当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to JVM basic concepts
Introduction to JVM basic concepts
2022-06-11 15:23:00 【Evader1997】
JVM What is it?
JVM also called Java virtual machine , yes Java The runtime environment of the program . It is to use C Write a software , Like other software, it runs on the operating system (LInux,win,mac etc. ) Of . Where does the operating system run ?
Before the birth of computer software , Our computer can only execute certain programs , To run a program by splicing circuits . If you need to run the second program, you need to splice a new set of circuits and run , This is the early computer hardware . Later, von Neumann led to the wave of computer software , It wants to **‘ preservation ’** get up , This is the beginning of computer software . So the operating system is running on the hardware .JVM, operating system , The relationship among computer hardware is :
JVM Architecture of
JVM The most common thing in is tuning , In fact, JVM Of the five areas of , The basic thing that involves tuning is heap memory tuning , This is determined by the mechanism of heap memory . For local method interfaces , Namely native Related methods of modification , These methods are C language-written . The local method information is stored in the local method interface , When called, the local method in the local method library will be called .
Class loader
species
Start class loader :Bootstrap ClassLoader
Extend the classloader :Extension ClassLoader
Application class loader :Application ClassLoader
Do not discuss custom class loaders
A simple loading process of a class

Test code , You can understand at a glance
 {
String str = new String("abc");
System.out.println(str.getClass().getClassLoader());
// System.out.println(classLoader.getParent());
System.out.println("====== I'm the divider ======");
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println(person.getClass().getClassLoader());
System.out.println(person.getClass().getClassLoader().getParent());
System.out.println(person.getClass().getClassLoader().getParent().getParent());
}
}
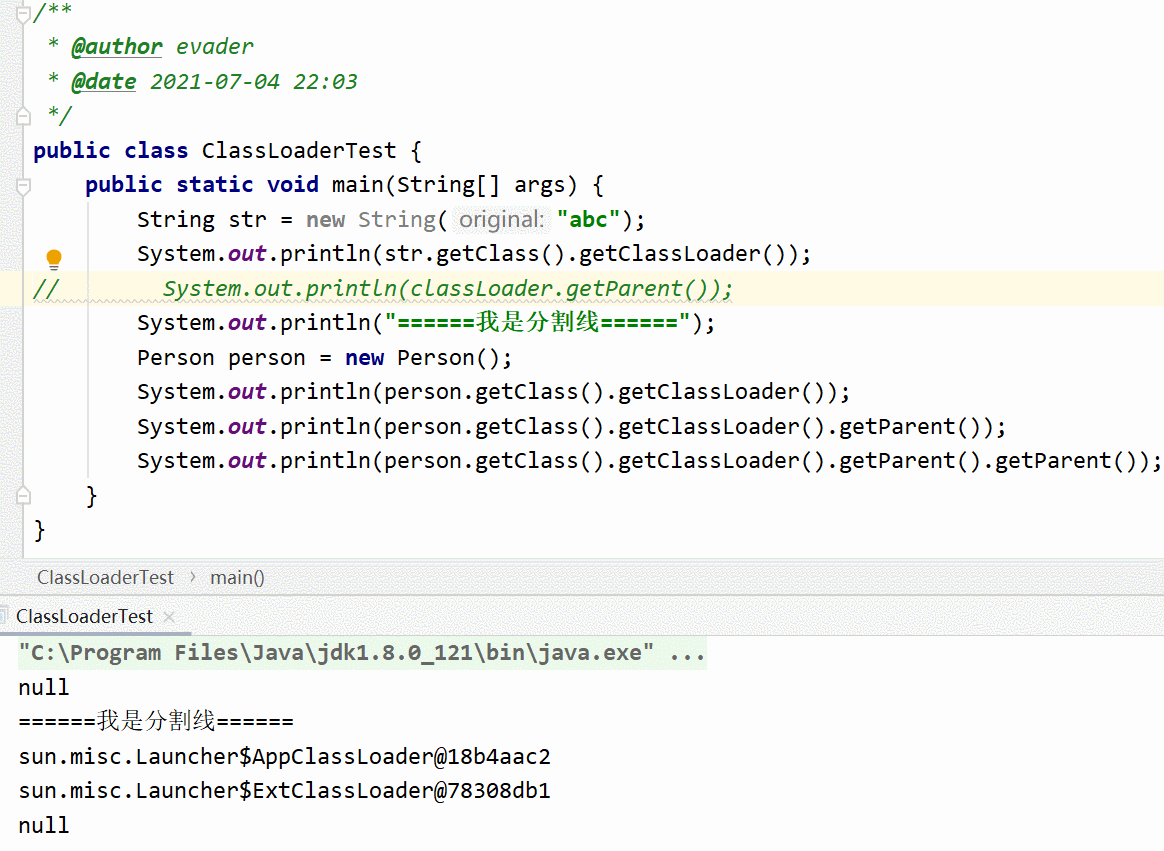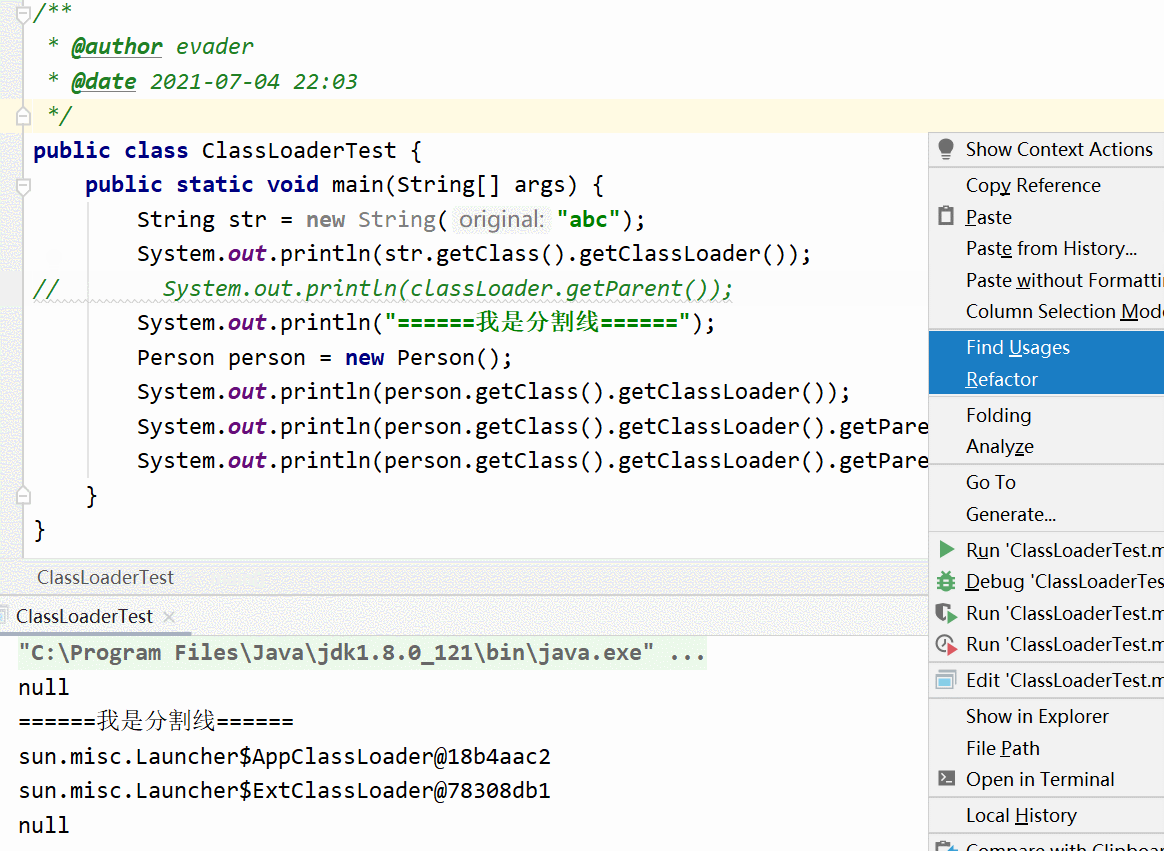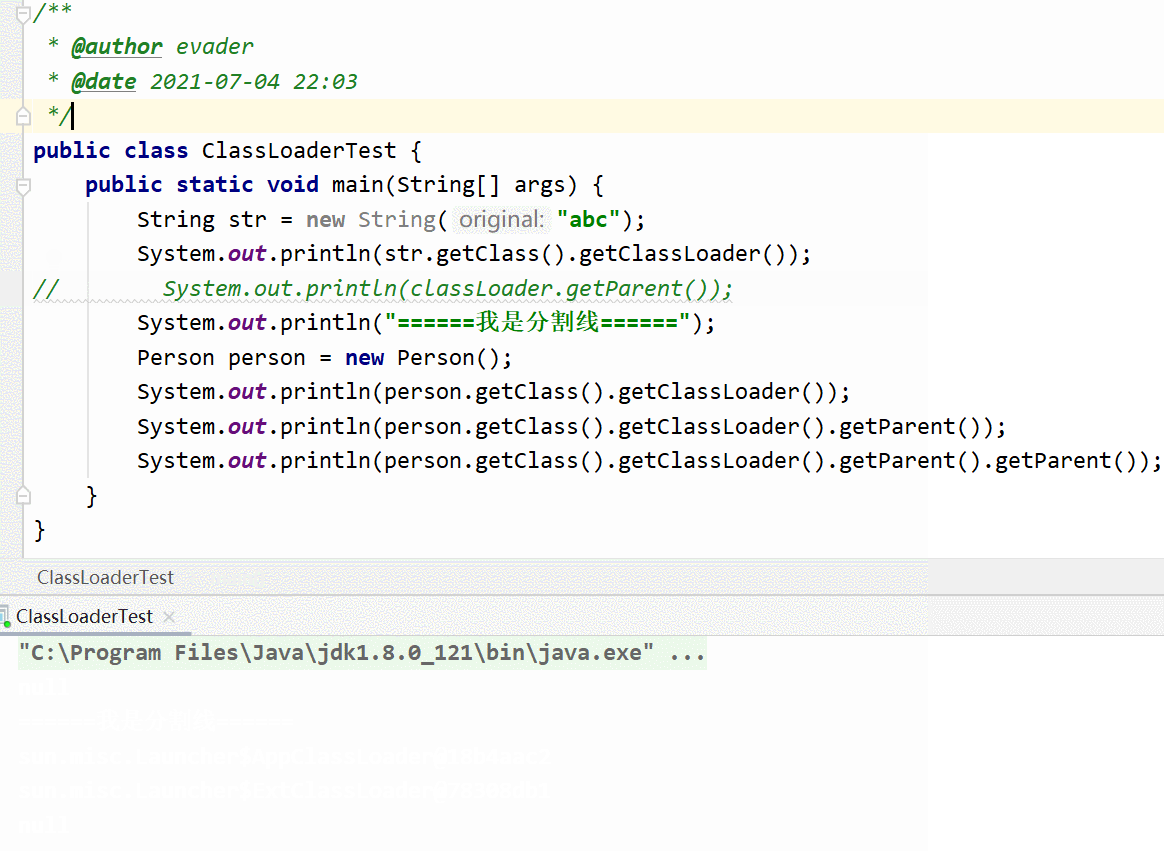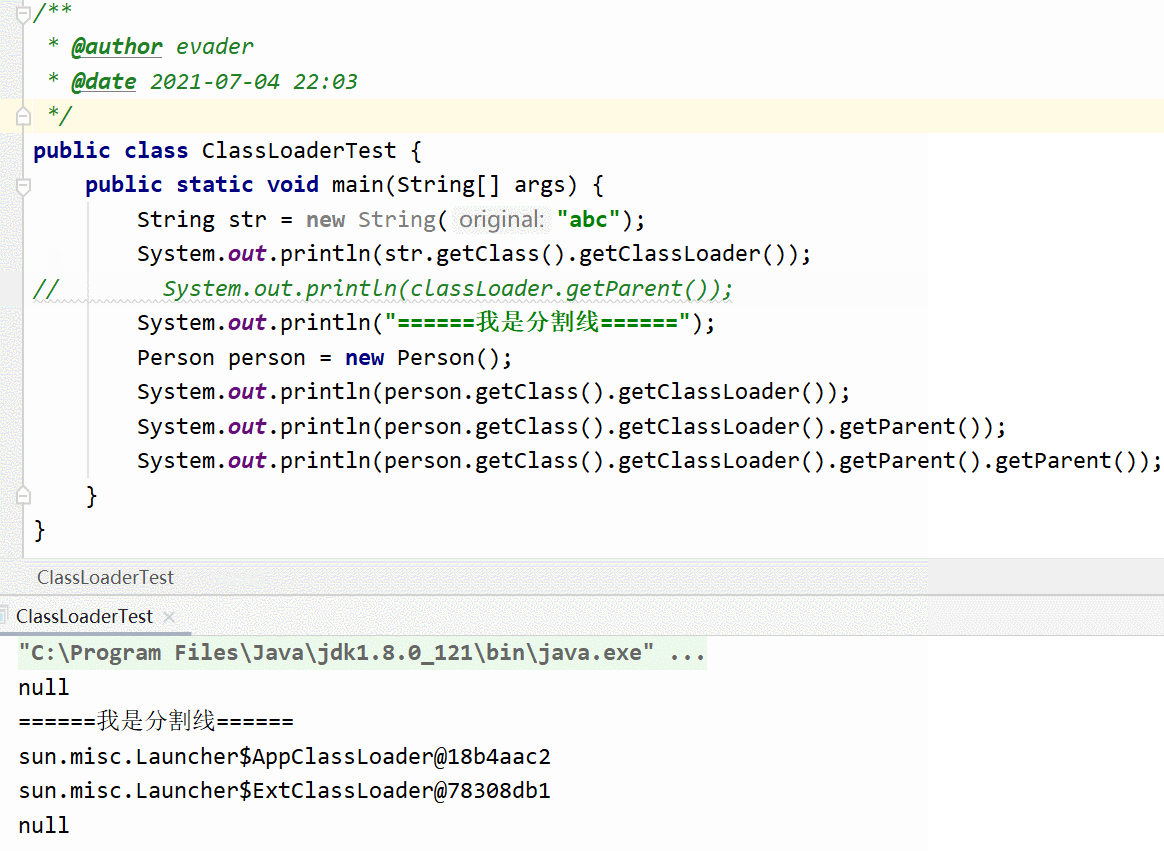
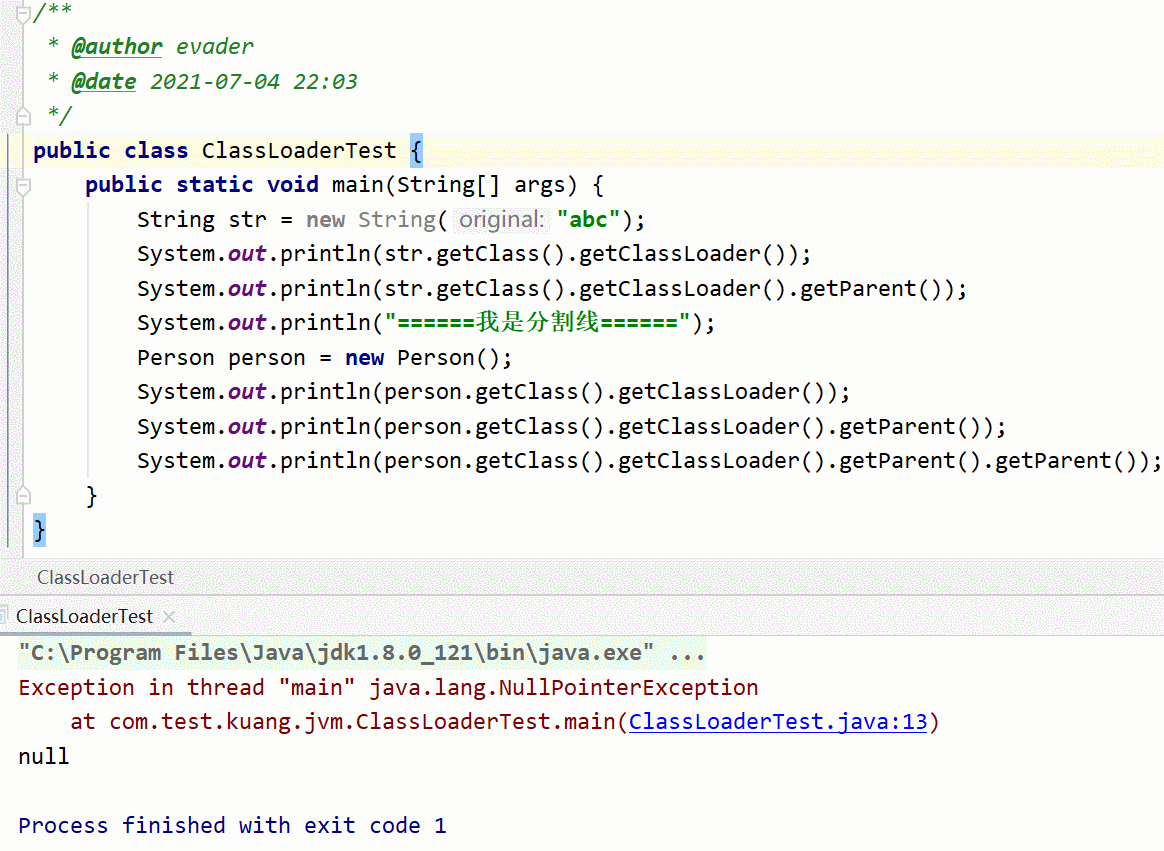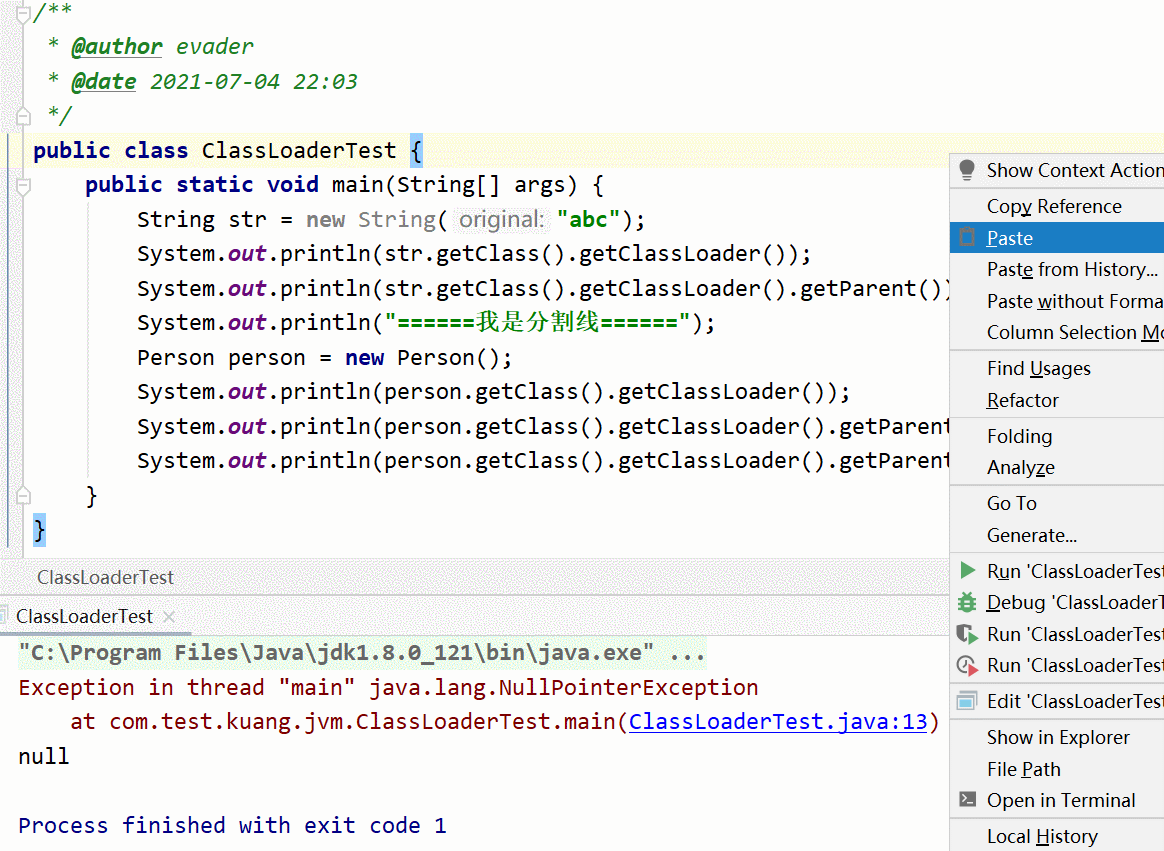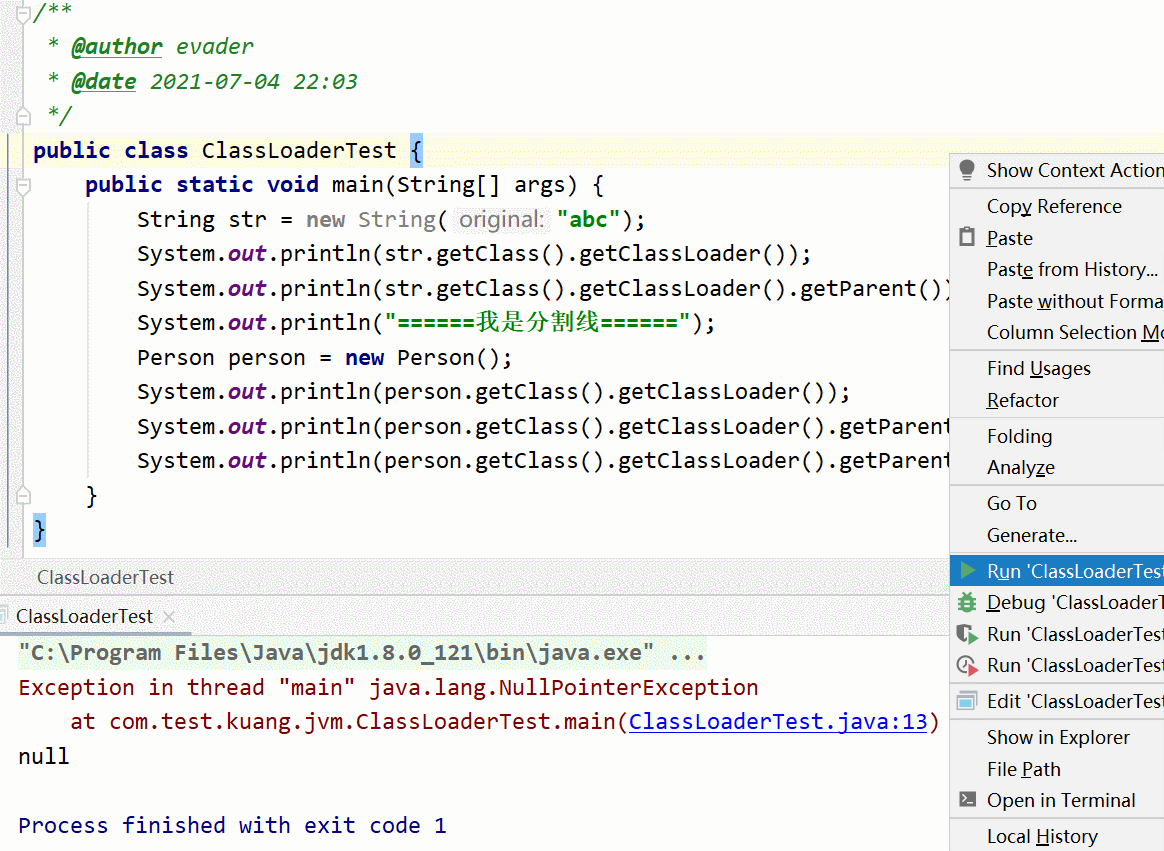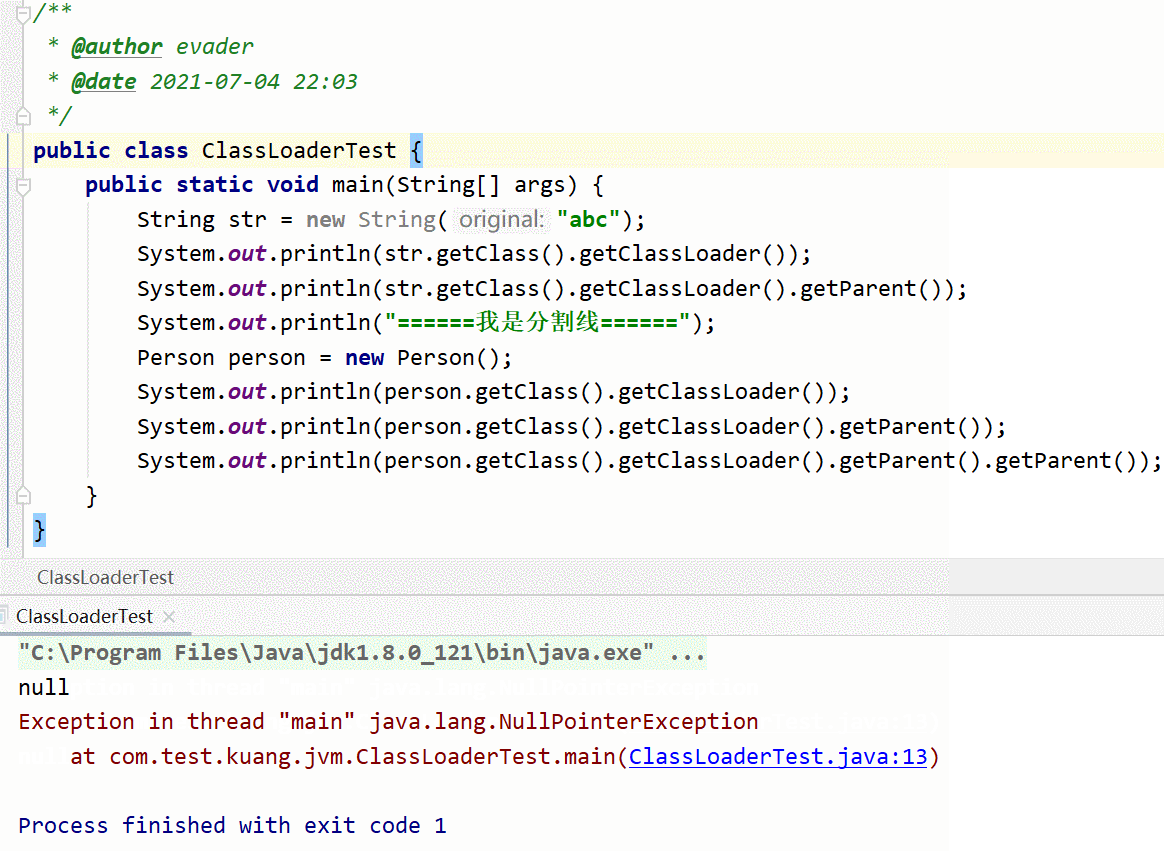
Ladies and gentlemen, just look at two moving pictures , We know String Class is JDK A self-contained class in , Is loaded by the boot class loader , Start class loader at Java You can't get it in . Therefore, the second dynamic graph generates a null pointer exception . Compare... In the first graph Peron Class is custom , So the loading is finally completed by the application loader . Why print three class loaders , Leave a suspense .
The role of the three class loaders
1. Start class loader : load <JAVA_HOME>\lib In the directory , Or be -Xbootclasspath The class of the path specified by the , And is JVM Identified class libraries , Users can't get .
2. Extend the classloader : load <JAVA_HOME>\lib\ext In the directory , Or be java.ext.dirs Class libraries in the path specified by the system variable . Users can get .
3. Application class loader : This loader is also known as the system loader (System), yes ClassLoader in getSystemClassLoader() Return value of method . Load user path (ClassPath) The specified class library . Users can use . Users can get
Parent delegate mechanism
There is a need for class loading
The subclass loader passes the request for class loading to the parent class , Layer by layer to start the class loader
If the parent class loader fails to load, it will feed back to the child class to load itself
The so-called parents , Is to extend the class loader and start the class loader . The advantage of parental delegation is that it doesn't make a class reload twice , For example, you can customize java.lang.String It's illegal .
Sandbox security mechanism
A sandbox can be understood as a closed box , Our program can only run in this box . We develop locally , The development is completed and deployed to the remote server , stay Java Local code in is trusted by default , It's safe . But remote code is not trusted , So we need to add some security mechanisms to ensure the operation of the program , For example, when the remote code operates the operating system and local resources, the credit granting steps should be added ,jdk6 Then the domain is proposed (domain) The concept of , Make sandbox safer .
Native

native The delegate is a local method , take Thread Class, for example , First Thread Not an abstract class, not an interface , Why is there a way to realize without writing methods ? The reason is that this method is native Modify the . stay Java in , All are native The modification is the local method .Java Only its mark is stored , Use it to call the local method library .
PC register
PC The register area is also called the program counter , We know that in the case of multithreading ,CPU It's a high-speed wheel , Each thread is allocated a time slice , There is ** Half the program is executed to execute other threads , Next time, go back to this thread ,CPU How to know where the program has been executed ?** The answer is the program counter , This can be understood as a pointer , It will point to the memory address of the next instruction .PC Registers are thread private , Every thread has a PC register , This ensures that threads are independent of each other .
Stack
Stack also known as Java Virtual machine stack , It is characterized by first in and last out , This is related to its data structure . Inside the stack are stack frames , Each stack frame actually corresponds to a method to be executed . After each method is executed, it will pop up and disappear , The sign that a program has finished executing is that there is no stack frame in the stack . Usually, what is stored in the stack is some references , So the program is finished , There is basically no garbage left in the stack , So it basically won't appear OOM. The possible exception is that the stack frame loaded into the stack exceeds the maximum stack frame that the stack can hold , A stack overflow exception will be reported , Another case is that the memory requested by the current stack frame exceeds the maximum memory , Will appear OOM The problem of .
Pile up
Java in new All objects are stored in the heap , The so-called garbage collection is the collection object . So most of the tuning we talk about is actually heap tuning . The following is the structure diagram of heap memory .

边栏推荐
- Analyse approfondie de la conception du système relationnel du Groupe de cercles
- Backtracking / activity scheduling maximum compatible activities
- 05 _ In simple terms index (Part 2)
- Lick the dog till the last one has nothing (linear DP)
- How to batch insert 100000 pieces of data
- Nexus of repository manager
- Uniapp settings page Jump effect - navigateto switching effect - Global animationtype animation
- 【创建型模式】工厂方法模式
- Uniapp develops wechat applet from build to launch
- 【创建型模式】抽象工厂模式
猜你喜欢

【Azure 应用服务】NodeJS Express + MSAL 实现API应用Token认证(AAD OAuth2 idToken)的认证实验 -- passport.authenticate()

05 _ In simple terms index (Part 2)

Oauth2的理解

深度剖析「圈组」关系系统设计 | 「圈组」技术系列文章

07 _ 行锁功过:怎么减少行锁对性能的影响?

Database optimization

2022.02.28
Implementation of the function of recording login status
06 _ 全局锁和表锁 :给表加个字段怎么有这么多阻碍?

高数_第6章无穷级数__马克劳林级数
随机推荐
3年亏损136亿,上市能救活威马吗?
Uniapp settings page Jump effect - navigateto switching effect - Global animationtype animation
2022 Tibet's latest eight major construction personnel (labor workers) simulation test question bank and answers
见微知著,细节上雕花:SVG生成矢量格式网站图标(Favicon)探究
[azure application service] nodejs express + msal realizes the authentication experiment of API Application token authentication (AAD oauth2 idtoken) -- passport authenticate()
企业开发如何写出优雅的二级分类【美团小案例】
In the "ten billion blue ocean" database, each player can find a boat | c-position face-to-face
2021 go developer survey
简单的C语言版本通讯录
汤峥嵘:CTO 是商业思维和技术思维交汇的那个点
硬核分析懒汉式单例
思科瑞递交科创板注册:拟募资6亿 年营收2.22亿
2022 Tibet's latest junior firefighter simulation test question bank and answers
Learnopongl notes (IV) - Advanced OpenGL II
A former employee of Baidu was awarded 1.07 million yuan for job hopping; Apple, Google and Microsoft plan to "kill" the password; It is said that Geely has acquired Meizu | Q information
Microservices - use of Nacos
What is excess product power? Find the secret key of the second generation cs75plus in the year of the tiger
Arthas practice documentation
07 _ 行锁功过:怎么减少行锁对性能的影响?
Intercept string (function)