当前位置:网站首页>Interprocess communication in the "Chris Richardson microservice series" microservice architecture
Interprocess communication in the "Chris Richardson microservice series" microservice architecture
2022-07-05 21:57:00 【yanhom. lin】
Editor's words | This article is from Nginx The official blog , It's the third in a series of articles on microservices , In the first article, we introduced the microservice architecture pattern , Compared with monomer model , The advantages and disadvantages of using microservice architecture are discussed . The second part describes how to use the micro service architecture between application clients API Gateway mode for communication . In this article , We'll discuss how system services communicate with each other .
The authors introduce :Chris Richardson, Is a world famous software master , Classic technical works 《POJOS IN ACTION》 The author of a Book , It's also cloudfoundry.com The original founder ,Chris Richardson And Martin Fowler、Sam Newman、Adrian Cockcroft He is also known as the top ten software architects in the world .
Chris Richardson Micro service series 7 piece :
1. The advantages and disadvantages of microservice architecture
2. Use API Gateway building microservices
3. Interprocess communication in microservice Architecture
4. Feasible solutions and practical cases of service discovery
5. Event driven data management for microservices
6. Choose microservice deployment strategy
7. Transform monomer applications into microservices
brief introduction
In monomer applications , The calls between modules are implemented by methods or functions at the programming language level . And distributed applications based on microservices run on multiple machines ; Generally speaking , Each service instance is a process .
therefore , As shown in the figure below , The interaction between services must be through inter process communication (IPC) To achieve .
We'll talk about it in detail later IPC technology , Now let's take a look at the design related issues .
Delivery model
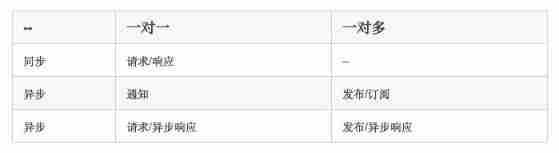
When choosing for a service IPC when , First of all, we need to consider the interaction between services . There are many interaction modes between client and server , We can classify it from two dimensions . The first dimension is one-to-one or one to many :
• one-on-one : Each client request has a service instance to respond to .
• One to many : There are multiple service instances per client request to respond .
The second dimension is whether these interactions are synchronous or asynchronous :
• Synchronous mode : Client requests require immediate response from the server , It may even be blocked by waiting .
• Asynchronous mode : Client requests do not block the process , The response of the server can be non instantaneous .
The following table shows the different interaction modes :
There are several ways of one-to-one interaction :
request / Respond to : A client sends a request to the server , Waiting response , The client expects this response to arrive immediately . In a thread based application , Waiting process may cause thread blocking .
notice ( That is to say, one-way request ): A client request is sent to the server , But the server is not expected to respond .
request / Asynchronous response : The client sends the request to the server , Server asynchronous response request . The client will not block , And it's designed so that the default response doesn't arrive immediately .
There are several ways of one to many interaction :
Release / A subscription model : The client issues a notification message , Consumed by zero or more interested Services .
Release / Asynchronous response mode : The client publishes the request message , Then wait for the response from the service of interest .
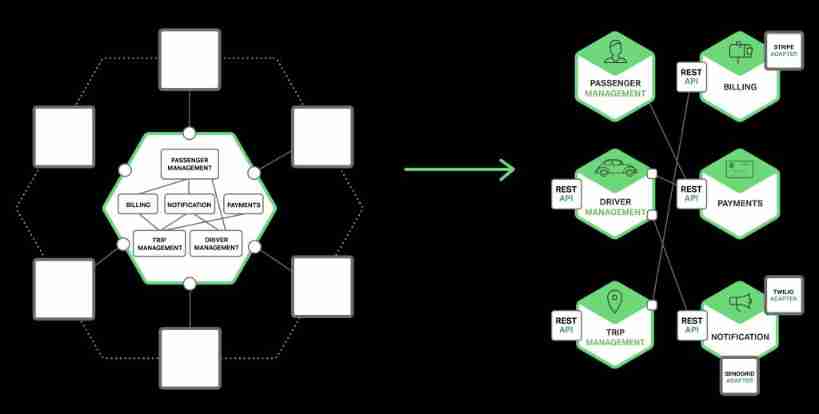
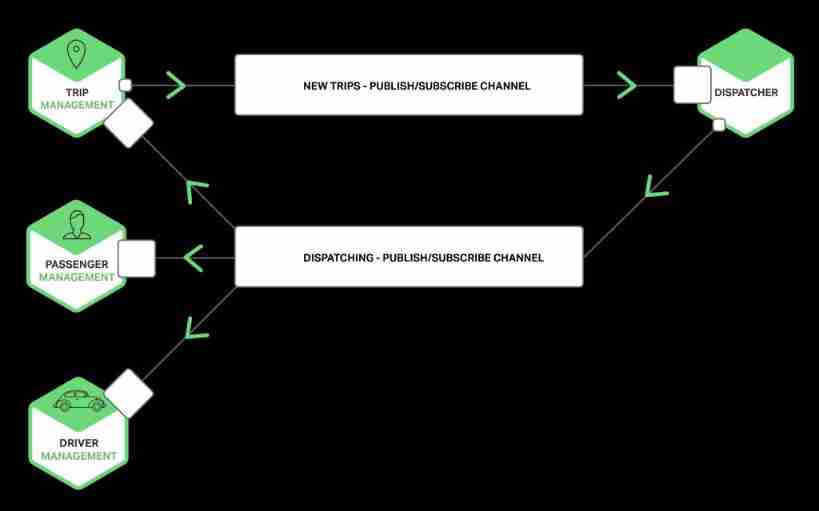
Each service is a combination of these patterns . For some services , One IPC The mechanism is enough ; For other services, there are many kinds of IPC Mechanism combination . The figure below shows when the user calls , How the services in the taxi app interact .
The service communication in the figure above uses notifications 、 request / Respond to 、 Release / Subscription, etc . for example , Passengers are moving towards “ Itinerary management ” Services send notifications , Request a pick-up service .“ Itinerary management ” Service by using request / Respond to wake up “ Passenger service ” To verify that the passenger account is valid , Then create the trip , And use the release / Subscribe to notify other services , This includes scheduling services to locate available drivers .
Now we understand the interaction pattern , Let's see how to define API.
Definition API
API Is the contract between the server and the client . Whatever you choose IPC Mechanism , The point is to use some kind of interactive definition language (IDL) To accurately define the API. For how to use API Define services in a priority way , There have been some good discussions . Before you develop a service , Define the service interface and discuss it with the client developer , You just need to iterate API Definition . Such a design can greatly improve the availability of services .
You will see in the second half of this article ,API The definition essentially depends on the chosen IPC Mechanism . If you use the message mechanism ,API By the message channel (channel) And message types ; If you choose to use HTTP Mechanism ,API By URL And request 、 The response format consists of . It will be described in detail later IDL.
Evolving API
Service API Will change over time . In monomer applications , It's often modified directly API And update all callers . But in microservice based applications , Even if all API Of users are in the same application , It's also very difficult , It's usually not possible to force all clients to keep up-to-date with the service . Besides , You may incrementally deploy a new version of the service , The old version will run at the same time as the new version . It's important to understand the strategies for dealing with these problems .
Yes API The way changes are handled is related to the size of the changes . Some changes are very small , And compatible with previous versions ; For example, adding properties to a request or response . When designing clients and services , It is necessary to follow the principle of robustness . After service update , Use the old version API The client should continue to use . The service provides default values for the missing request properties , The client ignores any additional responses . Use IPC Mechanisms and message formats make it easy for you to improve API.
But sometimes ,API Large scale changes are needed , And not compatible with older versions . Since it is not possible to force all clients to upgrade immediately , Support for older versions API The service will be running for a while . If you use something like REST This is based on HTTP The mechanism IPC, One way is to embed the version number into URL in , Each service instance can handle multiple versions at the same time . Another way is to deploy different instances , Each instance handles a version of the request .
Processing partial failure
In the last article about API Gateway article , We learned that , Distributed system has the problem of local failure . Because the client and the server are independent processes , The server may not be able to respond to the client's request in time . The server may be temporarily unavailable due to failure or maintenance . The server may also be overloaded , Resulting in extremely slow response to requests .
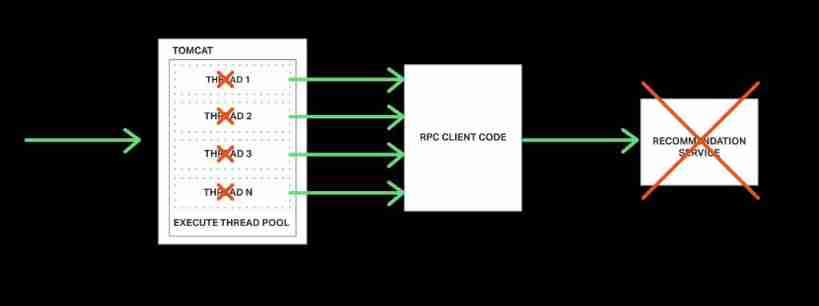
For example, the product page mentioned in the above article , Suppose the recommendation service doesn't respond , The client may block due to waiting for a response indefinitely . This not only leads to a poor user experience , And in many applications, it will occupy the previous resources , Like threads ; Final , As shown in the figure below , Run time running out of thread resources , Unable to respond .
In order to prevent this kind of problem , Some failures must be considered when designing services .
Netfilix Provides a better solution , Specific countermeasures include :
- Network timeout : While waiting for a response , Do not set infinite blocking , It's a timeout strategy . Using a timeout policy ensures that resources are not consumed indefinitely .
- Limit the number of requests : You can set an access limit for client requests for a specific service . If the request has reached the limit , It's about to terminate the request service immediately .
- Breaker mode (Circuit Breaker Pattern): Record the number of successful and failed requests . If the failure rate exceeds a threshold , Triggering the circuit breaker causes subsequent requests to fail immediately . If a large number of requests fail , Maybe this service is not available , It doesn't make sense to ask again . After a failure period , The client can try again , If it works , Close the circuit breaker .
- Provide rollback : When a request fails, it can be rolled back . for example , Returns cached data or a system default value .
Netflix Hystrix It's an open source library to implement related patterns . If you use JVM, Recommended Hystrix. And if not JVM Environmental Science , You can use libraries with similar functions .
IPC technology
Now there are many different IPC technology . Communication between services can use synchronous requests / Response patterns , For example, based on HTTP Of REST perhaps Thrift. in addition , You can also choose asynchronous 、 Message based communication mode , such as AMQP perhaps STOMP. Besides , You can also choose JSON perhaps XML This kind of readable 、 Text based message format . Of course , There are also more efficient binary formats , such as Avro and Protocol Buffer. We're talking about synchronous IPC Before the mechanism , Let's start with asynchronous IPC Mechanism .
Message based asynchronous communication
When using message mode , Processes communicate with each other by exchanging messages asynchronously . The client submits a request by sending a message to the server , If the server needs to reply , Another independent message will be sent to the client . Because of asynchronous communication , The client will not be blocked by waiting , On the contrary, the response will not be received immediately .
The message is composed of data headers ( Metadata like the sender ) And the body of the message . Messages are sent through channels , Any number of producers can send messages to channels , Again , Any number of consumers can receive data from the channel . There are two types of channels , Including point-to-point channels and releases / Subscription channels . Point to point channel will send the message to the user who reads the message from the channel , The server uses point-to-point to implement the one-to-one interaction mode mentioned earlier ; And release / Subscriptions send messages to all users who read data from the channel , The server uses publishing / Subscription channels to implement the one to many interaction mode mentioned above .
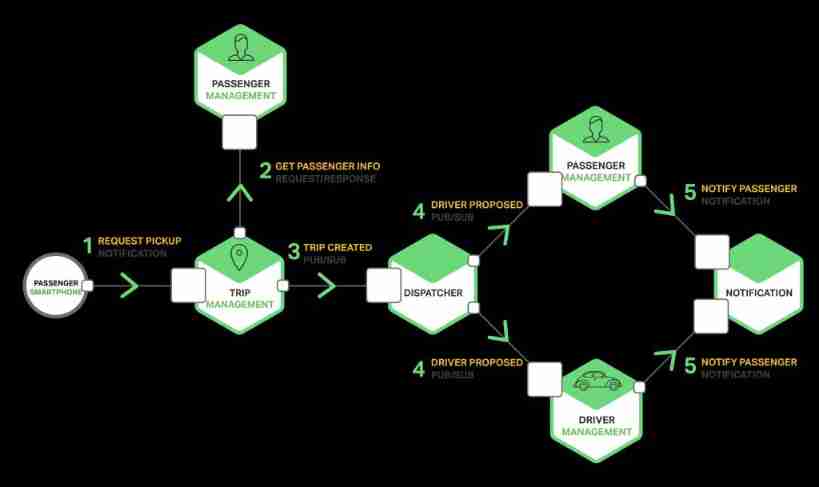
The figure below shows how to use the taxi software to publish / subscribe :
By releasing / The subscription channel writes a message to create a trip , The travel management service will notify the scheduling service of new travel requests . The dispatch service will release the available drivers to / The subscription channel writes a message of recommended driver , And inform other services .
There are a variety of messaging systems to choose from , It's best to choose one that supports multiple programming languages . Some messaging systems support AMQP and STOMP Such a standard agreement , Some support patent agreements . There are also a large number of open source message systems available , for example RabbitMQ、Apache Kafka、Apache ActiveMQ and NSQ. On the macro , They all support some message and channel formats , And try to improve reliability 、 High performance and scalability . However , In detail , Their message models are quite different .
There are many advantages to using message mechanism :
- Decouple client and server : The client just needs to send the message to the right channel . The client does not need to know the specific service instance at all , There is no need for a discovery mechanism to determine the location of service instances .
- Message buffering : stay HTTP Such a synchronization request / In the response protocol , All clients and servers must be available during the interaction . And in message mode , The message broker manages all messages written to the channel in a queued way , Until it's handled by consumers . in other words , Online stores can accept customer orders , Even if the ordering system is slow or unavailable , Just keep the order message in the queue .
- client - Flexible interaction on the server side : The message mechanism supports all of the above interaction patterns .
- Clear interprocess communication : be based on RPC The communication mechanism tries to wake up the remote server just like calling the local service , However , Limited by the laws of physics and possible local failures , The two are very different . The messaging mechanism makes these differences intuitive , Developers don't have the illusion of security .
However , The messaging mechanism also has its own disadvantages :
- Additional operational complexity : The message system needs to be installed separately 、 Configure and deploy . news broker( agent ) Must be highly available , Otherwise, the system reliability will be affected .
- Implementation is based on request / The complexity of the response interaction pattern : request / Responding to interaction patterns requires extra work . Each request message must contain a reply channel ID And the related ID. The server sends an include correlation ID The response message to the channel , Use related ID To map the response to the requesting client . In this case , Use a direct support request / Responsive IPC The mechanism will be easier .
Now we've learned about message based IPC, Next let's look at request based / Response mode IPC.
Based on the request / Synchronization of responses IPC
Use synchronous 、 Based on the request / Responsive IPC When it comes to mechanisms , The client sends the request to the server , The server processes the request and returns the response . Some clients will be blocked due to waiting for the server to respond , Other clients may use asynchronous 、 Based on the event driven client code , This code may be passed through Future perhaps Rx Observable encapsulation . However , Different from using message mechanism , The client needs to respond in time . There are many optional protocols in this pattern , But the two most common protocols are REST and Thrift. First of all, let's understand REST.
REST
It's very popular to develop RESTful Style API.REST be based on HTTP agreement , The core concept is that resources typically represent a single business object or a group of business objects , Business objects include “ consumer ” or “ product ”.REST Use HTTP Protocol to control resources , adopt URL Realization . for example ,GET The request will return the containing information of a resource , May be XML Document or JSON Object format .POST The request creates a new resource , and PUT The request updates the resource .REST The father of Roy Fielding Once said :
REST A series of architecture system parameters are provided , Use as a whole , Emphasize the extensibility of component interaction 、 Interface versatility 、 Independent deployment of components 、 And middleware to reduce interaction delay , It enhances security , It can also encapsulate legacy systems .
— Fielding, Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures
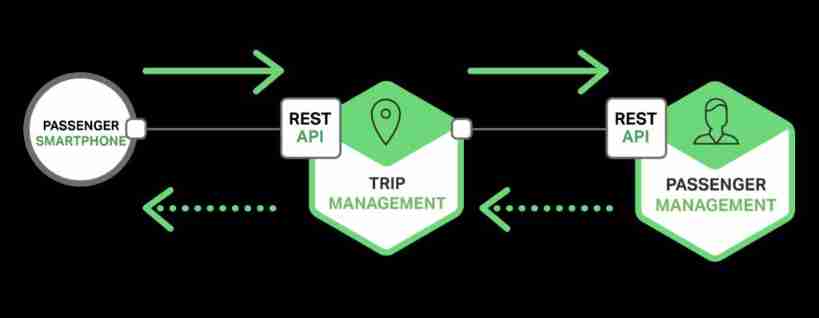
The figure below shows how to use the taxi Software REST.
Passengers through mobile end-to-end travel management services /trips The resource submitted a POST request . After the travel management service receives the request , Will send a GET Request to passenger management service for passenger information . After confirming the passenger information , Create a trip , And return to the mobile end 201 Respond to .
Many developers say they are based on HTTP Of API yes RESTful style . however , Like Fielding In his blog , Not all of this API All are RESTful.Leonard Richardson( notes : With the author of this article Chris It doesn't matter ) by REST Define a maturity model , It includes the following four levels :
- Level 0: At this level Web The service just uses HTTP As a means of transmission , It's actually just a remote method call (RPC) A concrete form of .SOAP and XML-RPC All belong to this kind of .
- Level 1:Level 1 Hierarchical API Introduced the concept of resources . To perform operations on resources , The client issues... That specifies the operation to be performed and any parameters
POSTrequest . - Level 2:Level 2 Hierarchical API Use HTTP Syntax to perform operations , for example
GETSaid to get 、POSTRepresentation creation 、PUTUpdate . If necessary, , Request parameters and parameters of the principal specified operation . This can make service impact web Infrastructure services , CachingGETrequest . - Level 3:Level 3 Hierarchical API be based on HATEOAS(Hypertext As The Engine Of Application State) Principle design , The basic idea is that
GETThe resource information returned by the request contains links , These links can perform the operations allowed by the resource . for example , The client cancels an order through a link contained in the order resource ,GETThe request is sent to get the order .HATEOAS The advantages include no need to write hard links in the client code URL. Besides , Because the resource information contains links that allow operations , The client doesn't have to guess what to do in the current state of the resource .
Using a HTTP Our agreement has the following advantages :
- HTTP It's very simple and everyone is familiar with .
- You can use browser extensions ( such as Postman) perhaps curl The command line to test API.
- Built in support request / Communication in response mode .
- HTTP Firewall friendly .
- No intermediate agent is needed , Simplified system architecture .
Shortcomings include :
- Only requests... Are supported / Response mode interaction . Although you can use HTTP notice , But the server must always send HTTP Respond to .
- Because the client and the server communicate directly ( There is no proxy or buffer mechanism ), Must be online during the interaction .
- The client must know the... Of each service instance URL. As in the previous article “API gateway ” Described , It's also an annoying question . The client must use the service instance discovery mechanism .
The developer community has recently come to realize RESTful API Interface defines the value of language , So it was born including RAML and Swagger Service framework inside .Swagger In this way IDL Allows you to define the format of request and response messages , and RAML Allow to use JSON Schema This independent norm . For description API,IDL There are usually tools to generate client stubs and server frameworks from interface definitions .
Thrift
Apache Thrift It's a very interesting REST substitute , The realization of multilingualism RPC Client and server call .Thrift Provides a C Style IDL Definition API. adopt Thrift The compiler can generate client stubs and server frameworks . The compiler can generate code in multiple languages , Include C++、Java、Python、PHP、Ruby, Erlang and Node.js.
Thrift An interface consists of one or more services , Service definition and Java Similar interface , Is a set of strongly typed methods .Thrift Able to return to ( May not be valid ) value , It can also be defined as one-way . The return value method can implement the interactive request / Response patterns . Client waiting for response , Exception may be thrown . A one-way method corresponds to an interactive notification pattern . The server will not send a response .
Thrift Support JSON、 Binary and compressed binary message formats . Because decoding is faster , Binary ratio JSON More efficient ; As the name suggests , Compression binary format can provide a higher level of compression efficiency ; meanwhile JSON Easy to read .Thrift It also allows you to choose the transmission protocol , Including the original TCP and HTTP. original TCP Than HTTP More efficient , However HTTP For firewalls 、 Browsers are more user-friendly .
The message format
understand HTTP and Thrift after , We have to think about the message format . If you use a messaging system or REST, You need to choose the message format . image Thrift In this way IPC The mechanism may only support a few message formats , Maybe only one format is supported . In either case , It's important to use a cross language message format . Even if you now use a single language to implement microservices , But it's likely that other languages will be needed in the future .
At present, there are two main message formats: text and binary . The text format includes JSON and XML. The advantage of this format is that it's not only readable , And it's self describing . stay JSON in , The property of the object is the name - Set of value pairs . A similar , stay XML in , Attributes are represented as named elements and values . Consumers can choose the value they are interested in and ignore other parts . Accordingly , Small changes to the message format can also be easily backward compatible .
XML The document structure of is composed of XML schema Definition . Over time , The developer community is aware of JSON A similar mechanism is needed . One way is to use JSON Schema, Or use it alone , Or as Swagger This kind of IDL Part of .
One of the disadvantages of text message format is that the message becomes verbose , especially XML. Because the message is self describing , So every message contains properties and values . Another disadvantage is that parsing the text is too much . therefore , You may need to consider using binary formats .
There are also many binary formats . If you are using Thrift RPC, You can use binary Thrift. If you choose the message format , Common ones include Protocol Buffers and Apache Avro, Both provide types IDL To define the message structure . The difference is Protocol Buffers Use the tagged fields (tagged fields), and Avro Consumers need to understand patterns to parse messages .
Martin Kleppmann Of Blog posts Yes Thrift、Protocol Buffers and Avor A detailed comparison is made .
summary
Microservices must use interprocess communication mechanisms to interact . When designing the communication mode of a service , You need to think about a few things : How services interact , How each service identifies API, How to upgrade API, And how to deal with local failures . Microservice architecture asynchronous message mechanism and synchronous request / There are two types of response mechanisms IPC Mechanism available . In the next article , We will discuss the service discovery problem in the microservice architecture .
Next topic : Feasible solutions and practical cases of service discovery , Coming soon !
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

2.2.3 output of documents

Yolov5 training custom data set (pycharm ultra detailed version)
Cold violence -- another perspective of objective function setting
Reptile practice

An exception occurred in Huawei game multimedia calling the room switching method internal system error Reason:90000017
Huawei cloud modelarts text classification - takeout comments

Some common processing problems of structural equation model Amos software
AD637 usage notes
1.2 download and installation of the help software rstudio

深信服X计划-网络协议基础 DNS
随机推荐
Uni app Bluetooth communication
K210学习笔记(四) K210同时运行多个模型
KingbaseES V8R3集群维护案例之---在线添加备库管理节点
华为游戏多媒体调用切换房间方法出现异常Internal system error. Reason:90000017
PIP install beatifulsoup4 installation failed
Daily question brushing record (XIV)
Objects in the list, sorted by a field
Drawing HSV color wheel with MATLAB
Dbeaver executes multiple insert into error processing at the same time
Environment configuration problem record
Parker驱动器维修COMPAX控制器维修CPX0200H
POJ 3237 tree (tree chain splitting)
ESP32
Huawei game multimedia service calls the method of shielding the voice of the specified player, and the error code 3010 is returned
Li Kou ----- the maximum profit of operating Ferris wheel
Exercise 1 simple training of R language drawing
华为游戏多媒体服务调用屏蔽指定玩家语音方法,返回错误码3010
K210 learning notes (IV) k210 runs multiple models at the same time
初级软件测试必问面试题
华为云ModelArts文本分类–外卖评论