当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of react high order components
Analysis of react high order components
2020-11-06 01:17:00 【:::::::】
background
This way of writing high-order components comes from the practice of the community , The goal is to solve some cross cutting problems (Cross-Cutting Concerns). And the earliest time React The official solution is to use mixin . and React It also wrote on the official website :
We previously recommended mixins as a way to handle cross-cutting concerns. We've since realized that mixins create more trouble than they are worth.
Officials are clearly aware of the use of mixins Technology to solve such problems brings much more trouble than its own value . More information You can refer to the official instructions .
The definition of higher order function
When it comes to high-level components , We have to briefly introduce higher-order functions first . Here's a simple high-order function
const add = (x,y,f) => f(x)+f(y)
When we call add(-5, 6, Math.abs) when , Parameters x,y and f Receive separately -5,6 and Math.abs, According to the function definition , We can deduce the calculation process as :
x ==> -5 y ==> 6 f ==> abs f(x) + f(y) ==> Math.abs(-5) + Math.abs(6) ==> 11
Use code to verify :
add(-5, 6, Math.abs); //11
Higher order is defined in Wikipedia as follows
A higher-order function is a function that satisfies at least one of the following conditions :
- Accept one or more functions as input
- Output a function
Definition of higher-order components
that , What are high-level components ? Analogy to the definition of higher order functions , A higher-order component is a function that takes a component as an argument and returns a new component . Here we need to pay attention to A higher-order component is a function , It's not a component , This must be noted . At the same time, it's important to emphasize that higher-order components themselves are not React API. It's just a pattern , This pattern is made up of React The combination of its own nature is inevitable . More generally speaking , High level components pass through packages (wrapped) Introduced into React Components , After a series of processing , Finally, it returns a relative enhancement (enhanced) Of React Components , For other components to call .
<!-- more -->
A simple high-level component
Let's implement a simple high-order component
export default WrappedComponent => class HOC extends Component {
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend> Default title </legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
};
In other components , We refer to this high-level component to reinforce it
export default class Demo extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
I'm a normal component
</div>
);
}
}
const WithHeaderDemo = withHeader(Demo);
So let's see React DOM Tree, After calling a higher-level component , What happened? :
You can see ,Demo By HOC The parcel (wrapped) Added a title after the default title . But it will also be found that , If more than one HOC after , We'll see a lot of HOC, So we should It's time to optimize , In other words, it is wrapped in high-level components (wrapped) in the future , The original name should be kept .
Let's rewrite the high-level component code above , Add one more getDisplayName function , For after Demo Add a static property displayName.
const getDisplayName = component => component.displayName || component.name || 'Component';
export default WrappedComponent => class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `HOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend> Default title </legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
};
Observe again React DOM Tree
You can see , The original name of the component is shown in React DOM Tree Yes . This HOC Add a title to the original component , In other words, all components that need to add a title can call this HOC Package (wrapped) After the implementation of this function .
Transfer parameters for higher-order components
Now? , our HOC You can already provide titles for any other component , But we also want to be able to modify the fields in the title . Because our higher-order component is a function , So you can add a parameter to it title. Now we're right HOC To rewrite :
export default (WrappedComponent, title = ' Default title ') => class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `HOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>{title}</legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
};
Then we call :
const WithHeaderDemo = withHeader(Demo,' High level components add titles ');
Now observe React DOM Tree.
You can see , The title has been set correctly .
Of course, we can also coricize it :
export default (title = ' Default title ') => WrappedComponent => class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `HOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>{title}</legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
};
const WithHeaderDemo = withHeader(' High level components add titles ')(Demo);
common HOC Realization way
Based on property proxy (Props Proxy) The way
Property proxies are the most common use of high-level components , The high-order components mentioned above are in this way . It does something by doing something , That will be wrapped in components props And the new props Pass it to this component together , This is called a property proxy .
export default function GenerateId(WrappedComponent) {
return class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `PropsBorkerHOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
const newProps = {
id: Math.random().toString(36).substring(2).toUpperCase()
};
return createElement(WrappedComponent, {
...this.props,
...newProps
});
}
};
}
call GenerateId:
const PropsBorkerDemo = GenerateId(Demo);
Then we observe React Dom Tree:
We can see through GenerateId Well done Demo Added id.
Based on reverse inheritance (Inheritance Inversion) The way
Let's start with a simple example of reverse inheritance :
export default function (WrappedComponent) {
return class Enhancer extends WrappedComponent {
static displayName = `InheritanceHOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
componentWillMount() {
// It's easy to get state, Make some more in-depth changes .
this.setState({
innerText: ' I was Inheritance Changed the value '
});
}
render() {
return super.render();
}
};
}
As you can see, the high-level component class returned (Enhancer) Inherited WrappedComponent. And it's called reverse inheritance because WrappedComponent Passively by Enhancer Inherit , instead of WrappedComponent To inherit Enhancer. In this way, the relationship between them reversed .
Reverse inheritance allows higher-order components to pass through this Keyword acquisition WrappedComponent, It means that it can get state,props, Component lifecycle (Component Lifecycle) hook , And rendering methods (render). Deepen understanding You can read __@Wenliang__ In the article Inheritance Inversion(II) The content of this section .
Problems with high-level components
Static method lost
When packaging components with high-level components , The original component is wrapped in a container component , This means that the new component will lose all static methods of the original component . The following is Demo Add a static method :
Demo.getDisplayName = () => 'Demo';
Then call HOC:
// Use high-level components const WithHeaderDemo = HOC(Demo); // The component after calling does not have `getDisplayName` Methodical typeof WithHeaderDemo.getDisplayName === 'undefined' // true
The easiest way to solve this problem is (Yǘ Chǚn) The way is , Copy all static methods of the original component to the new component :
export default (title = ' Default title ') => (WrappedComponent) => {
class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `HOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>{title}</legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
}
HOC.getDisplayName = WrappedComponent.getDisplayName;
return HOC;
};
To do so , You need to know what static methods need to be copied . Or you can use hoist-non-react-statics To help you automatically handle , It will automatically copy all non React Static method of :
import hoistNonReactStatic from 'hoist-non-react-statics';
export default (title = ' Default title ') => (WrappedComponent) => {
class HOC extends Component {
static displayName = `HOC(${getDisplayName(WrappedComponent)})`;
render() {
return (
<fieldset>
<legend>{title}</legend>
<WrappedComponent {...this.props} />
</fieldset>
);
}
}
// Copy static methods
hoistNonReactStatic(HOC, WrappedComponent);
return HOC;
};
Refs Properties cannot be passed
Generally speaking , Higher level components can pass all props Attributes to package components , But it can't deliver refs quote . Because it's not like key equally ,refs It's a pseudo property ,React It has been specially treated . If you add... To an element of a component created by an advanced component ref application , that ref Point to the instance of the outermost container component , Not package components . But sometimes , We are bound to use refs, The official solution is :
Pass a ref Callback function properties , That is to give ref Apply a different name
He also stressed that :React It is not recommended to use at any time ref application rewrite Demo
class Demo extends Component {
static propTypes = {
getRef: PropTypes.func
}
static getDisplayName() {
return 'Demo';
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
innerText: ' I'm a normal component '
};
}
render() {
const { getRef, ...props } = this.props;
return (
<div ref={getRef} {...props}>
{this.state.innerText}
</div>
);
}
}
Then we call :
<WithHeaderDemo
getRef={(ref) => {
// The callback function is treated as normal props Attribute passing
this.headerDemo = ref;
}}
/>
Although this is not the perfect solution , however React Officials say they are exploring ways to solve the problem , It allows us to use high-level components without paying attention to this problem .
Conclusion
This article is just a brief introduction to the two most common uses of high-level components : Property agent and Reverse inheritance . And common problems with high-level components . I hope that through the reading of this article, you can have a basic understanding of high-level components . The code generated by writing this article is in study-hoc in .
The author of this article :Godfery This article is published in :HYPERS Front end blogs
Reference article :
Higher-Order Components Explain profound theories in simple language React High order component With three questions, let's talk in simple terms React High order component Ruan Yifeng - Higher order function Deep understanding of high-level components
Participation of this paper Tencent cloud media sharing plan , You are welcome to join us , share .
版权声明
本文为[:::::::]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- DRF JWT authentication module and self customization
- How to demote a domain controller in Windows Server 2012 and later
- X Window System介紹
- 3分钟读懂Wi-Fi 6于Wi-Fi 5的优势
- 中国提出的AI方法影响越来越大,天大等从大量文献中挖掘AI发展规律
- Tool class under JUC package, its name is locksupport! Did you make it?
- Leetcode's ransom letter
- 使用NLP和ML来提取和构造Web数据
- TRON智能钱包PHP开发包【零TRX归集】
- 助力金融科技创新发展,ATFX走在行业最前列
猜你喜欢

全球疫情加速互联网企业转型,区块链会是解药吗?

EOS创始人BM: UE,UBI,URI有什么区别?

Didi elasticsearch cluster cross version upgrade and platform reconfiguration

PN8162 20W PD快充芯片,PD快充充电器方案
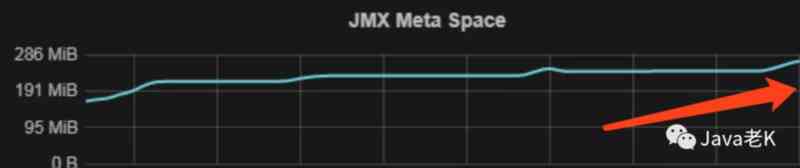
Troubleshooting and summary of JVM Metaspace memory overflow
快快使用ModelArts,零基礎小白也能玩轉AI!
自然语言处理之命名实体识别-tanfordcorenlp-NER(一)
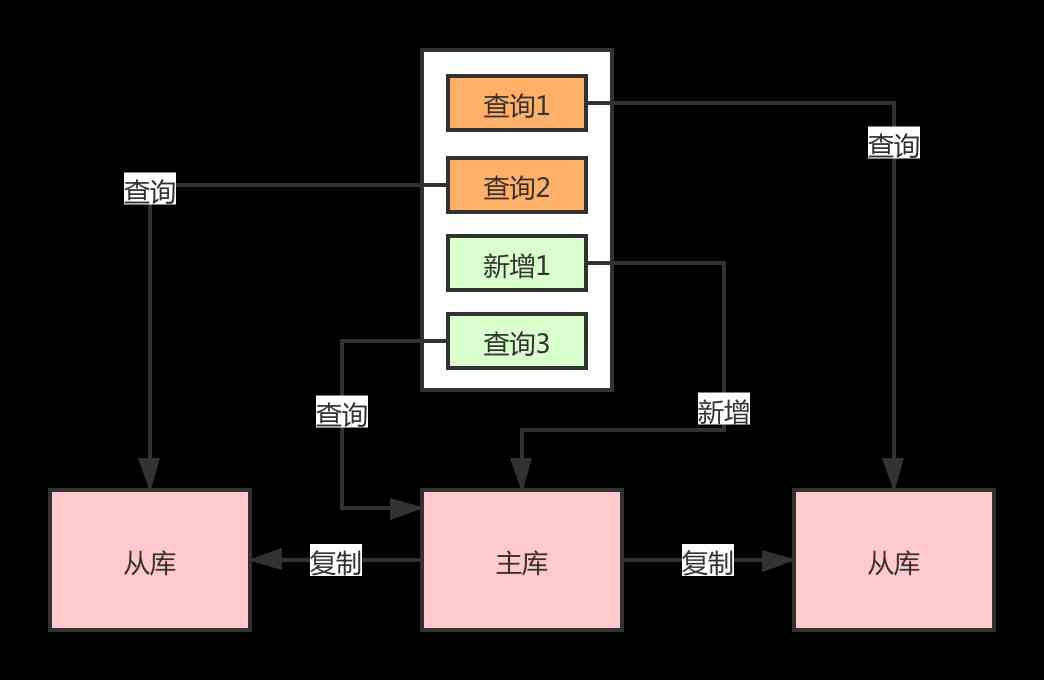
Want to do read-write separation, give you some small experience

Filecoin最新动态 完成重大升级 已实现四大项目进展!

TRON智能钱包PHP开发包【零TRX归集】
随机推荐
在大规模 Kubernetes 集群上实现高 SLO 的方法
速看!互联网、电商离线大数据分析最佳实践!(附网盘链接)
Flink on paasta: yelp's new stream processing platform running on kubernetes
Troubleshooting and summary of JVM Metaspace memory overflow
连肝三个通宵,JVM77道高频面试题详细分析,就这?
连肝三个通宵,JVM77道高频面试题详细分析,就这?
深度揭祕垃圾回收底層,這次讓你徹底弄懂她
快快使用ModelArts,零基礎小白也能玩轉AI!
How to select the evaluation index of classification model
Keyboard entry lottery random draw
100元扫货阿里云是怎样的体验?
The difference between Es5 class and ES6 class
遞迴思想的巧妙理解
技術總監,送給剛畢業的程式設計師們一句話——做好小事,才能成就大事
分布式ID生成服务,真的有必要搞一个
网络安全工程师演示:原来***是这样获取你的计算机管理员权限的!【维持】
Vue 3 responsive Foundation
Existence judgment in structured data
(1)ASP.NET Core3.1 Ocelot介紹
JetCache埋点的骚操作,不服不行啊