当前位置:网站首页>Talk about 10 tips to ensure thread safety
Talk about 10 tips to ensure thread safety
2022-07-04 14:23:00 【51CTO】
Preface
For students engaged in back-end development , Thread safety The problem is something we need to consider every day .
Thread safety is a popular topic : Mainly in the multi-threaded environment , Different threads read and write public resources at the same time ( Critical resources ), Data exception caused by .
such as : Variable a=0, Threads 1 Give this variable +1, Threads 2 Also give this variable +1. here , Threads 3 obtain a The value of may not be 2, It is 1. Threads 3 This is not to get the wrong data ?
Thread safety issues can directly lead to data exceptions , This will affect the normal use of business functions , So this problem is still very serious .
that , How to solve the thread safety problem ?
Let's talk with you today , Thread safe 10 A little trick , I hope it helped you .
1. No state
We all know that only multiple threads can access public resource When , Data security issues may arise , So if we don't have public resources , Is there no such problem ?
for example :
In this case NoStatusService There is no public resource defined , In other words No state Of .
In this scenario ,NoStatusService Class must be thread safe .
2. immutable
If the common resource accessed by multiple threads is immutable Of , There will be no data security issues .
for example :
DEFAULT_NAME Defined as static final The constant , It will not be modified in a multithreaded environment , So in this case , There will be no thread safety issues .
3. No permission to modify
occasionally , We define public resources , But this resource only exposes the read permission , No permission to expose changes , This is also thread safe .
for example :
In this case , No external exposure modification name Entry to the field , So there's no thread safety issue .
3. synchronized
Use JDK Provided internally Synchronization mechanism , This is also a means of using more , It is divided into : Synchronization method and Synchronization code block .
We prefer to use synchronized code blocks , Because the granularity of synchronous method is the whole method , Range is too big , relatively speaking , It consumes more code performance .
Actually , Inside each object there is a lock , Only those who snatched the lock Threads , Is allowed to enter the corresponding code block and execute the corresponding code .
After the contemporary code block is executed ,JVM The bottom layer will automatically release the lock .
for example :
public
class
SyncService {
private
int
age
=
1;
private
Object
object
=
new
Object();
public
synchronized
void
add(
int
i) {
age
=
age
+
i;
System.
out.
println(
"age:"
+
age);
}
public
void
update(
int
i) {
synchronized (
object) {
age
=
age
+
i;
System.
out.
println(
"age:"
+
age);
}
}
public
void
update(
int
i) {
synchronized (
SyncService.
class) {
age
=
age
+
i;
System.
out.
println(
"age:"
+
age);
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
4. Lock
Besides using synchronized Keyword to achieve synchronization function ,JDK It also provides Lock Interface , This way of displaying locks .
Usually we use Lock Implementation class of interface :ReentrantLock, It contains : Fair lock 、 Not fair lock 、 Reentrant lock 、 Read-write lock More and more powerful functions .
for example :
public
class
LockService {
private
ReentrantLock
reentrantLock
=
new
ReentrantLock();
public
int
age
=
1;
public
void
add(
int
i) {
try {
reentrantLock.
lock();
age
=
age
+
i;
System.
out.
println(
"age:"
+
age);
}
finally {
reentrantLock.
unlock();
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
But if ReentrantLock, It also brings a small problem that : Need to be in finally Manually release the lock in the code block .
But to be honest , In the use of Lock Show the way the lock , Solving thread safety problems , Gives developers more flexibility .
5. Distributed lock
If it is in the case of a single machine , Use synchronized and Lock There is no problem with thread safety .
But in a distributed environment , That is, if an application deploys multiple nodes , Each node can use synchronized and Lock Ensure thread safety , But between different nodes , There is no way to guarantee thread safety .
That's what you need to use : Distributed lock 了 .
There are many kinds of distributed locks , such as : Database distributed lock ,zookeeper Distributed lock ,redis Distributed locks, etc .
I personally recommend redis Distributed lock , Its efficiency is relatively higher .
Use redis The pseudo code of distributed lock is as follows :
It also needs to be in finally Release lock in code block .
If you are right about redis Usage of distributed locks and common pitfalls , If you are more interested , Take a look at my other article 《 Chat redis Distributed locked 8 hole 》, There is a more detailed introduction .
6. volatile
occasionally , We have such a need : If in multiple threads , There is any thread , Set the state of a switch to false, Then the whole function stops .
After a simple requirement analysis, it is found that : Just ask for the number of threads visibility , Does not require Atomicity .
If a thread changes its state , All other threads can get the latest status value .
With such an analysis, it will be easy to do , Use volatile Can quickly meet the needs .
for example :
public
CanalService {
private
volatile
boolean
running
=
false;
private
Thread
thread;
private
CanalConnector
canalConnector;
public
void
handle() {
while(
running) {
}
}
public
void
start() {
thread
=
new
Thread(
this::
handle,
"name");
running
=
true;
thread.
start();
}
public
void
stop() {
if(
!
running) {
return;
}
running
=
false;
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
What needs special attention is :
volatile It cannot be used in business scenarios such as counting and statistics . because volatile The atomicity of the operation cannot be guaranteed , May cause data exceptions .
7. ThreadLocal
In addition to the above solutions ,JDK It also provides another way to use Space for time New ideas :ThreadLocal.
Of course ThreadLocal It does not completely replace locks , Especially in some seckill update inventory , A lock must be used .
ThreadLocal The core idea of : Shared variables have a copy in each thread , Each thread operates its own copy , No effect on other threads .
A warm reminder : We usually use ThreadLocal when , If after use , Be sure to remember in
finally Block of code , Call it the remove Method to clear the data , Otherwise, there may be Memory leak problem .
for example :
If the ThreadLocal Interested partners , Take a look at my other article 《 ThreadLocal Life taking 11 Continuous questioning 》, There's right in it ThreadLocal Principle 、 Usage and pit , There is a very detailed introduction .
8. Thread safe collection
occasionally , The public resources we need to use are placed in a collection , such as :ArrayList、HashMap、HashSet etc. .
If in a multithreaded environment , Wired programs write data to these sets , Another thread reads data from the collection , There may be thread safety problems .
To solve the thread safety problem of collections ,JDK It provides us with thread safe collections .
such as :CopyOnWriteArrayList、ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArraySet、ArrayBlockingQueue wait .
for example :
public
class
HashMapTest {
private
static
ConcurrentHashMap
<
String,
Object
>
hashMap
=
new
ConcurrentHashMap
<>();
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args) {
new
Thread(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
hashMap.
put(
"key1",
"value1");
}
}).
start();
new
Thread(
new
Runnable() {
public
void
run() {
hashMap.
put(
"key2",
"value2");
}
}).
start();
try {
Thread.
sleep(
50);
}
catch (
InterruptedException
e) {
e.
printStackTrace();
}
System.
out.
println(
hashMap);
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
stay JDK Bottom , perhaps spring In the frame , Use ConcurrentHashMap There are many scenarios where loading configuration parameters are saved .
What is more famous is spring Of refresh In the method , Will read the configuration file , Put the configuration into many ConcurrentHashMap cached .
9. CAS
JDK In addition to using the lock mechanism to solve the data security problem in the case of multithreading , It also provides CAS Mechanism .
This mechanism uses CPU Compare and exchange atomicity of instructions in ,JDK It's through Unsafe Class implements the .
CAS There are four values inside : Old data 、 Expect data 、 The new data and Address , Compare old data and Expected data , If it's the same , Change old data into new data . If it's not the same , The current thread is constantly The spin , Until we succeed .
however , Use CAS Ensure thread safety , There may be ABA problem , Need to use AtomicStampedReference Add the version number to solve the problem .
Actually , It is seldom used directly in practical work Unsafe Class , It's usually used atomic The classes under the package are sufficient .
10. Data isolation
occasionally , When we operate on set data , Can pass Data isolation , To ensure thread safety .
for example :
public
class
ThreadPoolTest {
public
static
void
main(
String[]
args) {
ExecutorService
threadPool
=
new
ThreadPoolExecutor(
8,
10,
60,
TimeUnit.
SECONDS,
new
ArrayBlockingQueue(
500),
new
ThreadPoolExecutor.
CallerRunsPolicy());
List
<
User
>
userList
=
Lists.
newArrayList(
new
User(
1L,
" Su three ",
18,
" Chengdu "),
new
User(
2L,
" Su San said technology ",
20,
" sichuan "),
new
User(
3L,
" technology ",
25,
" yunnan "));
for (
User
user :
userList) {
threadPool.
submit(
new
Work(
user));
}
try {
Thread.
sleep(
100);
}
catch (
InterruptedException
e) {
e.
printStackTrace();
}
System.
out.
println(
userList);
}
static
class
Work
implements
Runnable {
private
User
user;
public
Work(
User
user) {
this.
user
=
user;
}
public
void
run() {
user.
setName(
user.
getName()
+
" test ");
}
}
}
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
- 8.
- 9.
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
- 15.
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
- 27.
- 28.
- 29.
- 30.
- 31.
- 32.
- 33.
- 34.
- 35.
- 36.
- 37.
- 38.
- 39.
- 40.
- 41.
In this case , Use Thread pool Handle user information .
Each user is only Thread pool One of them Threads Handle , There is no case where multiple threads process a user at the same time . So this artificial data isolation mechanism , It can also ensure thread safety .
There is another scenario for data isolation :kafka The producer sends the same order message , Send to the same partion in . every last partion Deploy a consumer , stay kafka Among consumers , Use a single thread to receive messages , And do business processing .
In this case , On the whole , Different partion It uses multithreading to process data , But the same partion Is handled by a single thread , So it can also solve the thread safety problem .
边栏推荐
- Use of arouter
- Xcode 异常图片导致ipa包增大问题
- 商業智能BI財務分析,狹義的財務分析和廣義的財務分析有何不同?
- R language uses the DOTPLOT function of epidisplay package to visualize the frequency of data points in different intervals in the form of point graph, and uses the by parameter to specify the groupin
- Basic mode of service mesh
- Popular framework: the use of glide
- Redis daily notes
- Can mortgage with housing exclude compulsory execution
- Gorm data insertion (transfer)
- GCC [6] - 4 stages of compilation
猜你喜欢
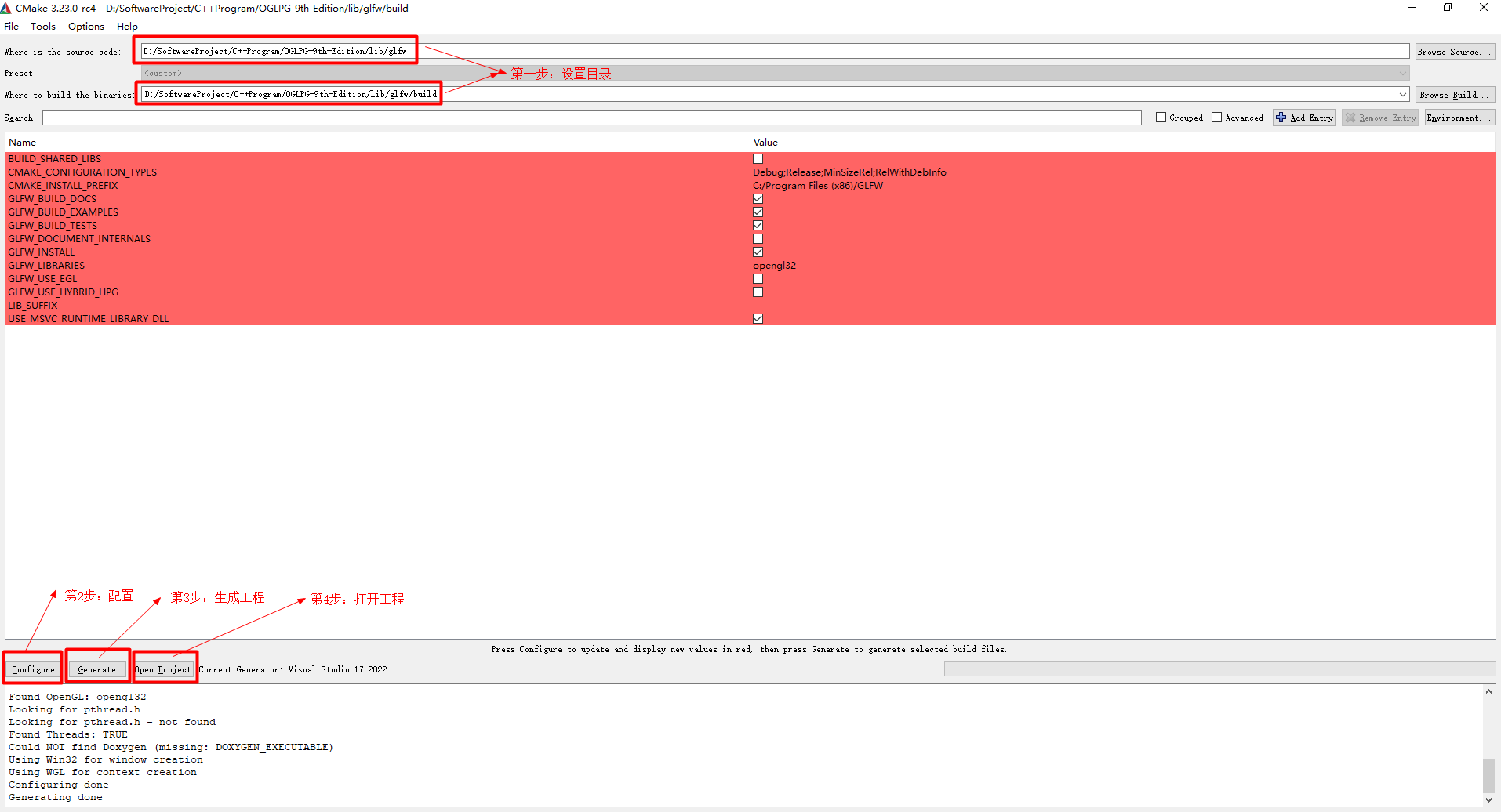
使用CLion编译OGLPG-9th-Edition源码
Innovation and development of independent industrial software

富文本编辑:wangEditor使用教程

Xcode 异常图片导致ipa包增大问题
![[FAQ] summary of common causes and solutions of Huawei account service error 907135701](/img/43/1a9786c89a5ab21d1fb8903cb7b77e.png)
[FAQ] summary of common causes and solutions of Huawei account service error 907135701
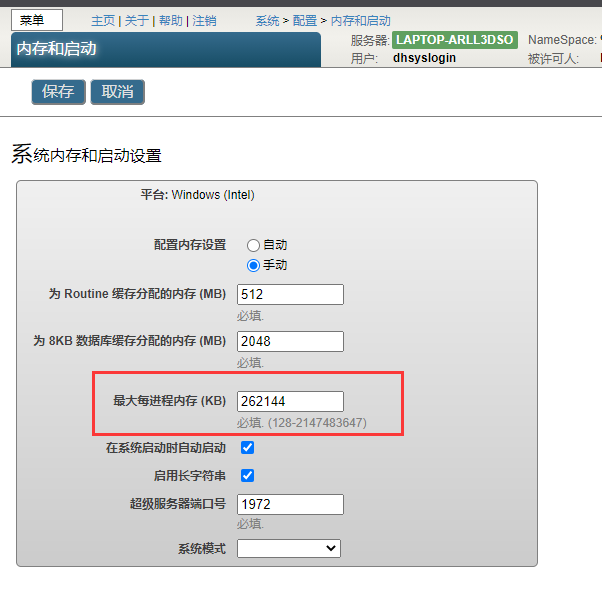
第十七章 进程内存
gin集成支付宝支付
sql优化之查询优化器
Use of tiledlayout function in MATLAB
商業智能BI財務分析,狹義的財務分析和廣義的財務分析有何不同?
随机推荐
【算法leetcode】面试题 04.03. 特定深度节点链表(多语言实现)
QT how to detect whether the mouse is on a control
Test process arrangement (2)
IP lab monthly resumption · issue 5
Map of mL: Based on Boston house price regression prediction data set, an interpretable case of xgboost model using map value
Understand chisel language thoroughly 08. Chisel Foundation (V) -- wire, REG and IO, and how to understand chisel generation hardware
2022 practice questions and mock exams for the main principals of hazardous chemical business units
Understand chisel language thoroughly 10. Chisel project construction, operation and testing (II) -- Verilog code generation in chisel & chisel development process
Mask wearing detection based on yolov1
Install and use MAC redis, connect to remote server redis
Data warehouse interview question preparation
Introducing testfixture into unittest framework
实时数据仓库
opencv3.2 和opencv2.4安装
Incremental ternary subsequence [greedy training]
Understand chisel language thoroughly 05. Chisel Foundation (II) -- combinational circuits and operators
R语言ggplot2可视化:gganimate包创建动画图(gif)、使用anim_save函数保存gif可视化动图
Matters needing attention in overseas game Investment Agency
The game goes to sea and operates globally
测试流程整理(3)