当前位置:网站首页>[combinatorics] permutation and combination (summary of permutation and combination content | selection problem | set permutation | set combination)
[combinatorics] permutation and combination (summary of permutation and combination content | selection problem | set permutation | set combination)
2022-07-03 12:06:00 【Programmer community】
List of articles
- One 、 Arrange and combine content summary
- Two 、 Select the question
- 3、 ... and 、 Set arrangement
- Four 、 Ring arrangement
- 5、 ... and 、 Set combination
Reference blog :
- 【 Combinatorial mathematics 】 Basic counting principle ( The principle of addition | Multiplication principle )
- 【 Combinatorial mathematics 】 Examples of permutation and combination of sets ( array | Combine | Circular arrangement | binomial theorem )
One 、 Arrange and combine content summary
Arrange and combine content summary :
- Select the question
- The arrangement and combination of sets
- Application of basic counting formula
- The arrangement and combination of multiple sets
Two 、 Select the question
n
n
n Meta set
S
S
S , from
S
S
S Select... From the set
r
r
r Elements ;
according to Whether the element can be repeated , Whether the selection process is orderly , The selection question is divided into four sub types :
| Elements do not repeat | Elements can be repeated | |
|---|---|---|
| Orderly selection | Set arrangement P ( n , r ) P(n,r) P(n,r) | Multiset arrangement |
| Unordered selection | Set combination C ( n , r ) C(n,r) C(n,r) | Combination of multiple sets |
Select the question :
- Non repeatable elements , Orderly selection , Corresponding Arrangement of sets
- Non repeatable elements , Unordered selection , Corresponding A combination of sets
- Repeatable elements , Orderly selection , Corresponding Arrangement of multiple sets
- Repeatable elements , Unordered selection , Corresponding Combination of multiple sets
3、 ... and 、 Set arrangement
n
n
n Meta set
S
S
S , from
S
S
S Collection Orderly , No repetition selection
r
r
r Elements ,
This operation is called
S
S
S One of the sets
r
−
r-
r− array ,
S
S
S A collection of
r
−
r-
r− The arrangement is recorded as
P
(
n
,
r
)
P(n, r)
P(n,r)
P
(
n
,
r
)
=
{
n
!
(
n
−
r
)
!
n
≥
r
0
n
<
r
P(n,r)=\begin{cases} \dfrac{n!}{(n-r)!} & n \geq r \\\\ 0 & n < r \end{cases}
P(n,r)=⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧(n−r)!n!0n≥rn<r
The permutation formula uses the multiplication rule to get : Think of the whole arrangement as
r
r
r A place
- The first
1
1
1 There are two positions
n
n
n
n
n Choose one of the elements , be left over
n
−
1
n-1
n−1 Elements ;
n There are two ways to place , That is, from the current
- The first
2
2
2 There are two positions
n
−
1
n-1
n
−
1
n-1
n−1 Choose one of the elements , be left over
n
−
2
n-2
n−2 Elements ;
n−1 There are two ways to place , That is, from the current
- The first
3
3
3 There are two positions
n
−
2
n-2
n
−
2
n-2
n−2 Choose one of the elements , be left over
n
−
3
n-3
n−3 Elements ;
n−2 There are two ways to place , That is, from the current
⋮
\vdots
⋮
- The first
r
r
r There are two positions
n
−
(
r
−
1
)
=
n
−
r
+
1
n-(r-1) = n - r + 1
n
−
r
+
1
n - r + 1
n−r+1 Choose one of the elements , be left over
n
−
r
n-r
n−r Elements ;
n−(r−1)=n−r+1 There are two ways to place , That is, from the current
0
!
=
1
0! = 1
0!=1
Four 、 Ring arrangement
n
n
n Meta set
S
S
S , from
S
S
S Collection Orderly , No repetition selection
r
r
r Elements ,
S
S
S A collection of
r
−
r-
r− Ring arrangement number
=
P
(
n
,
r
)
r
=
n
!
r
(
n
−
r
)
!
= \dfrac{P(n,r)}{r} = \dfrac{n!}{r (n-r)!}
=rP(n,r)=r(n−r)!n!
r
r
r Different linear permutations , Equivalent to the same ring arrangement ;
A ring arrangement , Cut from any position , Can constitute a
r
r
r Different linear arrangements ;
5、 ... and 、 Set combination
n
n
n Meta set
S
S
S , from
S
S
S Collection disorder , No repetition selection
r
r
r Elements ,
This operation is called
S
S
S One of the sets
r
−
r-
r− Combine ,
S
S
S A collection of
r
−
r-
r− The combination is written as
C
(
n
,
r
)
C(n, r)
C(n,r)
C
(
n
,
r
)
=
{
P
(
n
,
r
)
r
!
=
n
!
r
!
(
n
−
r
)
!
n
≥
r
0
n
<
r
C(n,r)=\begin{cases} \dfrac{P(n,r)}{r!} = \dfrac{n!}{r!(n-r)!} & n \geq r \\\\ 0 & n < r \end{cases}
C(n,r)=⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧r!P(n,r)=r!(n−r)!n!0n≥rn<r
r
−
r-
r− Arrangement can also be understood in this way ( Combine first and then arrange ) : elect
r
r
r An orderly arrangement
C
(
n
,
r
)
C(n,r)
C(n,r) , It can be
r
r
r Make a disordered choice , Then arrange all the selected elements
C
(
n
,
r
)
r
!
=
P
(
n
,
r
)
C(n,r) r! = P(n,r)
C(n,r)r!=P(n,r) ;
Combinatorial identity :
C
(
n
,
r
)
=
C
(
n
,
n
−
r
)
C(n,r) = C(n, n-r)
C(n,r)=C(n,n−r)
边栏推荐
- vulnhub之presidential
- MCDF Experiment 1
- Raven2 of vulnhub
- Unity3d learning notes 5 - create sub mesh
- Visual Studio 2022下载及配置OpenCV4.5.5
- Cacti monitors redis implementation process
- Solution to the second weekly test of ACM intensive training of Hunan Institute of technology in 2022
- Test classification in openstack
- Vulnhub narak
- Talk about the state management mechanism in Flink framework
猜你喜欢
(database authorization - redis) summary of unauthorized access vulnerabilities in redis
vulnhub之Ripper
Kubernetes three dozen probes and probe mode
Visual studio 2022 downloading and configuring opencv4.5.5
Vulnhub geminiinc
Vulnhub's presidential

Momentum of vulnhub
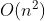
2022年湖南工学院ACM集训第二次周测题解

Groovy test class and JUnit test
Unity3D学习笔记5——创建子Mesh
随机推荐
OpenGL 绘制彩色的三角形
vulnhub之narak
CGroup introduction
vulnhub之momentum
Groovy测试类 和 Junit测试
vulnhub之Ripper
vulnhub之Nagini
Dart: about grpc (I)
OpenGL shader use
STL tutorial 8-map
(database authorization - redis) summary of unauthorized access vulnerabilities in redis
牛牛的组队竞赛
Ripper of vulnhub
PHP导出word方法(一mht)
MySQL uses the method of updating linked tables with update
Go language to realize static server
Qt+vtk+occt reading iges/step model
Why can't my MySQL container start
Apprendre à concevoir des entités logicielles réutilisables à partir de la classe, de l'API et du cadre
4000字超详解指针