当前位置:网站首页>Understanding of processes, threads, coroutines, synchronization, asynchrony, blocking, non blocking, concurrency, parallelism, and serialization
Understanding of processes, threads, coroutines, synchronization, asynchrony, blocking, non blocking, concurrency, parallelism, and serialization
2022-07-06 04:09:00 【YZL40514131】
One 、 process
1、 Open a browser , Is to start a browser process .
2、 A running program ( Code ) It's a process , No running code is called a program .
3、 Process is the smallest unit of system resource allocation , Processes have their own independent memory space , All inter process data is not shared , Spending big .
4、 A process is the basic unit of executing a task , It is also the basic unit for the operating system to perform tasks . The process contains a collection of program instructions and related resources .
5、 Create a process : Import first multiprocessing Medium Process
6、 Do not share global variables between processes
p = Process(target=XXX,args=(tuple,),kwargs={key:value})
target = XXX Specified task function , Don't have to add (),
args=(tuple,)
kwargs={key:value} Parameters passed to the task function
import os
from multiprocessing import Process
import time
def pro_func(name):
for i in range(5):
print(f' Subprocesses {
name+str(i)} Start execution ')
time.sleep(2)
print(f' Subprocesses {
name+str(i)} End to perform ')
if __name__ == '__main__':
p=Process(target=pro_func,args=('kobe',))
p.start()
print(' The execution of the main process is over ')
Two 、 Threads
1、 In a process , At least one thread , This thread is the main thread of the current process ,
2、 Thread is the basic unit of executing tasks in a process
3、 Thread cannot exist independently , Dependent processes exist
4、 Multiple threads share memory ( Data sharing , Share global variables ), Thus greatly improving the efficiency of the program .
5、 Multithreading may cause data chaos or even deadlock
6、 Create thread : Import first threading Medium Thread
import threading
import time
def thread():
for i in range(5):
print(f' Sub thread {
i} Start execution ')
time.sleep(2)
print(f' Sub thread {
i} End to perform ')
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=threading.Thread(target=thread)
t.start()
print(' Main thread execution completed ')
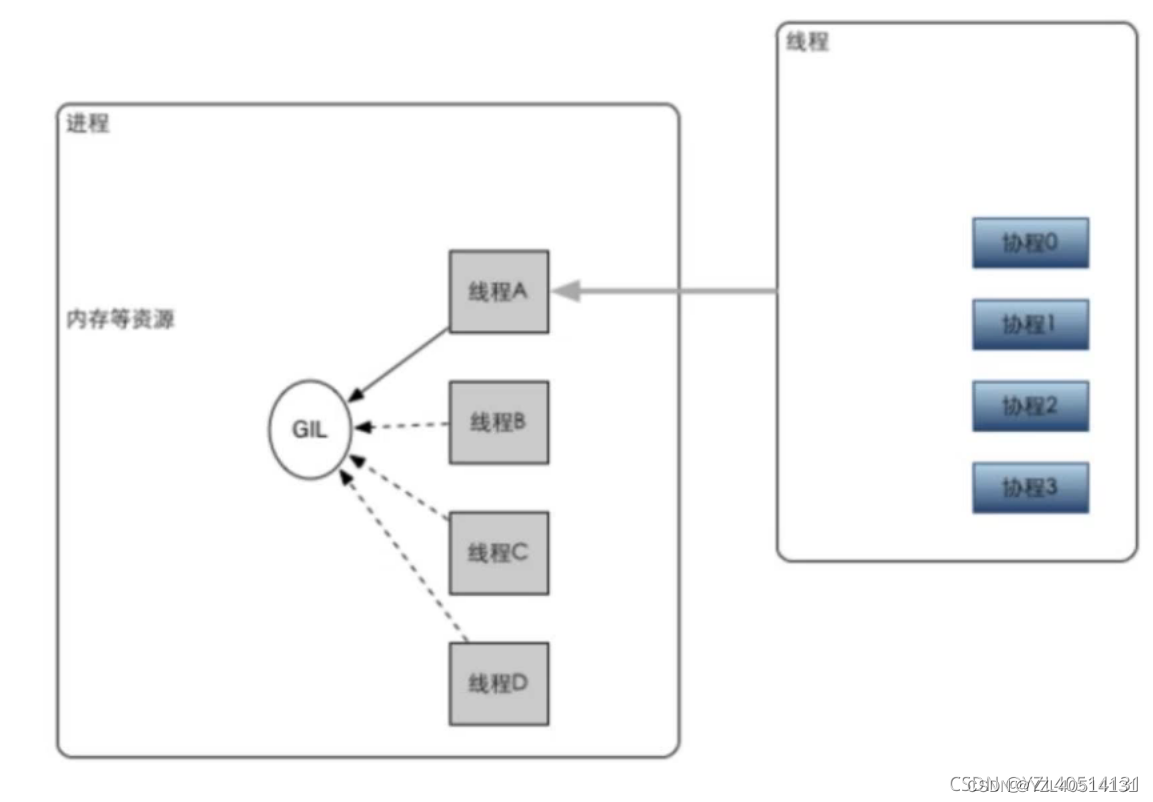
3、 ... and 、 coroutines
1、 Coroutine is a lightweight thread in user mode , The scheduling of the process is completely controlled by the user ; The benefit of this is that the performance has been greatly improved , It doesn't consume resources like thread switching .
2、 Synergetics generally use gevent library
3、 A thread can also have multiple coroutines
Four 、 Sync
Multiple tasks are executed in sequence , Only after one execution can the next be executed .
5、 ... and 、 asynchronous
Relative to synchronization , Synchronization is performed sequentially , Asynchrony is independent of each other , Continue to do your own thing while waiting for an event , Don't wait for this event to complete before you work . Threads are a way to achieve asynchrony , Asynchrony means that the main thread calling a method does not need to wait for another thread to complete synchronously , So that the main thread can do other things .
6、 ... and 、 Blocking
If the caller gets stuck , The caller cannot continue to execute , That is, the caller is blocking .
For example, the blocking function when multithreading executes tasks t.join(), The main route is blocked first , Wait for the sub thread to finish executing , End of main thread execution .
import threading
import time
def thread():
for i in range(5):
print(f' Sub thread {
i} Start execution ')
time.sleep(2)
print(f' Sub thread {
i} End to perform ')
if __name__ == '__main__':
t=threading.Thread(target=thread)
t.start()
t.join()
print(' Main thread execution completed ')
7、 ... and 、 Non blocking
If it doesn't get stuck , Can continue to execute , That means non blocking .
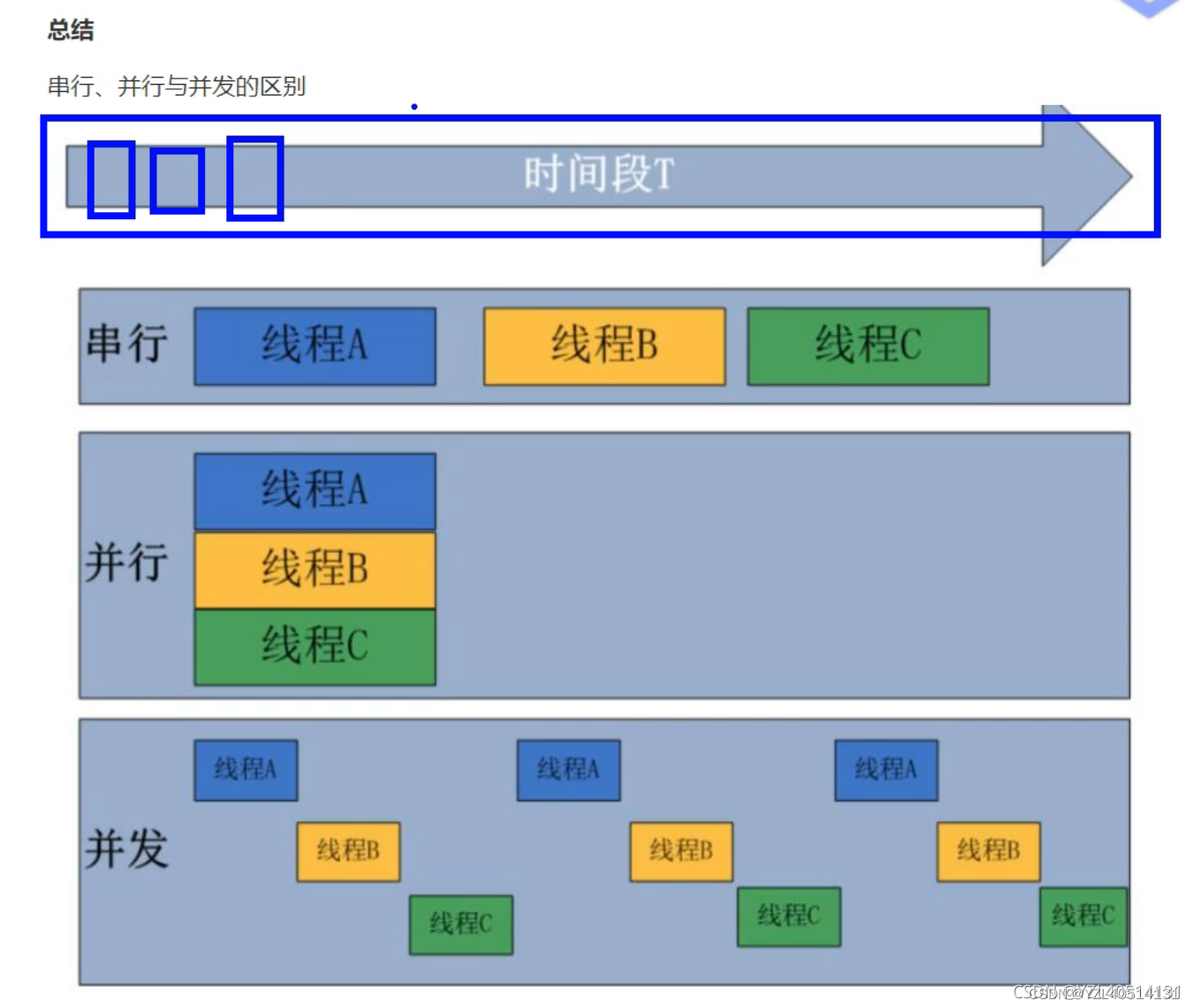
8、 ... and 、 Concurrent
1、 Only one instruction can be executed at the same time , But multiple process instructions are executed in rapid rotation , It has the effect of multiple processes executing at the same time , But at the micro level, it is not carried out at the same time , Just divide the time into periods , Make multiple processes execute alternately quickly .
2、 The key to concurrency is your ability to handle multiple tasks , Not necessarily at the same time .
Nine 、 parallel
1、 At the same time , There are multiple instructions executing on multiple processors at the same time . So whether from the micro or from the macro point of view , Both are carried out together .
2、 The key to parallelism is your ability to handle multiple tasks at the same time .
Ten 、 Serial
Simply put, you can only do one thing at a time , And it has to be executed in sequence , The later code segment can only be executed after the task of the previous code segment is executed .

边栏推荐
- C form application of C (27)
- Pandora IOT development board learning (HAL Library) - Experiment 9 PWM output experiment (learning notes)
- 【PSO】基于PSO粒子群优化的物料点货物运输成本最低值计算matlab仿真,包括运输费用、代理人转换费用、运输方式转化费用和时间惩罚费用
- 自动化测试的好处
- 颠覆你的认知?get和post请求的本质
- Prime protocol announces cross chain interconnection applications on moonbeam
- 关于进程、线程、协程、同步、异步、阻塞、非阻塞、并发、并行、串行的理解
- 2/13 review Backpack + monotonic queue variant
- Hashcode and equals
- Facebook等大厂超十亿用户数据遭泄露,早该关注DID了
猜你喜欢
MySql数据库root账户无法远程登陆解决办法
Esp32 (based on Arduino) connects the mqtt server of emqx to upload information and command control
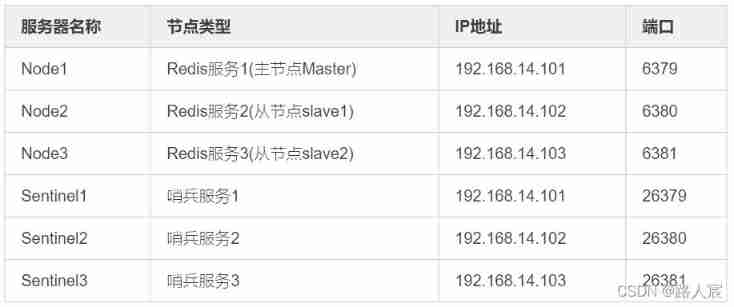
Redis (replicate dictionary server) cache
DM8 backup set deletion
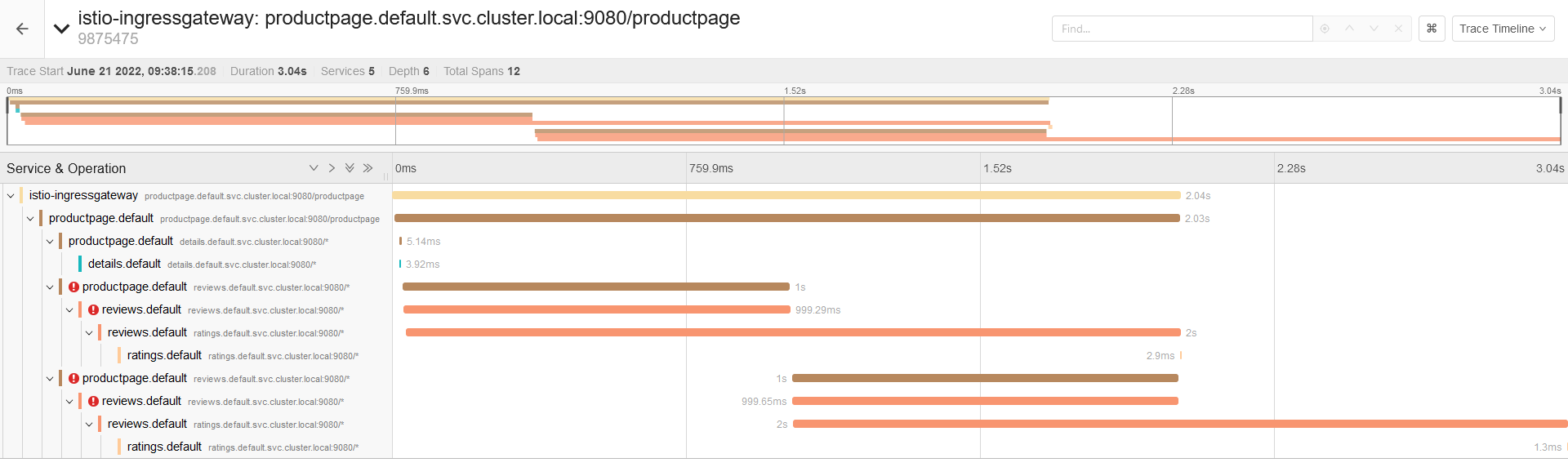
10個 Istio 流量管理 最常用的例子,你知道幾個?
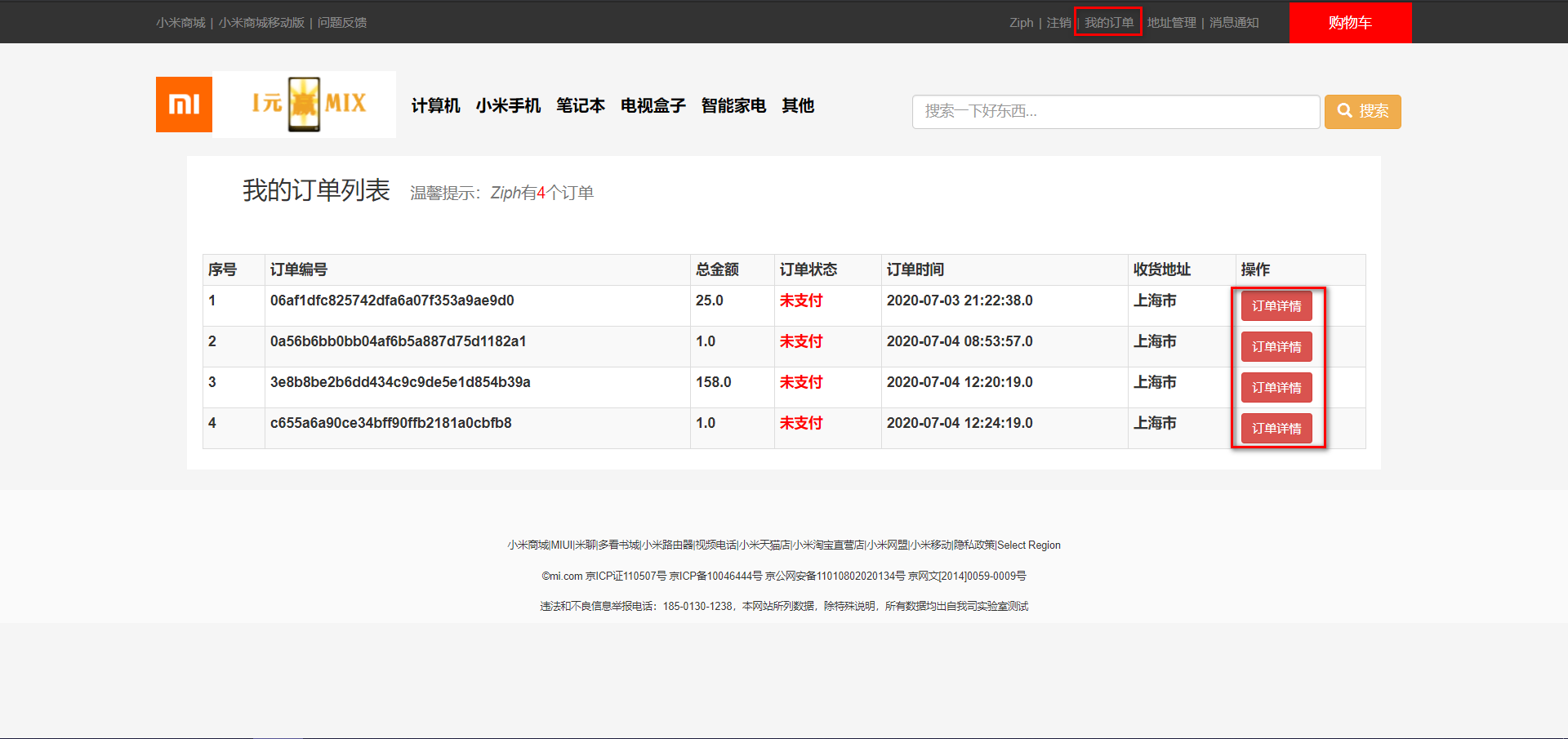
Ks003 mall system based on JSP and Servlet
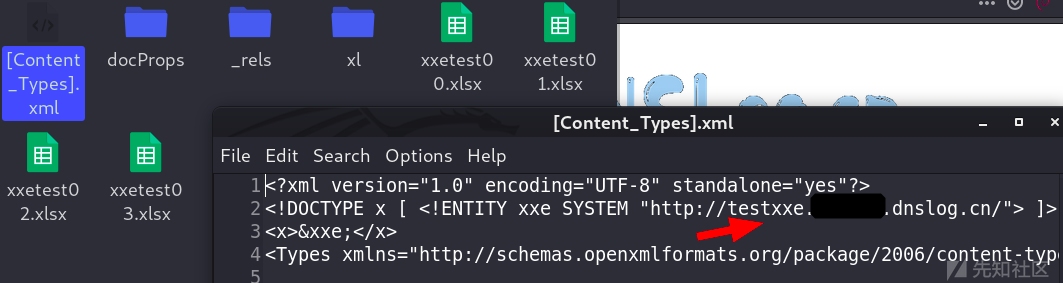
Record an excel xxE vulnerability

关于进程、线程、协程、同步、异步、阻塞、非阻塞、并发、并行、串行的理解
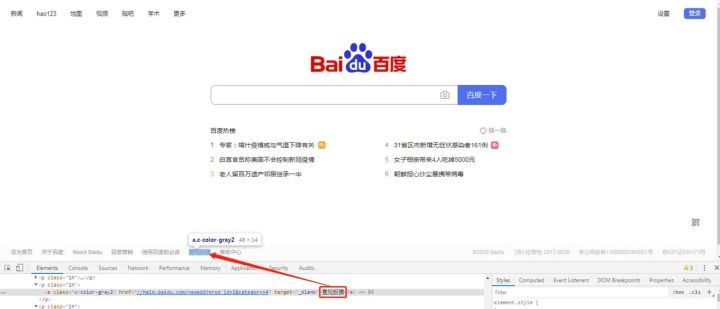
Alibaba testers use UI automated testing to achieve element positioning
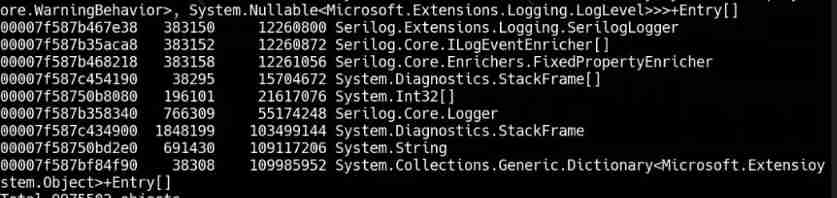
Record the pit of NETCORE's memory surge
随机推荐
Benefits of automated testing
[Zhao Yuqiang] deploy kubernetes cluster with binary package
Prime protocol announces cross chain interconnection applications on moonbeam
Cf464e the classic problem [shortest path, chairman tree]
Global and Chinese markets for MRI safe implants 2022-2028: technology, participants, trends, market size and share Research Report
After five years of testing in byte, I was ruthlessly dismissed in July, hoping to wake up my brother who was paddling
脚本生命周期
Determine which week of the month the day is
IDEA编译JSP页面生成的class文件路径
Record the pit of NETCORE's memory surge
DM8 archive log file manual switching
Leetcode32 longest valid bracket (dynamic programming difficult problem)
Ks003 mall system based on JSP and Servlet
[adjustable delay network] development of FPGA based adjustable delay network system Verilog
Do you know cookies, sessions, tokens?
软考 系统架构设计师 简明教程 | 总目录
How to modify field constraints (type, default, null, etc.) in a table
KS003基于JSP和Servlet实现的商城系统
Execution order of scripts bound to game objects
P2648 make money