当前位置:网站首页>Leetcode brush questions - binary search tree related topics (98. Verify binary search tree, 235. The nearest common ancestor of binary search tree, 1038. From binary search tree to bigger sum tree, 5
Leetcode brush questions - binary search tree related topics (98. Verify binary search tree, 235. The nearest common ancestor of binary search tree, 1038. From binary search tree to bigger sum tree, 5
2022-08-04 11:12:00 【lonelyMangoo】
概念
二叉搜索树:
- 节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点.
- 节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点.
- 左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树.
The in-order traversal of a binary search tree is in ascending order.
98. 验证二叉搜索树
题目:98. 验证二叉搜索树
思路:Use in-order traversal to judge,Whether the current node is greater than the previous one.
//迭代写法
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode pre = null;
while (cur!=null || !stack.isEmpty()){
if(cur != null){
stack.add(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
else {
cur = stack.pop();
if(pre!=null && pre.val>= cur.val){
return false;
}
//记录前一个节点
pre=cur;
cur=cur.right;
}
}
return true;
}
The level traversal I used at first,Because it ignores the situation that the whole is also greater than:
也就是例子中的5、3这种情况.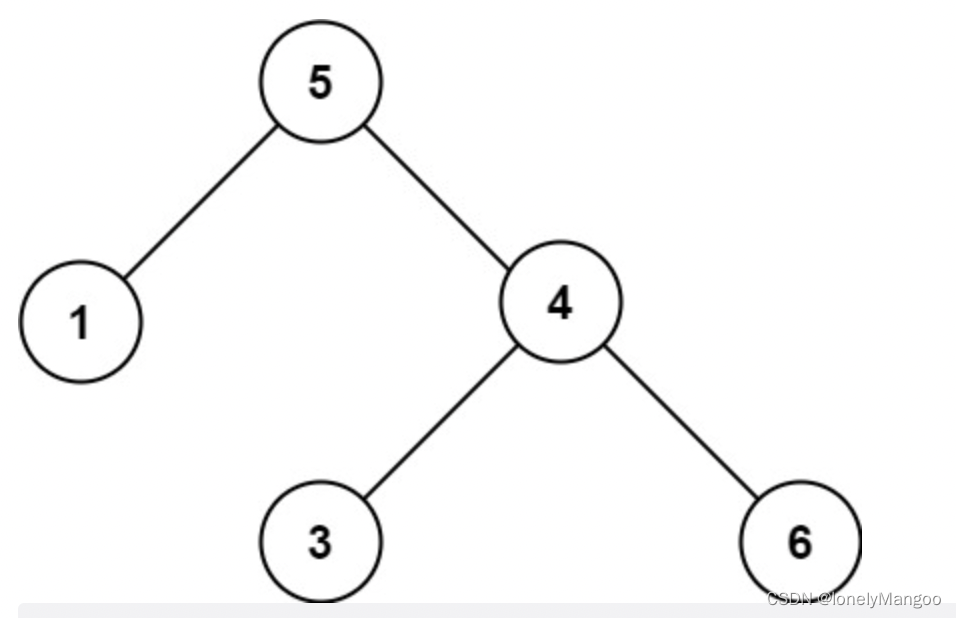
Of course, recursion can also be used here,It is also an in-order traversal and records the previous node
TreeNode pre=null;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null ) return true;
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
//Inorder traversal operation part
if(pre!=null && root.val <= pre.val){
return false;
}
pre = root;
boolean right =isValidBST(root.right);
return left && right;
}

I think recursion is a bit tricky to understand,Although the idea is the same, you may not know which layer is the problem,Therefore, it is not easy to make mistakes in interviews or use iterations.
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
题目:235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
This question only needs someone else to provide an idea to write it:
Both requested nodes are smaller than the current node,到左子树中去找
Both requested nodes are larger than the current node,到右子树中去找
If one is larger than the current node,一个比当前节点小,is the requested node.
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p.val<root.val && q.val<root.val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
else if(p.val>root.val && q.val>root.val){
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
}
return root;
}

538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
这两道题是一样的
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
1038. 从二叉搜索树到更大和树
重新建树
The first idea is easy to think of,First in-order traversal to get all the required values,Then inorder traversal again to assign values to the tree.
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
inorder(root, list);
//将listThe value is set to what the title requires
for (int i = list.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
list.set(i, list.get(i) + list.get(i + 1));
}
//重新赋值
build(root, list);
return root;
}
private static void build(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
int i = 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
if (cur!=null){
cur.val = list.get(i++);
}
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}
private static void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
if (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
} else {
cur = stack.pop();
//Get the value of inorder traversal
list.add(cur.val);
cur = cur.right;
}
}
}

递归
Reverse inorder traversal is from big to small,用一个sumThe record can be accumulated.
int sum = 0;
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
build(root);
return root;
}
//逆中序
private void build(TreeNode root){
if(root!=null){
build(root.right);
root.val+=sum;
sum=root.val;
build(root.left);
}
}

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Four ways to traverse a Map
mae,mse,rmse分别利用sklearn和numpy实现
zabbix deployment
SkiaSharp 之 WPF 自绘 粒子花园(案例版)
章节小测一
深度强化学习与APS的一些感想
WPF 截图控件之画笔(八)「仿微信」
*SEO*
数字知识库及考学一体化平台
遍历Map的四种方法
Super Learning Method
数据化管理洞悉零售及电子商务运营——零售密码
【Idea系列】idea配置
【LeetCode】653. 两数之和 IV - 输入 BST
Why are all hotel bathrooms transparent?
【Inspirational】The importance of review
音频编辑 合唱
Google Earth Engine APP ——制作上传GIF动图并添加全球矢量位置
Jenkins User Manual (1) - Software Installation
Difference between ArrayList and LinkedList