当前位置:网站首页>View workflow
View workflow
2022-07-06 04:21:00 【jthou20121212】
Tips : This article is based on Android API 31
List of articles
ViewRootImpl
Any control is displayed through WindowManager.addView To achieve and WindowManager Is an interface. The real implementation is WindowManagerImpl It directly calls WindowManagerGlobal Of addView Method is created in this method ViewRootImpl It is the abstract parent control of all controls , It does not inherit from View But it did ViewParent Interface is DecorView Of parent, stay Activity Pass through setContentView The layout passed in by the method is set to DecorView One of the id by android.R.id.content Of child controls
// android.view.WindowManagerGlobal#addView
public void addView(View view, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params,
Display display, Window parentWindow, int userId) {
// Code ellipsis ..
ViewRootImpl root;
View panelParentView = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// establish ViewRootImpl object
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
view.setLayoutParams(wparams);
mViews.add(view);
mRoots.add(root);
mParams.add(wparams);
// do this last because it fires off messages to start doing things
try {
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView, userId);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// BadTokenException or InvalidDisplayException, clean up.
if (index >= 0) {
removeViewLocked(index, true);
}
throw e;
}
}
}
stay ViewRootImpl Of setView Method requestLayout() Method triggers measurement 、 Layout 、 Drawing work
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#requestLayout
public void requestLayout() {
if (!mHandlingLayoutInLayoutRequest) {
checkThread();
// The mark position is true
mLayoutRequested = true;
// Dispatch
scheduleTraversals();
}
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#scheduleTraversals
void scheduleTraversals() {
if (!mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = true;
// Send a synchronous barrier message and give priority to asynchronous messages
mTraversalBarrier = mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().postSyncBarrier();
// Send a mTraversalRunnable
mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL, mTraversalRunnable, null);
notifyRendererOfFramePending();
pokeDrawLockIfNeeded();
}
}
mTraversalRunnable yes TraversalRunnable Object in the next Vsync When the signal comes, it will call run Method
// android.view.ViewRootImpl.TraversalRunnable
final class TraversalRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
doTraversal();
}
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#doTraversal
void doTraversal() {
if (mTraversalScheduled) {
mTraversalScheduled = false;
// Remove synchronization barrier messages
mHandler.getLooper().getQueue().removeSyncBarrier(mTraversalBarrier);
if (mProfile) {
Debug.startMethodTracing("ViewAncestor");
}
// The real beginning View workflow
performTraversals();
if (mProfile) {
Debug.stopMethodTracing();
mProfile = false;
}
}
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#performTraversals
private void performTraversals() {
// Code ellipsis ..
performMeasure
// Code ellipsis ..
performLayout
// Code ellipsis ..
performDraw
// Code ellipsis ..
}
performTraversals Method will be called once 、 Layout 、 The method of drawing , Take a look at
measurement
// mWidth mHeight Is the screen width and height
// lp yes android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams
// lp.width lp.height The default is MATCH_PARENT
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height);
// Ask host how big it wants to be
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
DecorView Because it's the top floor View There is no actual parent, only abstract parent ViewRootImpl So its measurement process is different from ordinary controls , Other controls MeasureSpec All through the parent MeasureSpec Own ViewGroup.LayoutParams Get and DecorView Of MeasureSpec It is through the width and height of the screen WindowManager.LayoutParams Got , Let's introduce MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec Representing one 32 position int value , high 2 On behalf of SpecMode, low 30 On behalf of SpecSize,SpecMode Measurement mode , and SpecSize It refers to the specification size in a certain measurement mode .
SpecMode There are three categories , Each class has a special meaning , As shown below .
UNSPECIFIED: The parent container is not right View There are any restrictions , How big to give , This situation is generally used inside the system , Indicates a state of measurement .
EXACTLY: The parent container has detected View The exact size required , This is the time View The final size of SpecSize Specified value . It corresponds to LayoutParams Medium match_parent And specific numerical values .
AT_MOST: The parent container specifies an available size, that is SpecSize,View The size of cannot be greater than this value , The specific value depends on the difference View The concrete realization of . It corresponds to LayoutParams Medium wrap_content
《Android Exploration of development Art 》
// determine DecorView Of MeasureSpec Then measure the sub control
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) {
if (mView == null) {
return;
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure");
try {
// Measure all controls recursively
mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}
// android.view.View#measure
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// If set PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT The tag indicates that forced layout is required
final boolean forceLayout = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT) == PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
// If the size changes, it needs to be measured again
final boolean needsLayout = specChanged
&& (sAlwaysRemeasureExactly || !isSpecExactly || !matchesSpecSize);
if (forceLayout || needsLayout) {
// Code ellipsis ..
onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// Code ellipsis ..
// Set up PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED The tag will be mentioned below
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED;
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
stay view.measure() In the method of , Only when given MeasureSpec When something changes , Or when forced rearrangement is required , Will be measured .
Force a rearrangement : When the content of a child control in the control tree changes , Situations requiring re measurement and layout , under these circumstances , The parent control of this child control ( And the parent control of the parent control ) Provided by the MeasureSpec It must be the same as the last measurement , As a result, from ViewRootImpl To the path of this control , Of the parent control measure() Method cannot be executed , As a result, the layout and size of child controls cannot be re measured .
The solution : therefore , When the child control changes due to its content , Trace back from child control to parent control to ViewRootImpl, And call the parent control's requestLayout() Method . This method will be in mPrivateFlags Add a mark in PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT, So that these parent controls measure() The method was successfully implemented , Then this sub control has the opportunity to re layout and measure . This is the meaning of forced relocation .
measure yes View Of final Methods cannot be overridden by subclasses , In this method, we call onMeasure Of the incoming control MeasureSpec Complete the measurement of the child control ,ViewGroup I didn't rewrite it onMeasure The method is different ViewGroup The measurement rules of subclasses of are different, so subclasses need to implement themselves , because DecorView Inherited from FrameLayout So take a look FrameLayout Of onMeasure Method
// android.widget.FrameLayout#onMeasure
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int count = getChildCount();
// If the measurement mode of one of your width and height is not EXACTLY Pattern
final boolean measureMatchParentChildren =
MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ||
MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec) != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
mMatchParentChildren.clear();
int maxHeight = 0;
int maxWidth = 0;
int childState = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (mMeasureAllChildren || child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// Traverse all child controls and measure them one by one
// If the child control is ViewGroup Then repeat this process in the child control
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
final LayoutParams lp = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// Record the maximum width and height for the last FrameLayout Measure yourself
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth,
child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight,
child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
childState = combineMeasuredStates(childState, child.getMeasuredState());
if (measureMatchParentChildren) {
// If one of the width and height of the child control is MATCH_PARENT Then write it down
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT ||
lp.height == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
mMatchParentChildren.add(child);
}
}
}
}
// Omit some maximum checks ..
// Set your own size
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
resolveSizeAndState(maxHeight, heightMeasureSpec,
childState << MEASURED_HEIGHT_STATE_SHIFT));
count = mMatchParentChildren.size();
// If FrameLayout One of my width and height is wrap_content And one of the width and height of more than one child control is MATCH_PARENT Then measure again
// because MATCH_PARENT Child controls of need to follow FrameLayout Same size but FrameLayout Only after measuring all the controls and getting the maximum size of the controls can you know your size
// therefore FrameLayout Once you know your size, re measure the child controls
if (count > 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = mMatchParentChildren.get(i);
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec;
if (lp.width == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
final int width = Math.max(0, getMeasuredWidth()
- getPaddingLeftWithForeground() - getPaddingRightWithForeground()
- lp.leftMargin - lp.rightMargin);
childWidthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
width, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
} else {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(widthMeasureSpec,
getPaddingLeftWithForeground() + getPaddingRightWithForeground() +
lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin,
lp.width);
}
// High logic is consistent with wide
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
FrameLayout Of onMeasure The method is roughly to measure all the child controls one by one, and then use the width and height of the largest child control to set its own size , If there are special circumstances, measure the sub control again , Take a look at the method of measuring child controls
// android.view.ViewGroup#measureChildWithMargins
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
measureChildWithMargins s yes ViewGroup Methods , Handled spacing calls getChildMeasureSpec Method , stay FrameLayout This method is also called when secondary measurement is required
// android.view.ViewGroup#getChildMeasureSpec
// Parameters spec Is the parent control MeasureSpec
// Parameters padding It's spacing , That represents the parent control padding + Child controls own margin
// Parameters childDimension Is a child control LayoutParams The size of is in xml The width and height stated in the document
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
// The measurement mode of the parent control
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
// The measured size of the parent control
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
// Available size of parent control ( Measure the size - spacing )
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// The parent control is in precise mode
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// If the width and height of the child control is an exact value xxdp Then use this value directly
resultSize = childDimension;
// The measurement mode of the sub control is also the precise mode
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// If the width and height of the child control is MATCH_PARENT Then fill the parent control with the size of the parent control
resultSize = size;
// The measurement mode of the sub control is also the precise mode
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// The width and height of the child control are WRAP_CONTENT Fill mode
resultSize = size;
// The measurement mode of the child control is ' Maximum ' Mode indicates that the maximum size of the parent control is not exceeded size
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// The parent control is ' Maximum ' Pattern
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// If the width and height of the child control is an exact value xxdp Then use this value directly
resultSize = childDimension;
// The measurement mode of the sub control is also the precise mode
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// If the width and height of the child control is MATCH_PARENT Then fill the parent control with the size of the parent control
resultSize = size;
// Usually at this time, the parent control has not determined its size, so the child control is also ' Maximum ' Pattern
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// The width and height of the child control are WRAP_CONTENT Fill mode
resultSize = size;
// Usually at this time, the parent control has not determined its size, so the child control is also ' Maximum ' Pattern
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// The parent control does not limit the size of the child control
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// If the child control is a definite size, the size mode is ' accurate ' Pattern
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// If the width and height of the child control is MATCH_PARENT The size depends on View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec Value
// View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec The default value of is true That is, the size of the child control is 0
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// If the width and height of the child control is WRAP_CONTENT The size depends on View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec Value
// View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec The default value of is true That is, the size of the child control is 0
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
// Package one according to the measured width and height MeasureSpec object
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
The method has been commented in detail , The specific logic can be presented through a table :
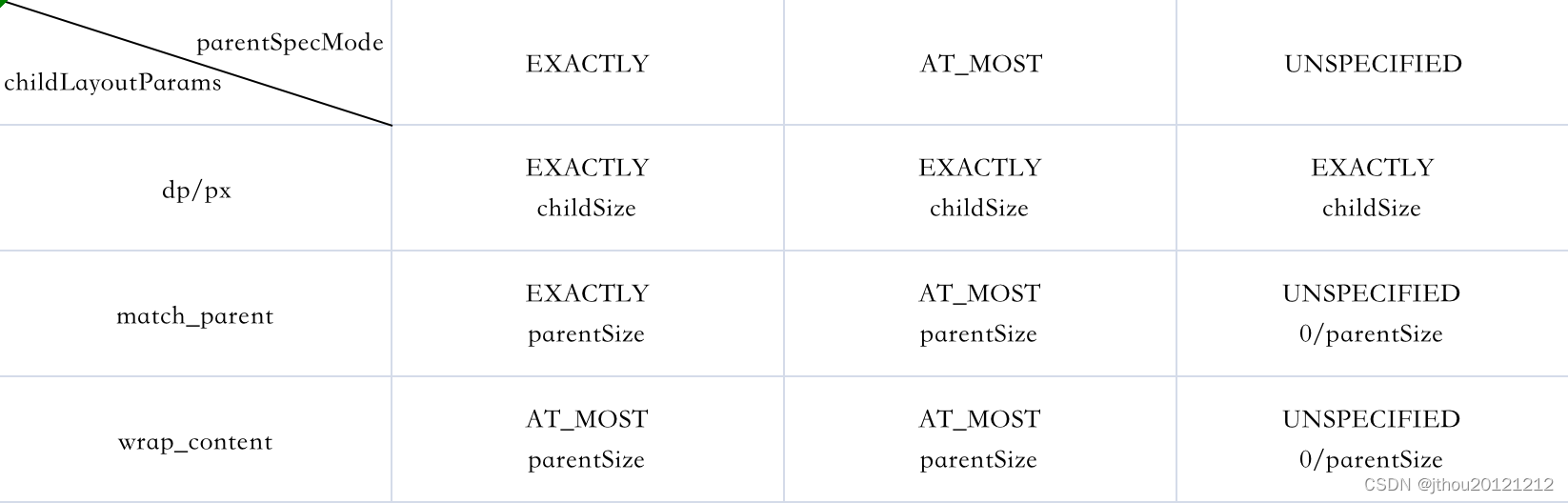
Two items in the lower right corner UNSPECIFIED by 0 or parentSize Depending on View Static variables in sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec Value , Its value is sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec = targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.M
Finally, according to the measurement size and measurement mode, it is packaged into a MeasureSpec Then measure the child controls , Of the child control measure call onMeasure Next, let's take a look View Of onMeasure Method
// android.view.View#onMeasure
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
// If there are settings background Then take background The original width and minWidth The big value of
// If not set background Then take minWidth Corresponding androind:minWidth attribute
// getSuggestedMinimumHeight This logic is also equivalent to obtaining the default size of the control
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
// The measurement mode of the parent control
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
// The measured size of the parent control
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
// If the measurement mode is UNSPECIFIED The default size is used
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
// The measurement mode is AT_MOST or EXACTLY Use the size of the parent control
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
adopt getDefaultSize The method can be known in View In the default implementation , Whether it's EXACTLY still AT_MOST The mode gets the available size of the parent control , That is to say in xml Whether it is set to match_parent still wrap_content The displayed size is the same, so when customizing View You usually have to rewrite onMeasure Method according to the demand, give a AT_MOST Default size in mode
To sum up View The measurement process is from DecorView Start , According to the screen width and height WindowManager.LayoutParams(width, height The default is MATCH_PARENT) obtain MeasureSpec Then measure yourself , Because I am ViewGroup Therefore, all child controls will be measured first to know their size , If the child control is View The measurement is over. If it is ViewGroup Then repeat the process , Here are ordinary controls ( Not DecorView other View) And DecorView The difference is that of ordinary controls MeasureSpec It is through the parent control MeasureSpec Own ViewGroup.LayoutParams Got
Layout
Layout from ViewRootImpl Of performLayout Start and call the real top-level control DecorView Of layout Method ,FrameLayout I didn't rewrite it layout Method ViewGroup It is also a simple call super.layout So look directly View Of layout Method
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#performLayout
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth,
int desiredWindowHeight) {
// Code ellipsis ..
host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight());
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.View#layout
// Parameters l Corresponding to the above 0
// Parameters t Corresponding to the above 0
// Parameters r Corresponding to the above host.getMeasuredWidth() Measure the width
// Parameters b Corresponding to the above host.getMeasuredHeight() Measure the height
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// adopt setFrame Set the position of the child control in the parent control
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
// If the position changes or is set PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED Mark ( adopt view.requestLayout Trigger remeasurement 、 Layout in view.measure Middle mark ) call onLayout Rearrange , This is for ViewGroup Let it traverse the layout sub control
// View Of onLayout Is empty implementation
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.View#setFrame
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
boolean changed = false;
// Code ellipsis ..
// Change of position
if (mLeft != left || mRight != right || mTop != top || mBottom != bottom) {
changed = true;
// Remember our drawn bit
int drawn = mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWN;
int oldWidth = mRight - mLeft;
int oldHeight = mBottom - mTop;
int newWidth = right - left;
int newHeight = bottom - top;
boolean sizeChanged = (newWidth != oldWidth) || (newHeight != oldHeight);
// Redraw is triggered
invalidate(sizeChanged);
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS;
if (sizeChanged) {
sizeChange(newWidth, newHeight, oldWidth, oldHeight);
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
return changed;
}
The so-called layout is actually to record its coordinates in the parent control , And then you can go through getWidth/getHeight Got the width and height , therefore getWidth/getHeight And getMeasureWidth/getMeasureHeight The difference is the timing ,getMeasureWidth/getMeasureHeight It can be obtained after the measurement getWidth/getHeight You can get it after the layout is completed , And the result is usually the same ( It can be handled differently in layout, but it doesn't make sense )
ViewGroup in onLayout Abstract methods need subclasses to rewrite according to their own needs , In detail ViewGroup Subclasses will traverse all child controls , If the child control is View The process ends if the child control is ViewGroup Then execute this process recursively
draw
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#performDraw
private void performDraw() {
// Code ellipsis ..
try {
boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded);
if (usingAsyncReport && !canUseAsync) {
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.setFrameCompleteCallback(null);
usingAsyncReport = false;
}
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#draw
private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) {
// Code ellipsis ..
if (!dirty.isEmpty() || mIsAnimating || accessibilityFocusDirty || mNextDrawUseBlastSync) {
// If hardware acceleration is turned on
if (isHardwareEnabled()) {
// Code ellipsis ..
mAttachInfo.mThreadedRenderer.draw(mView, mAttachInfo, this);
} else {
// Code ellipsis ..
if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset,
scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
// Let's first look at the situation that hardware acceleration is not enabled
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#drawSoftware
private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff,
boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// Get canvas
final Canvas = mSurface.lockCanvas(dirty);
// Code ellipsis ..
// Start drawing process
mView.draw(canvas);
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.View#draw(android.graphics.Canvas)
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// The drawing background cannot be overwritten
drawBackground(canvas);
// Code ellipsis ..
// Draw yourself
onDraw(canvas);
// Draw child controls
// in the light of ViewGroup To distribute drawing child controls
// about View It makes no sense
dispatchDraw(canvas);
// Draw auto fill
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
// draw Overlay Below the foreground
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().dispatchDraw(canvas);
}
// Draw decorations , prospects 、 Precision bar, etc
onDrawForeground(canvas);
// Paint highlight
drawDefaultFocusHighlight(canvas);
}
View The drawing process of is mainly onDraw Draw yourself dispatchDraw Distribute draw child controls , For customization View You don't have to rewrite it dispatchDraw Need to rewrite onDraw Draw your own logic , For customization ViewGroup Generally, there is no need to rewrite onDraw Draw yourself ( also ViewGroup Of onDraw By default, do not execute ) Need to rewrite dispatchDraw Distribute and draw all child controls , If the child control is also ViewGroup Repeat the process
// android.view.ViewGroup#dispatchDraw
protected void dispatchDraw(Canvas canvas) {
// Code ellipsis ..
for (int i = 0; i < childrenCount; i++) {
// Code ellipsis ..
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(preorderedList, children, childIndex);
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null) {
// Draw child controls
more |= drawChild(canvas, child, drawingTime);
}
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.ViewGroup#drawChild
protected boolean drawChild(Canvas canvas, View child, long drawingTime) {
return child.draw(canvas, this, drawingTime);
}
// android.view.View#draw(android.graphics.Canvas, android.view.ViewGroup, long)
boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) {
// Code ellipsis ..
if (!drawingWithDrawingCache) {
if (drawingWithRenderNode) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
((RecordingCanvas) canvas).drawRenderNode(renderNode);
} else {
// If View Set up WILL_NOT_DRAW Mark and background 、 prospects 、 If the highlight is empty, it will be set PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW Tags skip drawing themselves
// ViewGroup It will be set by default during initialization WILL_NOT_DRAW Mark
// So if ViewGroup Generally, it will not be executed without setting the background onDraw Method will only try to draw child controls
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) {
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
dispatchDraw(canvas);
} else {
// Otherwise, execute the drawing process completed by yourself
draw(canvas);
}
}
}
// Code ellipsis ..
mRecreateDisplayList = false;
return more;
}
To sum up, the process of not enabling hardware acceleration starts from android.view.ViewRootImpl#performDraw Call start call android.view.ViewRootImpl#draw adopt Surface Object requests a canvas to call com.android.internal.policy.DecorView#draw Pass this canvas through onDraw Method to draw yourself ( You can also set not to draw yourself ) Call again dispatchDraw Draw all child controls if the child control is ViewGroup Then execute this process recursively . Before looking at the process of hardware acceleration android.view.View#invalidate() This method (postInvalidate Is used in sub threads through Handler Indirectly called invalidate Method )
invalidate
// android.view.View#invalidate()
public void invalidate() {
// Parameter values for true
invalidate(true);
}
public void invalidate(boolean invalidateCache) {
invalidateInternal(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, invalidateCache, true);
}
void invalidateInternal(int l, int t, int r, int b, boolean invalidateCache,
boolean fullInvalidate) {
// Code ellipsis ..
if ((mPrivateFlags & (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)) == (PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_HAS_BOUNDS)
|| (invalidateCache && (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID)
|| (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != PFLAG_INVALIDATED
|| (fullInvalidate && isOpaque() != mLastIsOpaque)) {
// Code ellipsis ..
if (invalidateCache) {
// add to PFLAG_INVALIDATED Mark
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
// remove PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID Mark
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
}
final AttachInfo ai = mAttachInfo;
final ViewParent p = mParent;
if (p != null && ai != null && l < r && t < b) {
final Rect damage = ai.mTmpInvalRect;
damage.set(l, t, r, b);
// Call the redrawing method of the parent control and pass it into the dirty area you want to draw
p.invalidateChild(this, damage);
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
}
// android.view.ViewGroup#invalidateChild
public final void invalidateChild(View child, final Rect dirty) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null && attachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated) {
// If hardware acceleration is turned on
onDescendantInvalidated(child, child);
return;
}
ViewParent parent = this;
if (attachInfo != null) {
// If hardware acceleration is turned off, this should be LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE So it will be implemented
if (child.mLayerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
}
// Code ellipsis ..
do {
View view = null;
if (parent instanceof View) {
view = (View) parent;
}
// Code ellipsis ..
// Call the parent control's invalidateChildInParent Method
// because ViewRootImpl yes DecorView Of parent
// So we call the ViewRootImple Of invalidateChildInParent Method
parent = parent.invalidateChildInParent(location, dirty);
// Code ellipsis ..
} while (parent != null);
}
}
// android.view.ViewGroup#onDescendantInvalidated
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target) {
// Code ellipsis ..
// Call is a circular call parent Of onDescendantInvalidated Method until ViewRootImpl
if (mParent != null) {
mParent.onDescendantInvalidated(this, target);
}
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#onDescendantInvalidated
public void onDescendantInvalidated(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View descendant) {
// Code ellipsis ..
invalidate();
}
// android.view.ViewRootImpl#invalidate
void invalidate() {
// Code ellipsis ..
// Trigger View Workflow ( Measurements are not necessarily performed 、 Layout 、 Draw all processes )
scheduleTraversals();
}
From the above analysis, we know scheduleTraversals Next time Vsync Call when the signal comes performTraversals Call again performDraw Trigger redraw , If hardware acceleration is enabled, continue to android.view.ThreadedRenderer#draw
// android.view.ThreadedRenderer#draw
void draw(View view, AttachInfo attachInfo, DrawCallbacks callbacks) {
// Code ellipsis ..
updateRootDisplayList(view, callbacks);
// Code ellipsis ..
}
private void updateRootDisplayList(View view, DrawCallbacks callbacks) {
// Code ellipsis ..
updateViewTreeDisplayList(view);
// Code ellipsis ..
}
private void updateViewTreeDisplayList(View view) {
view.mPrivateFlags |= View.PFLAG_DRAWN;
// Because in calling invalidate It's set to PFLAG_INVALIDATED therefore mRecreateDisplayList by true
view.mRecreateDisplayList = (view.mPrivateFlags & View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED)
== View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.mPrivateFlags &= ~View.PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
view.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
view.mRecreateDisplayList = false;
}
// android.view.View#updateDisplayListIfDirty
public RenderNode updateDisplayListIfDirty() {
// Code ellipsis ..
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID) == 0
|| !renderNode.hasDisplayList()
|| (mRecreateDisplayList)) {
if (renderNode.hasDisplayList()
&& !mRecreateDisplayList) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
// If you don't need to redraw, continue to distribute the drawing process
dispatchGetDisplayList();
return renderNode; // no work needed
}
mRecreateDisplayList = true;
// Code ellipsis ..
final RecordingCanvas canvas = renderNode.beginRecording(width, height);
try {
if (layerType == LAYER_TYPE_SOFTWARE) {
buildDrawingCache(true);
Bitmap cache = getDrawingCache(true);
if (cache != null) {
canvas.drawBitmap(cache, 0, 0, mLayerPaint);
}
} else {
// Code ellipsis ..
// It is the same as software drawing to judge whether you need to skip drawing yourself
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) == PFLAG_SKIP_DRAW) {
// If you skip, you can directly distribute the drawing sub controls
dispatchDraw(canvas);
drawAutofilledHighlight(canvas);
if (mOverlay != null && !mOverlay.isEmpty()) {
mOverlay.getOverlayView().draw(canvas);
}
if (isShowingLayoutBounds()) {
debugDrawFocus(canvas);
}
} else {
// Execute the complete drawing process
draw(canvas);
}
}
}
// Code ellipsis ..
} else {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_DRAWN | PFLAG_DRAWING_CACHE_VALID;
mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_DIRTY_MASK;
}
return renderNode;
}
// In this method View Middle is empty method because View There is no need to distribute the drawing
// android.view.ViewGroup#dispatchGetDisplayList
protected void dispatchGetDisplayList() {
final int count = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = children[i];
if (((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) == VISIBLE || child.getAnimation() != null)) {
recreateChildDisplayList(child);
}
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
// android.view.ViewGroup#recreateChildDisplayList
private void recreateChildDisplayList(View child) {
child.mRecreateDisplayList = (child.mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_INVALIDATED) != 0;
child.mPrivateFlags &= ~PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
child.updateDisplayListIfDirty();
child.mRecreateDisplayList = false;
}
To sum up, when passing invalidate Called when redrawing is requested invalidate Child controls of will be added PFLAG_INVALIDATED Mark and pass the parent Request redrawing level by level until ViewRootImpl Of scheduleTraversals Method next time Vsync Perform the real redrawing operation when the signal comes And because only direct calls invalidate The control of is set PFLAG_INVALIDATED Mark view.mRecreateDisplayList by true Will perform redrawing , Other controls call dispatchGetDisplayList Distribute the redrawing operation of child controls and will also be based on whether PFLAG_INVALIDATED Mark to determine whether to perform redrawing until the redrawing action of all controls is completed , If you are opening the page for the first time, you can directly go through android.view.ViewRootImpl#requestLayout Triggering the whole process should be that all controls will be redrawn
Simply put, when hardware acceleration is turned off, all subsystems View Will be redrawn , When hardware acceleration is turned on, only call invalidate Methodical View To redraw
requestLayout
// android.view.View#requestLayout
public void requestLayout() {
// Code ellipsis ..
// Set forced layout flag
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT;
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_INVALIDATED;
// call parent requestLayout
if (mParent != null && !mParent.isLayoutRequested()) {
mParent.requestLayout();
}
// Code ellipsis ..
}
Finally, take a look at View Of requestLayout Methods are indeed set PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT Force layout tags .invalidate And requestLayout Is the difference between the invalidate Only the drawing operation will be triggered, and the measurement will not be triggered 、 Layout process because invalidate Method is not set PFLAG_FORCE_LAYOUT Mark ,requestLayout Usually, only the measurement will be triggered 、 The layout process will not trigger the redrawing process , But if the size of the control changes, the drawing process will also be triggered .
summary : For the first time View The workflow is through android.view.ViewRootImpl#requestLayout The trigger , It calls for scheduleTraversals Method direction Choreographer Send a Runnable And a synchronous barrier message ( Make sure to give priority to this Runnable Asynchronous messaging ) The next time Vsync Execute this after the signal arrives Runnable perform View Real work measurement 、 Layout 、 draw . The entrance of measurement is perfromMeasure Method, it will call DecorView Of measure From the top floor View Start the whole thing View Measurement of trees , If View It's just View Then it's over just measuring yourself. If it's ViewGroup Measure all child controls first, and then measure yourself if the child control is still ViewGroup Recursive execution . The entrance of the layout is performLayout Method, it will call DecorView Of layout From the top floor View Start the whole thing View The layout of the tree , If View It's just View Then the layout itself is over. If it is ViewGroup Layout yourself first, and then recursively layout all child controls . The entry drawn is performDraw Method, it will call DecorView Of draw Start the whole thing View Drawing of trees , If View It's just View Then just draw yourself and it's over. If it's ViewGroup First draw yourself (ViewGroup By default, you don't draw yourself ) Then recursively draw all child controls , And there are two cases of whether hardware acceleration is enabled for rendering , When hardware acceleration is turned on, only direct calls are drawn invalidate Trigger redraw View Draw all controls when hardware acceleration is not turned on .
Reference and thanks
Compare the requestLayout and invalidate Method
Article to read View Of Measure、Layout、Draw technological process
边栏推荐
- HotSpot VM
- 综合能力测评系统
- 电脑钉钉怎么调整声音
- Implementation of knowledge consolidation source code 1: epoll implementation of TCP server
- 【leetcode】1189. Maximum number of "balloons"
- pd. to_ numeric
- [Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package
- [leetcode question brushing day 33] 1189 The maximum number of "balloons", 201. The number range is bitwise AND
- asp. Core is compatible with both JWT authentication and cookies authentication
- Recommendation | recommendation of 9 psychotherapy books
猜你喜欢

User datagram protocol UDP
Figure application details
Yyds dry goods inventory hcie security Day11: preliminary study of firewall dual machine hot standby and vgmp concepts
IDEA编译JSP页面生成的class文件路径
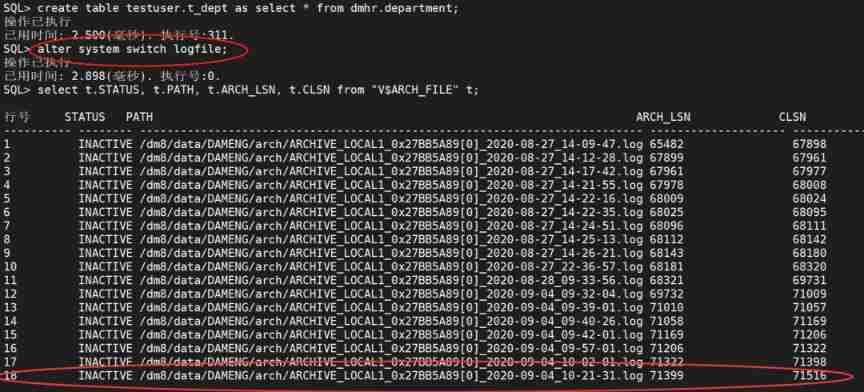
DM8 archive log file manual switching

Lombok原理和同时使⽤@Data和@Builder 的坑
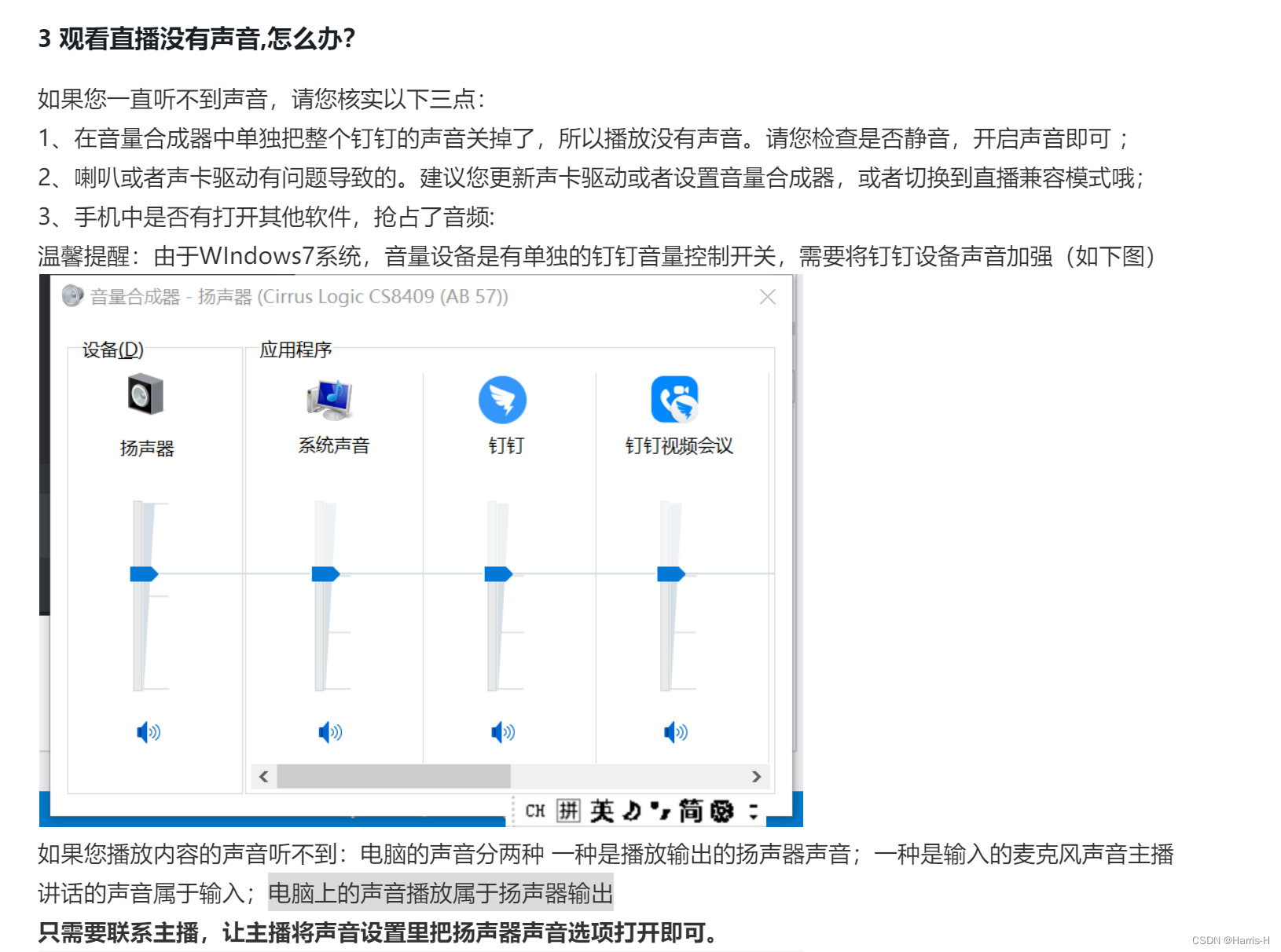
How does computer nail adjust sound
![[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package](/img/45/6777fa919386e526dbb0d2c808a7f2.jpg)
[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package
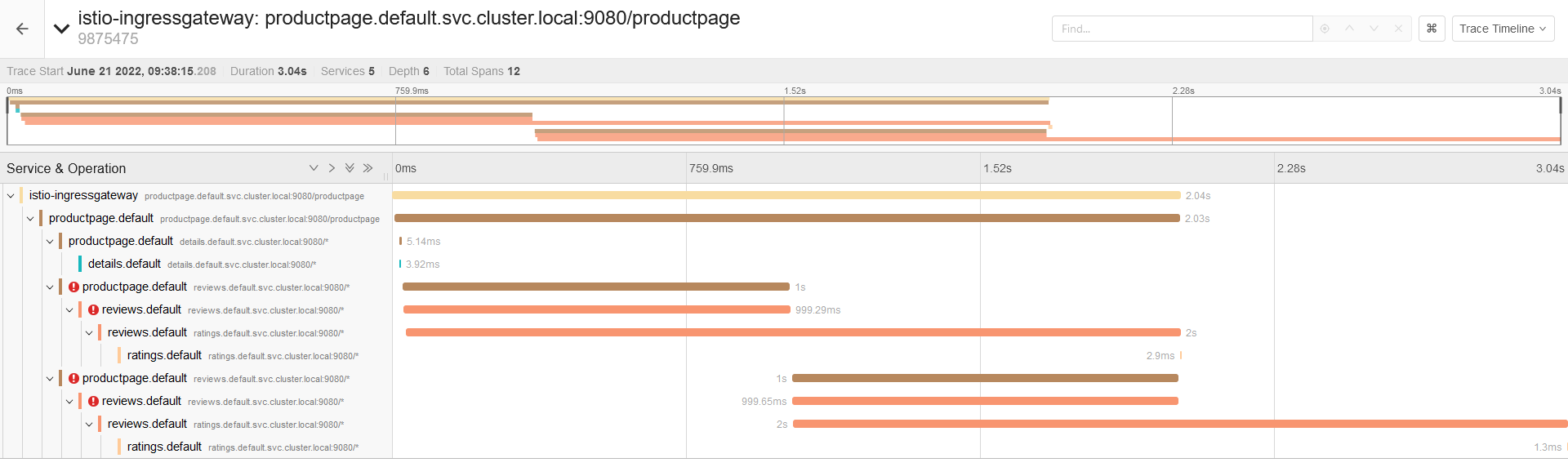
How many of the 10 most common examples of istio traffic management do you know?

MLAPI系列 - 04 - 网络变量和网络序列化【网络同步】
随机推荐
Global and Chinese markets for fire resistant conveyor belts 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
npm命令--安装依赖包--用法/详解
MySQL learning record 13 database connection pool, pooling technology, DBCP, c3p0
Global and Chinese markets for medical gas manifolds 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
题解:《单词覆盖还原》、《最长连号》、《小玉买文具》、《小玉家的电费》
VPP性能测试
CADD课程学习(7)-- 模拟靶点和小分子相互作用 (柔性对接 AutoDock)
POI add border
Recommendation | recommendation of 9 psychotherapy books
Web components series (VII) -- life cycle of custom components
In depth MySQL transactions, stored procedures and triggers
Patent | subject classification method based on graph convolution neural network fusion of multiple human brain maps
DM8 backup set deletion
Implementation of knowledge consolidation source code 1: epoll implementation of TCP server
Introduction to hashtable
Figure application details
HotSpot VM
HotSpot VM
Data processing methods - smote series and adasyn
Stable Huawei micro certification, stable Huawei cloud database service practice