heap space still exists .
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
//}
// Modern writing , There is no need to consider the problem of self assignment and releasing the same space multiple times
string tmp(s);//
std::swap(_str, tmp._str);
_size = tmp._size;
_capacity = tmp._capacity;
return *this;
}
Destructor
My_Str::string::~string()// Destructor
{
delete[]_str;
_str = nullptr;
_size =_capacity= 0;
}
c_str()
const char* My_Str::string::c_str()
{
return _str;
}
const char* My_Str::string::c_str()const
{
return _str;
}
clear()
void My_Str::string::clear()
{
_size = 0;
}
size()
size_t My_Str::string::size()
{
return _size;
}
size_t My_Str::string::size()const
{
return _size;
}
The operator []
char& My_Str::string::operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& My_Str::string::operator[](size_t pos)const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
iterator
iterator , For the time being, the pointer
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
My_Str::string::iterator My_Str::string::begin()
{
return _str;
}
My_Str::string::iterator My_Str::string::end()
{
return _str + _size ;
}
My_Str::string::const_iterator My_Str::string::begin()const
{
return _str;
}
My_Str::string::const_iterator My_Str::string::end()const
{
return _str + _size;
}
Expansion function
reserve()
Scaling down is not supported , So just think about n>_capacity The situation of
void My_Str::string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if(n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n+1];
strcpy(tmp,_str);
delete[]_str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
resize()
Support shrinking and expanding , So we need to size As a boundary , Consideration
void My_Str::string::resize(size_t n, char ch)
{
//resize Scaling down is not supported _capacity;
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
memset(_str + _size, ch, n - _size);
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
Insert
Tail insertion
- Single character , Just expand the capacity according to the situation 2 Times ,
- But for Strings , Its number cannot be empty , Therefore, the expansion depends on the situation .
- It is more recommended to use +=;
push_back()
void My_Str::string::push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity==0?4:_capacity*2);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
append()
void My_Str::string::append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if ((len + _size) > _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
}
The operator +=
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator +=(const char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator +=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
Head insertion
insert()
Head insertion , It is generally not recommended to use , Low efficiency
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::insert(size_t pos, const char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
// Because it is an unsigned integer , In the subtraction operation, we should pay attention to the problem of dead circulation
size_t end = _size+1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
return *this;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos+len)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
--end;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str,len);
//strcpy Will '\0 Add in '
return *this;
}
check
find()
size_t My_Str::string::find(char ch)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (ch == _str[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t My_Str::string::find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size&& strlen(str)<_size);
const char* ret = strstr(_str, str);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
return ret - _str;
}
return npos;
}
Delete
erase()
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::erase(size_t pos , size_t len )
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos))// Delete all
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
I / O function
operator<<()
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const My_Str::string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)// Finite cycles , You can avoid strings containing '\0' The situation of
{
out << s[i];
}
//cout<<s.c_str();
return out;
}
operator>>()
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, My_Str::string& s)
{
char ch = 0;
//ch = getchar();
//while (ch != ' '&&ch!='\n')
//{
// s += ch;
// ch = getchar();
//}
s.clear();
ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' '&&ch!='\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
Comparison function
because string There are a lot of interfaces for , Here, overloaded functions are defined as global functions
operator<()
//"abcd" "abcd" false
//"abcd" "abcde"true
//"abcde" "abcd"false
bool operator<(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
size_t i1 = 0;
size_t i2 = 0;
while ( i1< s1.size()&& i2<s2.size())
{
if (s1[i1] < s2[i2])
{
return false;
}
++i1;
++i2;
}
return i1 < s1.size() ? false : true;
}
operator==()
bool operator==(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
size_t i1 = 0;
size_t i2 = 0;
while (i1 < s1.size() && i2 < s2.size())
{
if (s1[i1] != s2[i2])
{
return false;
}
++i1;
++i2;
}
return i1 == s1.size() && i2 == s2.size() ? true : false;
}
operator!=()
bool operator!=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
operator<=()
bool operator<=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;
}
operator>()
bool operator>(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
operator>=()
bool operator>=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
All the code
String.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<assert.h>
// complete string Add, delete, check, modify, duplicate
namespace My_Str // To prevent pollution std Namespace
{
class string
{
private:
char* _str;
int _size;// Number of valid characters
int _capacity;// The capacity of valid characters , It doesn't contain '\0', But because when opening up space, open up one more ,
// Therefore, one is reserved by default '\0', Easy to carry out C function
public:
static const size_t npos;
// All default constructors , Cannot assign with null pointer , There will be a wild pointer problem
string(const char* str="");
// Custom copy construction ,
// 1. Without reference , The transfer of arguments to formal parameters is also a copy
// 2. The default copy structure is shallow copy , When there are members who need dynamic management , Prevent shallow copy from causing multiple attacks on the same space delete problem
// This is also the reason for modern writing
string(const string& s);
// Destructor
~string();
void swap(string& s);
// Assignment operator
string& operator=(const string& s);
// The first address of the character .
const char* c_str();
const char* c_str()const;
size_t size();
size_t size()const ;
char& operator[](size_t pos);
const char& operator[](size_t pos)const;
// iterator , For the time being, the pointer
// Ordinary objects overlap
typedef char* iterator;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
// Regular object
typedef const char* const_iterator;
const_iterator begin()const;
const_iterator end()const;
// Capacity expansion
void reserve(size_t n);// Scaling down is not supported
void resize(size_t n, char ch='\0');// Support shrinking and expanding
// Insert , It's more about use +=
// Head insertion , It is generally not recommended to use , Low efficiency
string& insert(size_t pos, const char ch);
string& insert(size_t pos, const char *str);
// Tail insertion ,
// Single character , Just expand the capacity according to the situation 2 Times ,
// But for Strings , Its number cannot be empty , Therefore, the expansion depends on the situation .
//
void push_back(char ch);
void append( const char* str);
string& operator +=(const char ch);
string& operator +=(const char* str);
// Delete
string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
// check
size_t find(char ch);
size_t find(const char* str, size_t pos = 0);
};
}
std::ostream &operator<<(std::ostream& out, const My_Str::string& s);
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, My_Str::string& s);
bool operator<(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
bool operator==(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
bool operator!=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
bool operator<=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
bool operator>(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
bool operator>=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2);
String.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"String.h"
const size_t My_Str::string::npos=-1;
// All default constructors , For empty strings ,_size by 0, Pay attention to when expanding
My_Str::string::string(const char* str)
:_size(strlen(str)), _capacity( _size)
{
_str = new char[_capacity+1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
// Copy structure , Be careful
// 1. Without reference , The transfer of arguments to formal parameters is also a copy
// 2. When there are members who need dynamic management , Prevent shallow copy from causing multiple attacks on the same space delete problem
// 3. This is also the reason for modern writing
My_Str::string::string(const string& s)
{
General writing
//_str = new char[strlen(s._str) + 1];
//strcpy(_str, s._str);
//_size = s._size;
//_capacity = s._capacity;
Modern writing , The essence is the reuse of code and the post frame destruction of local variable function stack
string tmp(s._str);// A custom constructor was called
_str = nullptr;// This step must have , Otherwise, the random values are delete
swap(tmp);//string Under the swap function
//std::swap(_str,tmp._str);// Under the standard library swap template function
_size = tmp._size;
_capacity = tmp._capacity;
}
My_Str::string::~string()// Destructor
{
delete[]_str;
_str = nullptr;
_size =_capacity= 0;
}
void My_Str::string::swap(string& s)
{
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator=(const My_Str::string& s)
{
// Assignment of itself
//if (&s != this)
//{
// // General writing :
// char *tmp = new char[s._size + 1];// Prevent application failure ,C++ Of new Would throw exceptions , Not learned
// strcpy(tmp, s._str);
// delete[]_str;// Release the original space
// _str = tmp;// After the local variable is destroyed , Heap space still exists .
// _size = s._size;
// _capacity = s._capacity;
//}
// Modern writing , There is no need to consider the problem of self assignment and releasing the same space multiple times
string tmp(s);//
std::swap(_str, tmp._str);
_size = tmp._size;
_capacity = tmp._capacity;
return *this;
}
// The first address of the character .
const char* My_Str::string::c_str()
{
return _str;
}
const char* My_Str::string::c_str()const
{
return _str;
}
size_t My_Str::string::size()
{
return _size;
}
size_t My_Str::string::size()const
{
return _size;
}
char& My_Str::string::operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
const char& My_Str::string::operator[](size_t pos)const
{
assert(pos < _size);
return _str[pos];
}
My_Str::string::iterator My_Str::string::begin()
{
return _str;
}
My_Str::string::iterator My_Str::string::end()
{
return _str + _size ;
}
My_Str::string::const_iterator My_Str::string::begin()const
{
return _str;
}
My_Str::string::const_iterator My_Str::string::end()const
{
return _str + _size;
}
void My_Str::string::reserve(size_t n)
{
if(n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n+1];
strcpy(tmp,_str);
delete[]_str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
void My_Str::string::resize(size_t n, char ch)
{
//resize Scaling down is not supported _capacity;
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
memset(_str + _size, ch, n - _size);
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
void My_Str::string::push_back(char ch)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity==0?4:_capacity*2);
}
_str[_size] = ch;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void My_Str::string::append(const char* str)
{
size_t len = strlen(str);
if ((len + _size) > _capacity)
{
reserve(len + _size);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator +=(const char ch)
{
push_back(ch);
return *this;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::operator +=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
size_t My_Str::string::find(char ch)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (ch == _str[i])
{
return i;
}
}
return npos;
}
size_t My_Str::string::find(const char* str, size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < _size&& strlen(str)<_size);
const char* ret = strstr(_str, str);
if (ret != nullptr)
{
return ret - _str;
}
return npos;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::insert(size_t pos, const char ch)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
if (_size == _capacity)
{
reserve(_capacity == 0 ? 4 : _capacity * 2);
}
// Because it is an unsigned integer , In the subtraction operation, we should pay attention to the problem of dead circulation
size_t end = _size+1;
while (end > pos)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - 1];
--end;
}
_str[pos] = ch;
return *this;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert(pos <= _size);
size_t len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
size_t end = _size + len;
while (end > pos+len)
{
_str[end] = _str[end - len];
--end;
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str,len);
//strcpy Will '\0 Add in '
return *this;
}
My_Str::string& My_Str::string::erase(size_t pos , size_t len )
{
assert(pos < _size);
if (len == npos || len >= (_size - pos))// Delete all
{
_str[pos] = '\0';
_size = pos;
}
else
{
strcpy(_str + pos, _str + pos + len);
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
//
//"abcd" "abcd" false
//"abcd" "abcde"true
//"abcde" "abcd"false
bool operator<(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
size_t i1 = 0;
size_t i2 = 0;
while ( i1< s1.size()&& i2<s2.size())
{
if (s1[i1] < s2[i2])
{
return false;
}
++i1;
++i2;
}
return i1 < s1.size() ? false : true;
}
bool operator==(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
size_t i1 = 0;
size_t i2 = 0;
while (i1 < s1.size() && i2 < s2.size())
{
if (s1[i1] != s2[i2])
{
return false;
}
++i1;
++i2;
}
return i1 == s1.size() && i2 == s2.size() ? true : false;
}
bool operator!=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 == s2);
}
bool operator<=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return s1 < s2 || s1 == s2;
}
bool operator>(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 <= s2);
}
bool operator>=(const My_Str::string& s1, const My_Str::string& s2)
{
return !(s1 < s2);
}
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& out, const My_Str::string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)// Finite cycles , You can avoid strings containing '\0' The situation of
{
out << s[i];
}
//cout<<s.c_str();
return out;
}
std::istream& operator >> (std::istream& in, My_Str::string& s)
{
char ch = 0;
//ch = getchar();
//while (ch != ' '&&ch!='\n')
//{
// s += ch;
// ch = getchar();
//}
ch = in.get();
while (ch != ' '&&ch!='\n')
{
s += ch;
ch = in.get();
}
return in;
}
summary
Dealing with boundary problems , Be careful , Otherwise, the program may CREASH
边栏推荐
- 5g NR system messages
- Leetcode brush questions
- An error is reported during the process of setting up ADG. Rman-03009 ora-03113
- 华泰证券官方网站开户安全吗?
- 爬虫实战(八):爬表情包
- redis你到底懂不懂之list
- 【愚公系列】2022年7月 Go教学课程 006-自动推导类型和输入输出
- C# 泛型及性能比较
- How can CSDN indent the first line of a paragraph by 2 characters?
- Sqlite数据库存储目录结构邻接表的实现2-目录树的构建
猜你喜欢
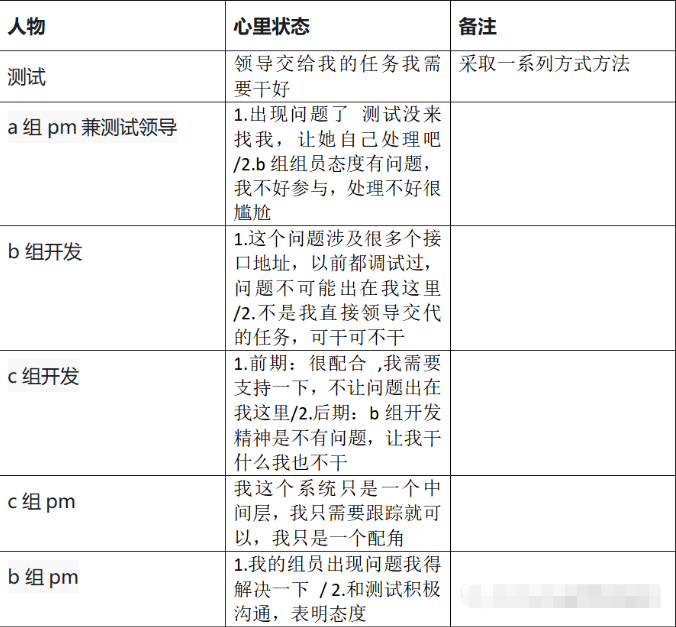
What if the testing process is not perfect and the development is not active?
![Cause analysis and solution of too laggy page of [test interview questions]](/img/8d/3ca92ce5f9cdc85d52dbcd826e477d.jpg)
Cause analysis and solution of too laggy page of [test interview questions]
fabulous! How does idea open multiple projects in a single window?
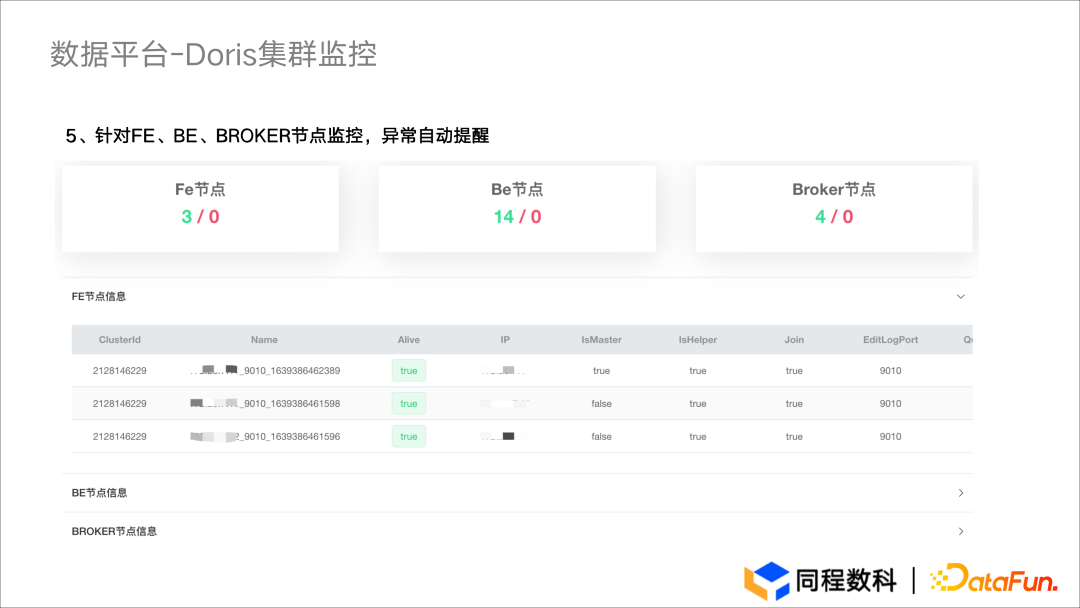
Application practice | the efficiency of the data warehouse system has been comprehensively improved! Data warehouse construction based on Apache Doris in Tongcheng digital Department
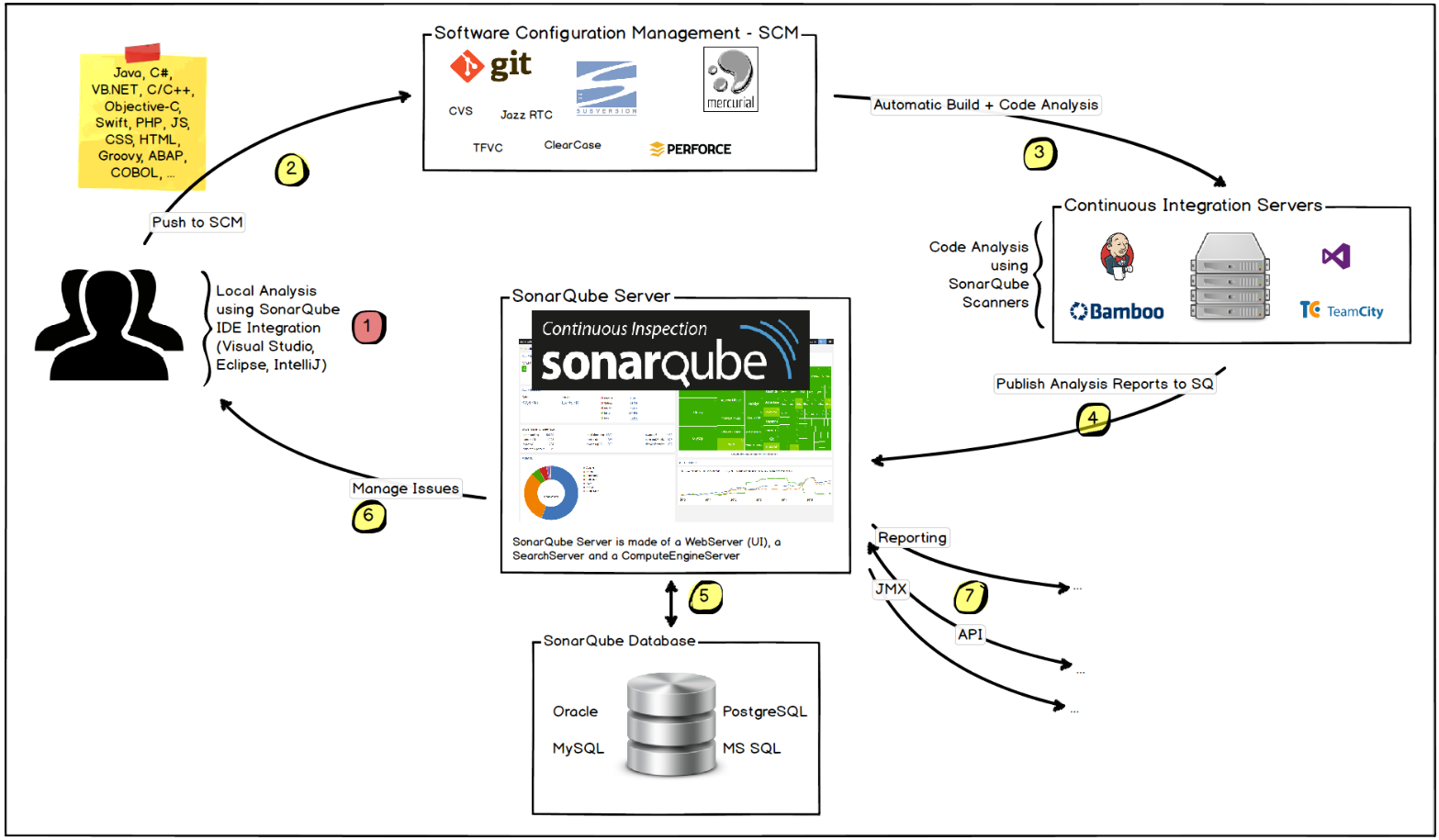
Play sonar
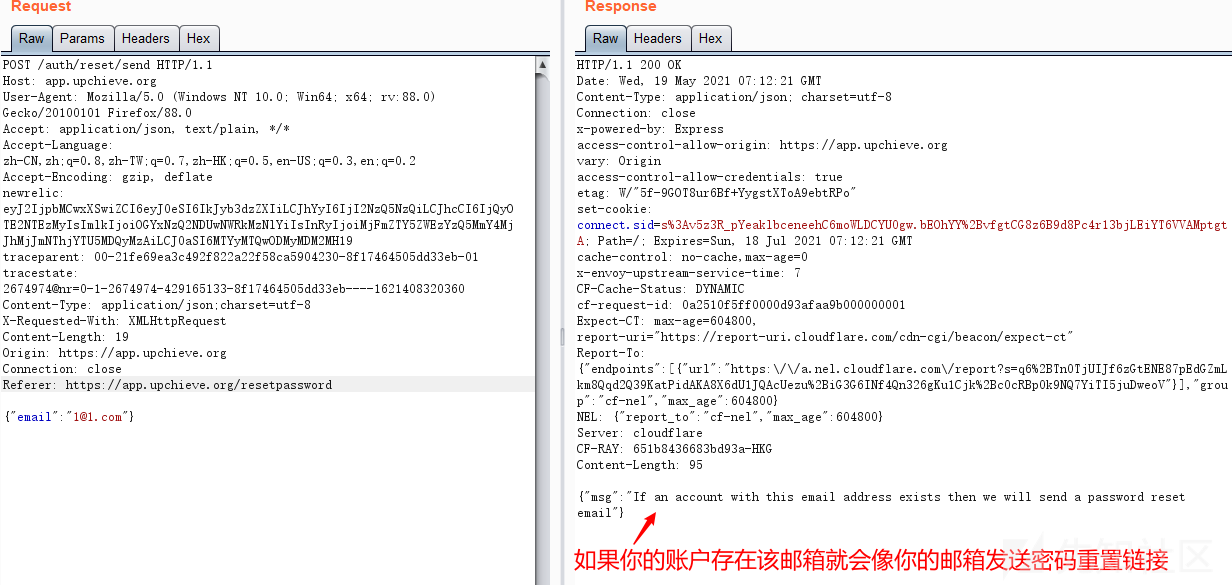
国外众测之密码找回漏洞
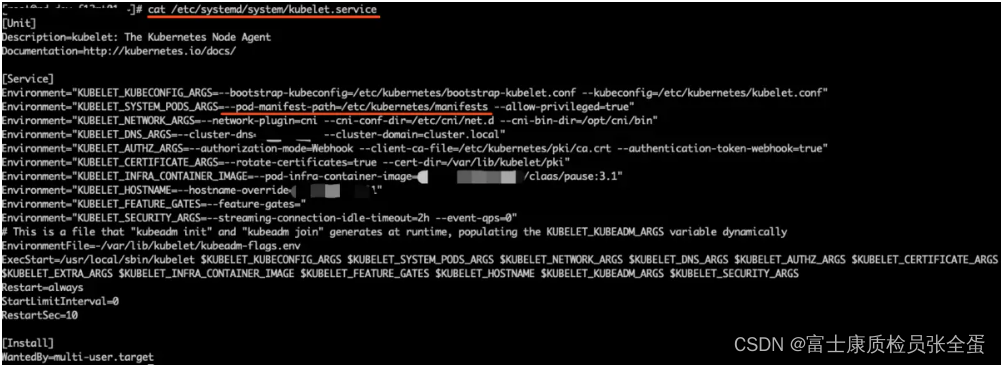
Kubernetes static pod (static POD)
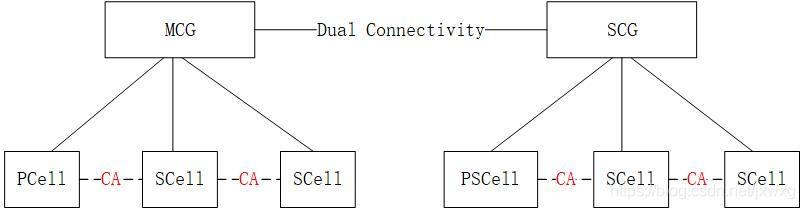
5G NR 系统消息
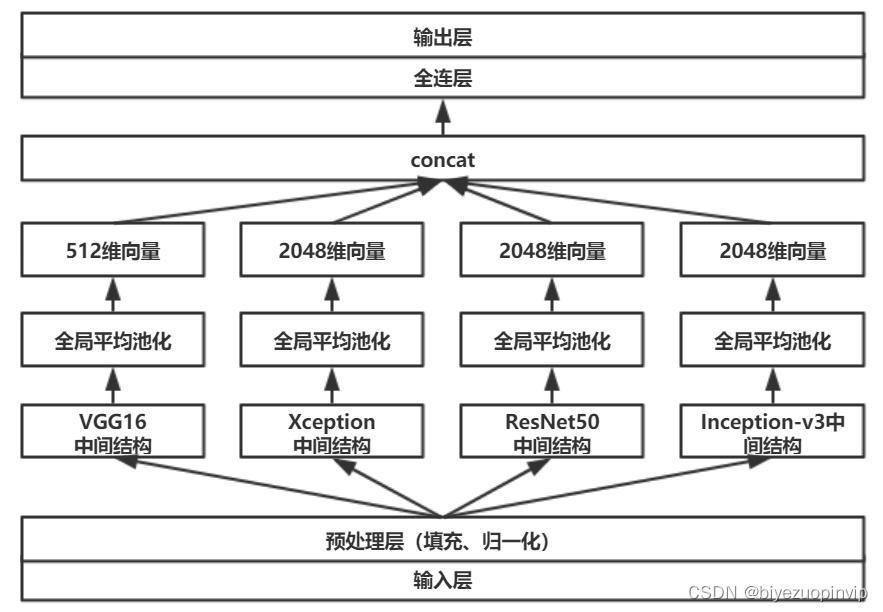
基于卷积神经网络的恶意软件检测方法
Interface test advanced interface script use - apipost (pre / post execution script)
随机推荐
搭建ADG过程中复制报错 RMAN-03009 ORA-03113
jemter分布式
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2)(A~D)
ReentrantLock 公平锁源码 第0篇
股票开户免费办理佣金最低的券商,手机上开户安全吗
丸子官网小程序配置教程来了(附详细步骤)
3 years of experience, can't you get 20K for the interview and test post? Such a hole?
【obs】Impossible to find entrance point CreateDirect3D11DeviceFromDXGIDevice
fabulous! How does idea open multiple projects in a single window?
语义分割模型库segmentation_models_pytorch的详细使用介绍
韦东山第二期课程内容概要
Service Mesh介绍,Istio概述
炒股开户怎么最方便,手机上开户安全吗
Stock account opening is free of charge. Is it safe to open an account on your mobile phone
取消select的默认样式的向下箭头和设置select默认字样
DNS 系列(一):为什么更新了 DNS 记录不生效?
测试流程不完善,又遇到不积极的开发怎么办?
Is Zhou Hongyi, 52, still young?
Hotel
ABAP ALV LVC模板