当前位置:网站首页>LeetCode刷题 —— 手撕二叉树
LeetCode刷题 —— 手撕二叉树
2022-06-11 09:15:00 【命由己造~】
1.单值二叉树

思路:
1️⃣如果节点为空,就不用判断,返回true
2️⃣如果节点不为空,则判断他的左右子节点的值,只要不同,就返回false,相同就继续递归(走到最后会返回true)
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isUnivalTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(root->left)
{
if(root->val != root->left->val)
{
return false;
}
}
if(root->right)
{
if(root->val != root->right->val)
{
return false;
}
}
return isUnivalTree(root->left) && isUnivalTree(root->right);
}
递归发现不同的时候(不管是左还是右)返回false,而最后又是&&关系,所以只要有不同就返回false
流程图:

2.二叉树的最大深度

思路:
这颗树的层数等于左右子树层数大的那个加1,慢慢递归下去,
1️⃣是空就返回0
2️⃣是叶子节点就返回1
很容易写出代码:
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
return maxDepth(root->left) > maxDepth(root->right) ?
maxDepth(root->left) + 1 : maxDepth(root->right) + 1 ;
}
但是这种代码会超出时间限制,原因是判断左右子树层数时会递归两遍,后面+1时又要递归一遍,所以我们可以用变量先存取来,比较完就返回大的那个。
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL)
{
return 1;
}
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
流程图:
3.二叉树的前序遍历

这道题首先要知道有多少个节点,前序遍历存到数组,要考虑到递归时临时变量不会影响递归前的,所以要传指针变量
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
/** * Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free(). */
int TreeSize(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
return TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
void _preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* a, int* k)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return;
}
a[(*k)++] = root->val;
_preorderTraversal(root->left, a, k);
_preorderTraversal(root->right, a, k);
}
int* preorderTraversal(struct TreeNode* root, int* returnSize){
int size = TreeSize(root);
int* arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
int a = 0;
_preorderTraversal(root, arr, &a);
*returnSize = size;
return arr;
}
4.翻转二叉树

思路:
从根节点往下递归,如果递归到当前节点root时root的左右子树都已经翻转,那么直接交换左右子树的位置。所以大思想时后序遍历
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
struct TreeNode* invertTree(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct TreeNode* left = invertTree(root->left);
struct TreeNode* right = invertTree(root->right);
root->left = right;
root->right = left;
return root;
}
流程图:
5.相同的树

这道题比较简单,当同时到NULL的时候就返回true,中间只要有不相同就返回false
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool isSameTree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q){
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return isSameTree(p->left, q->left) && isSameTree(p->right, q->right);
}
图跟第二题一样
6.对称二叉树

思路:
如果是空树,就返回true,不是的话就像判断相同树那道题一样,分成两个树往下递归
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool _isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* left, struct TreeNode* right)
{
if(left == NULL && right == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(left == NULL || right == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(left->val != right->val)
{
return false;
}
return _isSymmetric(left->left, right->right) && _isSymmetric(left->right , right->left);
}
bool isSymmetric(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
return _isSymmetric(root->left, root->right);
}
这道题也是上面翻转二叉树和相同的树两道题结合,先翻转再判断是否相同
7.另一棵树的子树

思路:
遍历所有节点,判断root树的每个节点是否是subroot的子树,如果都没有则返回false,只要有就返回true 所以用 ||
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool _isSubtree(struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q)
{
if(p == NULL && q == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(p == NULL || q == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(p->val != q->val)
{
return false;
}
return _isSubtree(p->left, q->left) && _isSubtree(p->right, q->right);
}
bool isSubtree(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* subRoot){
//遍历root所有节点比较
//没有则false
if(root == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if(_isSubtree(root, subRoot))
{
return true;
}
return isSubtree(root->left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root->right, subRoot);
}
8.平衡二叉树️️

这道题可以用上面求最大深度的题求,把每个节点的左右子树深度差都算一下,只要有>1的就false
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode* root)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
int left = maxDepth(root->left);
int right = maxDepth(root->right);
return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
if(root == NULL)
{
return true;
}
if(abs(maxDepth(root->left) - maxDepth(root->right)) > 1)
{
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
但是我们来看看他的时间复杂度
递归的时间复杂度就是递归次数
isBalanced递归次数:N
每次递归次数:N + N / 2 + N / 2 + N / 4 + N / 4 + N / 4 + N / 4……(假设是满二叉树)
所以总体是O(N^2)
要求优化到O(N)
8.1时间复杂度优化
先搞清楚为什么复杂度会高?
判断平衡时会算左右子树的高度,而从上往下递归下面的高度会重复计算,那么我没让你可以用后序遍历从下往上计算,就不会有重复
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * struct TreeNode *left; * struct TreeNode *right; * }; */
bool _isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root, int* ph)
{
if(root == NULL)
{
*ph = 0;
return true;
}
int lefthight = 0;
if(!_isBalanced(root->left, &lefthight))
{
return false;
}
int righthight = 0;
if(!_isBalanced(root->right, &righthight))
{
return false;
}
*ph = lefthight > righthight ? lefthight + 1 : righthight + 1;
return abs(lefthight - righthight) < 2;
}
bool isBalanced(struct TreeNode* root){
int hight = 0;
return _isBalanced(root, &hight);
}
边栏推荐
- Why is it difficult to implement informatization in manufacturing industry?
- js基础--Date对象
- 1400. construct K palindrome strings
- Openstack explanation (21) -- installation and configuration of neutron components
- Day44 database
- Day 47 how to query a table
- 面试题 17.10. 主要元素
- Package details
- Remote office related issues to be considered by enterprises
- 报错[error] input tesnor exceeds available data range [NeuralNetwork(3)] [error] Input tensor ‘0‘ (0)
猜你喜欢

实现边充边OTG的PD芯片GA670-10

Ecological co construction | 2021 streamnational excellent partner of the year comes out!
Machine learning notes - in depth Learning Skills Checklist

ESP8266_SNTP(Simple Network Time Protocol)

document对象

Zhiyun health submitted the statement to HKEx again: the loss in 2021 exceeded 4billion yuan, an increase of 43% year-on-year
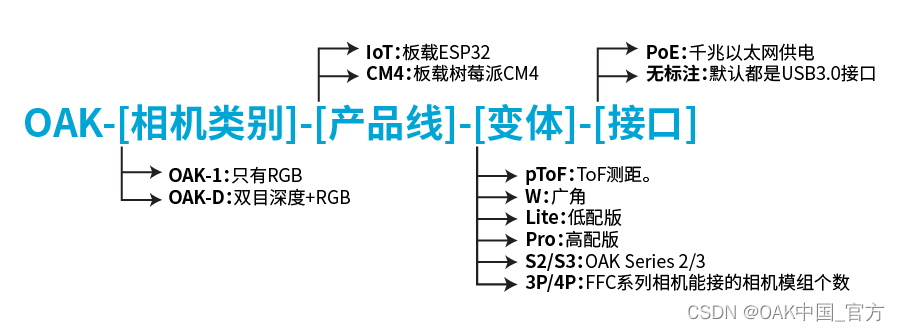
Comparison and introduction of OpenCV oak cameras

Analysis of high frequency interview questions in massive data processing

Detailed explanation of the difference between construction method and method
![Error [detectionnetwork (1)][warning]network compiled for 6 shapes, maximum available 10, compiling for 5 S](/img/54/f42146ae649836fe7070ac90f2160e.png)
Error [detectionnetwork (1)][warning]network compiled for 6 shapes, maximum available 10, compiling for 5 S
随机推荐
Pytorch installation for getting started with deep learning
[scheme development] scheme of infrared thermometer
The mobile terminal page uses REM for adaptation
Concurrent programming
Analysis of high frequency interview questions in massive data processing
js基础--Array对象
OpenCV CEO教你用OAK(五):基于OAK-D和DepthAI的反欺骗人脸识别系统
JS foundation -- Operator
POJ3250「Bad Hair Day」
Don't use redis list to implement message queue. Stream is designed for queues
ESP8266_SmartConfig
1493. 删掉一个元素以后全为 1 的最长子数组
js基础--关于DOM
Pulsar job Plaza | Tencent, Huawei cloud, shrimp skin, Zhong'an insurance, streamnational and other hot jobs
我们是如何连上WiFi的?
ESP8266_接入百度物联网核心套件、使用MQTT协议通信
1400. construct K palindrome strings
1854. the most populous year
Bucket sort
ESP8266_通过MQTT协议连接阿里云