当前位置:网站首页>Topological sorting
Topological sorting
2022-06-11 05:04:00 【bolite】
One . What is topological sort
A topological sort (Topological Sorting) It's a directed acyclic graph (DAG, Directed Acyclic Graph) The linear sequence of all vertices of . And the sequence must satisfy the following two conditions : Every vertex appears and only once . If there is one from the top A To the top B The path of , So the vertices in the sequence A Appear at the top B In front of .
Two . Picture description
The problem solved by this algorithm is similar to the process of handling affairs
One or more related things that must be done before doing one thing 
3、 ... and . Code implementation diagram

1. First of all, find the tasks that do not need other tasks to pave the way , Points in the picture 1. take 1 Join the team first , Look for other points , After the first search , Start to get out of the team , take 1 Out of the team , Look for tasks related to him , A condition for unlocking subsequent tasks .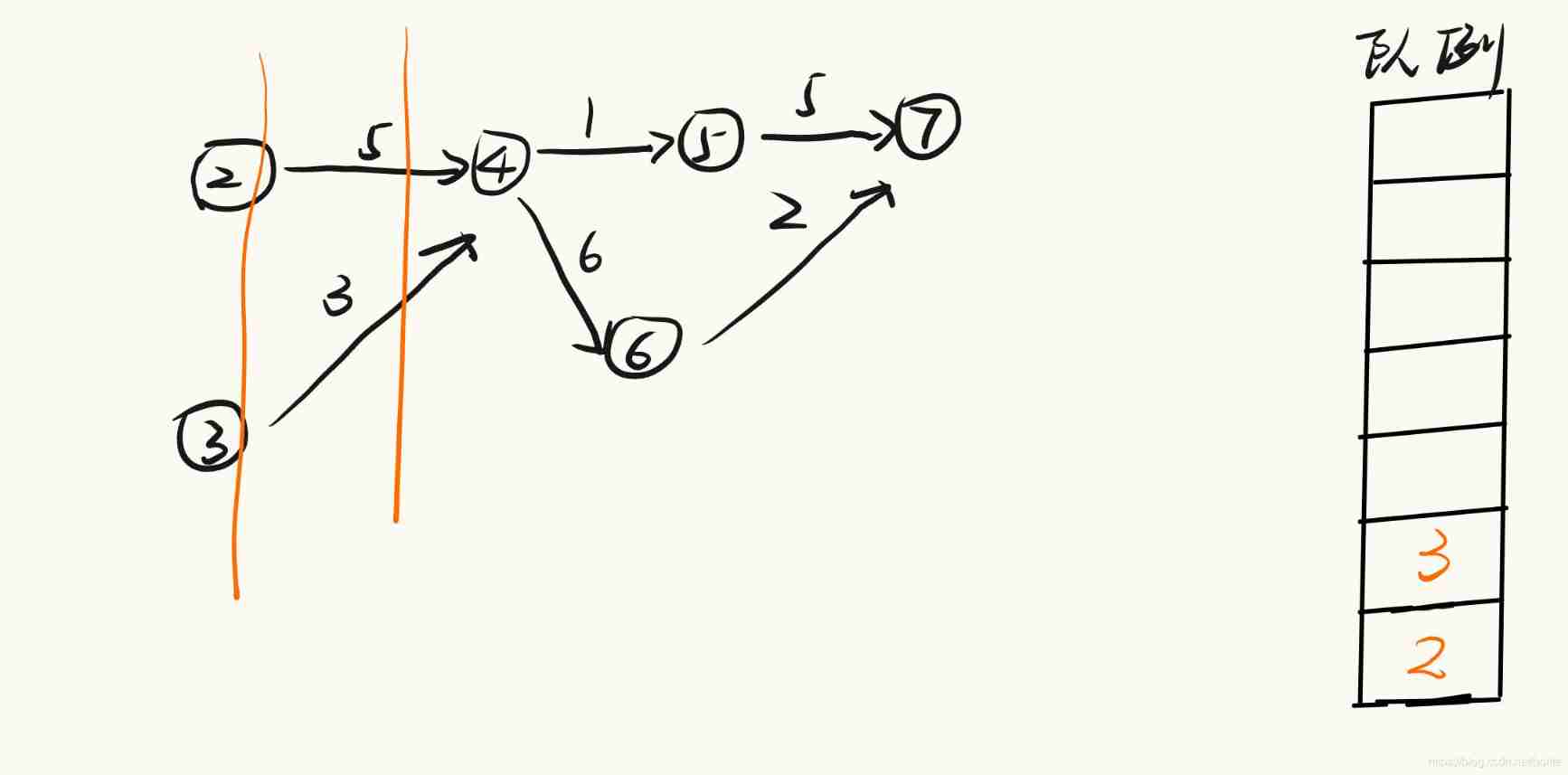
Once again, the task that looks for the current fully unlocked condition will join the team again , In turn, cycle , Until the team is empty
Four . Related examples
1. 6-5- A topological sort The rationality of task scheduling (25 branch )
Suppose an engineering project consists of a set of subtasks , Some of the subtasks can be executed in parallel , Some can only be executed after completing other subtasks .“ Task scheduling ” Includes a set of subtasks 、 And the set of subtasks on which each subtask can execute .
For example, completing all courses and graduation design of a major can be regarded as a project to be completed by an undergraduate , Each course can be regarded as a sub task . Some courses can be offered at the same time , Such as English and C Programming , They don't have to fix which door first ; Some courses cannot be offered at the same time , Because they have sequential dependencies , such as C Programming and data structure , We must learn the former first .
But here's the thing , For a set of subtasks , Not any task scheduling is a feasible scheme . For example, there are “ The subtasks A Dependent on subtasks B, The subtasks B Dependent on subtasks C, The subtasks C And depends on subtasks A”, Then none of these three tasks can be performed first , This is an infeasible solution . Your job now is to write a program to determine whether any given task scheduling is feasible .
Input format :
Enter description : Enter the first line to give the number of subtasks N(≤100), Subtasks by 1~N Number . And then N That's ok , Each row gives a dependent set of subtasks : First, the number of subtasks in the dependent set is given K, Subsequently given K Subtask number , Integers are separated by spaces .
Output format :
If the scheme is feasible , The output 1, Otherwise output 0.
sample input 1:
12
0
0
2 1 2
0
1 4
1 5
2 3 6
1 3
2 7 8
1 7
1 10
1 7
sample output 1:
1
sample input 2:
5
1 4
2 1 4
2 2 5
1 3
0
sample output 2:
0
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 120
int main()
{
int a[N][N] = {
0 };
int size[N] = {
0 };
queue<int>q;// Build a team to save unlocked tasks
int n;
cin >> n;
int i = 0;
int m;
int aim;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> m;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
cin >> aim;
a[i][aim] = 1;// Link the task to the unlock condition
size[i]++;// Record the number of unlocked conditions , When the number is 0 Unlock when
}
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!size[i]) {
q.push(i);// Look for unconditional tasks for the first time
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
aim = q.front();
q.pop();
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Find the task that needs this task as the unlocking condition
if (a[i][aim]) {
size[i]--;// The number of a condition that cancels the task
if(!size[i]) q.push(i);// If the task reaches unlock , Join the team
}
}
}
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (size[i] != 0) {
cout << "0";
return 0;
}
}
cout << "1" << endl;
}
2. 7-99 Minimum working period (25 branch )
A project consists of several tasks , There is sequence dependence between tasks . The project manager needs to set a series of milestones , Check the completion of the task at each milestone node , And start the following tasks . Given the relationship between tasks in a project , Please calculate the earliest completion time of this project .
Input format :
First, the first line gives two positive integers : Number of project milestones N(≤100) And the total number of tasks M. The milestones here are from 0 To N−1 Number . And then M That's ok , Each line gives a description of the task , The format is “ Task start milestone Task end milestone Working hours ”, All three numbers are non negative integers , Space off .
Output format :
If the arrangement of the whole project is reasonable and feasible , Output the earliest completion time in one line ; Otherwise output "Impossible".
sample input 1:
9 12
0 1 6
0 2 4
0 3 5
1 4 1
2 4 1
3 5 2
5 4 0
4 6 9
4 7 7
5 7 4
6 8 2
7 8 4
sample output 1:
18
sample input 2:
4 5
0 1 1
0 2 2
2 1 3
1 3 4
3 2 5
sample output 2:
Impossible
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 120
int main()
{
int map[N][N];
int cost[N] = {
0 };
int size[N] = {
0 };
queue<int> q;
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) {
map[i][j] = -1;// Because the duration is 0 The situation of , So the initial words are -1
}
}
int a1, a2, w;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> a1 >> a2 >> w;
map[a1][a2] = w;
size[a2]++;
}
int aim;
int sum = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!size[i]) q.push(i);
}
while (!q.empty()) {
aim = q.front();
q.pop();
if (cost[aim] > sum)sum = cost[aim];
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (map[aim][i] != -1) {
size[i]--;
if (!size[i])q.push(i);
if (cost[i] < cost[aim] + map[aim][i])
cost[i] = cost[aim] + map[aim][i];// Refresh the duration of the current node
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (size[i]) {
cout << "Impossible" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
}
5、 ... and . Key code
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!size[i]) {
q.push(i);// Look for unconditional tasks for the first time
}
}
while (!q.empty()) {
aim = q.front();
q.pop();
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
// Find the task that needs this task as the unlocking condition
if (a[i][aim]) {
size[i]--;// The number of a condition that cancels the task
if(!size[i]) q.push(i);// If the task reaches unlock , Join the team
}
}
}
This code can achieve the effect of topological sorting , And some problems need the expansion of the code
边栏推荐
- [markdown syntax advanced] make your blog more exciting (III: common icon templates)
- The data center is evolving towards the "four high" trend, and the OCP network card and the whole cabinet will be delivered into the mainstream of the future data center
- Leetcode 161 Editing distance of 1 (2022.06.10)
- Share | defend against physically realizable image classification attacks
- Use of mmdetection
- Leetcode question brushing series - mode 2 (datastructure linked list) - 21:merge two sorted lists merge two ordered linked lists
- [Transformer]Is it Time to Replace CNNs with Transformers for Medical Images?
- Huawei device configuration bgp/mpls IP virtual private network command
- The central rural work conference has released important signals. Ten ways for AI technology to help agriculture can be expected in the future
- Using keras to build the basic model yingtailing flower
猜你喜欢
MySQL regularly deletes expired data.
![[aaai 2021 timing action nomination generation] detailed interpretation of bsn++ long article](/img/28/d69a7583036a2076facffcf9098d7e.jpg)
[aaai 2021 timing action nomination generation] detailed interpretation of bsn++ long article

Paper recommendation: relicv2, can the new self supervised learning surpass supervised learning on RESNET?

Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure

Click the icon is not sensitive how to adjust?

New product pre-sale: 25g optical network card based on Intel 800 series is coming

An adaptive chat site - anonymous online chat room PHP source code

Thesis 𞓜 jointly pre training transformers on unpaired images and text

Paper reproduction: pare

Free data | new library online | cnopendata data data of national heritage stores and auction enterprises
随机推荐
C语言试题三(语法选择题——含知识点详解)
RGB image histogram equalization and visualization matlab code
[markdown syntax advanced] make your blog more exciting (III: common icon templates)
Overview of self attention acceleration methods: Issa, CCNET, cgnl, linformer
Leetcode question brushing series - mode 2 (datastructure linked list) - 19:remove nth node from end of list (medium) delete the penultimate node in the linked list
Huawei equipment is configured with bgp/mpls IP virtual private network address space overlap
DL deep learning experiment management script
JVM tuning 6: GC log analysis and constant pool explanation
Preliminary test of running vins-fusion with zed2 binocular camera
Anaconda installation and use process
Yolact paper reading and analysis
Reverse thinking: making cartoon photos real
Yolov5 training personal data set summary
Deep extension technology: intelligent OCR recognition technology based on deep learning has great potential
[Transformer]AutoFormerV2:Searching the Search Space of Vision Transformer
How to purchase 25g optical network card
jvm调优六:GC日志分析和常量池详解
The programmers of a large factory after 95 were dissatisfied with the department leaders, and were sentenced for deleting the database and running away
【入门级基础】Node基础知识总结
The data center is evolving towards the "four high" trend, and the OCP network card and the whole cabinet will be delivered into the mainstream of the future data center