当前位置:网站首页>Common lipophilic cell membrane dyes DiO, Dil, DiR, Did spectrograms and experimental procedures
Common lipophilic cell membrane dyes DiO, Dil, DiR, Did spectrograms and experimental procedures
2022-08-03 04:45:00 【Fluorescent House】
Di belongs to long-chain dialkyl carbocyanine dyes. Its unique structure makes it extremely lipophilic and can be combined with lipid-soluble biological structures. At a certain concentration, it can completely dye cell membranes.Di dyes have high quenching coefficients and excited state lifetimes after being excited, and play a great role in the localization and tracing of cells and tissues.
DiD (CAS: 127274-91-3), DiO (CAS: 34215-57-1), DiI (CAS: 41085-99-8), DiR (CAS: 100068-60-8) and DiS dyes areA family of lipophilic fluorescent dyes that can be used to stain cell membranes and other lipid-soluble biological structures.When bound to the cell membrane, its fluorescence intensity is greatly enhanced, and these dyes have high quenching constants and excited-state lifetimes.Once cells are stained, these dyes spread across the cell membrane, and at optimal concentrations can stain the entire cell membrane.Their fluorescence colors are distinct: DiI (orange fluorescence), DiO (green fluorescence), DiD (red fluorescence) and DiR (dark red fluorescence) which allows them to be used for multicolor imaging and flow analysis of live cells.DiI and DiO can be used with standard FITC and TRITC filters, respectively.DiD can be excited by a 633 nm He–Ne laser, has longer excitation and emission wavelengths than DiI, and is more valuable in cell and tissue staining.The infrared fluorescence of DiR penetrates cells and tissues and is used for tracking in in vivo imaging.
Common Di dyes include DiO, DiI, DiD, and DiR, which form fluorescence of different colors after being excited (see Figure 1).

Figure 1. DiO, DiI, DiD, DiR spectra
Supplier: Xi'an Kaixin Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
■ DiO staining as an example, briefly throw out the in vitro experimental steps
a) Inoculate an appropriate number of cells and incubate at 37°C overnight.
b) Remove the medium, collect the cells by centrifugation, add PBS and wash 2-3 times, 5 minutes each time.
c) Add the corresponding concentration of DiO working solution (5-10 μM) and incubate at room temperature for 30 minutes.
d) Centrifuge at 400 g for 3-4 minutes at 4°C and discard the supernatant.Wash the cells 2-3 times by adding PBS again to fully remove the DiO that did not enter the cells.
f) Cells were resuspended in serum-free medium or PBS and examined under a fluorescence microscope or flow cytometer.

Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the experimental process
■ DiO
DiO is a green fluorescent dye with excitation/emission wavelengths of 483/501 nM, DiO is often used in forward orBacktracking of various types of cells or tissues.(However, compared with the other three dyes, DiO dyes have weaker fluorescence intensity and are slightly less effective for some fixed tissue sections).
Xin Li et al. investigated whether CPCs (cardiac progenitor cell)-derived exosomes (CPCs-Ex) could utilize the mTOR signaling pathway to reduce apoptosis in viral myocarditis.The researchers labelled CPCs-Ex with DiO (Dio can be incorporated into the cell membrane by selective segmentation), and assessed the in vitro uptake of CPCs-Ex by H9C2 cells. Fluorescence microscopy revealed that each cytoplasm of H9C2 cells contained a fluorescent signal (Figure 2).), and reduced apoptosis in H9C2 cells, confirming the anti-apoptotic effect of CPCs-Ex in CVB3-infected cells.

Figure 3. Uptake of DiO-labeled exosomes by H9C2 cells[1]
■ DiI
DiI is a orange-red fluorescent dye with excitation/emission wavelengths of 551/569 nM, DiI was used for forward orFor reverse tracing of various cells or tissues, the fluorescence signal intensity is higher than that of DiO, and its fluorescence signal will be greatly amplified when it enters the cell membrane.
As shown in Figure 4, Dil dye-labeled exosomes were then co-cultured with target cells.Confocal microscopy was used to capture the uptake of Dil-labeled exosomes by HOS cells, where the labeled exosomes emit specific orange-red fluorescence.

Figure 4. Uptake of red fluorescent dye Dil-labeled hBMSC-Exos[2] by HOS and MG63 cells
■ DiD
DiD is a red fluorescent dye with excitation/emission wavelengths of 646/663 nM. DiD has a high fluorescence signal and is not easy toQuenching, low autofluorescence interference, not only for cell/tissue staining, but also most commonly used in small animal live imaging.
Yuxuan Fu et al. developed a drug delivery method to achieve the goal of better entry of anti-COVID-19 drugs into target organs. The researchers used DiD to label the receptor binding domain of extracellular vesicle (EV) viral protein (EV-RBD), and injected into the mouse tail vein, it can be seen by fluorescence imaging that the signal mainly accumulates in the heart, lung, and kidney, and it is worth noting that at 96 h, the fluorescent signal accumulated by the labeled EV-RBD is stillretained in lung tissue, demonstrating the feasibility of the method.

Figure 5. Distribution of DiD-labeled EV-RBD in mice [3]
■ DiR
DiR is a near-infrared dye with excitation/emission wavelengths of 754/778 nm for forward or reverse tracking of various cells or tissues. Like DiD, DiR has a low autofluorescence background and is also used inIn vivo imaging.
Today's introduction is here for the time being. Do you guys have a little gain after reading it?
■ Xi'an Kaixin Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Product Summary:

边栏推荐
- UV decomposition of biotin - PEG2 - azide | CAS: 1192802-98-4 biotin connectors
- 刚上线就狂吸70W粉,新型商业模式“分享购”来了,你知道吗?
- 4.深度学习的几何解释与梯度的优化
- Interface testing framework combat (3) | JSON request and response assertion
- Flink state
- typescript43-类型兼容性说明
- 8.电影评论分类:二分类问题
- 【Biotin Azide|cas:908007-17-0】Price_Manufacturer
- How to use the interface management tool YApi?Beautiful, easy to manage, super easy to use
- Create a tree structure
猜你喜欢
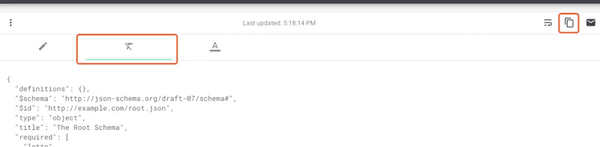
接口测试框架实战(四)| 搞定 Schema 断言
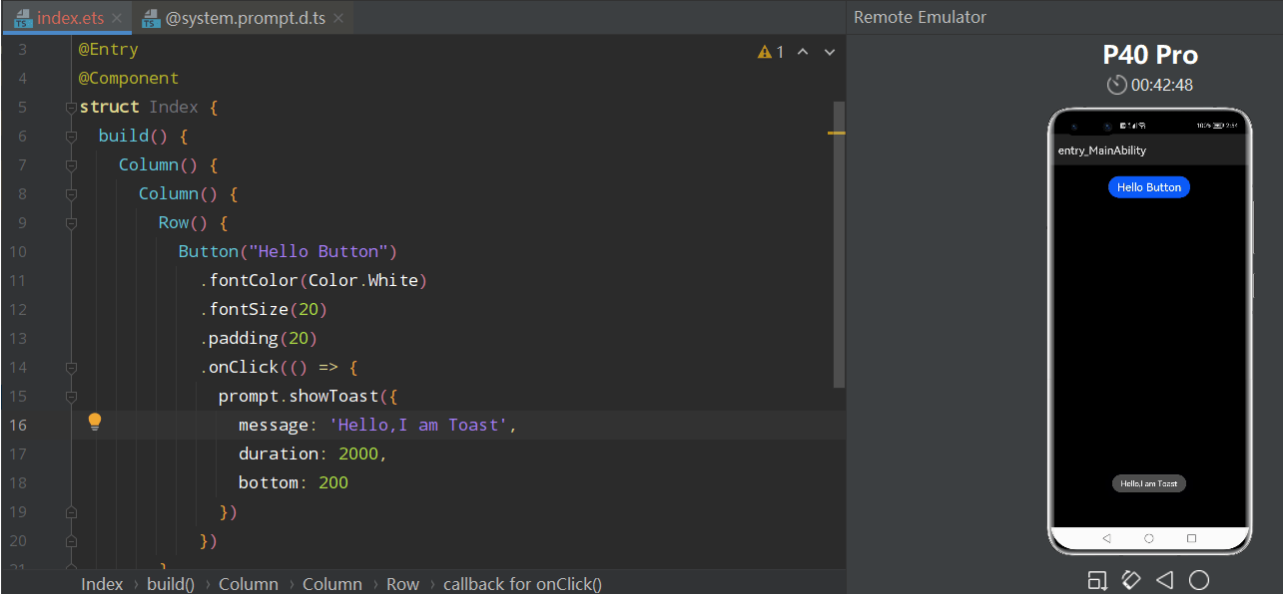
【Harmony OS】【FAQ】鸿蒙问题合集1

链动2+1模式简单,奖励结构丰厚,自主裂变?

在线密码生成工具推荐
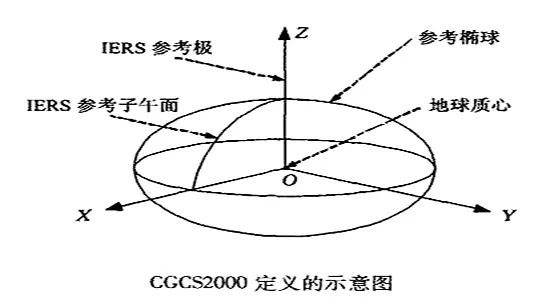
GIS数据漫谈(五)— 地理坐标系统
Interface Test Framework Practice | Process Encapsulation and Test Case Design Based on Encrypted Interface

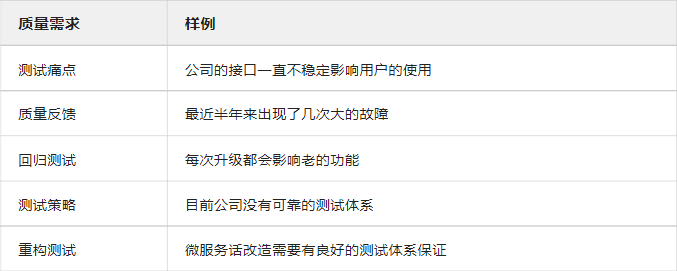
测试人员的价值体现在哪里
Two ways to simulate multi-user login in Jmeter
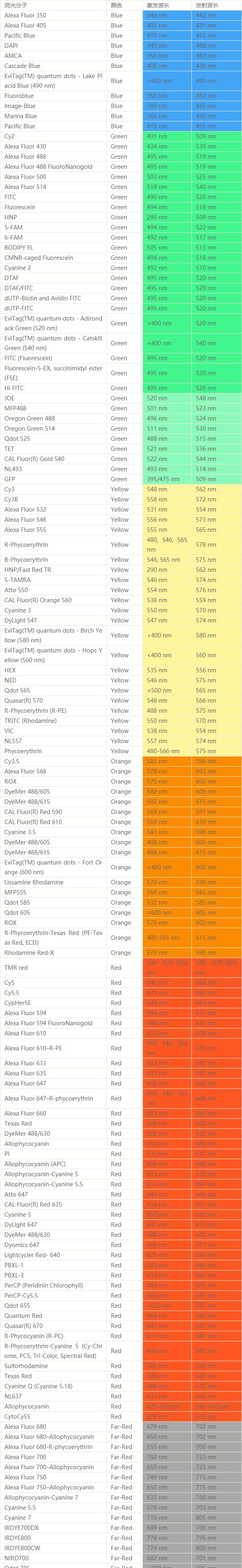
常见荧光染料修饰多种基团及其激发和发射波长数据一览数据
GIS数据漫谈(六)— 投影坐标系统
随机推荐
Online password generator tool recommendation
如何利用 Flutter 实现炫酷的 3D 卡片和帅气的 360° 展示效果
Test drive: project management module - curd development project
The flink sql task is changed, and after adding several fields to the sql, an error occurs when restoring from the previously saved savepoint.
【生物素叠氮化物|cas:908007-17-0】价格_厂家
C#异步和多线程
Interface test practice | Detailed explanation of the difference between GET / POST requests
Concepts and Methods of Exploratory Testing
「短视频+社交电商」营销模式爆发式发展,带来的好处有什么?
[Harmony OS] [ArkUI] ets development graphics and animation drawing
接口测试框架实战 | 流程封装与基于加密接口的测试用例设计
【Harmony OS】【ArkUI】ets开发 基础页面布局与数据连接
【Harmony OS】【ARK UI】ETS 上下文基本操作
Record some bugs encountered - when mapstruct and lombok are used at the same time, the problem of data loss when converting entity classes
DFS's complement to pruning
链动2+1模式简单,奖励结构丰厚,自主裂变?
BIOTIN ALKYNE CAS: 773888-45-2 Price, Supplier
8.电影评论分类:二分类问题
常见亲脂性细胞膜染料DiO, Dil, DiR, Did光谱图和实验操作流程
软件开发的最大的区别是什么?