当前位置:网站首页>Collection + interview questions
Collection + interview questions
2022-07-06 04:50:00 【d_ xia】
Set detailed explanation Collection + Interview questions
Let's first look at the inheritance graph of a set , As shown in the figure below :
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-JGioHRiC-1657027750280)(https://images.gitbook.cn/ae489970-ca62-11e9-bd50-998f3938aecb)]
among :
- The outer frame is the dotted line interface , The border is a solid line representation class ;
- The arrow implements the interface for the dotted line , Arrows inherit classes for the representation of solid lines .
For ease of understanding , I've hidden some information that has nothing to do with the content of this article , The hidden content will be described in detail in later chapters .
As you can see from the diagram , The root node of the collection is Collection, and Collection Next there are two common collections , Namely :
- List: Use the most ordered set , Provide convenient addition 、 modify 、 Deleted actions ;
- Set: Collection does not allow duplicate elements , Use... In many scenarios where element uniqueness needs to be guaranteed .
Next, we will introduce the collection classes in detail .
Use together
1)Vector
Vector yes Java Early thread safe ordered collections , If thread safety is not required , This collection is not recommended , After all, synchronization has thread overhead .
Use sample code :
Vector vector = new Vector();
vector.add("dog");
vector.add("cat");
vector.remove("cat");
System.out.println(vector);
Program execution result :[dog]
2)ArrayList
ArrayList Is the most common non thread safe ordered collection , Because the inside is stored in an array , So random access is very efficient , But the insertion and deletion performance of non tail is low , If you insert elements in the middle , All elements after that have to be moved back .ArrayList Use and Vector similar .
3)LinkedList
LinkedList It is realized by using the data structure of two-way linked list , So it is more efficient to add and delete , And random access efficiency is poor .
LinkedList In addition to the operation methods that contain the above two classes , There are also several new methods of operation , Such as offer() 、peek() etc. , Details , Please refer to the following code :
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
// Additive elements
linkedList.offer("bird");
linkedList.push("cat");
linkedList.push("dog");
// Get first element
System.out.println(linkedList.peek());
// Get first element , And delete this element
System.out.println(linkedList.poll());
System.out.println(linkedList);
The execution result of the program :
dog
dog
[cat, bird]
4)HashSet
HashSet Is a collection without repeating elements . Although it is Set Subclass of collection , It's actually HashMap Example , The relevant source code is as follows :
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
therefore HashSet Is an unordered set , There's no way to guarantee the order of elements .
HashSet Default capacity is 16, Every expansion 0.75 times , The relevant source code is as follows :
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
HashSet Use and Vector similar .
5)TreeSet
TreeSet Set to achieve automatic sorting , in other words TreeSet Will automatically sort your inserted data .
The sample code is as follows :
TreeSet treeSet = new TreeSet();
treeSet.add("dog");
treeSet.add("camel");
treeSet.add("cat");
treeSet.add("ant");
System.out.println(treeSet);
Program execution result :[ant, camel, cat, dog]
It can be seen that ,TreeSet Use and Vector similar , It's just automatic sorting .
6)LinkedHashSet
LinkedHashSet According to the elements hashCode Value to determine where the element is stored , But at the same time, the chain list is used to maintain the order of elements , This makes it look like it's saved in insert order .
LinkedHashSet Use and Vector similar .
Sets and arrays
The conversion of sets and arrays can be used toArray() and Arrays.asList() To achieve , Please refer to the following code example :
List<String> list = new ArrayList();
list.add("cat");
list.add("dog");
// Set array
String[] arr = list.toArray(new String[list.size()]);
// Array to set
List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList(arr);
The difference between a set and an array , You can refer to 「 Application of array and sorting algorithm + Interview questions 」 The content of .
Collection sorting
stay Java There are two ways to sort in a language :Comparable and Comparator, The difference is also one of the common interview questions . Let's have a thorough understanding of Comparable and Comparator The use and difference of .
1)Comparable
Comparable be located java.lang It's a bag , Is a sort interface , That is, if a class implements Comparable Interface , It means that this class has sorting function .
Comparable The interface contains only one function , The definition is as follows :
package java.lang;
import java.util.*;
public interface Comparable {
public int compareTo(T o);
}
Comparable Examples of use , Please refer to the following code :
class ComparableTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog[] dogs = new Dog[]{
new Dog(" Old Wangcai ", 10),
new Dog(" Xiaowangcai ", 3),
new Dog(" 2. Wangcai ", 5),
};
// Comparable Sort
Arrays.sort(dogs);
for (Dog d : dogs) {
System.out.println(d.getName() + ":" + d.getAge());
}
}
}
class Dog implements Comparable<Dog> {
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public int compareTo(Dog o) {
return age - o.age;
}
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
Program execution result :
Xiaowangcai :3
2. Wangcai :5
Old Wangcai :10
If Dog Class does not implement Comparable The execution code will report the abnormal information of the program , The error message is :
Exception in thread “main” java.lang.ClassCastException: xxx cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable
compareTo() There are three return values :
- e1.compareTo(e2) > 0 namely e1 > e2;
- e1.compareTo(e2) = 0 namely e1 = e2;
- e1.compareTo(e2) < 0 namely e1 < e2.
2)Comparator
Comparator It's an external comparator , be located java.util It's a bag , Reason why Comparator It's an external comparator , Because it doesn't need to be implemented in a comparison class Comparator Interface , Instead, create a new comparer class to compare and sort .
Comparator The main methods included in the interface are compare(), The definition is as follows :
public interface Comparator<T> {
int compare(T o1, T o2);
}
Comparator Examples of use , Please refer to the following code :
class ComparatorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog[] dogs = new Dog[]{
new Dog(" Old Wangcai ", 10),
new Dog(" Xiaowangcai ", 3),
new Dog(" 2. Wangcai ", 5),
};
// Comparator Sort
Arrays.sort(dogs,new DogComparator());
for (Dog d : dogs) {
System.out.println(d.getName() + ":" + d.getAge());
}
}
}
class DogComparator implements Comparator<Dog> {
@Override
public int compare(Dog o1, Dog o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge();
}
}
class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
public Dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
Program execution result :
Xiaowangcai :3
2. Wangcai :5
Old Wangcai :10
Relevant interview questions
1.List and Set What's the difference? ?
answer : The differences are as follows :
- List More than one is allowed null value ,Set Only one is allowed null value ;
- List Duplicate elements are allowed ,Set Duplicate elements are not allowed ;
- List The storage order of each element can be guaranteed ,Set There is no guarantee about the order in which elements are stored .
2. Which set can achieve automatic sorting ?
answer :TreeSet Collection implements the automatic sorting of elements , That is to say, no operation is needed , The automatic sorting function of elements can be realized .
3.Vector and ArrayList What's the difference between initialization size and capacity expansion ?
answer :Vector and ArrayList The default capacity of is 10, Source code is as follows .
Vector Default capacity source code :
public Vector() {
this(10);
}
ArrayList Default capacity source code :
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
Vector Capacity expansion is increased by default 1 times , Source code is as follows :
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
among capacityIncrement For initialization Vector designated , The default is 0.
ArrayList Capacity expansion will increase by default 0.5 times (oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1)), Source code is as follows (JDK 8):
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
4.Vector、ArrayList、LinkedList What's the difference? ?
answer : All three are List Subclasses of , So the function is similar , For example, add and delete operations 、 Find elements, etc , But in performance 、 Thread safety and other aspects of performance are not the same , The differences are as follows :
- Vector yes Java The dynamic array provided earlier , It USES synchronized To ensure thread safety , It is not recommended if non thread safety is required , After all, thread synchronization has performance overhead ;
- ArrayList Is the most commonly used dynamic array , It's not thread safe in itself , So the performance is much better , And Vector similar , It also dynamically adjusts capacity , It's just Vector The expansion will increase 1 times , and ArrayList Will increase 50%;
- LinkedList Is a set of two-way linked lists , So it doesn't need to adjust the capacity like the two above , It's also a non thread safe collection .
5.Vector、ArrayList、LinkedList What's the difference between using scenarios ?
answer :Vector and ArrayList The internal structure of is stored as an array , So it's very suitable for random access , But non tail deletion or new performance is poor , Let's insert an element in the middle , You need to move all the subsequent elements .
LinkedList Insert and delete elements are more efficient , But random access performance will be slower than the above two dynamic arrays .
6.Collection and Collections What's the difference? ?
answer :Collection and Collections The difference is as follows :
- Collection Is the parent interface of a collection class , The main inheritors of it are List and Set;
- Collections Is a help class for collection classes , It provides a static method implementation of some columns , Such as Collections.sort() Sort 、Collections.reverse() Reverse order, etc. .
7. The following options are not inherited Collection The interface is ?
A:List
B:Set
C:Map
D:HashSet
answer :C
8.LinkedHashSet How to ensure order and uniqueness ?
answer :LinkedHashSet The underlying data structure consists of a hash table and a linked list , The linked list ensures the order of elements, that is, the consistency of storage and retrieval , The hash table guarantees the uniqueness of the elements .
9.HashSet How to ensure that data is not repeatable ?
answer :HashSet The bottom layer is actually HashMap, It's just HashSet Realized Set Interface and treat data as K value , and V Value always uses the same virtual value to hold , We can see the source code :
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;// call HashMap Of put Method ,PRESENT It's a virtual value that's the same from beginning to end
}
because HashMap Of K Value itself is not allowed to repeat , And in HashMap If K/V Phase at the same time , Will use the new V Cover up the old V, Then go back to the old V, So in HashSet This sentence will always return a false, Cause insertion failure , This ensures that the data is not repeatable .
10. What is the output of the following program ? Why? ?
Integer num = 10;
Integer num2 = 5;
System.out.println(num.compareTo(num2));
answer : The output of the program is 1, because Integer By default compareTo Method , The natural sorting rules are defined , So when num Than num2 Return when large 1,Integer The relevant source code is as follows :
public int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger) {
return compare(this.value, anotherInteger.value);
}
public static int compare(int x, int y) {
return (x < y) ? -1 : ((x == y) ? 0 : 1);
}
11. How to use the program to realize the last in first out stack structure ?
answer : You can use... In the collection Stack Realization ,Stack It's a standard LIFO stack structure , Use Stack Medium pop() Method to return the top element of the stack and delete the element , The sample code is as follows .
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push("a");
stack.push("b");
stack.push("c");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Remove and return the top element of the stack
System.out.print(stack.pop() + " ");
}
Program execution result :c b a
12.LinkedList Medium peek() and poll() What's the difference? ?
answer :peek() Method returns the first element , But don't delete the current element , Returns... When the element does not exist null;poll() Method returns the first element and deletes the element , Returns... When the element does not exist null.
13.Comparable and Comparator What are the differences ?
answer :Comparable and Comparator The main differences are as follows :
- Comparable be located java.lang It's a bag , and Comparator be located java.util It's a bag ;
- Comparable Internal implementation of sorting class , and Comparator Outside of the sort class ;
- Comparable Need to rewrite CompareTo() Method , and Comparator Need to rewrite Compare() Method ;
- Comparator Implemented outside of the class , More flexible and convenient .
summary
The collections introduced in this article are all implemented from Collection, So they all have the same way of doing things , Such as add()、addAll()、remove() etc. ,Collection The method list of the interface is shown in the figure below :
[ Failed to transfer the external chain picture , The origin station may have anti-theft chain mechanism , It is suggested to save the pictures and upload them directly (img-e1nIoJzZ-1657027750282)(https://images.gitbook.cn/4cfddf30-ca63-11e9-bd50-998f3938aecb)]
Of course, some sets also expand their own unique methods in the original methods , Such as LinkedList Of offer()、push() Other methods . This article also provides the method of mutual conversion between array and set ,List.toArray() Convert a set to an array ,Arrays.asList(array) Convert an array to a collection . Finally, it introduces Comparable and Comparator The use and difference of ,Comparable and Comparator yes Java There are two ways to sort languages ,Comparable be located java.lang It's a bag , If a class implements Comparable Interface , It means that this class has sorting function ; and Comparator be located java.util It's a bag , It's an external comparator , It doesn't need to be implemented in a comparison class Comparator Interface , Instead, create a new comparer class to compare and sort .
Ensemble classification
The overall Ensemble classification Whether threads are safe Order or disorder List ArrayList unsafe Orderly LinkLedList Vector Set HashSet LinkedHashSet TreeSet
边栏推荐
- [buuctf.reverse] 159_ [watevrCTF 2019]Watshell
- RTP gb28181 document testing tool
- 集合详解之 Collection + 面试题
- I'd like to ask about the current MySQL CDC design. In the full volume phase, if a chunk's binlog backfill phase,
- What should the project manager do if there is something wrong with team collaboration?
- [lgr-109] Luogu may race II & windy round 6
- The implementation of the maize negotiable digital warehouse receipt standard will speed up the asset digitization process of the industry
- 优秀PM必须经历这3层蜕变!
- Postman测试报告
- Is the mode of education together - on campus + off campus reliable
猜你喜欢
Visio draw fan
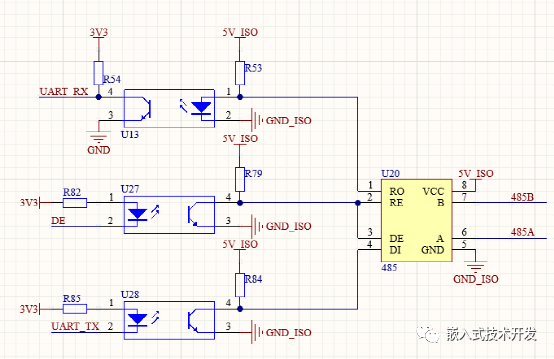
Introduction of several RS485 isolated communication schemes

ETCD数据库源码分析——etcdserver bootstrap初始化存储
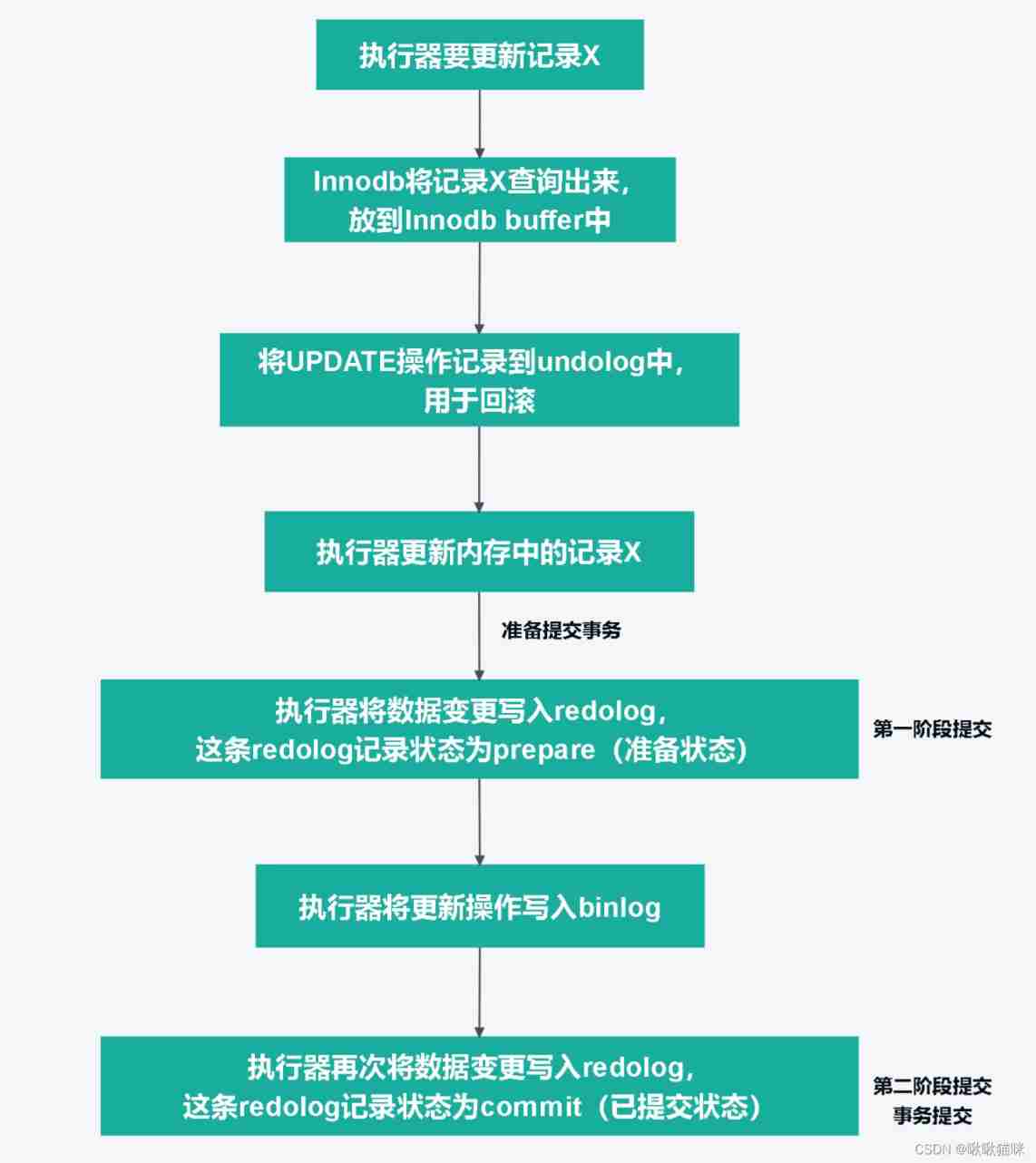
Why does MySQL need two-phase commit
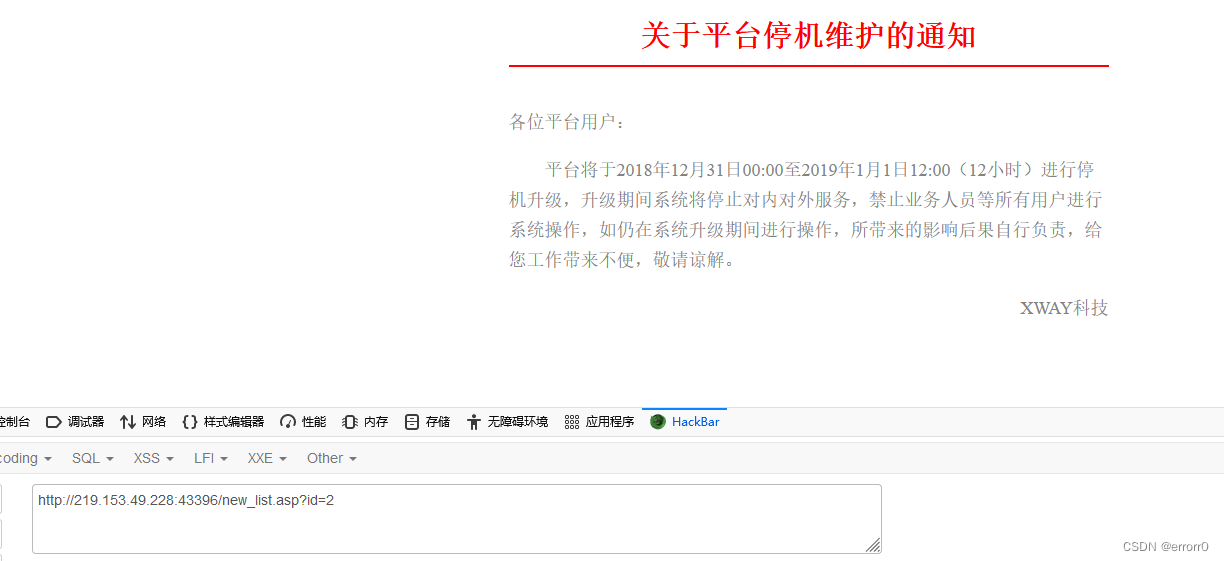
SQL注入漏洞(MSSQL注入)
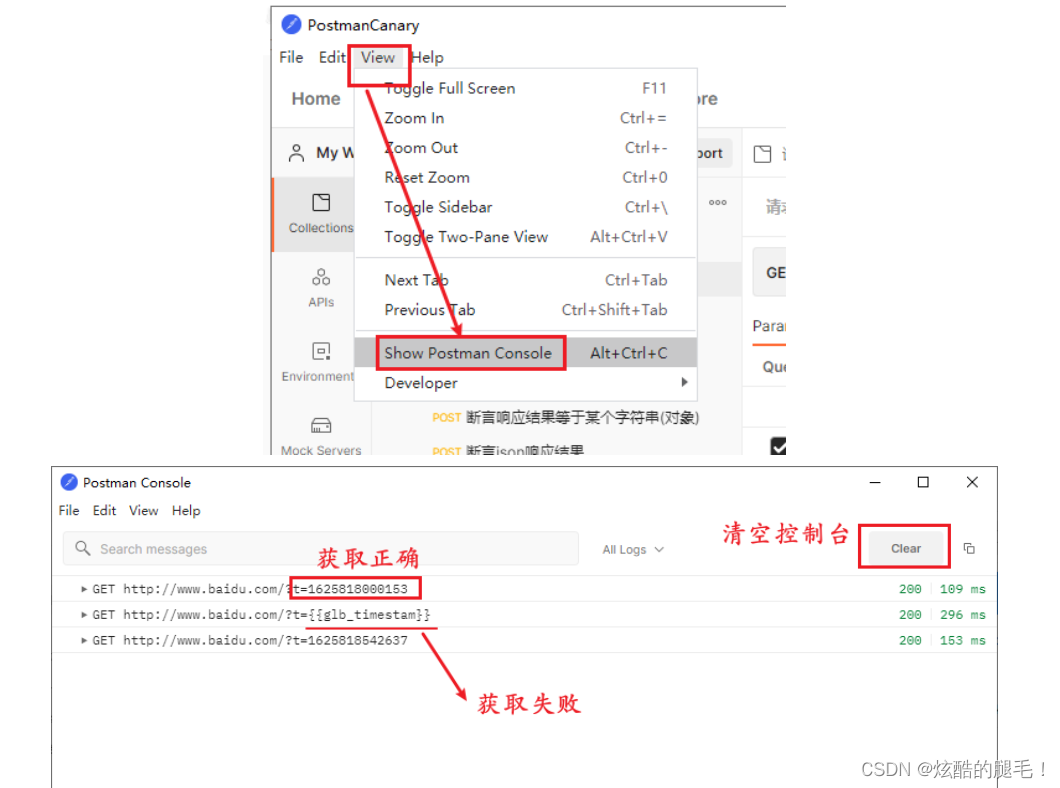
Postman pre script - global variables and environment variables
8. Static file
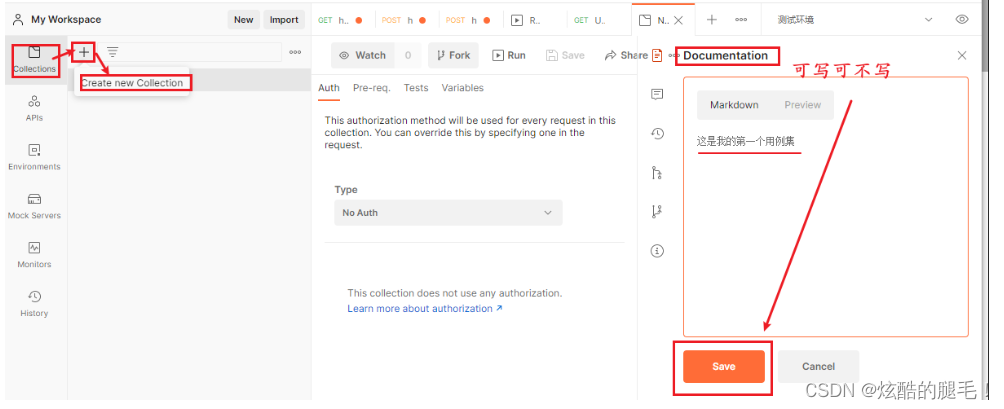
Postman管理测试用例
English Vocabulary - life scene memory method
Fuzzy -- basic application method of AFL
随机推荐
ISP学习(2)
Complete list of common functions of turtle module
EditorUtility.SetDirty在Untiy中的作用以及应用
The video in win10 computer system does not display thumbnails
ISP learning (2)
What should the project manager do if there is something wrong with team collaboration?
Chip debugging of es8316 of imx8mp
11. Intranet penetration and automatic refresh
Microservice resource address
[buuctf.reverse] 159_ [watevrCTF 2019]Watshell
2021 robocom world robot developer competition - undergraduate group (semi-finals)
Sqlserver query results are not displayed in tabular form. How to modify them
从0到1建设智能灰度数据体系:以vivo游戏中心为例
Crazy God said redis notes
L'introduction en bourse de MSK Electronics a pris fin: 800 millions de RMB d'actifs de Henan étaient des actionnaires
Selection of slow motion function
8. Static file
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
Use sentinel to interface locally
Postman测试报告