当前位置:网站首页>Sentinel Alibaba open source traffic protection component
Sentinel Alibaba open source traffic protection component
2022-07-02 06:26:00 【dotaer-df】
One 、 Preface
Sentinel High availability for distributed service architecture Flow protection assembly
Sentinel It has the following characteristics :
- Rich application scenarios :Sentinel To undertake Alibaba near 10 The core scene of promoting traffic in the double 11 of , For example, seckill ( That is to say, the burst flow is controlled within the range of system capacity )、 Cut the peak and fill the valley 、 Cluster flow control 、 Real time fuse downstream unavailable applications, etc .
- Complete real-time monitoring :Sentinel At the same time, it provides real-time monitoring function . You can see the second level data of a single machine accessing the application in the console , even to the extent that 500 Summary operation of clusters below Taiwan .
- Broad open source ecosystem :Sentinel Provides out of the box and other open source frameworks / The integration module of the library , For example, Spring Cloud、Dubbo、gRPC Integration of . You only need to introduce corresponding dependency and make simple configuration to access quickly Sentinel.
- Perfect SPI The extension point :Sentinel Easy to use 、 Perfect SPI Extension interface . You can quickly customize the logic by implementing the extension interface . For example, custom rule management 、 Adapt to dynamic data sources, etc .
Two 、Sentinel Basic concepts
resources
Resources are Sentinel Key concepts of . It can be Java Anything in the application , for example , Services provided by applications , Or services provided by other applications called by the application , It could even be a piece of code , In short, it is a very broad concept . As long as through the Sentinel API Defined code , It's resources , It can be Sentinel Protect it . In most cases , You can use method signature ,URL, Even the service name identifies the resource as the resource name .
The rules
Rules around the real-time state of resources , It can include flow control rules 、 Fusing degradation rules and system protection rules . All rules can be adjusted dynamically and in real time .
Let's go through a Demo Let's get familiar with these two concepts
private static final String sourceName = "s1";
public static void main(String[] args) {
initFlowRules();
while (true) {
Entry entry = null;
try {
// Protected resources
entry = SphU.entry(sourceName);
// Execute business logic
System.out.println("hello world");
} catch (BlockException e) {
// Resource access blocked , Being restricted or degraded will trigger BlockException
// Do the corresponding processing operation here
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("block exception");
}finally {
if(entry != null) {
entry.exit();
}
}
}
}
// Hard coding rules
private static void initFlowRules(){
// This resource can only pass at most 20 A request .
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<>();
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
rule.setResource(sourceName);
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
rule.setCount(20);
rules.add(rule);
// Load flow control rules
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
} Demo After running , We can do it in the journal ~/logs/csp/${appName}-metrics.log.xxx See the output below :(~ Represents the root directory of the current user )
|--timestamp-----|------date time----------|-resource-|p|block|s|e|rt
1655778763000|2022-06-21 10:32:43|s1|20|48|20|0|1
1655778764000|2022-06-21 10:32:44|s1|20|36641|20|0|0
1655778765000|2022-06-21 10:32:45|s1|20|80100|20|0|0
1655778766000|2022-06-21 10:32:46|s1|20|144822|20|0|0
among resource Represents the resource name , p A request passed on behalf of , block On behalf of a blocked request , s Represents the number of requests successfully executed , e Represents a user-defined exception , rt Represents the average response time .
The above method is to modify rules manually ( Hard coding ) Generally only for testing and demonstration , In production, rules are managed dynamically through dynamic rule sources , That is, on the console api Set rules , Now try this method
3、 ... and 、 Dynamic rule source
(1) download sentinel Console jar package
(2) because Sentinel It's a springboot The project passes directly through java -jar start-up
java -Dserver.port=8080 -Dcsp.sentinel.dashboard.server=localhost:8080 -Dproject.name=sentinel-dashboard -jar sentinel-dashboard.jar
(3) visit sentinel Console (localhost:8080) The default username and password are sentinel
(4) Client access sentinel Console
Related dependencies
<!-- rely on web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel springboot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
<version>2021.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- sentinel Core dependence -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-core</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>Configure console information
server:
port: 8081
spring:
cloud:
sentinel:
transport:
port: 8719
dashboard: localhost:8080 # Appoint sentinel dashboard web Address among spring.cloud.sentinel.transport.port Port configuration will start a... On the corresponding machine of the application Http Server, The Server Will be with Sentinel Console interaction . such as Sentinel A current limiting rule has been added to the console , Will put the rule data push Here it is Http Server receive ,Http Server Then register the rules to Sentinel in .
(5) Official test code part
@RestController
public class SentinelController {
@Autowired
SentinelService sentinelService;
@GetMapping("/foo")
public String apiFoo(@RequestParam(required = false) Long t) throws Exception {
if (t == null) {
t = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
sentinelService.test();
return sentinelService.hello(t);
}
@GetMapping("/baz/{name}")
public String apiBaz(@PathVariable("name") String name) {
return sentinelService.helloAnother(name);
}
}
@Service
public class SentinelService {
private static final String sourceName = "s1";
@SentinelResource(value = "test", blockHandlerClass = {ExceptionUtil.class})
public void test() {
System.out.println("Test");
}
@SentinelResource(value = "hello", fallback = "helloFallback")
public String hello(long s) {
if (s < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid arg");
}
return String.format("Hello at %d", s);
}
@SentinelResource(value = "helloAnother", defaultFallback = "defaultFallback",
exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalStateException.class})
public String helloAnother(String name) {
if (name == null || "bad".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("oops");
}
if ("foo".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("oops");
}
return "Hello, " + name;
}
public String helloFallback(long s, Throwable ex) {
// Do some log here.
ex.printStackTrace();
return "Oops, error occurred at " + s;
}
public String defaultFallback() {
System.out.println("Go to default fallback");
return "default_fallback";
}
}
public class ExceptionUtil {
public static void handleException(BlockException ex) {
System.out.println("Oops: " + ex.getClass().getCanonicalName());
}
}The core notes are @SentinelResource, Through this annotation, you can define a resource
@SentinelResource The annotation contains the following properties
value: Resource name , Required ( Can't be empty )entryType:entry type ( The traffic type of the resource call , Inlet flow or outlet flow ), optional ( The default isEntryType.OUT)blockHandler: Used to handle exceptions is BlockExceptionAnd its subclassesName of functionblockHandlerClass: Used to handle exceptions is BlockException And its subclasses,By default , blockHandler In the same class as the original method . however , If some methods share the same signature and intend to set up the same block handler , Then the user can set the class where the block handler exists . Please note that , Block handler methods must be static .
blockHandler andblockHandlerClass requirement :
1、 The method must bepublic2、 The return value type must be the same as the return value type of the original function ;
3、 The parameter type needs to match the original method and add an extra parameter , The type is
BlockException
4、blockHandler Function default needs to be in the same class as the original method . If you want to use functions of other classes , You can specifyblockHandlerClassFor the corresponding classClassobject , Note that the corresponding function must be static function , Otherwise, it cannot be parsed
- fallback:fallback The name of the function , optional , Used to provide... When an exception is thrown fallback Processing logic .fallback Functions can be used for all types of exceptions ( except
exceptionsToIgnoreThe types of exceptions excluded ) To deal with - fallbackClass: ditto
- defaultFallback: default fallback The name of the function , optional , Usually used for general purpose fallback Logic , If you configure fallback and defaultFallback, only fallback Will take effect
fallback
、fallbackClass and defaultFallback requirement :
1、 The method must bepublic
2、 The return value type must be the same as the return value type of the original function ;
3、 Method parameter list should be consistent with the original function , Or maybe one more Throwable The parameter of type is used to receive the corresponding exception .
4、fallback Function default needs to be in the same class as the original method . If you want to use functions of other classes , You can specify fallbackClass For the corresponding class Class object , Note that the corresponding function must be static function , Otherwise, it cannot be parsed
- exceptionsToIgnore: Used to specify which exceptions are excluded , It will not be included in the abnormal statistics , And will not enter fallback In the logic , But will throw out as is .
resourceType: Classification of resources ( type ) Used to identify the classification of resources ,0- Universal 、1-WEB、2-RPC、3-GATEWAY、4-SQL, stay ResourceTypeConstants There are definitions in the class .
(6) Start client , Trigger client initialization ,Sentinel Will be in When the client first calls To initialize ( So you need to trigger it first /foo Interface ), Start sending heartbeat packets to the console .
Access control , Wait a few seconds , You will see that our client has registered

(7) Configure flow control rules
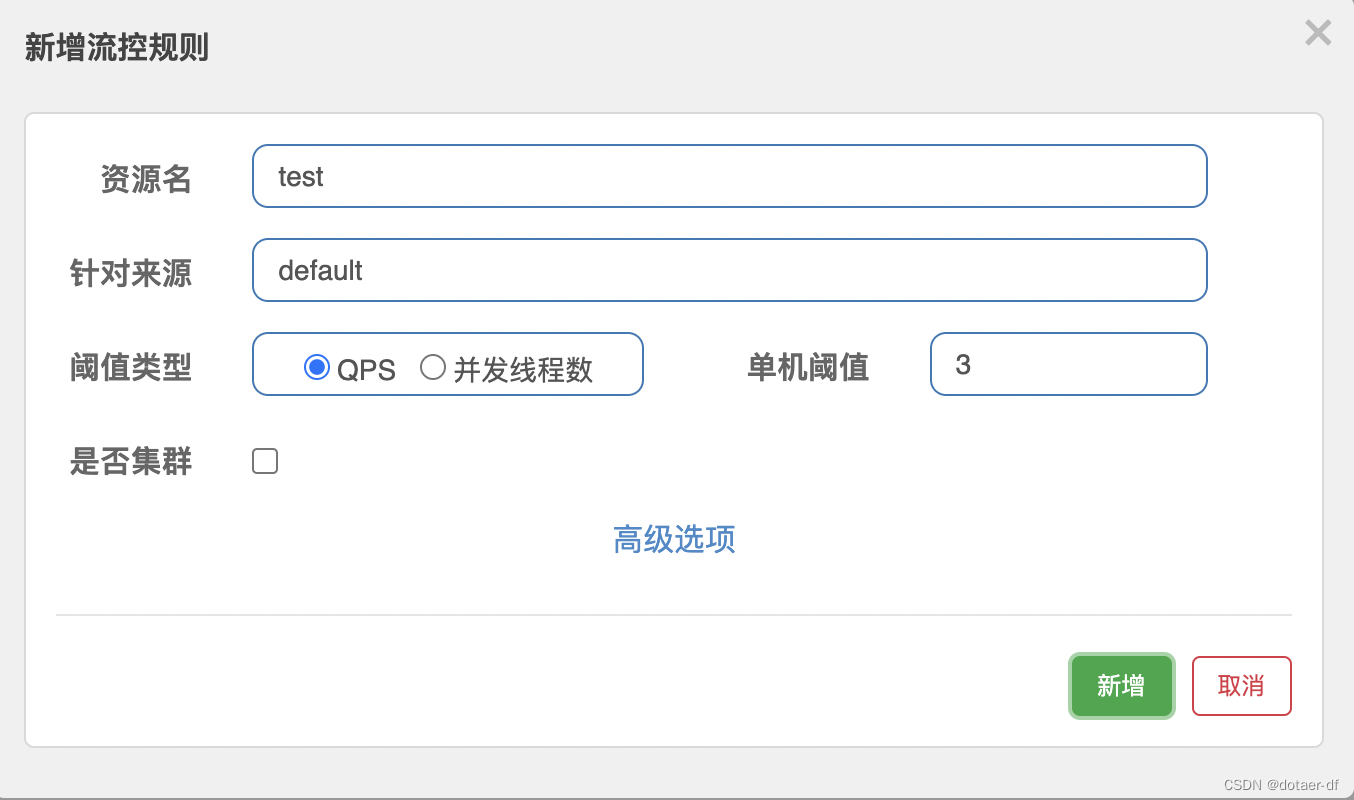
When we visit /foo Interface , When qps > 3 It will trigger FlowException, and FlowException Exception is inheritance BlockException, Then the console will see
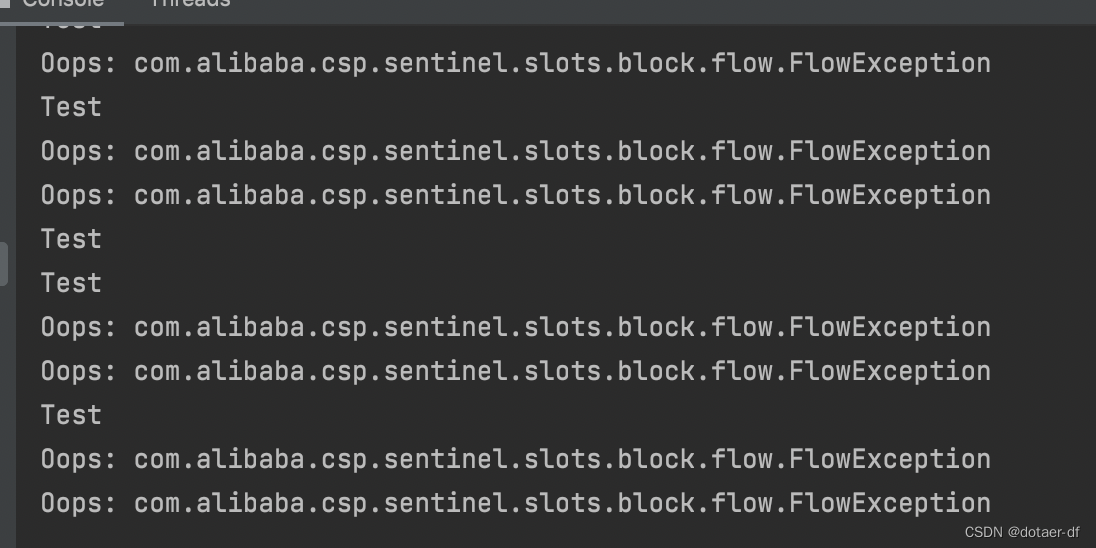
It can be found that the whole process above does not depend on the database , Where are the configured rule numbers stored ? The answer is : In the memory , The advantage of this approach is simplicity , Without relying on ; The disadvantage is that the application restart rule will disappear , For simple testing only , Cannot be used in production environment .
Sentinel There are three modes , among Pull Patterns and Push Patterns can ensure the persistence of rules , How to do it will be shown later
| Push mode | explain | advantage | shortcoming |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primitive mode | API Push the rules to the client and update them directly to memory , Extend write data source (WritableDataSource) | Simple , There is no dependence on | There is no guarantee of consistency ; Rules are stored in memory , Restart and disappear . Seriously not recommended for production environments |
| Pull Pattern | Extend write data source (WritableDataSource), The client takes the initiative to poll a rule management center regularly for pull rules , The center of the rule can be RDBMS、 file etc. | Simple , There is no dependence on ; Rule persistence | There is no guarantee of consistency ; Real time is not guaranteed , Pulling too often can also cause performance problems . |
| Push Pattern | Extended read data source (ReadableDataSource), The rule center pushes , The client listens for changes all the time by registering a listener , For example, use Nacos、Zookeeper Wait for the configuration center . This way has better real-time and consistency guarantee . It is generally used in production environment push Data sources for patterns . | Rule persistence ; Uniformity ; Fast | Introducing third party dependencies |
Reference link : Novice guide · alibaba/Sentinel Wiki · GitHub
边栏推荐
- 利用传统方法(N-gram,HMM等)、神经网络方法(CNN,LSTM等)和预训练方法(Bert等)的中文分词任务实现
- TensorRT的数据格式定义详解
- Sentinel 阿里开源流量防护组件
- IDEA公布全新默认UI,太清爽了(内含申请链接)
- js中正则表达式的使用
- Golang--map扩容机制(含源码)
- Redis---1. Data structure characteristics and operation
- The difference between session and cookies
- Invalid operation: Load into table ‘sources_ orderdata‘ failed. Check ‘stl_ load_ errors‘ system table
- DeprecationWarning: .ix is deprecated. Please use.loc for label based indexing or.iloc for positi
猜你喜欢
日期时间API详解
In depth understanding of JUC concurrency (II) concurrency theory

Sublime Text 配置php编译环境

Redis——大Key問題

阿里云MFA绑定Chrome浏览器
Hydration failed because the initial UI does not match what was rendered on the server. One of the reasons for the problem

【张三学C语言之】—深入理解数据存储

Linear DP (split)

Code skills - Controller Parameter annotation @requestparam

The intern left a big hole when he ran away and made two online problems, which made me miserable
随机推荐
Sublime Text 配置php编译环境
MySQL的10大经典错误
Cglib代理-代码增强测试
Redis - cluster data distribution algorithm & hash slot
Use of Arduino wire Library
DeprecationWarning: .ix is deprecated. Please use.loc for label based indexing or.iloc for positi
Redis——大Key问题
CUDA中的Warp Shuffle
Redis - grande question clé
CUDA中的函数执行空间说明符
TensorRT的命令行程序
BGP 路由优选规则和通告原则
Hydration failed because the initial UI does not match what was rendered on the server. One of the reasons for the problem
计算属性普通函数写法 和 set get 写法
New version of dedecms collection and release plug-in tutorial tool
介绍两款代码自动生成器,帮助提升工作效率
利用传统方法(N-gram,HMM等)、神经网络方法(CNN,LSTM等)和预训练方法(Bert等)的中文分词任务实现
Redis - big key problem
LeetCode 39. 组合总和
CUDA中的存储空间修饰符