当前位置:网站首页>Pki/ca and digital certificate
Pki/ca and digital certificate
2022-07-03 12:06:00 【J_ D_ Chi】
Write it at the front
It's time to get in touch CA Related content , I still don't know much about some nouns , I can't understand when I encounter some problems , I just read a book recently 《PKI/CA And digital certificate Technology Encyclopedia 》, The introduction is relatively systematic and comprehensive , It is also an introduction for people who are new to this field .
1. PKI
All kinds of concepts and technologies related to digital certificates , Collectively referred to as PKI( Public Key Infrastructure Public key infrastructure ).
PKI By introducing CA, digital certificate ,LDAP,CRL,OCSP And formulate corresponding standards , The mapping relationship between public key and user is effectively solved , Centralized service performance bottleneck , Offline status query and other issues . At the same time, in order to promote and improve the standardization of Certificate Application , There are also many standards related to the application of certificates .
So what we mentioned below CA, digital certificate ,OCSP And other nouns are in PKI Under the , namely PKI It contains these things . Then each of these nouns is produced to solve a problem , So when we understand these nouns , Can reflect what they mean , What problem is it to solve .
1.1 PKI System framework
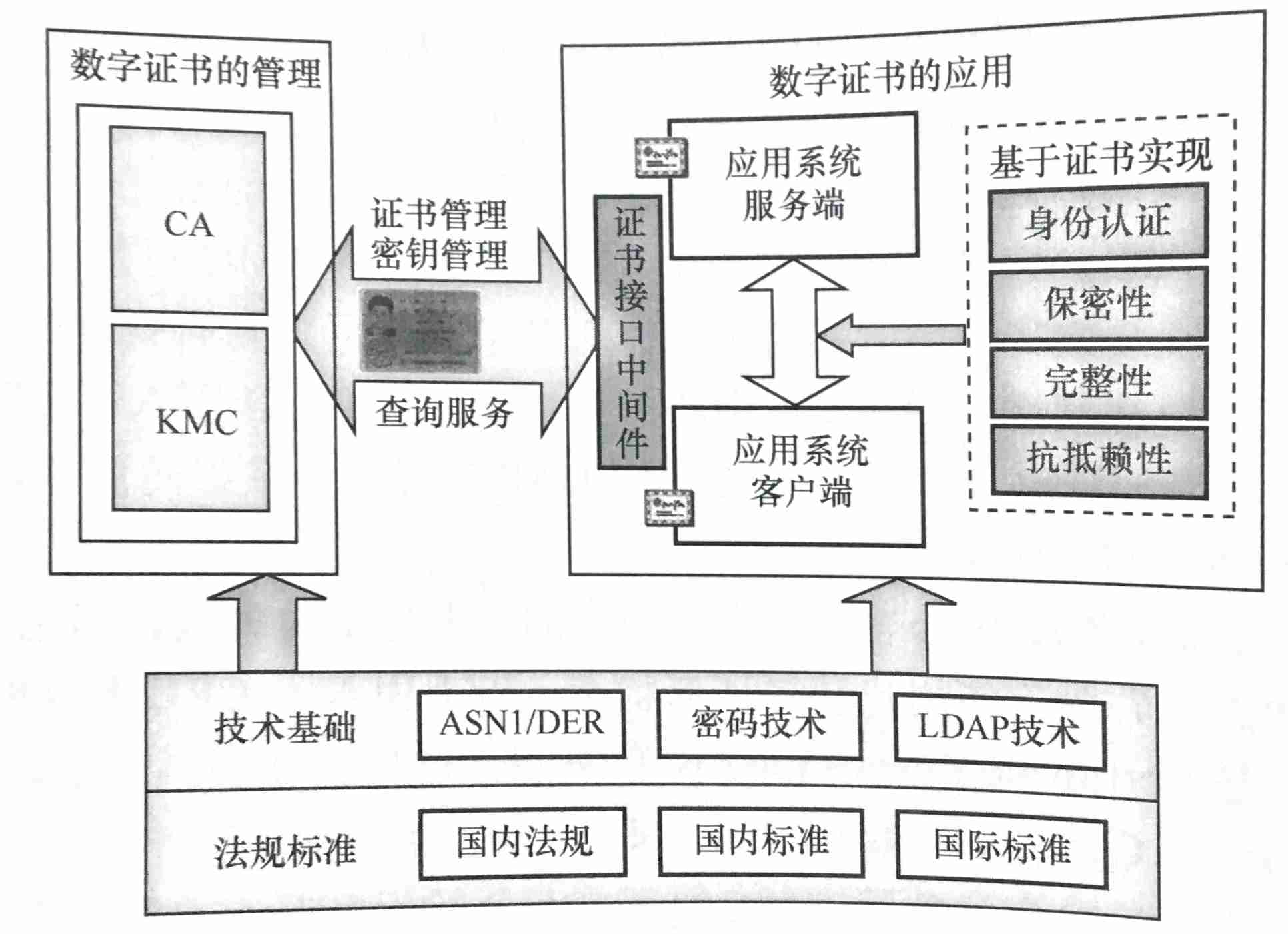
PKI The system framework mainly includes three contents :
1.1.1 Digital certificate and private key
About digital certificates
Users or systems only have their own public and private keys , To achieve digital signature and encryption and decryption functions , Because the public key is generated randomly , Therefore, it is impossible to directly determine which user belongs to from the public key .
To solve the mapping relationship between public key and user ,PKI The introduction of digital certificates . The digital certificate contains the user's identity information , User public key information *( Both are used to identify users ) and CA Private key digital signature ( Use CA The public key of can judge whether the certificate has been tampered )*.
The private key is usually stored in the hardware password device ( image U Shield or something ).
1.1.2 Digital certificate management
About CA
In order to solve the issue of digital certificates ,PKI Introduced CA(Certificate Authority), Centralized issuance of digital certificates .
It is actually a special public key management center , Manage the whole life cycle of digital certificates , Include : Issuance and renewal of digital certificates , Cancellation of digital certificates , Freeze and thaw , Query or download , Status query, etc .
Like guangzhou CA, Shenzhen CA It belongs to this category , Go to their official website for relevant information .
About KMC
To solve the problem of private key backup and recovery ,PKI Introduced KMC(Key Management Center).
The user's public-private key pair is determined by KMC produce ,KMC Back up the private key ; Public and private keys can also be generated by users , And submit the private key to KMC Make a backup .
About dual certificates
To prevent user identity from being falsely used , The uniqueness of the user's private key should be guaranteed , Backup recovery is not allowed ; To prevent the data encrypted by the public key from being decrypted , Should be Provide backup and recovery mechanism of user private key .
In order to solve these two contradictory needs ,PKI The dual certificate mechanism is introduced : Signing certificate and encryption certificate .
The public-private key pair of the signing certificate is generated by the user ,KMC Do not back up the private key ; Encryption certificate key pair by KMC produce , And KMC Backup the encrypted private key .
About LDAP
To solve the problem of CA Performance problems of certificate query or download ,PKI introduce LDAP(Light-weight Directory Access Protocol Lightweight Directory Access Protocol ) technology .
DAP(Directory Access Protocol Directory Access Protocol ) It is a technology that specially optimizes the reading function of data management , It is suitable for quick response and high-capacity query services , The application system only needs to pass X.500 The protocol can quickly query the data . But because the agreement is too complex , International organizations simplify it , To form the LDAP standard .
About CRL and OCSP
To solve the problem of CA Query on certificate validity ,PKI Introduced CRL(Certificate Revocation List) and OCSP(Online Certificate Status Protocol) technology . The former requires users to download regularly , It can be used offline ; The latter can be queried online in real time .
About RA
For users Face to face Certificate service , Handle user certificate / Void the application , User identity verification , Functions such as making certificates and handing them over to users .PKI Introduced RA(Registry Authority)
About electronic certification services
** To guarantee CA Standardization of the system in digital certificate management 、 Compliance and safety ,PKI The introduction of electronic certification services ,** Provide digital certificate related services in the form of third-party operation .

1.1.3 Application of digital certificate
Four basic security functions can be realized based on digital certificates : Identity Authentication , confidentiality , Integrity and non repudiation .
Identity Authentication
Such as network ID card .
confidentiality
If you don't disclose credit card information .
integrity
If the signed contract will not be modified by one party without permission .
Non repudiation
In case of transaction disputes , It can be confirmed by verifying the private key signature of the other party .
1.2 PKI Trust model
First, let's look at some concepts :
trust : stay ITU X.509 Specification ,“ trust ” Defined as “ When entity A Think of entities B The behavior and A When the expectations are exactly the same , It's called entity A Trust entities B”.
User trust CA center Refer to , Users believe that CA All digital certificate management behaviors of the center comply with policies and regulations , Requirements for operation specifications and information security .
Users trust digital certificates Refer to , The user believes that the identity of the digital certificate holder is really valid , It does not mean that the user trusts the holder of the digital certificate .
From trust CA The center trusts the user digital certificate issued by it , The premise of this trust transmission relationship is , The user digital certificate must pass the legitimacy verification in the following four aspects :
4.1 Verify whether the digital certificate is forged . Use CA The public key in the certificate can be verified offline .
4.2 Verify whether the information in the digital certificate is correct . from CA When issuing the digital certificate, the center has guaranteed .
4.3 Verify whether the digital certificate is consistent with the holder . The holder may be required to encrypt or sign specific data using a private key , Then use the public key in the digital certificate to decrypt or verify the signature .
4.4 Verify whether the digital certificate is on the blacklist . adopt CRL or OCSP Realization .Trust anchor :CA The center is the source or starting point of trust .
Authentication path : A trust relationship transmission path from trust anchor to digital certificate , Also called certificate path or trust chain .
1.2.1 root CA Trust model
The highest level CA There's only one center , Become the root CA, Other CA It's called Zi CA. root CA Your digital certificate is issued by yourself , Belongs to self signed certificate , Son CA The digital certificate is issued by the superior CA Certificate issue . Trust anchors can be roots CA, It can also be a son CA.
The following is an example : user X Trusted users A certificate , The trust chain is the root CA—— Son CA1—— user A certificate .

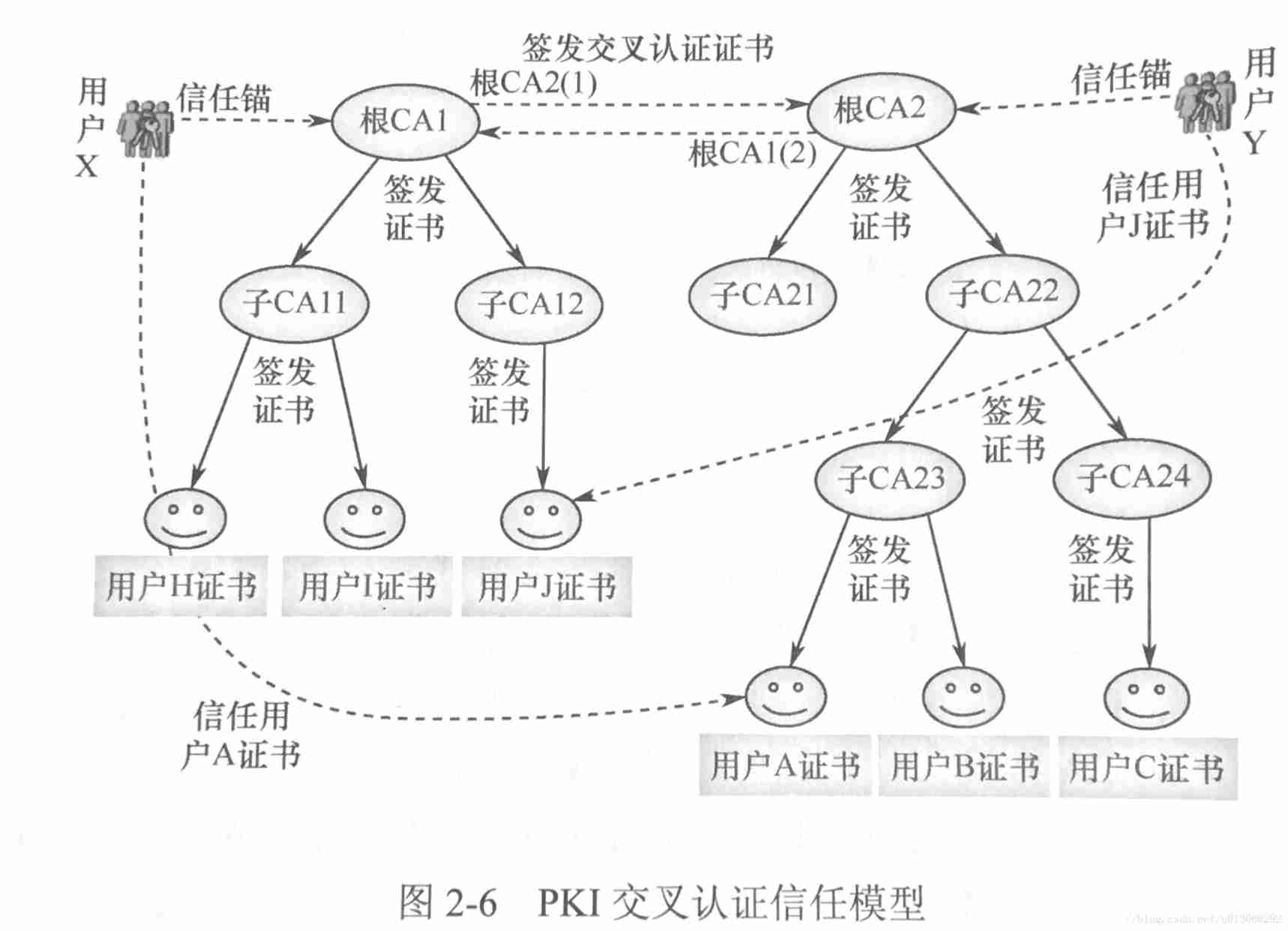
1.2.2 Cross certification trust model
root CA Cross certification certificates can be issued to each other .
The following is an example , user Y You can trust users J certificate . The trust chain is the root CA2—— root CA2(1)—— root CA1—— Son CA12—— user J certificate
1.2.3 Bridge CA Trust model
Introduce an independent bridge here CA center , Equivalent to virtual root CA. All roots CA And Bridge CA Issue cross certification certificates to each other . Similar to the cross certification trust model .

1.2.4 Trust list trust model
Enable users to have multiple trust anchors .

边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
QT OpenGL rotate, pan, zoom
(database authorization - redis) summary of unauthorized access vulnerabilities in redis
安裝electron失敗的解决辦法
previous permutation lintcode51
错排问题 (抽奖,发邮件)
Capturing and sorting out external Fiddler -- Conversation bar and filter [2]
Is BigDecimal safe to calculate the amount? Look at these five pits~~
vulnhub之cereal
OPenGL 基本知识(根据自己理解整理)
DEJA_ Vu3d - 054 of cesium feature set - simulate the whole process of rocket launch
Niuniu's team competition
安装electron失败的解决办法
(构造笔记)MIT reading部分学习心得
优化接口性能
网络通讯之Socket-Tcp(一)
cgroup简介
Symlink(): solution to protocol error in PHP artisan storage:link on win10
Vulnhub's Nagini
Visual Studio 2022下载及配置OpenCV4.5.5
Momentum of vulnhub