当前位置:网站首页>UCI and data multiplexing are transmitted on Pusch (Part V) -- polar coding
UCI and data multiplexing are transmitted on Pusch (Part V) -- polar coding
2022-07-03 09:39:00 【Communication pawn】
polar Encoding is UCI Greater than 12bit The coding ,PUCCH and PUSCH transmission UCI All of them are polar code
1.cb Block segmentation and crc add to

cb Block segmentation
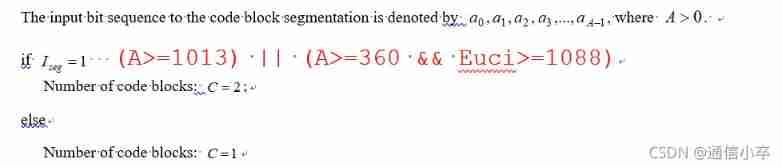


if (A>=1013) || (A>=360 && Euci>=1088) % Use Euci here
C = 2;
Aprime = ceil(A/C)*C;
paddedUCI = zeros(Aprime,1,typeIn);
if Aprime~=A
% prepend filler bit
paddedUCI(2:end) = uciBits;
else
% no filler bit
paddedUCI = uciBits;
end
uciCBs = reshape(paddedUCI,[],C);
Lcrc = '11';
else % no segmentation
C = 1;
uciCBs = uciBits;
if A<=19
Lcrc = '6';
else
Lcrc = '11';
end
end
if isempty(coder.target) % Simulation path
% Initialize CRC encoder system objects for each NR polynomial
if isempty(encoders)
encoders = cell(1,6);
polyCell = {
[1 1 0 0 0 0 1]', ... % '6'
[1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1]', ... % '11'
[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1]', .... % '16'
[1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1]', ... % '24A'
[1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1]', ... % '24B'
[1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1]'}; % '24C'
for i = 1:6
encoders{
i} = comm.CRCGenerator('Polynomial',polyCell{
i});
% This handlebar beg CRC It's encapsulated , The specific details will be added later .
end
end
encoder = encoders{
polyIndex};
for i = 1:numCodeBlocks
blkcrcL(:,i) = encoder(blkL(:,i));
end
How to find CRC This special note :
CRC24A =[1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1];
CRC24B =[1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1];
CRC24C =[1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1];
CRC16 =[1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1];
CRC11 = [1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1];
CRC6 = [1 1 0 0 0 0 1];
input = [1 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1];
type = 6;
switch type
case 240
CRC_G=CRC24A;
case 241
CRC_G=CRC24B;
case 242
CRC_G=CRC24C;
case 16
CRC_G=CRC16;
case 11
CRC_G=CRC16;
case 8
CRC_G=CRC8;
case 6
CRC_G=CRC6;
end %***end switch******
Input_Length = length(input);
Crc_Length = length(CRC_G);
Add_Crc_Bit = zeros(1,Crc_Length-1);
Uncode_Sequence = [input Add_Crc_Bit];
Crc_Register= Uncode_Sequence(1:Crc_Length);
% Crc_Register= fliplr(Uncode_Sequence(1:Crc_Length));
for k=1:1:Input_Length
if Crc_Register(1)==1
Crc_Register=bitxor(Crc_Register,CRC_G);
if (k~= Input_Length)
Crc_Register=[ Crc_Register(2:Crc_Length) Uncode_Sequence(k+Crc_Length)];
end
else
if (k~= Input_Length)
Crc_Register=[ Crc_Register(2:Crc_Length) Uncode_Sequence(k+Crc_Length) ];
end
end
end
2.UCI polar code
This is for each cb Block .
nMax = 10;
iIL = false;
% Check and set PC-Polar parameters
if (K>=18 && K<=25) % for PC-Polar, Section 6.3.1.3.1
nPC = 3;
if (E-K > 189)
nPCwm = 1;
else
nPCwm = 0;
end
else % for CA-Polar
nPC = 0;
nPCwm = 0;
end
1 . Calculation n, obtain N


% Get n, N, Section 5.3.1
cl2e = ceil(log2(E));
if (E <= (9/8) * 2^(cl2e-1)) && (K/E < 9/16)
n1 = cl2e-1;
else
n1 = cl2e;
end
rmin = 1/8;
n2 = ceil(log2(K/rmin));
nMin = 5;
n = max(min([n1 n2 nMax]),nMin);
N = 2^n;
end
2 . interweave :UCI There is no interweaving when .dl It's time to use it .

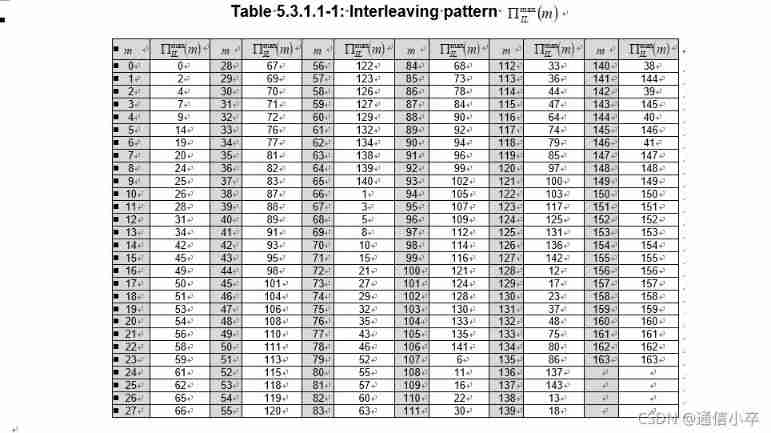
if iIL
pi = nr5g.internal.polar.interleaveMap(K);
inIntr = in(pi+1);
else
inIntr = in;
end
% Although again uci There is no interweaving , Let's introduce the interweaving process ,
Kilmax = 164;
pat = getPattern();
pi = zeros(K,1);
k = 0;
for m = 0:Kilmax-1
if pat(m+1) >= Kilmax-K
pi(k+1) = pat(m+1)-(Kilmax-K);
k = k+1;
end
end
end
3.polar code
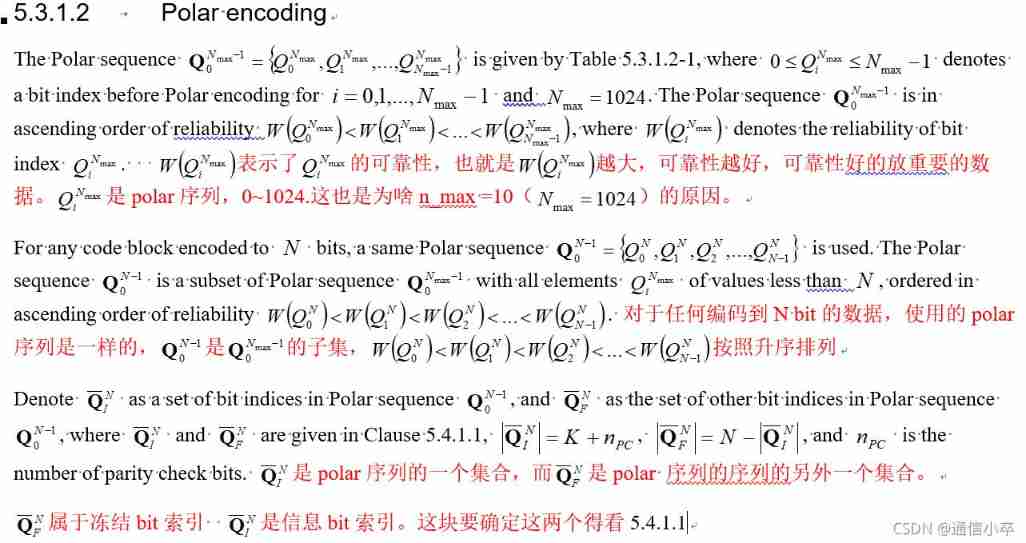
3.1 Here is only the order of interleaving , Not really intertwined , For this interwoven feature, we will further add , In order to determine Q_N_F and Q_N_I

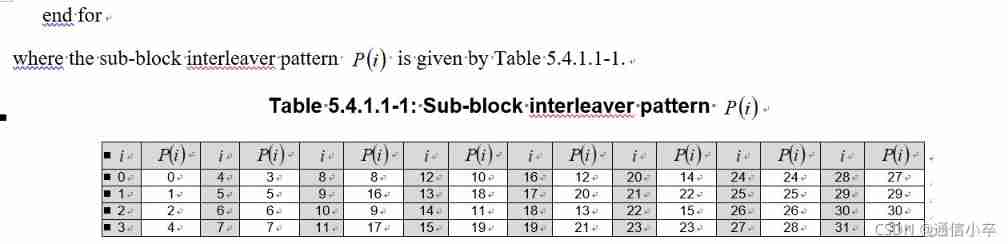


% Get sequence for N, ascending ordered, Section 5.3.1.2
s10 = nr5g.internal.polar.sequence; % for nMax=10
idx = (s10 < N);
qSeq = s10(idx); % 0-based Find out N, Corresponding
%polar Subset of sequence
% Get frozen, information bit indices sets, qF, qI Seek freezing bit And information bit Index set
jn = nr5g.internal.polar.subblockInterleaveMap(N); % 0-based
qFtmp = [];
if E < N
if K/E <= 7/16 % puncturing
for i = 0:(N-E-1)
qFtmp = [qFtmp; jn(i+1)]; %#ok
end
if E >= 3*N/4
uLim = ceil(3*N/4-E/2);
qFtmp = [qFtmp; (0:uLim-1).'];
else
uLim = ceil(9*N/16-E/4);
qFtmp = [qFtmp; (0:uLim-1).'];
end
qFtmp = unique(qFtmp);
else % shortening
for i = E:N-1
qFtmp = [qFtmp; jn(i+1)]; %#ok
end
end
end
3.2 Find out qPC The location of , It includes nPCwn And do not include two


% PC-Polar
qPC = zeros(nPC,1);
if nPC > 0
qPC(1:(nPC-nPCwm),1) = qI(end-(nPC-nPCwm)+1:end); % least reliable
% In itself qI It's about stability from high to low
if nPCwm>0 % assumes ==1, if >0. %nPCwm Again E-K>189 It will be 1
% Get G, nth Kronecker power of kernel
n = log2(N);
ak0 = [1 0; 1 1]; % Arikan's kernel
allG = cell(n,1); % Initialize cells
for i = 1:n
allG{
i} = zeros(2^i,2^i);
end
allG{
1} = ak0; % Assign cells
for i = 1:n-1 % This is a relatively simple way , You can directly calculate , The calculation workload will be large , A special section will be devoted to the following .
allG{
i+1} = kron(allG{
i},ak0);
end
G = allG{
n};
wg = sum(G,2); % row weight
qtildeI = qI(1:end-nPC,1); %
wt_qtildeI = wg(qtildeI+1);
minwt = min(wt_qtildeI); % minimum weight Get the minimum weight
allminwtIdx = find(wt_qtildeI==minwt); % Find the position corresponding to the minimum weight , There may be more than one
% most reliable, minimum row weight is first value
qPC(nPC,1) = qtildeI(allminwtIdx(1));% The first of multiple weights is the most stable position .
end
end
end
3.3 Find out u At this time, there is no sub block interleaving .



% Generate u
u = zeros(N,1); % doubles only
if nPC > 0
% Parity-Check Polar (PC-Polar)
y0 = 0; y1 = 0; y2 = 0; y3 = 0; y4 = 0;
k = 1;
for idx = 1:N
yt = y0; y0 = y1; y1 = y2; y2 = y3; y3 = y4; y4 = yt;
if F(idx) % frozen bits If it is frozen bytes , Just set zero
u(idx) = 0;
else % info bits If it's information bit
if any(idx==(qPC+1)) If it is qPC, Assignment verification bit
u(idx) = y0;
else
u(idx) = inIntr(k); % Set information bits (interleaved)
k = k+1;
y0 = double(xor(y0,u(idx))); % Find the check bit y0
end
end
end
else
% CRC-Aided Polar (CA-Polar)
u(F==0) = inIntr; % Set information bits (interleaved)
end
% Get G, nth Kronecker power of kernel Find out n Kronecker product
n = log2(N);
ak0 = [1 0; 1 1]; % Arikan's kernel
allG = cell(n,1); % Initialize cells
for i = 1:n
allG{
i} = zeros(2^i,2^i);
end
allG{
1} = ak0; % Assign cells
for i = 1:n-1
allG{
i+1} = kron(allG{
i},ak0);
end
G = allG{
n};
% Encode using matrix multiplication
outd = mod(u'*G,2)';
out = cast(outd,class(in));
3.4 Rate matched sub block interleaving
according to 3.1 The obtained interleaving order is reordered . Interlace according to the fixed table 
out = in(jn+1);
3.5 Rate matching bit choice


% Bit selection, Section 5.4.1.2
N = length(in);
outE = zeros(E,1,class(in));
if E >= N
% Bit repetition
for k = 0:E-1
outE(k+1) = y(mod(k,N)+1);
end
else
if K/E <= 7/16
% puncturing (take from the end)
outE = y(end-E+1:end);
else
% shortening (take from the start)
outE = y(1:E);
end
end
3.6 code bit The interweaving of — Triangle interweaving
The realization is to store it on the lower triangular matrix according to rows , Then extract in sequence according to the column , Realize the interweaving .

Go to this place cb The whole of the block polar The coding has been completed .
3.cb Block links
This is very simple , Will be cb Pieces are spliced to g Just a matter of .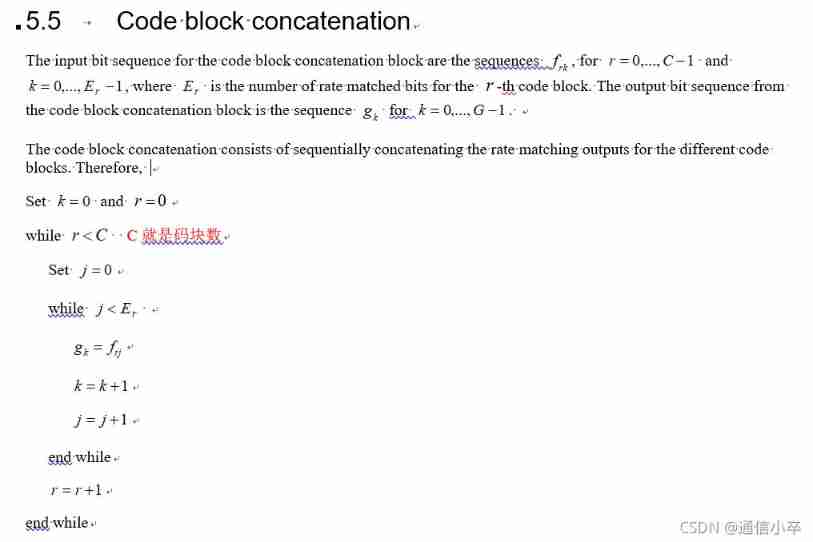
边栏推荐
- 解决Editor.md上传图片获取不到图片地址问题
- Flink学习笔记(九)状态编程
- Nodemcu-esp8266 development (vscode+platformio+arduino framework): Part 4 --blinker_ DHT_ WiFi (lighting technology app control + temperature and humidity data app display)
- Integrated use of interlij idea and sonarqube
- Installation and uninstallation of pyenv
- Jestson Nano自定义根文件系统创建(支持NVIDIA图形库的最小根文件系统)
- Error output redirection
- The rise and fall of mobile phones in my perspective these 10 years
- Leetcode daily question (1362. closest divisors)
- Shell logic case
猜你喜欢

LeetCode每日一题(2212. Maximum Points in an Archery Competition)

Development of fire power monitoring system
Intelligent home design and development

CATIA automation object architecture - detailed explanation of application objects (I) document/settingcontrollers
Modify idea code

NR technology -- MIMO
Flink learning notes (IX) status programming
PolyWorks script development learning notes (III) -treeview advanced operation
PolyWorks script development learning notes (4) - data import and alignment using file import

How MySQL modifies null to not null
随机推荐
Long类型的相等判断
Leetcode daily question (1362. closest divisors)
Development of electrical fire system
专利查询网站
The server denied password root remote connection access
Solve editor MD uploads pictures and cannot get the picture address
Leetcode daily question (2212. maximum points in an archery competition)
Flink学习笔记(八)多流转换
What do software test engineers do? Pass the technology to test whether there are loopholes in the software program
Flink learning notes (IX) status programming
Directory and switching operation in file system
Flask+supervisor installation realizes background process resident
[CSDN]C1训练题解析_第三部分_JS基础
Spark 集群安装与部署
PIP configuring domestic sources
LeetCode每日一题(931. Minimum Falling Path Sum)
There is no open in default browser option in the right click of the vscade editor
Development of fire evacuation system
CATIA automation object architecture - detailed explanation of application objects (I) document/settingcontrollers
PolyWorks script development learning notes (II) -treeview basic operations